Introduction
The Mindbody app is a business management tool that utilises internet technology to offer a variety of service solutions to customers. The Mindbody app is a SaaS application that manages millions of users under specific regulations. The management application integrates system security, software availability, and performance. The need for significant online presence supports many businesses to have real-time contact with customers. The business purpose seeks to bridge the gap between business and their customers. The business proposal seeks to expand the existing management of the SaaS to cover educational, transportation, maintenance, and essential services or bookings. The expansion relies on service demand from young individuals who are dependent on technology and online presence. These categories of customers require cloud service bookings to manage daily event planning and operations.
Business Model Development
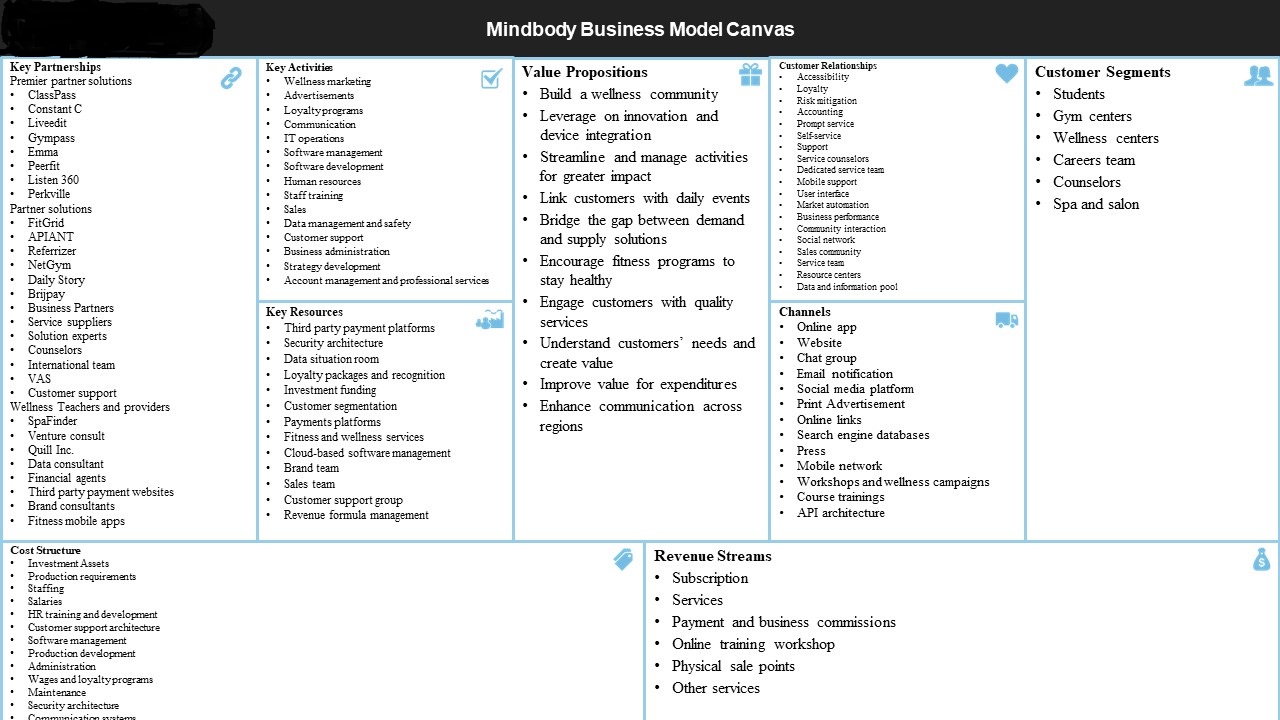
A business model is a framework that explains an investment’s impact on social space, cultural and economic environment. A business model development comprises the plan, marketing strategy, distribution systems, payment options, pricing, design, and other relevant solutions that support the investment (Ranjan and Read, 2016; Wirtz et al., 2016; Leischnig, Ivens and Kammerlander, 2017; Nyström and Mustonen, 2017; Wieland, Hartmann and Vargo, 2017; Crotty, Kinney and Farren, 2018; Balocco et al., 2019). As shown in appendix 1, a business model canvas summarizes the components of an investment plan. Thus, investors use the BMC to align their investments with profitable marking strategies.
