Introduction
Lenovo is the new computer company, which specializes in the production of computers and other electronic devices, which was established in 2004 (Lenovo: our company 2015). Additionally, Lenovo has the leading positions according to the Forbes ranking by acquiring the company’s in China (Mourdoukoutas 2015a). Lenovo operates in various countries including having its headquarters in cities such as North Carolina, Paris and Beijing (Lenovo: locations 2015). It remains evident that the company continues its expansion by being present in internationally.
Strategy Identification
Lenovo’s strategy can be identified as a combination of vehement acquisitions, absence of ‘yes, yes, yes’ corporate culture, and a strong focus on innovation (Mourdoukoutas 2015b). Firstly, it tends to expand to the foreign emerging markets by acquiring the aggressively acquiring the competitors (Fernando 2015). In this instance, the primary goal of Lenovo is to expand its areas of operation. Moreover, it uses the globalization strategy to building a sustainable brand image in the world (Dickie 2005).
As for the innovation, it plays a significant role today, but to maintain its positions in the Chinese market, Lenovo implemented the adoption strategy (Biedinger et al. 2005). Nowadays, Lenovo considers the development of the innovative products by establishing the right partnerships with companies such as Samsung and providing high quality (ThinkPad 2015). In this instance, it is evident that Lenovo implements the cost-leadership strategy with the elements of diversification.
Suitability
The primary goal of the suitability is to evaluate whether the company can utilize its strengths to overcome the potential weaknesses (Lowellyne 2014). In this instance, PEST analysis was used to evaluate the potential external factors. In turn, VRIO and TOWS matrix are utilized to evaluate and define the efficiency of Lenovo’s strategy while determining the potential reasons for its success in the future. The combination of these strategies and analyses will contribute to the understanding of the primary external forces, which define the company’s success and the applicability, feasibility, and suitability of the strategy.
In this instance, the cost-leadership strategy is aimed at differentiating itself from the competitors by proposing a relevant price to quality ratio (Peng 2013). As for Lenovo, it focuses on the high-quality of its products, as, in this case, it is the determinant of the company’s recognition on the market (ThinkPad 2015). As for the social forces, it remains evident that customers prefer high-quality products (Stutchey 2015). In this instance, Lenovo complies with this trend, as one of its critical success factors is the maintenance of the high quality of the products (see Appendix 1).
Nonetheless, the importance of innovation and ergonomics is also gaining popularity among the users of technology. In this instance, the company’s strategy might be questionable as the products are highly imitable, and the company does not use all the opportunities to outstanding its drawbacks and weaknesses. The existence and constant appearance of the new trends in the technological and computer segments contribute to the necessity of the utilization of the company’s strengths while discovering new opportunities.
As for the technological changes, the lack of design and innovation are the primary drawbacks of Lenovo, as it has been adopting the technologies of the competitors to remain on the market (Biedinger et al. 2005). Meanwhile, companies such as Apple and Samsung paid vehement attention to innovation and product design (Baer 2014). It could be said that the lack of investment in research and development questions the future sustainability of the company due to the high competition in the market.
TOWS Matrix
In turn, the TOWS matrix (see Appendix 2) helps reveal the primary strength and weaknesses of Lenovo’s strategy of introducing particular examples. It will contribute to the assessment of the Lenovo’s strategy while establishing a new approach in the context of the current situation.
SO
Firstly, speaking of SO, the company utilizes its strengths to take advantage of the opportunities. In this instance, Lenovo has to capacity to pursue continuous innovation, and the company started paying more attention to the R&D. It remains evident that Lenovo slowly changes its milestones to the cultivation of innovation within the organization (Helft 2014). Moreover, the company continues its globalization and expansion, as it is Lenovo’s primary goal to gain high recognition on the global scale (Zhijun 2006).
