Executive Summary
This report has been prepared for the purposes of developing a quality management system for a large USA-based department store chain Nordstrom to enhance its competitive advantage in the retail market. The report is based on the research of academic and business-related sources published within the past five years. The document contains an introductory part that outlines the objectives of the report and its overall purpose. The critical review of quality management’s strategic importance for the retail industry is provided with the evaluation of the basic principles of total quality management. Furthermore, there is a critical discussion of the elements of a quality management system that apply to Nordstrom based on its quality culture’s SWOT analysis. Additionally, the trends in quality management are reviewed to identify the ones that apply to the retail industry and the analyzed company. Finally, a set of recommendations for the development and implementation of a reliable quality management system for Nordstrom is listed.
Introduction
The contemporary economic environment has become driven by technological advancement, continuous innovation, and rapidly growing competition. These issues trigger the need for improving organizational performance through a variety of methods and practices. Indeed, the better an organization works, the better product or service it is capable of delivering, and the more competitive its position in the market will be. Thus, quality management is an essential component of any industry that works in a consumer-oriented segment. The ability of a company to balance bottom-line goals with the pursuit of customer satisfaction predetermines a company’s longevity, success, and competitiveness (Winata, Satria, and Adnyana, 2019). Therefore, it is imperative for a contemporary enterprise performing in a competitive environment to have a functional and updated quality management system.
The company under analysis is the department store chain Nordstrom which has been operating in the retail business for several decades. The company, with a long and successful history of market performance characterized by innovative solutions, technology-driven customer services, and high-quality shopping experiences provided to its clients, is currently in need of enhancing its position in the market. The most beneficial way to succeed at such a task is to develop a well-structured quality management system that would incorporate the company’s strengths and opportunities while properly addressing its weaknesses and threats. This report is designed to review and critically evaluate total quality management principles as they apply to the retail industry. Moreover, it will review the elements that should be contained in Nordstrom’s quality management system, as well as evaluate the most important trends in quality management available for implementation. These issues will be used as a basis for the further development of a quality management system for Nordstrom.
A Critical Evaluation of the Strategic Importance of Quality Management in the Retail Industry
Strategically important issues for a company are the ones that help it envision the future and plan its performance through risk mitigation and strengths and opportunities utilization (Varadaraja, 2020). When analyzing the retail industry, scholars identify customer-oriented business models as the most effective ones. As Figure 1 shows, customer focus is the leading principle in quality management.
Moreover, such researchers as Fazel-e-Hasan et al. (2019), Eger and Micik (2017), and Yrjola et al. (2019) argue that customer value is an immediate constituent of a successfully operating retail entity. However, to pursue high-quality customer service, the whole supply chain of a retail company must be aligned toward the strategic goals and business objectives. Thus, customer value will only be achieved if the design, manufacturing, brick-and-mortar and online store functioning, technology and innovation, as well as employee relations, are managed with accuracy and diligence.
While a company might strive for high-quality production without particularly addressing customer experience, the customer-oriented model deems effective within the retail context due to the primary orientation on the patterns in consumer buying behavior and ongoing long-term relationships between a brand and customers (Kumar, Singh, and Modgil, 2020). According to Nunkoo et al. (2020), “service quality is one of the main determinants of customer satisfaction” (p. 2). The researchers found that the more satisfied the customers were with the quality of service, the higher the rating of the company was (Nunkoo et al., 2020). Although the study was conducted for the tourism industry, the findings apply to the retail industry as well since it particularly depends on company-customer interaction.
A similar argument has been presented by Hamzah and Shamsudin (2020), who conducted a survey measuring the importance of customer satisfaction and loyalty to business performance. The researchers defined customer satisfaction as “how well the product use experience compares to the buyer’s value expectations” (Hamzah and Shamsudin, 2020, p. 2). Customer loyalty, in its turn, is the level of trust exhibited by customers toward a company that ensures them continuously use the products or services provided by the company to obtain the same high level of quality and exceptional experience (Hamzah and Shamsudin, 2020; Sesar, Buntak and Martincevic, 2019). On the contrary, poor service quality triggers excessive costs caused by gaps in needs identification, standards, communication, and performance (Soares, Soltani and Liao, 2017). For that matter, these and other issues must be addressed by a well-developed quality management system.