Desirability
The survey on the value proposition describes how services are delivered to the target customer segment. The proposal is the core objective of business advertising. Based on customer interviews, investors hypothesise business models as an arrangement of interdependent elements affecting the attainment of strategic aims (Bocken, Rana, and Short, 2015). The outcome showed that advertising supports customer segmentation. The explanation of the Mindbody application shows that investors must categorise its customer segmentation based on geography, psychographic and demographic traits. However, it is challenging to segment customers based on the business proposal for expansion. Its expansion seems highly profitable for investors. An in-depth comprehension of the way to segment markets is imperative to direct the best choices resulting in beneficial targeting. Industry markets are changing rapidly because of new technologies and a much more complex business environment. Under this expansion project, the organisation can adapt components in the lean start-up strategy to enhance the business model and build its competitive advantage. Sparviero (2019) noted that the wrong target group could demarket a product or service. According to institutional theory, investors could influence systemic change, which mitigates business challenges and creates trade potential.
Feasibility
Data analysis was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the key activities of the proposed business plan. The motive was to understand and manage the challenges of the expansion based on the value proposition. Brenner et al. (2018) argued that BMC acts as a business design instrument in expanding the range of business sections, producing solutions, which prioritise quality, expanding distribution channels. In addition, it enhances client relationships via direct online communication architectures and enhance business performance. Thus, the management must choose and adopt channels that would simplify and execute the company’s business model. The mapping of key activities within the business model facilitates development and improvement in every marketing element of the plan (Sorescu, 2017; Tower and Noble, 2017; Bruno Soares, Alexander and Dessai, 2018; Balocco et al., 2019).
For the proposed expansion, the management must update its web directory to cover optimised search strings for educational service transport schedules, maintenance solutions, and other appointments via online platforms. The data pool provides informed analysis on the effectiveness of operational and hardware design (Türko, 2016; Neus, Buder, and Galdino, 2017; Prabhu, Tracey, and Hassan, 2017; Seggie, Soyer, and Pauwels, 2017). Since the Mindbody app deals with problem-solving events, the key actives include creativity, knowledge management, continuous training, platform management, customer satisfaction agile development, and platform innovation. Thus, the elements in the business model drive the key activities of the Mindbody application. The outcome of interviews shows that customers are willing to use practical, fast, simple, and innovative applications regardless of their price. Based on these assumptions, the business plan seeks to target young individuals whose interest in innovative application drives their daily activities.
Viability
Cost structure reviews were carried out to evaluate the challenges of expanding the Mindbody app to accommodate different search solutions. The investor gathered data from existing expenditure and operational costing template. Based on the findings, the cost structure for the proposed business plan must cover operating and capitalised activities. Under the operating expenses, the management must consider the costs of performance advertising, brand marketing, sales recommendations, information technology employee rewards, depreciation, amortisation, and administration activities. Other costs of operations include point-of-sales operations, software migration, IT infrastructure, maintenance, security architecture, salaries or benefits, data centre management customers support, and research and development.
A useful business model supports operational performance, which influences product design and configuration (Widyastuti, Fahmi, and Maulana, 2019; Larosa and Mysiak, 2020). The cost structure decision occurs at all levels of business, covering short-term and long-term activities. As a result, the proposed business expansion is triggered by choices and fiscal evaluation for the logical decisions to be attained. Thus, cost structure analysis is critical and influences the decision-making process. Therefore, the management must control processes, operations, and activity industries for significant development. Although, in attaining the aims of the expansion, the manager must analyse the cost structure of the investment as it monitors the outcome of the other components of the business model canvas. The analysis of costs, operational costs, loss quantification, and task performance enables a strong foundation for fiscal management.
Risk and Opportunities
Risk
Financial risk is a significant challenge for the proposed business plan. The financial risk emerges in the form of income generation or returns on investment. The profitability of the investment depends on the marketability of the Mindbody application. As a result, the management must allocate huge capital funding to provide high-tech data architecture, search engine databases, customer support, user interface integration and links to service suppliers, and payment alternatives. These components must remain functional regardless of the customer traffic. The high cost of maintenance and service becomes a financial risk since the Mindbody application depends on customer patronage. As a result, low patronage will reduce revenue and vice versa. The Porter’s five forces show that Mindbody faces competition from rival apps that include Zen Planner, Virtuaagym, Teamup, SimpleyBook, Teamsnap, ClubExpress, EZFacility, Pike13, and Club Automation. As a result, the management must allocate resources to create a competitive advantage. Creating such advantage becomes a financial risk for the organisation. Allocating resources based on priority and critical evaluation of each sector could mitigate financial risk.
