Introduction to Drivers and Impact of Change
Change management has become one of the most challenging managerial tasks for large multinational corporations. It requires a deep understanding of the specific drivers of change, internal capabilities to embrace it, and the effect that it would have on the overall success of the organization. Jayatilleke and Lai (2018) explain that the management must understand ways of managing change in a way that will have a minimal negative impact on its operations. One of the best ways through which a multinational corporation can manage change is to understand its key drivers. In this case, the top management unit of ABC Company should understand how the following factors may drive change in its normal operations and the impact of the same within the automotive industry.
Technology has remained one of the most important drivers of change. As new inventions emerge, it becomes necessary for a firm to adjust its operations in line with the changes in the market. Organizational culture is another major driver of change. When a company embraces a culture of continuous improvement, there will be a constant change from one practice to the other. Organizational leadership is another major factor that facilitates change. Some leaders prefer embracing specific strategies and practices for a long period while others prefer dynamism in a firm. Competition in the market will also force a firm to adjust its operations. In 1992, IBM unveiled the first smartphone on the market (Al-Ali et al., 2017). All its rivals had to embrace the change and soon, smartphones became a common product in the market. Customers’ demand is a powerful driver of change. Changes in tastes and preferences in the market would force companies to redefine their products. The political environment in a country also defines the path that a firm takes in its operations in that market. The economic environment, demands of suppliers, and market research are the other critical drivers of change.
How Change Affects Organizational Strategy
Whenever there is a change in an organization, various strategies may be affected in different ways. When a new production technology is introduced, a firm may have to shift from a labor-intensive to a capital-intensive strategy. Some employees may be laid off, especially those whose functions can be performed by the machines. Change may also force a firm to redefine its approach to engaging customers. For a long time, large corporations had to send a team of experts to the market to physically meet with customers to collect data on issues such as tastes and preferences, expectations, and issues they feel should change. With the emergence of social media, the strategy has changed as firms are now using platforms such as Facebook, YouTube, Instagram, and Twitter to engage their customers. Whenever there is a change, an organization has to redefine its strategies to match the new system that has been created.
Overview of the Organization Case Studies
Case Study 1: Digital Camera Mishap at Eastman Kodak
Eastman Kodak was once the largest film company in the global market. It enjoyed 87% of the global market share by the mid-1970s. The firm’s continued research led to its invention of digital camera technology in 1975 (Welch and Lamphier, 2019). However, the top management feared that the new technology would threaten its photographic film business, which was considered the firm’s cash cow at the moment. A decision was made that the firm will reject change as a way of protecting its primary products. However, other firms understood the significance of embracing the new technology and went ahead to introduce digital cameras in the global market (Englund, 2019). As an industry leader, Kodak felt that it had the power to ignore technology-driven change without any significant consequence. However, it was a suicidal mistake as Fujifilm soon became the market leader in the industry because it was the first to introduce the new technology to the market. Its attempt to resist change almost forced this firm out of the market as it was forced to file for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in 2012 (Koirala, 2018). The company has been able to recover because the new management currently appreciates the need to monitor and respond effectively to changes in the market.
Case Study 2: Successful Introduction of iPhone 8 by Apple Inc.
Apply Inc. is one of the most successful multinational corporations in the United States. The company has been a change leader in the industry as it struggles to meet the current and emerging market needs in the most effective way possible. One of the recent products that it introduced in the market was the iPhone 8 (Mas, 2018). It was released in the market in 2017 as a smartphone that also doubles up as a powerful camera. Like its predecessors, this product received massive acceptance in the market not only in the United States but also in the global market (LoPucki and Verstein, 2020). The introduction of this new product is a sign that the firm understands the significance of embracing emerging technologies to ensure that it meets the expectations of its customers in the best way possible. Such strategies have enabled the firm to remain operational despite the challenges it has encountered in the recent past.
PEST Analysis of the Case Studies to Identify Drivers of Change
The two case studies show a major contrast in strategies that Eastman Kodak and Apple Inc. took when managing change in their operations. Using PEST analysis, it is possible to assess the drivers of change in each of them (Thakur and Mangla, 2019). In the first case, the management of this company decided to ignore change, and the outcome of the strategy was disastrous. It has been responsible for the drop of the company from being the market leader in the industry to being a struggling firm that needed the support of the government to stay afloat. In the second case, there is an indication of a commitment by the firm’s top management to embrace emerging technologies as a way of ensuring that its operations remain sustainable.
The political environment is one of the major drivers of change, as was mentioned in the first section of this paper. Regulatory policies that a country embraces define the approach that a firm takes in its operations. When the management of Eastman Kodak decided to ignore the change in 1975, there was no political force that propelled its decision to do so. As such, this was not a driver for change. In 2017 when Apple Inc. decided to introduce iPhone 8, there was a change in regime in the United States and the management felt that it was necessary to introduce a new product to take enable it to take advantage of the expected opportunities promised by the incoming administration.