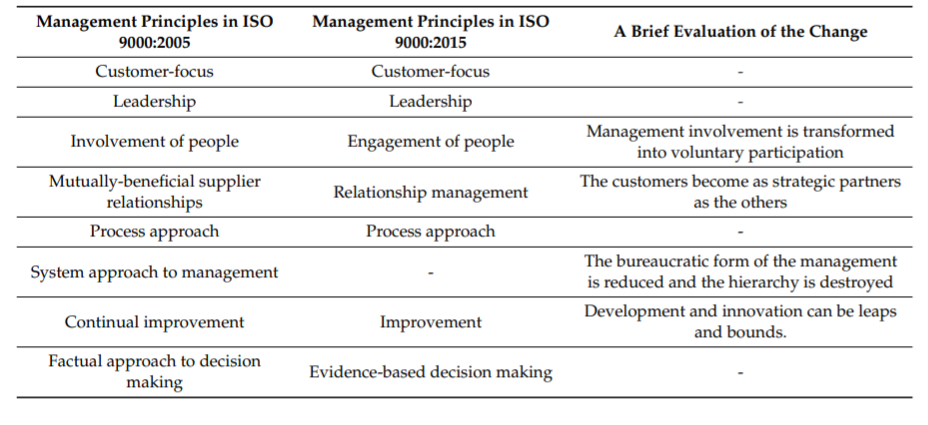
Total quality management entails a framework of service quality control across all business processes. It might be defined as “a set of opinions and ideas for improving the quality of products or services, which is widely called management philosophy” (Neyestani, 2017). Total quality management principles include several key points that establish the basis for the development of a reliable quality management system (Khan, 2015; Zanqar et al., 2019).
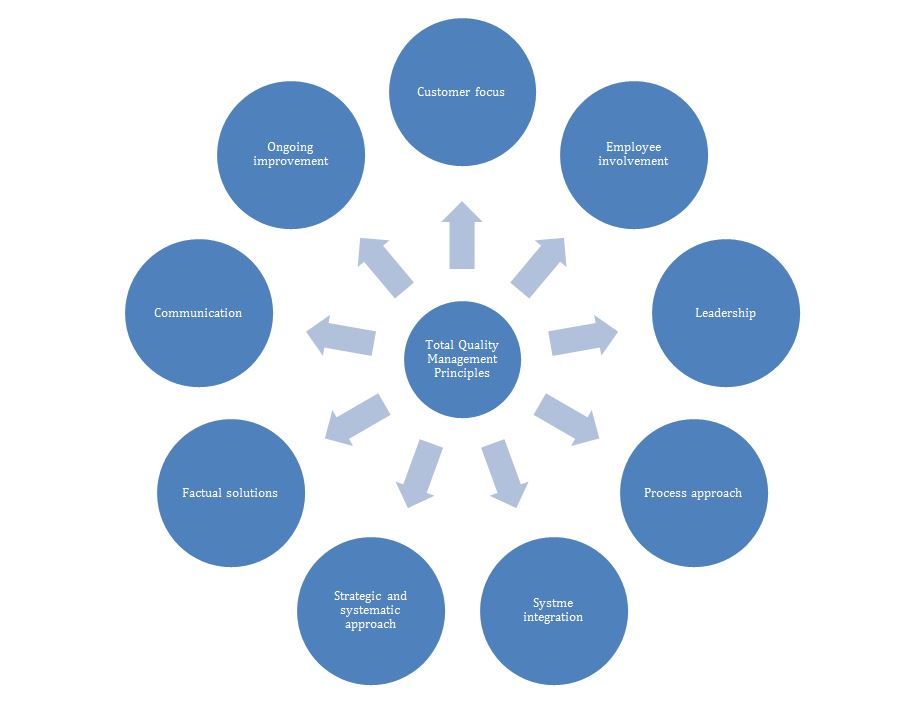
Each of these principles plays a significant role in quality management since it addresses the pivotal areas of performance control that influences service quality (See Figure 2). Customer focus is a central principle, which entails an all-time consideration of customer needs and expectations for ensuring their exceptional experiences when encountering a retail company (Zanqar et al., 2019). Employee involvement and leadership similarly relate to the engagement of both company management and employees at all levels and processes of the business in the organization and delivery of products and services of exceptional quality.