Operational risk occurs when expanding the business plan to cover more than one service. The plan seeks to include several search functions that link customers with suppliers. Therefore, the risk of operations includes server failure, cyber-attack, data loss, payment link integration, and other operational factors. The outcome affects service delivery and customer satisfaction. To avoid operational risk, the management must outsource relevant data service to qualified and competent firms (Brillinger et al., 2019). The outsourced services and solutions must align with the vision of the organisation. Thus, effective control of all components of operations would mitigate system saturation and employee negligence and inefficiency.
Opportunities
The environmental and direct competitive analysis would emerge from the expansion of the proposed business plan as opportunities for the organisation. The environmental analysis deals with innovation, server communication, digitisation, chat functions, and service-based solutions. The proposed plan seeks to deploy innovative system design that supports communication. For example, the web interface must be light to avoid poor communication between customers and suppliers. These variables create opportunities for the new plan to attract more customers. Under the market analysis, the high cost of entry may deter start-ups from saturating the sector. The expansion will allow users to grow their business, deliver daily targets, and attend fitness classes without hassle. Therefore, business innovation will be built on the B2C model.
Direct competitive analysis is a strategic assessment that evaluates business information of rival organisations. Based on the above description, Mindbody directors must collect and analyse rival brands before adopting an expansion plan. The analysis exposes threats from close substitutes and strategies to overcome them. This variation creates opportunities with the app design. The proposed online application will integrate four different areas of interest, which may not exist in rival apps. The capacity to integrate these solutions creates a competitive opportunity to attract customers. Business growth opportunities provide additional marketing strategies for the organisation. The expansion of the search engine to include maintenance service, travel booking plans, or educational solutions creates opportunities for new customers. However, risk elimination includes operations that mitigate threats to the business plan. Investors must evaluate, identify, assess, manage, and prioritise risks and opportunities to improve business performance. The capacity to identify opportunities and business risk must adopt business techniques to improve learning. The management must learn from past operations, collect information from rival firms, scan, and implement scenario planning.
Recommendations
The value proposition relies on the B2C model, which is a simple structure that describes key stakeholders. However, the value proposition must target customers’ needs based on content, service, and solutions. Poor judgment on a practical value proposition will negatively affect the proposed business plan. Thus, the value proposition canvas must be modified from the existing template to include new target groups and align with strategic objectives. As a recommendation, firms should gather information on new business tools that permit simple but precise business assessment and data analysis to improve their value proposition.
The BCM template is a visual chart that describes the investment flow. The chart elements show operational direction for each department within the organisation. Based on the recommendations for the new proposal, the BMC must be described in a simple and common language. Based on the proposed plan, this paper recommends the creation of knowledge dissemination links between managers and business analysts. The recommendation will boost the firm’s business modelling and strategy skills to align with its value proposition. Under this template, mangers will use internal variables and resources to redesign the business model rather than lift alien frameworks from other industries. The change decision must be inclusive to avoid employee resistance. The expansion plan must include options from top to bottom to bridge the communication gap between the board of directors and employers. To improve agility in operational structure, the paper recommends business iteration. The strategy that was suggested permits design thinking and regular upgrades.
Evaluation of Skills and Collaboration
Interviews were conducted with prospective customers to evaluate their perceptions about Mindbody app, and the interaction highlights arears of importance and weakness. The response indicated the need for strategic interaction between non-competitors. The collaboration with non-competitors includes outsourcing, data management, and supplier engagement. During the interviews, the researcher achieved data collection and transfer. The impact of such collaboration facilitated the approval of a robust business model canvas (Bocken, Rana, and Short, 2015; de Man and Luvison, 2019; Sparviero, 2019).
A face-to-face interview was conducted to gather information for the value proposition template. The interaction was held in a friendly environment to encourage honest responses from the participants. The interaction process displayed the interviewer’s communication skills and collaboration strategies. The assessment considered potential key partners and their requirements. The buyer-seller relationship is a component of key partners in the BMC. Since the expansion requires strategic alliances with educational, maintenance, transportation, and essential suppliers, the interview with suppliers under each field provides guidance in achieving significant outcomes. By implication, the interviewer utilised personal communication skills to gather an unbiased response and code and analyse the data. The findings will improve the value proposition of the proposed business plan. Thus, business expansion must be driven by quality service delivery, long-term goals, coordination, and consistent funding capabilities.