The economic environment is another major force that defines the need for a firm to embrace change. Gibson (2020) explains that when the economy is booming, there is always a demand for new classier products. In 1975 when the firm decided to resist change, the United States economy was relatively stable (Katzenbach, 2019). Customers could afford to purchase the new product that the firm had invented. However, the firm ignored the opportunity. The economic factor was one of the major drivers of the decision to ignore change. The management of the firm felt that the new product would have a negative impact on its revenue flow. In 2017 when Apple Inc. introduced the smartphone into its portfolio of products, the economy of the country was on a positive growth trajectory. The targeted customers could afford the product. As such, the economy was one of the drivers of change.
The social environment may also drive change within a given organization. The tastes and preferences of customers are often defined by social factors (Maoui et al., 2018). The beliefs and practices of a given group of people define whether they will purchase a given product. The failure of the management of Eastman Kodak to embrace change was motivated by a culture of protectionism. The firm felt that it has a responsibility of protecting its main product against the new one that they were about to introduce. It felt that the existing product in the market could not compete favorably against the new one. As it turned out, it was a wrong move that proved to be a costly mistake. In the second case study, the management of Apple Inc.’s decision to introduce the smartphone was partly driven by the social environment. Society has come to embrace the multipurpose nature of smartphones. The management knew that this product would be accepted by the targeted customers.
Technology is the fourth factor that drives change as indicated in the PEST model. Technological changes and trends tend to redefine the product and production strategies that a firm embraces. In 1975 when the company invented the first digital camera, technology was the leading driver that facilitated change. The company had been investing in innovative ideas to find ways of serving its customers in a better way. However, the management decided to ignore technology to protect its financial flow. In 2017 when Apple Inc. introduced iPhone 8, technology was also the central driver of change. The company embraced emerging technologies and integrated them with its traditional production strategies to develop a smartphone capable of taking high-quality pictures. Users of the phone no longer need to have a digital camera as long as they have their iPhone 8.
Impact of Change and its Effects on the Organizations’ Strategy and Operations
Each of the two organizations took different approaches to manage change and the outcome was also different. It is necessary to conduct an analysis for each organization on the impact of change and the effects it has upon the organization’s strategy and operations. As shown in the first case study, Eastman Kodak rejected change at a time when it dominated the market. It felt that introducing a new product would negatively affect its revenue stream. The failure to embrace change had a major impact on the firm’s strategies and operations. First, it embraced a strategy of promoting the existing product while at the same time trying to hide the existence of the new product. The outcome of this strategy had a devastating impact on the firm’s operations (Domingues et al., 2017). The firm lost its market lead not only in the global market but also in the United States. It was unable to redefine its operations in time to respond to the change and protect its market share.
Apple Inc.’s decision to introduce a new product in the market, the iPhone 8, was part of its tradition of producing a new better model of iPhone based on the changing customers’ tastes and preferences. The firm was responding directly to the needs of its customers. The change had a positive effect on the organization’s strategy and operations. It demonstrated to the management and its stakeholders that a culture of change is essential for the success of a firm (Akbar et al., 2019). As the firm’s market share and sales improved, the company had enough resources to invest in innovation. Apple brand has become one of the most powerful brands in the global market. The strategies that this firm embraces make it easy for it to embrace change whenever it is necessary. Since then, the firm has introduced other superior models of smartphones, which further confirms its commitment to change.
Effect of Change on Leadership, Team, and Individuals’ Behavior
Change may have a significant effect on an organization’s leadership, team, and individual’s behavior. Change may revolutionize the leadership strategies that a firm embraces in its operations. The disastrous performance of Eastman Kodak after it ignored the need to introduce the digital camera as a result of its leadership strategies. The management at that time felt that the dominance of the firm in the industry could allow it to ignore change. However, it turned out that it was a wrong assumption. Since then, the firm has redefined its leadership strategies, especially in change management. Currently, the firm has remained sensitive to change, always trying to ensure that the company embraces new strategies.
At Apple Inc., the management has realized the significance of change as a major success driver. As such, it has teams responsible for leading innovation to ensure that it is always a step ahead of competitors. The firm encourages its employees to work as a unit when tackling a given challenge, especially when it is necessary to introduce new technology. Individuals’ behavior has also been shaped by the constant change at this firm. Employees of Apple Inc. understand that the firm appreciates and rewards creativity. They have embraced a culture of change, where they always try to introduce a new way of undertaking their tasks.