The process approach “helps the organization to identify, understand and manage interrelated processes, so that contributes to the organization’s effectiveness and efficiency” (Zanqar et al., 2019, p. 103). System integration and strategic and systematic approaches address the necessity of making quality achievement an objective that should be pursued systematically and strategically. Fact-based decision-making is another significant principle that necessitates a continuous assessment of the performance outcomes and customer satisfaction for the purposes of timely identification of flaws and failures and their elimination (Khan, 2015). This consideration leads to the next principle called continuous improvement, which drives company development and enhances its competitive advantage (Zanqar et al., 2019). Finally, communication is considered to be a stepping stone of quality management since it helps to engage all stakeholders into the process of quality management system implementation and allows for the carrying out of all the remaining principles of total quality management. For a retail industry in general, and Nordstrom in particular, the consideration of these principles predetermines high-quality customer service and competitive advantage.
A Critical Review of Nordstrom’s Quality Management System Elements
When developing a quality management system, an organization should embrace total quality management as an overall company management philosophy. Indeed, according to Eniola et al. (2019), “total quality management implementation has a momentous association with firms’ performance” (p. 1). Therefore, the integration of the main principles, concepts, and elements of quality philosophy within the whole corporation should be a starting point of any quality management system.
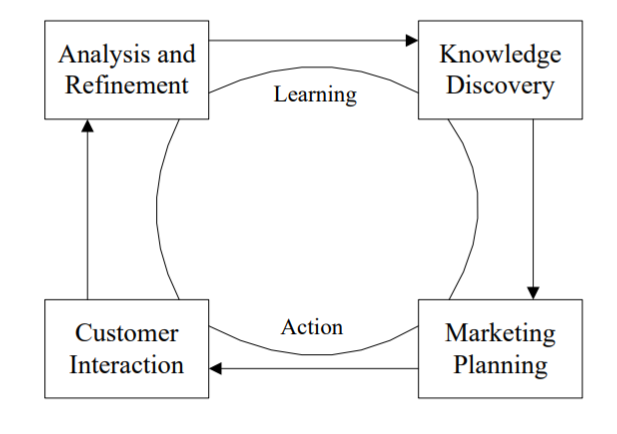
As defined by Li et al. (2018), quality management is a set of “various management measures and plans that are implemented to improve quality, reduce costs, and promote productivity, as well as to enhance corporate performance and competitiveness” (p. 464). In the case of Nordstrom, it is particularly relevant since the organization already has a well-developed quality culture that has helped the department store chain to generate a large population of loyal customers and a significant level of competitive advantage in the retail business in the USA and abroad. Customer relationships are essential for company continuous growth and quality control, which is achieved through ongoing learning and action (See Figure 3).
In order to assess and analyze the current quality-related situation in Nordstrom, one might apply a method of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) analysis (Nowotarski, Paslawski and Kadler, 2018).
Table 4. SWOT Analysis for Nordstrom’s quality culture
The conducted SWOT analysis (See Figure 4) results help in making an informed decision in relation to the elements of quality management. In particular, one might consider another critically important element of the quality management system, which is ethics concerned with quality objectives. The importance of establishing clear quality objectives for a retail business entity has been emphasized by Faraj et al. (2021), Goharshenasan and Shahin (2017), and Tannady, Nurprihatin, and Hartono (2018), who have all argued that the clearer the quality objectives, the more feasible is the development and implementation of a quality management system.
