Executive Summary
This is a report comparing internet marketing and interactive marketing. Apart from this comparison, the concept of Web2 applications, their relevance, and examples have been provided. The ethical issues of online marketing have also been discussed along with guidelines for developing websites. The report is useful for organizations for understanding the concept of online or interactive marketing as well as for developing websites of their own.
Introduction
Marketing is the function that exists in most business environments. Most of these activities are dependent upon the external factors and market in which a company operates. The external factors are demographic, social, economic, and technological. All of these affect the function of an organization very much. These changes need new trends in the marketing sector. One of the drastic changes in marketing is an internet marketing and interactive marketing.
For many years, a computer was standard household equipment. Its use was not limited to the particular age group. Everybody was using it for a different purpose. This facilitated the ability for it to reach the targeted market electronically. “The World Wide Web, the first and current networked global implementation of a Hypermedia computer-mediated environment (CME) is increasingly being recognized as an important emerging commercial medium and marketing environment.” (Hoffman and Novak 1996). The business has analyzed that the Web as a media has a unique characteristic that distinguishes it in important ways, as compared to the other traditional media’s for commercial purposes.
Literature Review
Internet marketing
Internet marketing is the media that reaches many without geographical considerations, by interacting with people and computers. It allows the users of the medium to provide and interactive access to hypermedia content and to communicate with each other. This facilitates an interactive virtual environment. The customer is experiencing a different environment for marketing activities. “Electronic marketing is a form of marketing that takes place on the internet. This includes an expansive range of services including websites, bulk mailing, search engine optimization, blogs, and more.” (Electronic Marketing. 2008).
It is also a cost-effective mechanism compared to many other marketing options. Its reach is wider – as far as the international market.
Internet marketing is a relatively new concept in the marketing arena; it helps in promoting products and services with the use of the internet. It is a constituent of e-commerce. Both internet marketing and e-commerce ensure to provide its customers with diverse facilities, which include the availability of information. Consumers can purchase any product at any time, which saves not only time but also money.
Internet marketing is similar to electronic marketing. Internet marketing is similar to electronic marketing. One advantage is that it is interactive in nature. It is able to accept customer responses as well as respond to them instantly. Many new components have been incorporated into the concept of internet marketing which is used by companies to increase sales and revenue. This is possible even if the company does not fully depend on the internet for its marketing The marketing strategy of today’s companies usually includes internet marketing.
The main objectives of internet marketing
- Communicating the company’s information about itself or about its products or services.
- To conduct market research to know the potential customers of the company.
- To sell goods and services.
- To advertise their products and services.
Components of internet marketing are
- A website, “consisting of text, images and possibly audio and video elements used to convey the company’s message, to inform existing and potential customers of the features and benefits of the company’s products and/or services.” (Duermyer 2008).
- Search Engine Marketing works based on the selected keywords and then displaying the results which contain the details with the specific keywords.
- Email marketing distributes the information about the product or services or solicited feedback from the customer about the purchased product and services.
- Banner advertising is the placement of advertising on the Web site after paying a fee for it.
- Online promotion, distributing press release which includes a story about the company, its website, its people, its products or services with comments and opinions or announcements.
For an internet strategy to be effective, a comprehensive strategy is required. If such a strategy is put in place, the company’s whole business gets a synergy that will help in achieving its business goals. This is due to the fact that internet marketing can target the proper market with an effective website that has the proper content, design, functions, and the way its copy is written,
Theories of internet marketing
Life is always governed by laws, principles, or theories. Internet marketing is also bound by many theories. There are three theories;
Theory of speed
This theory states that how fast the product or services are produced or delivered in comparison to the competitors. It is applicable more to the software development sector.
Theory of cost
The theory of cost emphasizes the cost-effectiveness of the product and services. People always want to purchase the product at the best possible rate. So the producer should be able to sell his product or service at a reasonable price which should be lower than its rivals.
Theory of quality
“Products and services should be of very high quality if producer really expects to make very high amount of money –it is said that only reap what you sow, only thieves or criminals are known for taking what they do not deserve.” (Theories of Internet Marketing. 2007).
The nature of the internet market allows consumers to research and purchase goods and services at their own convenience. They can make a purchase from any place at any time. It also helps the marketers to measure the statistics and other details of customers very easily.
The advantages and disadvantages of internet marketing
Advantages
- The internet marketing is marketing through internet, so unlike a brick and mortar store, all it needs is a computer, a web site with customers having access to it.
- The information is passed within seconds, faster that any other media without any constrain of distance to be covered.
- It can reach a global audience.
Disadvantages
- Information in the internet is overloaded.