How the Impact of Change Was Minimized and the Application of Appropriate Models to Process Change Efficiently
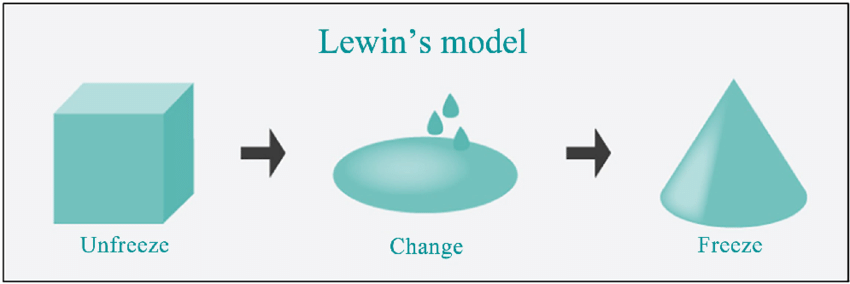
The management of Eastman Kodak was unable to manage change when it rejected the introduction of the digital camera. It was also unable to minimize the impact of change as it was effectively pushed out of its position as the market leader in the industry. The case study demonstrates the worst scenario of a firm’s failure to embrace change. Although the firm has remained operational, it is still struggling to ensure that it remains operational in the market. On the other hand, Apple Inc.’s case shows how a firm can achieve success by embracing change when it is necessary. The management of the firm uses an outward-in approach in its production, which involves understanding the needs and expectations of customers and using the information to develop new products. The management of Apple Inc. has been using Kurt Lewin’s model of change, shown in figure 1 below, to ensure that the process is efficient and with minimal experience.
When using this model, the management of a firm has to take three steps to achieve the intended goal. The first step is to unfreeze, which involves the preparation of all stakeholders for change. At this stage, the management explains the need for change, its benefit to the organization, and how it will affect the normal operations at the firm. The management may need to train its employees to ensure that they understand their new roles when the change is introduced (Matthews et al., 2018). When stakeholders are adequately prepared for the change, the model holds that the management should introduce the actual change in the second stage. In the case of Apple Inc., it will involve the introduction of a new product. Every department should understand what is expected of them under the new system. Further training may be needed at this stage. The last stage is to refreeze. It involves entrenching a new culture and practice in the organization based on the change that has been introduced.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Effective planning for change is critical to ensure that ABC Company’s operations remain sustainable. The case studies analyzed above show that the failure of a firm to embrace change may have disastrous consequences. Eastman Kodak’s case demonstrates the dangers of ignoring change even when a company is a leader in the industry. On the other hand, the case about the successful introduction of the iPhone 8 demonstrates that the market always rewards innovation. This firm should use Apple Inc.’s strategy towards change management as a benchmark for its strategies. ABC Company should be the driver of change in the automotive industry. In this industry, factors such as comfort, safety, speed, fuel efficiency, cost of maintenance, and physical appearance define consumers’ purchasing decisions. Continuous improvement in these areas can help ABC company to gain a competitive edge over its rivals in the market despite the stiff competition that it faces. Customers will believe that the firm is committed to offering them the best value. The following recommendations can help this firm to manage change effectively in the market as a way of gaining a competitive edge:
- The management should develop an innovation center where new ideas generated by employees can be tested to determine if they can be developed into new products and production strategies;
- The marketing unit should maintain regular market research, especially through social media platforms such as Facebook, YouTube, WhatsApp, and Twitter to understand emerging market trends;
- The marketing unit should maintain regular communication and sharing of data with the innovation center to ensure that inventions made by the center are based on the current market forces;
- The management of the firm should create a culture of change where employees are made to understand the need for change and are supported accordingly through training and other strategies.
Reference List
Akbar, M. et al. (2019) ‘Success factors influencing requirements to change management process in global software development, Journal of Computer Languages, 51(4), pp. 112-130.
Al-Ali, A. et al. (2017) ‘Change management through leadership: the mediating role of organizational culture’, International Journal of Organizational Analysis, 25(4), pp. 723-739.
Domingues, A. et al. (2017) ‘Sustainability reporting in public sector organizations: exploring the relationship between the reporting process and organizational change management for sustainability, Journal of Environmental Management, 192(1), pp. 292-301.
Englund, A. (2019) Complete project manager: integrating people, organizational, and technical skills. San Francisco: Berrett-Koehler.
Gibson, D. (2020) Managing risk in information systems. London: McMillan Publishers.
Jayatilleke, S. and Lai, R. (2018) ‘A systematic review of requirements change management, Information and Software Technology, 93(1), pp. 163-185.
Katzenbach, J. (2019) The critical few: energize your company’s culture by choosing what really matters. San Francisco: Berrett-Koehler Publishers.
Koirala, B. (2018) The rise and fall of Eastman Kodak: Will it survive beyond 2012? München: München GRIN Verlag.
Lauer, T. (2021) Change management: fundamentals and success factors. Berlin: Springer.
LoPucki, L. and Verstein, A. (2020) Business associations: a systems approach. New York: Wolters Kluwer.
Maoui, M. et al. (2018) Continuous API management: making the right decisions in an evolving landscape. Sebastopol: O’Reilly Media.
Mas, M. (2018) Definition and analysis of the market for the apple watch. München: München GRIN Verlag.
Matthews, J. et al. (2018) ‘Building information modeling in construction: insights from collaboration and change management perspectives, Production Planning & Control, 29(3), pp. 202-216.
Thakur, V. and Mangla, K. (2019) ‘Change management for sustainability: evaluating the role of human, operational and technological factors in leading Indian firms in home appliances sector’, Journal of Cleaner Production, 213(10), pp. 847-862.
Welch, R. and Lamphier, P. (2019) Technical innovation in American history: an encyclopedia of science and technology. Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO.