Teamwork should also be an integral element of Nordstrom’s quality management system since it allows for united efforts being directed at the achievement of the set goals and standards and helps to build another element, which is integrity (Ghasemi, Ahmadi and Ahghar, 2021). Moreover, trust is a very important quality management element since it is a foundation for long-term relationships inside the company between employees and management and outside the company between stores and customers (Dzimińska, Fijałkowska and Sułkowski, 2018). Nonetheless, communication and training are some of the most improvement-oriented elements of a quality management system that should be pursued by Nordstrom.
Indeed, since training and learning are the strengths of the company, they should be integrated into the organization’s quality management system for enhanced performance improvement and continuous competitive advantage in the retail industry (Bordonaro, 2018). Moreover, customer centricity has been a strong characteristic of Nordstrom, which needs to be enhanced throughout the process of quality management system implementation (Parvatiyar and Sisodia, 2019). Finally, strong leadership is another pivotal element of Nordstrom’s quality management since it will enable the practical and strategic implementation of quality objectives and standards throughout the corporation.
A Critical Evaluation of Key Trends in Quality Management
As research indicates, there are several tentative issues that are regarded as key trends in quality management. In particular, one of the most researched and discussed concerns in business quality management is the pursuit of a green economy and sustainable quality control. As investigated by Li et al. (2018), green innovation is unveiled in two domains, namely green technological innovation and green management innovation. Therefore, companies should rearrange their manufacturing technologies with the application of sustainable technologies and update organizational management styles in order to pursue better environmental outcomes of their operations (Li et al., 2018). Similarly, according to Bastas and Liyanage (2018), there is a need to incorporate sustainability and quality management into one framework “to achieve higher levels of customer satisfaction through enhanced collaboration within the network of firms and higher-performing processes upstream and downstream to organizations, for higher quality products and services” (p. 727). Indeed, the issues of the green economy play a significant role in a contemporary business environment, with more and more organizations embracing sustainability models to address customer needs. However, it is necessary to apply these trends to a given organization to ensure their applicability and feasibility.
Indeed, since the implementation of any trending practice requires substantial investment and might trigger additional costs, both monetary and non-monetary, it is imperative to conduct research into the target population of consumers. In the case of Nordstrom, it would be viable to conduct a survey that would evaluate the level of consumers’ concern with sustainability issues (Chan et al., 2019). It would allow for identifying their needs and consequently meeting them via quality management practices. Indeed, green economy trends in quality management envision shifting towards recyclable materials and sustainable production methods as a way to increase the quality of products and supply chain functioning. According to Kucukoglu and Pinar (2015), companies should implement proactive strategies in relation to environmental issues and the impact of their operations on them. Therefore, through the development of companies in the direction of green economy alignment “using talents and responsibilities accompanying all divisions within a company, combining eco-efficiency and continuous development processes of company and total quality management,” companies will gain a more sustainable business value (Kucukoglu and Pinar, 2015, p. 1234). Thus, shifting to green economy is a crucial quality management systems trend in the contemporary business world.
Another significant trend in quality management is the implementation of quality control systems through the 4.0 industry or digitalization. Indeed, in the light of the recent challenges in a global economy that have triggered remote cooperation, the integration of digital quality control systems has become a tentative issue for the majority of businesses (Pambreni et al., 2019; Sen and Sengupta, 2020). The increased relevance of digital technologies’ implementation as part of quality management systems has proven to add to efficiency to the production or distribution process as well as obtain refined supply chain functioning for company goals’ achievement.
This trend is evident in quality management of multiple industries and does not exclude retail business. According to Kovrigin and Vasiliev (2020), “throughout the life cycle of the product, data about it should be accumulated, which allows not only to obtain the most reliable and complete information about its quality, but also to evaluate the effectiveness of the measures taken” (p. 3). For example, a detailed schematic description of product life cycle marked with extensive and obligatory quality control data processing and accumulation is presented in Figure 5 (See Figure 5).
