Description of the client
Tea Station Company was formed in 1996. The company is a franchise of the Ten Ren Tea Company. At the end of 2013, the company had 12 outlets that were located in Nevada and California. The company deals with the growth and promotion of exceptional tea and other related products. Specifically, the company offers a variety of Chinese tea products. The paper seeks to prepare an audit plan for the human resource department in the company.
Process flow diagram
The figure presented below shows the process flow diagram for human resource activities.
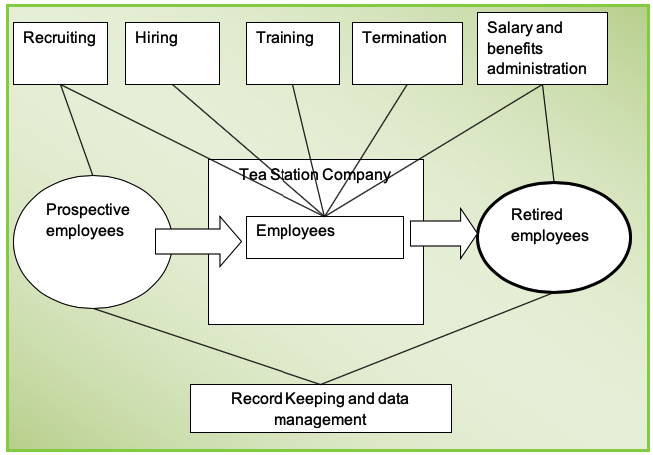
The human resource department carries out the function of recruitment, training, termination, salary and benefits administration, and record keeping. These activities are presented in the square boxes. The human resource function starts with the recruitment of potential employees. Once they are hired, they become employees of the company. Further, it can be observed that the company keeps records of prospective employees for future use. After they join the company, they go through training, which is organized by the department. Besides, the department prepares documents for the salary and benefits of the employees. Finally, the department prepares documentation and keeps records for the retired employees (Maund 17).
Audit planning
Audit objectives
- To verify that the company has established adequate policies and procedures to mitigate the risks in human n resource functions.
- To ascertain compliance with the company’s human resource policy & procedure manual, labor laws, and good practice in the industry.
- To determine that the human resource function’s contribution towards the attainment of the company’s strategic goals.
Risk analysis
The section will provide information on the risk assessment of the human resource department (Kumar and Virender 56). The areas that will be audited are human resource planning, recruitment, performance management , training, record keeping, leave management, and communication.
Work program
The section outlines the various audit procedures that will be followed when carrying out the human resource audit. It also provides the list of documents that will be reviewed under each area of audit (Burke 6). The information is presented in the table below.
Engagement letter
Introduction
The internal audit department will conduct a review of human resource functions as scheduled in the annual work plan for the year 2014. The report will commence on Monday, 17th March 2014, and run for 2 weeks.
Objectives
- To verify that the company has established adequate policies and procedures to mitigate the risks in human resource functions.
- To ascertain compliance with the company’s human resource policy & procedure manual and labor laws
- Determine the human resource function’s contribution to the attainment of the company’s strategic goals.
Scope and timing
The table listed below shows the areas that will be reviewed and the time allocated for each area.
Documents to be reviewed
Some of the documents that will be reviewed are listed below. However, more materials will be required as the need arises.
- Organogram
- Human resource plan for the year 2013 and 2014
- List of staff members as of 1st January 2013, 31st December 2013 and 1st March 2014.
- Minutes of management Committees
- Management reports that are prepared by the human resource department
Declaration
We agree with the planning document for the audit of the human resource department
Head of Human Resource Department
- Name:
- Signed:
- Date:
Head of Internal Audit
- Name:
- Signed:
- Date:
Works Cited
Allen, James, Jimmieson Nerina, Bordia Prashant, and Irmer Bernd. “Uncertainty During Organizational Change: Managing Perceptions Through Communication.” Journal of Change Management, 7.2 (2007): 187-210. Print.
Armstrong, Michael. Strategic HRM: A Guide to Action, London: Kogan Page, 2006. Print.
Bohlander, Gerald. Managing Human Resources, Mason, OH: Thomson Higher Education, 2007. Print.
Burke, Anne 2009, Introduction to Audit Planning. Web.
Cole, George. Personnel & HRM, London: Continuum, 2006. Print.
Kumar, Ravinder and Sharma Virender. Auditing: Principles and Practice, New Delhi: Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited, 2006. Print.
Lussier, Robert. Human Relations in Organizations, London: McGraw-Hill Publishers, 2009. Print.
Maund, Leon. Introduction to Human Resource Management: Theory and Practice, London: Palgrave Publisher, 2009. Print.
Pine, Brian 1998, Audit Planning. Web.
Rittenberg, Larry, Karla Johnstone and Audrey Gramling. Auditing: A Business Risk Approach, USA: Cengage Learning, 2012. Print.