Reference List
Balocco, R. et al. (2019) ‘Lean business models change process in digital entrepreneurship’, Business Process Management Journal, 25(7), pp. 1520-1542. Web.
Bocken, N. M. P., Rana, P. and Short, S. W. (2015) ‘Value mapping for sustainable business thinking’, Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering, 32(1), pp. 67-81. Web.
Brenner, T. et al. (2018) ‘Causal relations between knowledge-intensive business services and regional employment growth’, Regional Studies, 52(2), pp. 172-183. Web.
Brillinger, A. S. et al. (2019) ‘Business model risk and uncertainty factors: toward building and maintaining profitable and sustainable business models’, Business Horizons, 63(1), pp. 121-130 Web.
Bruno Soares, M., Alexander, M. and Dessai, S. (2018) ‘Sectoral use of climate information in Europe: a synoptic overview’, Climate Services, 9, pp. 5-20. Web.
Crotty, Y., Kinney, T. and Farren, M. (2018) ‘Using the business model canvas (BMC) strategy tool to support the play4guidance online entrepreneurial game’, International Journal for Transformative Research, 4(1), pp. 34-41. Web.
de Man, A. P. and Luvison, D. (2019) ‘Collaborative business models: aligning and operationalizing alliances’, Business Horizons, 62(4), pp. 473-482. Web.
Larosa, F. and Mysiak, J. (2020) ‘Business models for climate services: an analysis’, Climate Services, 17, pp. 1-13. Web.
Leischnig, A., Ivens, B. S. and Kammerlander, N. (2017) ‘A new conceptual lens for marketing: a configurational perspective based on the business model concept’, AMS Review, 7(3-4), pp. 138-153. Web.
Neus, A., Buder, F. and Galdino, F. (2017) ‘Are you too successful to digitalize? how to fight innovation blindness’, GfK Marketing Intelligence Review, 9(1), pp. 30-35. Web.
Nyström, A. G. and Mustonen, M. (2017) ‘The dynamic approach to business models’, AMS Review, 7(3-4), pp. 123-137. Web.
Prabhu, J., Tracey, P. and Hassan, M. (2017) ‘Marketing to the poor: an institutional model of exchange in emerging markets’, AMS Review, 7(3-4), pp. 101-122. Web.
Ranjan, K. R. and Read, S. (2016) ‘Value co-creation: concept and measurement’, Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 44(3), pp. 290-315. Web.
Seggie, S. H., Soyer, E. and Pauwels, K. H. (2017) ‘Combining big data and lean startup methods for business model evolution’, AMS Review, 7(3-4), pp. 154-169. Web.
Sorescu, A. (2017) ‘Data-driven business model innovation’, Journal of Product Innovation Management, 34(5), pp. 691-696. Web.
Sparviero, S. (2019) ‘The case for a socially oriented business model canvas: the social enterprise model canvas’, Journal of Social Entrepreneurship, 10(2), pp. 232-251. Web.
Tower, A. P. and Noble, C. H. (2017) ‘Exploring and extending a collective open business model’, AMS Review, 7(3-4), pp. 170-182. Web.
Türko, E. S. (2016) ‘Business plan vs business model canvas in entrepreneurship trainings: a comparison of students’ perceptions’, Asian Social Science, 12(10), pp. 55-62. Web.
Widyastuti, R. S., Fahmi, I. and Maulana, A. (2019) ‘Effect of adding new products on a company’s business model: a case study in Indonesia’, Russian Journal of Agricultural and Socio-Economic Sciences, 96(12), pp. 82-91. Web.
Wieland, H., Hartmann, N. N. and Vargo, S. L. (2017) ‘Business models as service strategy’, Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 45(6), pp. 925-943. Web.
Wirtz, B. W. et al. (2016) ‘Business models: origin, development and future research perspectives’, Long Range Planning, 49(1), pp. 36-54. Web.