TO
As for the TO, Lenovo is only partly able to overcome weaknesses, as the strategy does not cover all the particular aspects to assure the company’s position on the market. The lack of design and innovation determines the company’s position on the market. In this instance, Apple has the leading positions on the electronic consumer market due to its innovative design and individuality (Baer 2014). In this instance, providing the high quality of the product cannot outweigh the potential weaknesses of the company’s strategy.
ST and WT
Lastly, ST and WT have to be discussed simultaneously, as the company is not able to avoid the threat by maintaining the primary features of the strategy. In this instance, the intensified competition by the introduction of the tablets questions the positions of the newcomers (Arthur 2014). In the end, despite the expansion of the diversity of the products, and the position of Lenovo remains questionable.
In the end, the suitability of the strategy remains questionable, as the company might experience difficulties in the future during the implementation process while reaching the strategic objectives. Nonetheless, the utilization of the matrix and other analyses contributes to the understanding of the strategy’s drawbacks and benefits. Moreover, it portrays the potential areas, which require improvement.
Acceptability
Risks
In this instance, the perceptions of shareholders and risks have to be evaluated to measure the company’s acceptability. In this instance, the primary risks of the strategy application imply the economic fluctuations and changes in the prices of the competitors. Different economic conditions might adversely affect the choice of the strategy and requirements to introduce particular modifications to maintain competitiveness on the market (Ireland, Hoskisson & Hitt 2008). Another risk is the rapid technological development and the essentiality to respond to changes within the particular time frame. Taking into account these risks and threats will contribute to the achievement of the company’s profitability as these aspects determine the Lenovo’s ability to generate higher revenues and sustain on the market.
Reaction of Stakeholders
As for the stakeholders, Lenovo utilizes the joined management instrument to combine trademark and brand image under one definition (Han 2007). It could be said that the application of this approach assures Lenovo’s stakeholders that the company will be able to protect its intellectual rights and stay competitive on the market. Nonetheless, it remains evident that the application of this approach might not be the only solution to the arising threats, as the company might not be able to handle the competition in the future. In the end, the company has to continue the development of its strengths by taking into account external opportunities and threats, which arise during the implementation of the strategy.
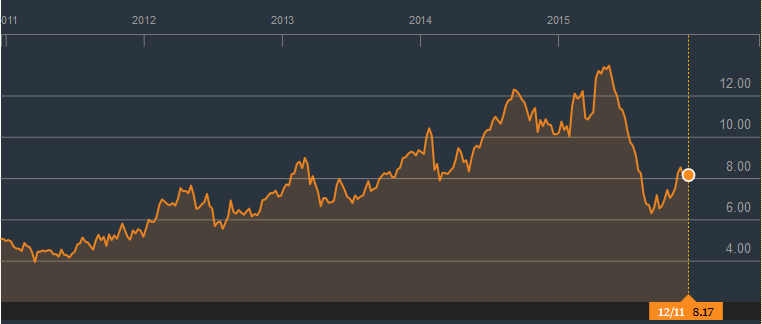
Speaking of the shareholders, the shares of Lenovo Group Ltd continue to rise after the experience of the significant drop in 2015 (Bloomberg Business: Lenovo Group Ltd 2015). The figure with the fluctuation of the Lenovo’s value per share is presented in Appendix 4. Nonetheless, the start of the growth of the company’s value by the market share is a positive sign, which can contribute to the company’s stability in the future. In this instance, the shareholders are the important contributors to the company’s success and performance.
As for the company’s revenues and profitability, in one of the press releases, the management of Lenovo claims that the company was able to increase its profitability by 20 % by gaining US$46.3 billion in revenues (Lenovo 2015). It could be said that the strategy, which is currently implemented by Lenovo is working, as the company is able to satisfy the core needs of its customers.