- In remote places internet access might not be available. The cost of software and hardware may not be affordable to a large section of the population.
- The low access of internet.
- It leaves the marketer isolated. Its makes marketing an inhuman activity.
- No replacement to the old customer services. Internet marketers lack customer service activity and inquiry response services. It also lacks the warmth that exists in personal relationships.
- Insecurity of site or the fear of insecurity in the minds of customer makes them hesitant to purchase online.
Applications of internet marketing
- Corporate domain: the marketers use internet marketing to provide the information about the organisation, product or services. It composes of several features like corporate site, portal strategy, micro sites for segmentation, interactive web marketing, intranet, extranet and regionalization.
- Search marketing: the search engines are used through which the company are listed in the search results. Search engine optimisation helps the company to make sure the web content easily found. The search engine marketing, the ads of the company are contextually displayed based upon the search query.
- Out bound an syndicated web marketing: “Used to help ideas spread off the corporate website, this list of tools extends reach by direct channels, and as well as ‘pull’ techniques where users opt-in. Be savvy when using these tools to respect the best interests of customers, otherwise it’s one-click to unsubscribe or spam.” (A Complete List of the Many Forms of Web Marketing for 2008. 2008). Email marketing, invasive marketing and syndicated content and RSS are its feature.
- Brand extension: it’s a simple strategy through web advertising through banner, tile or skyscraper adverting; contextual advertising, sponsorship or cross branding, social advertising, widget advertising and affiliate marketing.
- Community marketing and social media marketing: it is the fastest growing area in advertising. It includes ecommerce or rating sites, social networking, blogging, widget marketing, pod cast marketing, Online Video and Live Streaming, Instant Messaging, Tagging, Collective Tools, Macromedia and Voting Features are used for this marketing.
- Virtual worlds: It includes online gaming and social networks.
- Related mediums: The web is the platform for internet TV and mobile content.
- Experimental: Portability of the social graph and vendor relationship management are the different forms.
Traditional Marketing
Traditional marketing refers to the way organizations conducted their marketing activities before the advent of the World Wide Web. As new technologies emerge, the existing ones will be relegated to being called traditional. It is common knowledge that marketing was done by bartering of goods before the introduction of currency. Marketing was done by word of mouth in those days.
There were not too many goods and finding markets would not have been too difficult. The introduction of the print media changed marketing practices and companies began advertising through this medium. The telephone, radio and television followed in succession and organizations began to effectively use all these methods to market themselves. It would be interesting to note that the concept of the word ‘traditional‘ keeps changing once new technology develops.
While print media advertising was a trendsetter before the advent of radio and TV, it began to be referred to as traditional once these electronic media began to be used for advertising. Now with the advent of the internet, even those forms of marketing began to be referred to as traditional. There might come an age when internet marketing will be included in the category of ‘traditional’. In essence apart from the media used, marketing is the same everywhere. This can be made clear from the latest definition given by the American Marketing Association in 2007. In fact the association has given two definitions (one in 2994) both of which are given below.
The 2004 definition of marketing is “Marketing is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders.” The one created in 2007 says that “Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.” (Lotti and Lehmann 2007).
It can be seen that both definitions have not referred to the type of media used since it is what creates the difference between the concept of traditional and modern (in this context, the internet). The main difference between the two definitions is that the latter definition is broader in scope and has replaced the word ‘stakeholders’ with the words ‘society at large’. Anyway the definition clearly shows the broad scope of the word marketing. The growing complexity of today’s market place has put organizations in difficulty. This is mainly due to the sheer variety of traditional methods. With growing globalization products manufactured in a country are now globally available.
Print and media advertising has limitations in the sense that they are usually limited to a particular region or country. According to David C Court of McKinsey Corporation, this state of affairs has resulted in “an explosion of customer segments, products, media vehicles, and distribution channels has made marketing more complex, more costly, and less effective.” (Court 2004). Apart from this once companies needed only to advertise on two or three television channels and a few print media. Nowadays there are hundreds of television channels, radio networks, newspapers, magazines etc. This is confusing and also has become more expensive.
This is what prompts organizations to use the internet also as an alternative or as a complimentary method to market their goods and services. But it cannot be said that use of traditional marketing methods will become obsolete. The concept of direct marketing is catching up in many parts of the world years after it was popular in the west. It can be said that both these concepts will go hand in hand for a long time to come.
Web 2
The concept of the term Web 2 was first introduced during a conference conducted by the famous media publishing house O’Reilly. It was introduced by the vice-president of the company Dale Dougherty and Tim O’Reilly during a brainstorming session about the future of the web. This was quite some time after the first dot com bust and the people present were of the opinion that the internet was now stronger than ever with new applications and technology boosting its usefulness.