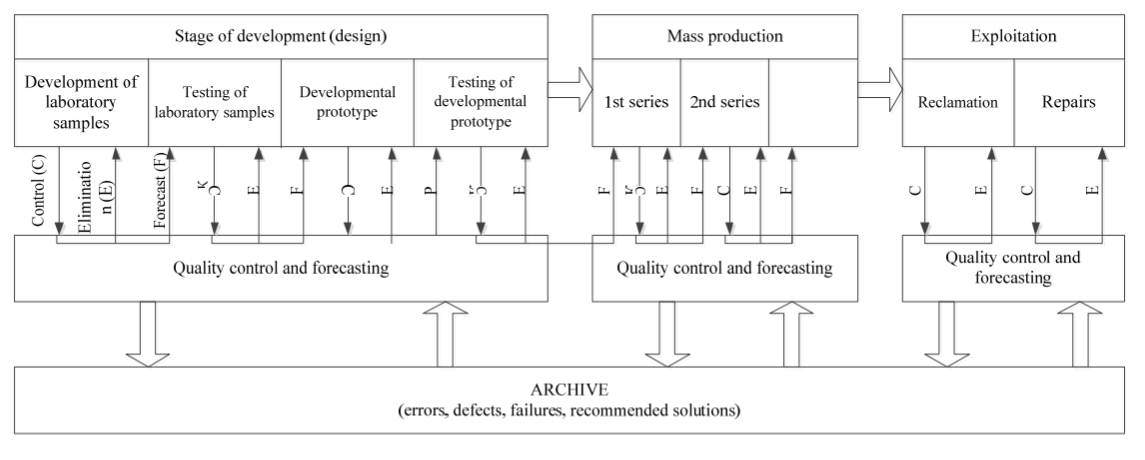
An important particularity of this approach is the ease of forecasting using digital technologies. By means of forecasting, companies have an opportunity to predict complications on the basis of data processing and attend to the problematic issues beforehand. Such a trending approach helps in building resilience, agility, and efficiency of any business, which is why Nordstrom might benefit from it too.
In addition, quality department advancement, and efficiency growth are the trends that might be considered by Nordstrom in order to ensure the implementation of the up-to-date quality management system. In particular, the quality department advancement trend is strongly associated with the training promotion and implementation for continuous improvement of employee accomplishments on the basis of company quality vision. According to Huang et al. (2017), the standards implemented internationally according to ISO 100015:2005 help organizations prioritize training needs as a significant part of quality management. In such a manner, the timely identification of training needs within the overall company needs allows for increasing employee efficiency and contribute to long-term company value. The final result of such a trending method is the enhancement of competitive advantage and company culture strengthening, which ultimately constitute a solid position in the market (See Figure 6).
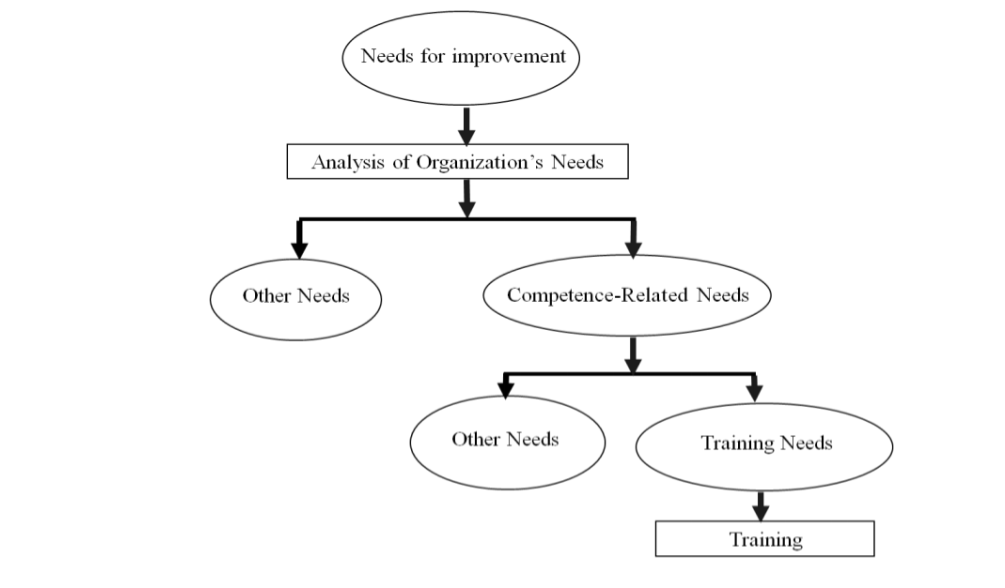
Consecutively, the application of talent management and the analysis of training needs of the company help to improve the quality management department. In the case of Nordstrom, the company might invest in recruiting more talent in the sphere of quality management who are competent in digital technology application to quality control. Moreover, returning to green economy trends, Nordstrom might consider enhancing its efforts in promoting sustainable product distribution to solidify its image as a proactive and environment-friendly brand. It will add to its social responsibility, thus building a more enhanced customer loyalty, and competitive advantage.
