Introduction
Geographic expanse has provided companies greater avenues to diversify their risk. For instance, multinational companies can look into other countries when one of the country’s economies is undergoing recession or political upheaval. Therefore, understanding the feasibility of a company operating in a certain location is important. The exercise to understand the location from the point of view of a company is undertaken in this brief report. The company we intend to study is General Motors (GM). The choice of GM pertains to the present situation of the company wherein it filed for interim bankruptcy. Further GM’s sales in the US, which was its largest market dropped considerably, therefore increasing the need for the company to expand internationally. Therefore, the need to ascertain international markets for the company is important. The country, we choose is India. The reason for choosing India is that India has posted an increase in automobile sales in 2008-09 when auto sales in US and Europe have been declining. In India, the overall passenger car segment increased by 2.48 percent and GM posted a sales increase of 1.28 percent. Given this background, it is therefore important to understand if India is really a lucrative location for GM to expand business. In order to understand the location’s viability the tool used to do the analysis is called PEST analysis. This will enable us to so a political, economic, social, and technological understanding in India related to the operations of GM in the country’s automobile sector.
GM is one of world’s largest automobile manufacturers, developers, and marketers of cars, trucks, and automobiles. The primary operation of the company was in North America and Europe. Tough presently the company has expanded into the Asian countries. Worldwide the company posted a decline in its revenue by 17.2 percent in 2007. The decline in sales has been the outcome of declining automobile sales in North American and Europe. Given this situation the company annual report suggested that the company must expand its sales in Asian market where auto sales have not as much been hit due to the global recession.
Therefore, this report undertakes a PEST analysis of India where GM has started its operations. This report will allow us to understand the true viability of India as a location for manufacturing and marketing of GM products.
PEST Analysis
Political
Political History: India is the largest democracy in the world. The government type is federal republic. The constitution had been drafted based on English common law, judicial review of legislative acts and different personal law codes apply to Muslims, Christians, and Hindus. The political scenario of the country has been dominated by various national parties like Indian National Congress (from here on referred to as Congress), Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), the Communist Party of India (CPI), and other regional parties.
Government: The political situation of India has been described in the following paragraphs. Congress emerged as India’s single largest Party in 2009 Lok Sabha Elections. The present Prime Minister of the country is Manmohan Singh. The party, which heads the nation, is a “secular, left of center party, with a long history political dominance”. As no single party gained a maximum majority of Congress-led UPA government, an ally of regional parties under the leadership of Congress came into power in 2009. As has been stated in a report in BBC News: “Regional players… now hope to move from sharing power to shaping the federal government”.
Terrorism: India has been facing problem of terrorism internally in states like Jammu and Kashmir, North-Eastern states of Nagaland, Manipur, Assam, Mizoram, etc. the problem of Maoists has increased in the Indian states of Jharkhand, West Bengal and Bihar. There have been repeated terrorist attacks in India. Most prominent of which has been that of the attack on Mumbai’s Taj Hotel in 20087. The Washington Post has reported that the advent of terrorism in India has been growing. According to a report by Newsweek, “India faces more terrorism than anywhere in the world other than Iraq, Afghanistan and Pakistan.” The states that have been soft targets of terrorism have been Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), Andhra Pradesh, and North Eastern States. In J&K the problem has been from the 1947 – when British colonial rule ended. The dispute has been between India, Pakistan, and China. The dispute has led to many armed conflicts. This has led to two-third of fatalities in India due to terrorist attacks. In Andhra Pradesh, Orissa, Jharkhand the problem has been due to the Naxalites, who are revolutionary communists.
External Affairs: India’s relation with neighboring countries like Pakistan and China has been strained. India has though maintained positive bilateral relations with China; however, its relation with Pakistan has been full of political rhetoric. SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation) is a main body through which India maintains certain aspects of its relations with countries in the subcontinent. India had a good relationship with the former Soviet Union and India trade plummeted once the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) was formed which had a major repercussion on Indian foreign policy. India’s relation with the US has gained momentum due to their similar interest in free trade and fighting terrorism. Their relation is being alleviated into strategic partnership to “include cooperation in counter-terrorism, defense cooperation, education, and joint democracy promotion”.
Political Protest: One problem that must be mentioned in case of the automobile industry in India is political protests. One such instance was staged in Singur, West Bengal where protests had been faced by Tata Motors for Nano car project. This protest has affected the intent for investment in India for many automobile manufacturers in India who were ready to invest in the country’s auto sector.
Economic
GDP Growth: India has been facing rapid modernization and the economy has been facing an average growth rate of 5.6 percent in 2009. The real GDP growth rate of the country has been shown in figure 1. Figure 1 shows that the real GDP growth of the country has been increasing at 5.6 percent even though the growth rate has considerably declined since 2006. The growth of real per capita income has been declining though the rate of growth in 2009 has been 4 percent (approx.).