Feasibility
In this instance, the analysis of the VRIO model (Appendix 3) will contribute to the understanding of the capabilities of Lenovo, which will help the company to stay competitive on the market and release its full potential while discovering the opportunities of the current strategy. In this instance, it could be said that in the context of the strategic implementation, the company uses all capacities to comply with the satisfaction and the maintenance of the high quality of the products. In this instance, the maintenance of high quality is one of Lenovo’s milestones while establishing the corporates image (ThinkPad 2015). In this case, this approach is the primary contributor to the future development of the company due to the positive portrayal in the society.
Despite the presence of the diversification and different product lines, Lenovo’s products can be imitable due to the lack of the design and sufficiency of ergonomics. In comparison to Apple, Lenovo does not have a unique design and operation system (Baer 2014). In this instance, using the opportunities for innovation might assist in the development of a distinct competitive advantage, which will contribute to the increased share of Lenovo on the market. Nonetheless, despite not being unique and the absence of the particular distinguishing attributes, Lenovo is able to compete efficiently on the market now due to the focus on the high quality of the products and globalization intention of the brand differentiation.
Alternative Strategy
As for the alternative strategy, Lenovo has to combine differentiation and cost-leadership strategy to compete with the technological giants such as Samsung and Apple (Ireland, Hoskisson & Hitt 2011). Despite being focused on the building of the brand and internationalization of Lenovo products with the assistance of acquisitions, Lenovo would not be able to compete continuously on the market without paying a high focus on innovation.
As nowadays, the leaders of the companies with high profitability and positive social image claim that innovation is the key determinant of the company’s success (Fischer 2011). In this instance, a combination of these principles will allow the company to improve its company’s image, as this strategy contributes to the ability to covering the weaknesses and threats by actively employing the existing strengths and developing the new strategies to take advantage of the potential opportunities.
In this instance, learning from the leaders of the industry such as Samsung and Apple will contribute to the understanding of the key trends of the technological market such as providing high-quality products with exceptional design (Shaughnessy 2013). Additionally, focusing on design is one of the determinants of the Apple’s popularity on the global market, as these principles combine innovation and ergonomics of the products (Baer 2014). It could be said that the application of these principles while maintaining the positive brand image and the global recognition of Lenovo, will help the company to gain a larger market share. It remains evident that nowadays it lacks focus on innovation and R&D due to the necessity to gain greater popularity on the market than it has today.
In this case, the VRIO model (Appendix 3) refers to the fact that the company does not use its full potential, as the product is highly imitable, and similar products are presented among the competitors in the industry. Furthermore, the TOWS Matrix (Appendix 2) underlines that the company does not use its capacities entirely due to the lack of innovation and necessity to the brand building in the world. These analyses underline the insufficiency of the Lenovo’s strategy, as nowadays it is not enough to focus on the cost-leadership by providing high-quality products. Consequently, focusing on the elimination of the weaknesses will contribute to the introduction of the cost-leadership and differentiation strategy as it is the most applicable approach to future sustainability.
In the end, innovation plays an important role in the development of a sufficient company’s image, which contributes to the growth and development of the organization. The compliance with the new trends and advancements will assist in the development of the distinct competitive advantage. In this instance, Lenovo currently focuses on the application of the cost-leadership with some principles of differentiation. Nonetheless, focus on R&D and innovation will bring the company to the new level and help it gain a larger market share. The analysis reveals that by paying vehement attention to the principles of innovation will contribute to the advancement of the ability to enhance its organizational performance, as now Lenovo has enough capacities to enhance its strategy and bring its products to the new level.
Reference List
Arthur, C. 2014. ‘PC market still shrinking, with smaller firms squeezes out’. The Guardian. Web.
Baer, D. 2014. ‘7 philosophies that have made Apple designer Jony Ive a legend’. Business Insider. Web.
Biedinger, J, Deciccoa, T, Green, T, Hoffman, G, Leia, D, Mahadevan, K, Ojeda, J, Slocum, J & Ward, K. 2005. Strategic action at Lenovo’, Organizational Dynamics, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 89-102.
Bloomberg Business: Lenovo Group Ltd. 2015. Web.