Conclusion and Recommendations
In summation, the development and implementation of a reliable quality management system for Nordstrom should integrate a multitude of issues. Overall, the importance of quality control for the corporation is essential since the company operates in a highly competitive retail industry environment and seeks to enhance its competitive advantage in its respective market. Several important recommendations for Nordstrom have been generated throughout the report. Firstly, the main principles of total quality management should be considered with a priority set on customer satisfaction, communication, leadership, process, and systemic approaches. Secondly, the results of the SWOT analysis should be taken into consideration to enhance strengths and opportunities and eliminate threats and weaknesses. In particular, the company’s quality management system should be based on ongoing employee training, customer shopping experience improvement, and leadership involvement in quality control. Thirdly, such elements as trust, ethics, integrity, teamwork, leadership, and communication should be immediate constituents of Nordstrom’s quality management system. Finally, green economy trends, digitalization, performance efficiency, and quality department management should be a part of quality management system.
Reference List
Bastas, A. and Liyanage, K. (2018) ‘Sustainable supply chain quality management: a systematic review’, Journal of Cleaner Production, 181, pp. 726-744.
Bordonaro, A. (2018) ‘The business of development’, Chief Learning Officer. Web.
Chan, C.W., Green, L.V., Lekwijit, S., Lu, L. and Escobar, G. (2019) ‘Assessing the impact of service level when customer needs are uncertain: an empirical investigation of hospital step-down units’, Management Science, 65(2), pp. 751-775.
Dzimińska, M., Fijałkowska, J. and Sułkowski, Ł. (2018) ‘Trust-based quality culture conceptual model for higher education institutions’, Sustainability, 10(8), p.2599.
Eger, L. and Micik, M. (2017) Customer-oriented communication in retail and Net Promoter Score. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 35, pp. 142-149.
Eniola, A.A., Olorunleke, G.K., Akintimehin, O.O., Ojeka, J.D. and Oyetunji, B. (2019) ‘The impact of organizational culture on total quality management in SMEs in Nigeria’, Heliyon, 5(8), p.e02293.
Faraj, K.M., Faeq, D.K., Abdulla, D.F., Ali, B.J., & Sadq, Z.M. (2021) ‘Total quality management and hotel employee creative performance: the mediation role of job embeddedment’, Journal of Contemporary Issues in Business and Government, 27(1), pp. 3838-3855.
Fazel-e-Hasan, S.M., Mortimer, G., Lings, I. and Drennan, J. (2019) ‘Examining customer-oriented positive deviance intentions of retail employees’, International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 47(8), pp. 836-854.
Ghasemi, A., Ahmadi, A. and Ahghar, G. (2021) ‘Dimensions of educational total quality management of knowledge based on teamwork and technology acceptance with combined research approach’, Journal of New Approaches in Educational Administration, 11(46), pp. 1-20.
Goharshenasan, A. and Shahin, A. (2017) ‘Prioritisation of quality management principles based on critical success factors of TQM using integrated approach of MCDM and IPA-the case of Marjan Tile Company’, International Journal of Productivity and Quality Management, 21(1), pp. 112-128.
Hamzah, A.A. and Shamsudin, M.F. (2020) ‘Why customer satisfaction is important to business?’, Journal of Undergraduate Social Science and Technology, 2(1), pp. 1-14.