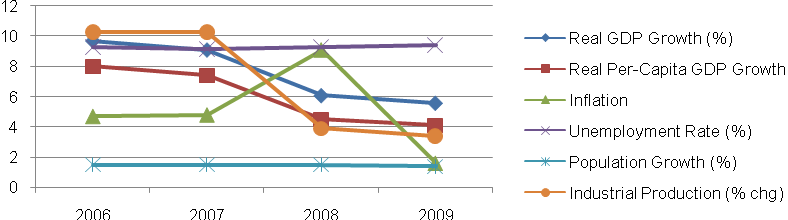
Inflation: the inflation has been increasing from 2006 through 2008. However, it declined sharply in 2008-09. This indicates that the fundamentals of the Indian economy are strong.
Industrial Production: The growth rate of industrial production of the country has been declining. This has been due to the global recession, which has reduced the industrial production worldwide. This has again increased unemployment rate marginally in the country.
Foreign Direct Invest (FDI): FDI inflow in the country has been increasing constantly in the country. It has increased from $17.5 billion in 2006 to $29.1 billion in 2009. Even with the present global economic crisis and liquidity crunch, India has remained a preferred destination for FDI. According to the report by United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) “China is the most preferred investment location, followed by India and the United States”. In automobile sector, FDI has been strong with companies like Honda, Ford, Hyundai, etc.
Auto Tax: The taxes on Indian cars is double than that of China. Though in 2008, the central value-added tax on cars has been reduced, which the car manufacturer has passed on to the customers. The annual budget in 2009 had a positive impact on automobile industry. Moreover, vehicles over 2000 cc have gained a reduction on excise duty by Rs. 20000.
Social
Social History: India has the second-largest population in the world. The country has a rich history and heritage of numerous foreign attacks through the ages, which has turned it into an amalgamation of races that thrive together. The Indian median age is 25 years.
Religion: The country’s religion, caste, and languages are numerous and varied. There are three main religions like Hindus, Muslims, and Christians with numerous other minority religions. Every state has a different regional language. The Hindu caste system defines the social mores of the Indian society.
Hofstede’s Dimension: according to Hofstede’s cultural dimensions, India ranks high on power distance indicating that higher level of inequality of power and wealth. Higher long-term orientation in India represents a culture that is “perseverant and parsimonious”. India ranks third highest in masculinity indicating the distance between and women to be very high. India ranks lowest in uncertainty avoidance indicative of the country’s openness to unstructured ideas.
Demographics: India has the youngest population in the world. It has a death rate of 8 per 1000 populations and birth rate of 24 per 1000 population. Maximum population of the country is above 15 and less than 65 years of age. The average annual change in urban population in 2005-10 is 2.4 percent. Rate of poverty is high in countries with mounting inequality of income. The population of the country has been growing. The population growth of the country has been stable. India has the youngest population in the world with the least average age.
Environment Indicators: the CO2 emission per capita in India has been 1.1 metric tons. 36 percent of the country’s natural habitat remains untouched. Only 18 per 1000 population have motor vehicles in 2000-05.
Technology
The India’s spending on technology has gone up considerably. The IT spending for 2009 has gone up by 5.5 percent. Spending on infrastructure has slowed down. The construction of roads has also met with setbacks. There has been increased spending in infrastructure and roads in 2009.
From the above PEST analysis, it can be deduced that India is a lucrative place for a company like GM to advent out. Though the country faces certain political and extremist problems, overall the country has a stable economy. The most important aspect is the market is large and there is huge scope for auto industry as the sector has been growing even when other developed markets have shown a slack.
Reference
ENS Economic Bureau. “India will remain a favored FDI destination despite crunch: Report.” 2009. Indian Express. Web.
Aiyar, Swaminathan S Anklesaria. “Unanticipated consequences of FDI.” 2003. The Times of India. 2009. Web.
Anand, Rajeev. “Positive Impact on Automobile industry in Budget 2009.” Web.
BBC. “Decline of India’s political leviathans.” 2009. BBC News/South Asia. Web.
Bureau of South and Central Asian Affairs. “Background Note: India.” 2009. U.S. Department of State. Web.
Datamonitor. General Motors Corporation. Company Report [Retreived from EBSCO Host 2009]. New York: Datamonitor.
ET Bureau. “India’s IT spend may grow at lower rate of 5.5%” 2009. The Economic Times. Web.
“Most auto investors decide to play safe after Singur row.” 2008. The Economic Times. 2009. Web.
ITIM International. Geert Hofstede™ Cultural Dimensions. 2009. Web.
Kaplan, Eben and Jayshree Bajoria. “Counterterrorism in India.” 2008. Newsweek. Web.
Lakshmi, Rama. “India’s Growing Terrorism.” 2008. The Washington Post. Web.
Meredith, Robyn. “Courting India And China.” 2009. Forbes. Web.
Narasimhan, Jyoti. “India.” Global Insight. 2009.
PRB. Data by Geography > India > Summary. 2009. Web.
PTI. “Luxury car sales fall 8 per cent.” 2009. The Economic Times. Web.
—. “Tax burden on Indian cars more than double of China.” 2007. Access my Library. Web.
Reuters. “Tata, Mahindra to pass tax cut to customers.” 2008. The Economic Times. Web.
Sharma, Ashok. “Protests threaten India’s $2,500 Nano car project.” 2008. USA Today. Web.
Shukla, Saurabh. “Pak still epicentre of terrorism.” 2008. India Today. Web.