Appendix 1
Appendix 2
Amended Business Model Canvas
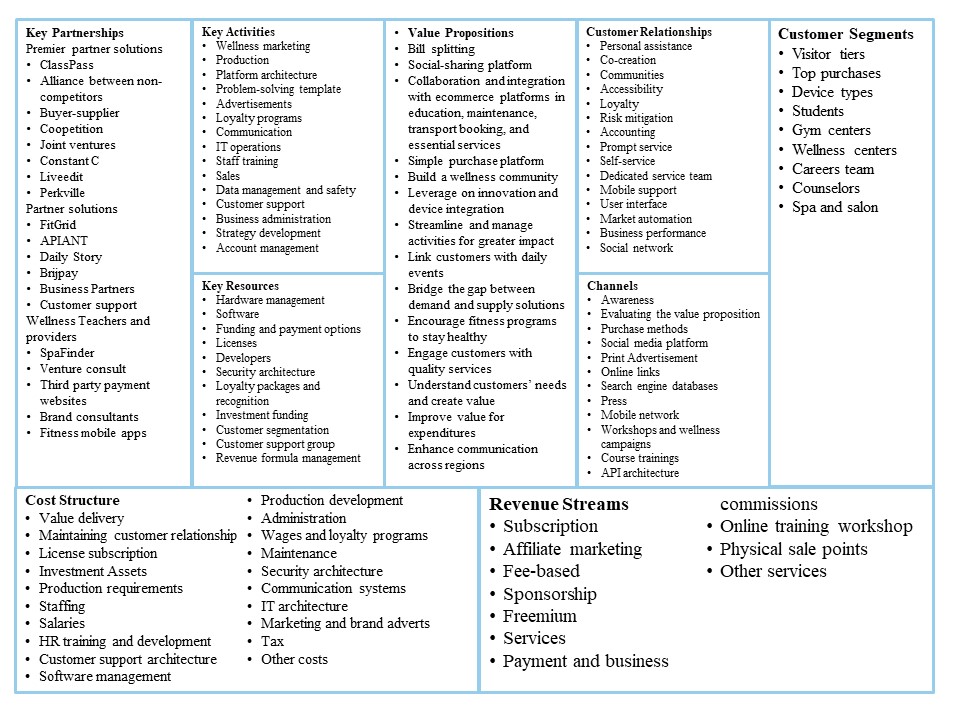
Appendix 3
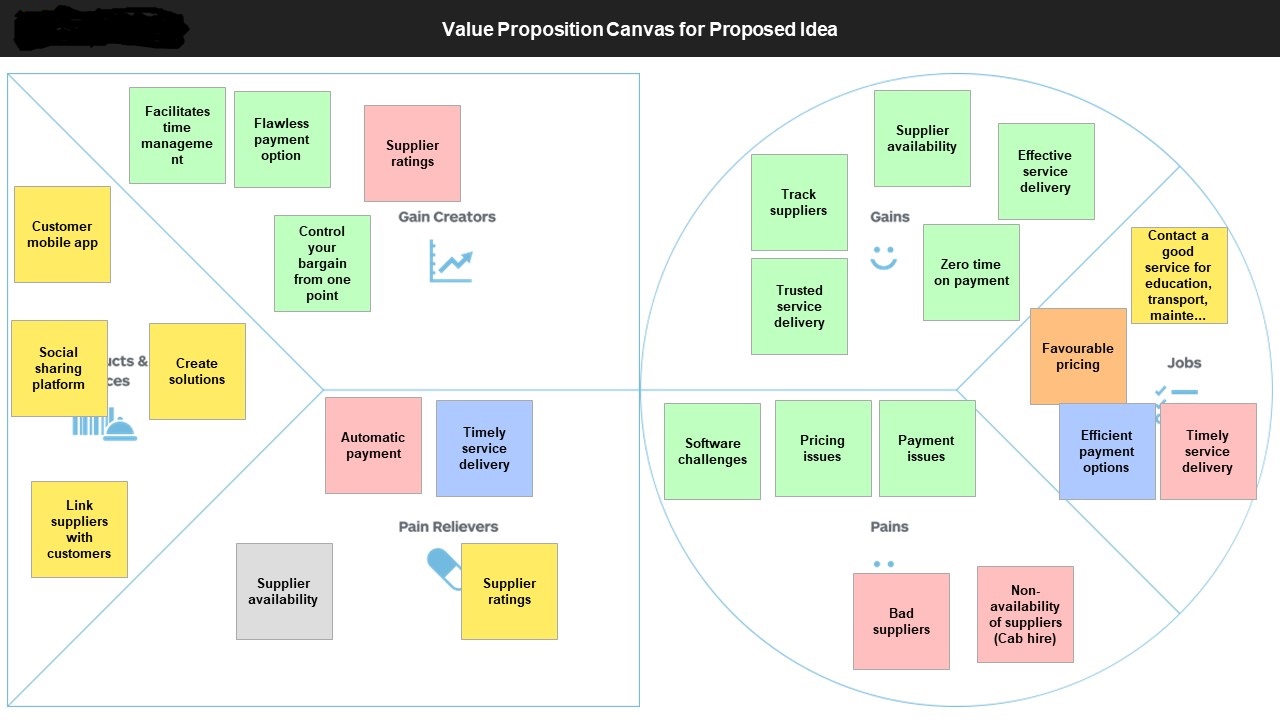
Appendix 4
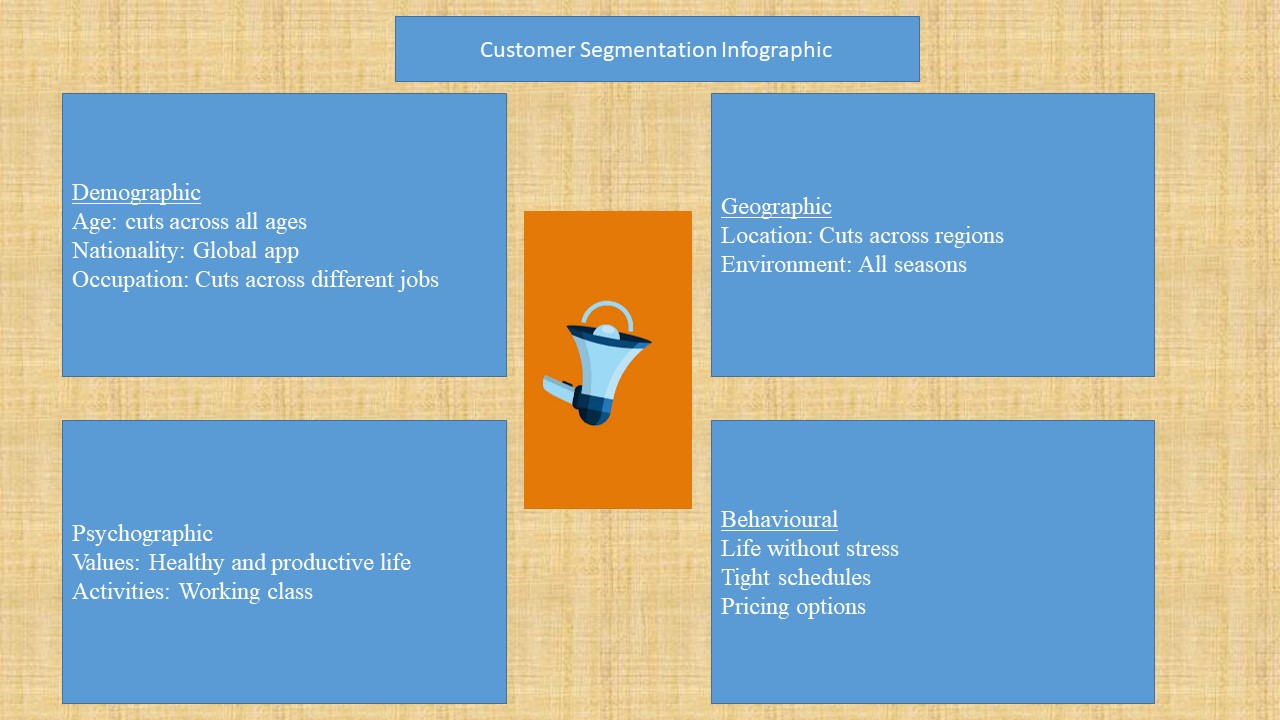
Appendix 5
Test card

Interview with a Professional
Industry drivers are events and operations that shape associations towards particular types. Organisations with similar tactical characteristics form tactical classes. Based on this premise, the participant argued that company assessment provides insight suitable for production. The participant believes that competition is a traditional strategy to attain a competitive edge. Thus, the proposed business plan must assume a tough environment, which influences the decision-making process. To achieve success in performance and revenue generation, strategic alliances involving key partners and businesses must be established. The participant believes that service booking requires a practical business framework that suits the customer segment. For example, during rush hours, cab hire may become difficult around the school environment, office location, and markets. To reduce such challenge, the investors must evaluate traffic data to increase cab drivers. Thus, software developer and supplier availability will improve service quality for the proposed business expansion.