The name was given because of the new applications brought the web to a higher level than what was previously possible. Hence the older technology and applications were referred to as Web 1. In a widely appreciated article by Tim O’Reilly he gives seven factors that differentiate a Web2 site from a Web1 site. The author adds that some of the most successful applications in the older category may share a few of the following features also.
- The web as a platform: The Web2 platforms were seen rather as a core with a gravitational force rather than one with boundaries. This is shown graphically below.
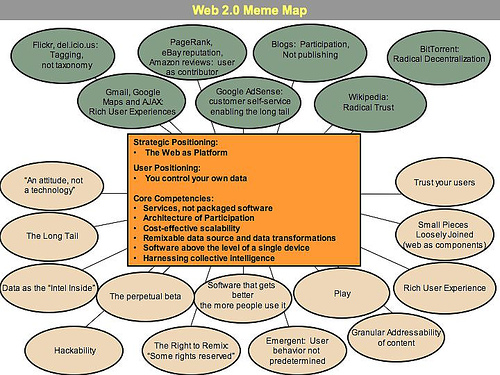
(O’reilly 2005). The paper says that traditional websites were commodities that could be brought by users. But Web2 applications were seen more as service providers who act as bridge between two parties. The example given was the Google search engine which does not store any content on its own. It just displays the results taken from other websites and provides it to the searcher. In effect it acts as a platform between two parties.
- Harnessing collective intelligence: The concept of users contributing to the content of the web is a feature of Web2 applications. The author says that such applications are dynamic because the website grows with user activity. Examples given include Wikipedia, blog sites and eBay.
- Data is the next Intel inside: The content owned or displayed the websites will ultimately lead to its dominance. Web2 applications are at an advantage because of user generated content which grows without any activity from the service provider
- End of the software release cycle: Web2 applications are not products but services (E.g. Google). But this requires continuous up gradation even on a daily basis unlike software products.
- Lightweight programming models: Software applications of Web2 applications have simple designs and usability. Even the software programming itself is simple.
- Software above the level of a single device: Web2 applications can be used on other platforms like handheld divides apart from the computers themselves.
- Rich user experience: Web2 applications usually provide the user with a lot of information. User experience is also increased by the way the content is provided. The author concludes that the following factors are the ones which totally differentiate Web2 applications from Web1 applications. They are Services and not products.
Control over data created by users themselves
- Trust on the user
- Harness collective intelligence
- Customer self service
- Can be used on multiple platforms (e.g. on handheld devices).
- Easy to use as well as simple software. (O’reilly 2007, Page 36).
The legal and ethical issues in internet marketing
All the legal and ethical issues that are applicable to traditional marketing is applicable to internet marketing as well. But due to its unique nature, there are some areas that need to be specially mentioned. They are given below: (Gauzente and Ranchhod, 2002,P. 1).
Gathering information
Due to the nature of the internet, companies can use websites to gather a large amount of personal data of the individual. For example, registering to buy products online usually requires the customer to provide standard data like name, address, age, sex etc. apart from this some websites also require personal preferences and tastes to be provided. The prevalence of cookies is also another source to gather information unnoticed by the customer. The following standards will determine the ethical and legal practices followed by companies.
Information as to how the information is used have to be shown prominently. Disclosure policies also have to be mentioned. Another factor is the level of choice given to the customer about giving the information. Once the data is provided whether he/she has the facility to access it again to edit or correct the data. The level of protection that the company can provide to the data should also be mentioned. The company should also provide a contact number or email address if the customer needs to contact the company.
Advertising
Many companies advertise on the internet through pop up ads, banners etc. some follow the practice of deceiving customers by incorporating false ‘ok’ buttons. The paper gives three factors taken from other research sources as critical in determining the ethics followed by companies. They are individual autonomy, consumer sovereignty and harmfulness of product. The first factor refers to how well the customer understands the power of advertising to manipulate them. Customer sovereignty refers to level of knowledge of customers in their ability to see an advertising statement as false.
The following figure shows the position of different internet advertising methods to customers sovereignty and intrusiveness.