Huang, P.L., Lee, B.C., Wang, C.S. and Sun, C.T. (2017) ‘Relative importance of the factors under the ISO-10015 quality management guidelines that influence the service quality of certification bodies’, Journal of Economics and Management, 13(1), pp.105-137.
Khan, S. (2015) Total quality management. Web.
Kovrigin, E. and Vasiliev, V. (2020) ‘Trends in the development of a digital quality management system in the aerospace industry’, In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 868, No. 1, pp. 1-8). IOP Publishing.
Krajcsak, Z. (2019) ‘Implementing open innovation using quality management systems: the role of organizational commitment and customer loyalty’, Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 5(4), pp. 1-10.
Kucukoglu, M.T. and Pinar, R.I. (2015) ‘Positive influences of green innovation on company performance’, Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 195, pp. 1232-1237.
Kumar, A., Singh, R.K. and Modgil, S. (2020) ‘Influence of data-driven supply chain quality management on organizational performance: evidences from retail industry’, The TQM Journal. Web.
Li, D., Zhao, Y., Zhang, L., Chen, X. and Cao, C. (2018) ‘Impact of quality management on green innovation’, Journal of Cleaner Production, 170, pp. 462-470.
Neyestani, B. (2017) ‘Principles and contributions of total quality mangement (TQM) gurus on business quality improvement’. Web.
Nowotarski, P., Paslawski, J. and Kadler, A. (2018) ‘Quality Management Systems as a key element for company strategy selection-case study’, In MATEC Web of Conferences (Vol. 222, p. 01012). EDP Sciences.
Nunkoo, R., Teeroovengadum, V., Ringle, C.M. and Sunnassee, V. (2020) ‘Service quality and customer satisfaction: the moderating effects of hotel star rating’, International Journal of Hospitality Management, 91, pp. 1-51.
Pambreni, Y., Khatibi, A., Azam, S. and Tham, J.J.M.S.L. (2019) ‘The influence of total quality management toward organization performance’, Management Science Letters, 9(9), pp. 1397-1406.
Parvatiyar, A. and Sisodia, R. eds. (2019) Handbook of advances in marketing in an era of disruptions: Essays in Honour of Jagdish N. Sheth. SAGE Publications India.
Sen, P. and Sengupta, G. (2020) ‘Challenges of implementing Industry 4.0 for emerging supply chains in developing countries in pursuit of reaching the level of excellence through the principles of Total Quality Management’, AEGAEUM Journal, 8(4), pp. 1667-1673.
Sesar, V., Buntak, K. and Martincevic, I. (2019) ‘Measuring the level of quality maturity in organizations’, Advances in Business-Related Scientific Research Journal, 10(1), pp.22-28.
Soares, A., Soltani, E. and Liao, Y.Y. (2017) ‘The influence of supply chain quality management practices on quality performance: an empirical investigation’, Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 22(2), pp. 122-144.
Tannady, H., Nurprihatin, F. and Hartono, H. (2018) ‘Service quality analysis of two of the largest retail chains with minimart concept in Indonesia’. Business: Theory and Practice, 19, pp.177-185.
Varadarajan, R. (2020) ‘Customer information resources advantage, marketing strategy and business performance: a market resources based view’, Industrial Marketing Management, 89, pp. 89-97.
Winata, I.G.K.A., Satria, G.A. and Adnyana, I.P.A. (2019) ‘The role of the business environment, supply chain management and quality management in improving the competitive advantage of small business retail’, International Journal of Social Science and Business, 3(3), pp. 314-320.
Yrjola, M., Kuusela, H., Narvanen, E., Rintamaki, T. and Saarijarvi, H. (2019) ‘Leading change: a customer value framework’, in Kangas, A. et al. (eds.) Leading change in a complex world: transdisciplinary perspectives. Tampere: Tampere University Press, pp. 145-165.
Zanqar, F.S.M., Khatibi, A., Azam, S.F. and Tham, J. (2019) ‘The impact of ISO principles of total quality management on higher education quality’, European Journal of Management and Marketing Studies, 4(1), pp. 100-108.