Dickie, M. 2005. ‘Global brand strategy key for Lenovo computer hardware’, The Financial Times, p. 8.
Fernando, J. 2015. A look at Lenovo’s strategy and business model. Web.
Fischer, B 2011, ‘CEO’s say innovation is the most important factor for growth‘. Forbes. Web.
Han, G 2007, ‘Lenovo’s brand management strategy: promotion and protection’, China Intellectual Property, Web.
Helft, M 2014, ‘In pursuit of innovation, a milestone for Lenovo’. The Fortune. Web.
Ireland, D, Hoskisson, R, & Hitt, M. 2011. Understanding business strategy, South-Western Cengage Learning, Mason.
Ireland, D, Hoskisson, R, & Hitt, M. 2008. Understanding business strategy: concepts and cases, South-Western Cengage Learning, Mason.
Lenovo. 2015. Lenovo delivers solid fourth quarter and full year 2014/15 results, media release. Web.
Lenovo: locations. 2015. Web.
Lenovo: our company. 2015. Web.
Lowellyne, J. 2014. Sustainability footprints in SMEs: strategy and case studies for entrepreneurs and small business, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken.
Mourdoukoutas, P. 2015a. ‘Lenovo joins the ranks of the best global brands‘. Forbes. Web.
Mourdoukoutas, P. 2015b. ‘The global rise of Lenovo‘. Forbes. Web.
Peng, M. 2013. Global strategy, South-Western Cengage Learning, Mason.
Shaughnessy, H. 2013. ‘8 leadership lessons from Apple and Samsung’. Forbes, Web.
Stutchey, M. 2015, ‘Three biggest circular economy myths holding back businesses’. The Guardian, Web.
The Stationary Office. 2010. Management of risk: guidance for practitioners, TSO, Belfast.
ThinkPad. 2015. Web.
Zhijun, L. 2006. Lenovo’s affair: the growth of China’s computer giant and its take-over of IBM-PC, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken.
Appendix 1: PEST Analysis (Critical Success Factors)
The primary goal of PEST analysis is to determine the company’s success factors while evaluating and understanding the forces, which influence the organizational performance, externally (The Stationary Office 2010). Nonetheless, in this instance, PEST is used critical success factors of Lenovo.
Economic
As for the economic forces, the currency exchange is one of the aspects, which might negatively affect the sales of any international company. In this instance, Lenovo might experience difficulties during the recession stage as it operates on multiple continents. Moreover, the recession stage might require the introduction of modifications in the context of the strategical perceptions (Ireland, Hoskisson & Hitt 2008).
Social
CSF- Ability to provide high-quality products
As for the social forces, the customers always look forwards for high-quality products. It remains evident that this approach attracts consumers, as this feature is highly cherished. In this instance, Lenovo’s critical success factors are satisfying the consumer needs while providing reasonable price to quality ratio, as Lenovo pays attention to the quality of its products (ThinkPad 2015).
CSF- Ability to maintain global brand image
Moreover, the customers remain loyal to the brands, and brand image plays an essential role while being competitive on the market. In this case, the key success factor of Lenovo is the utilization of the globalization strategy in the context of building brand image in the world (Dickie 2005).
Technological
CSF- Ability to adopt the strategies of the competitors
Moreover, the technological development and continuous advancement in this area contribute to the development of innovation products and features. Nowadays, the CEOs of the leading companies define innovation as an essential element for the company’s growth and development (Shaughnessy 2013). Nonetheless, the key success factor of Lenovo is the ability to adopt the technologies of the competitors and maintain the quality on the high level (Biedinger et al. 2005). This factor contributes to the sufficient position on the company on the market
Appendix 2 – TOWS Matrix
Appendix 3 – VRIO Model
Appendix 4 – Lenovo’s Price per Share

![Lenovo Strategy Evaluation [SWOT & PEST Analysis]. Page 1](/wp-content/themes/business-essay/images/placeholder-w1.png)