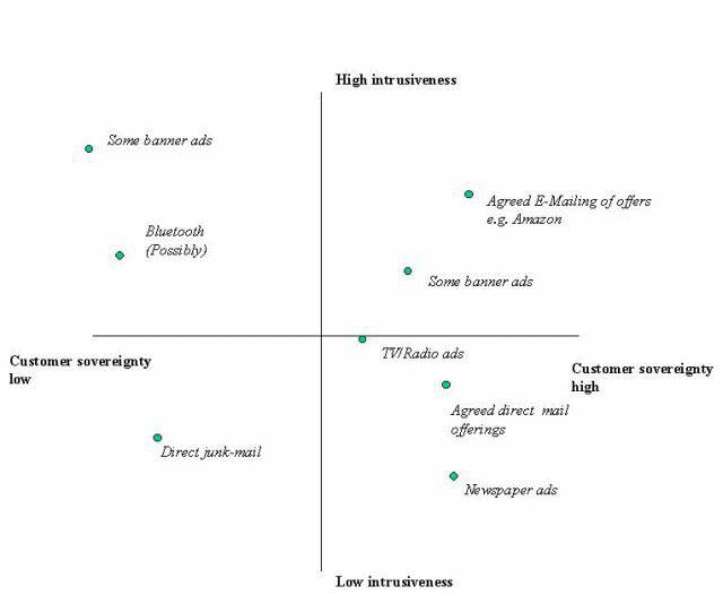
Guidelines for building websites
Most websites have visuals and text in their pages. The basic principles to be followed should for print and electronic media are quite the same. The main guidelines when building a website is given below.
- Purpose: The purpose of the website should be made clear first. For example, it should be decided whether the site is only an advertisement or is there interactive faculties and online purchasing incorporated.
- Target audience: Like any advertising strategy, the target audience should be identified and the website developed accordingly.
- Budget: Websites can be expensive to building depending on its complexity. The budget should be fixed beforehand and strictly adhered to.
- Professional help: It would be better to hire professionals to build sites if it incorporates a lot of complexities and features.
- Web copy: The language used in websites can influence customer behaviour and should be used well. Again, hiring professional help in writing the copy would be better.
- Looks and functions: A well designed site using the correct colours and fonts will be more pleasing to customers. It should also be seen whether Web2 applications like blogs should be incorporated. (Tips for Successful Website Development).
- Security: If the company plans to conduct financial transactions, adequate security arrangements should be incorporated.
Examples of Web2 applications
Terry O’Reilly in his article mentioned above has also given a few examples of Web1 applications and their Web2 counterparts. The list is given below.
Conclusion
Interactive marketing and internet marketing have components in common, but there are areas of differences as well. The purpose of both strategies is to promote business, enhance customer service, build customer relationship, provide good customer service, build brand as well as product image, provide the company profile etc. The concept of Web2 applications too have been given in detail. Some examples of such applications have also been given.
It can be said that the importance and use of such applications are on the rise. Companies are now using them even on commercial sites as well. Apart from this ethics of online marketing and guidelines in building a site have also been provided. This report can be used by organizations for understanding the concept of online marketing as well as a guideline for developing online marketing sites.
Bibliography
A Complete List of the Many Forms of Web Marketing for 2008. (2008). Web Strategy by Jeremiah. Web.
DUERMYER, Randy. (2008). Internet Marketing 101. About. Home Business. Web.
eDynamic’s Interactive Marketing & Web Strategy Capabilities. (2008). eDynamic. Web.
Electronic Marketing. (2008). DataPro. Web.
HOFFMAN, Donna L., and NOVAK, Thomas P. (1996). A New Marketing Paradigm for Electronic Commerce. Web.
Interactive Marketing: Definition. Business Dictionary. Web.
Interactive Online Marketing Strategy. (2007). Machinteractive. Web.
Concepts and Principles: Principles of 1 to 1 Marketing. (1998). Managing Change, Strategic Interactive Marketing. Web.
No One Way Road, This! Moving Towards Interactive Marketing. (2008). Online Marketing Software. Web.
Online Promotion Company – What Should you Look for? (2008). Online Marketing Software. Web.
Theories of Internet Marketing. (2007). Webmarketing beyond the basics. Web.
LOTTI, Mike., and LEHMANN, Don. (2007). Community: AMA Definition of Marketing. American Marketing Association: Marketing Power. Web.
COURT, David C. (2004). A new model for marketing. McKinsey on Marketing. The McKinsey Quarterly. Web.
O’REILLY, Tim. (2005). What Is Web 2.0: Design Patterns and Business Models for the Next Generation of Software. O’REILLY. Web.
O’REILLY, Tim. (2007). Communications and Strategies: What Is Web 2.0: Design Patterns and Business Models for the Next Generation of Software. O’Reilly Media Inc. Page 36. Web.
Tips for Successful Website Development. Small business bible. Web.
GAUZENTE, Claire., and RANCHHOD, Ashok. (2002). Ethical Marketing for Competitive Advantage on the Internet: Delineating Ethical Marketing Practices. P. 1. Academy of Marketing Science Review. Web.
