Introduction
In the current stage of society’s development, the trend toward rapid dynamic business change is evident, in which the rules and patterns that existed decades ago are no longer relevant to today’s agenda. While the central core of the creation of any enterprise — which entails attracting profits with the formation of favorable economic relationships in the environment — remains unchanged, the forms through which businesses realize their key objectives have been modified under the pressure of time. More specifically, the spectrum of modern business includes the clever use of digital technology, a focus on the customer, the creation of favorable working conditions for employees, and social responsibility. The above aspects should be seen as the driving forces that determine the development of an enterprise throughout its existence. At the same time, such differences are quickly confirmed by a retrospective comparison. In particular, the factories of the beginning of the last century were mainly focused on making profits, with no increased comfort or social security for workers (Tadajewski, 2017; Freeman, 2018). At the same time, those factories did not seek to comply with the trends of the times, including the promotion of environmental, mental, and informational security of society. On the contrary, more often than not, such factories were seen as large enterprises that littered the environment and made inefficient use of social and natural resources. Finally, the most crucial difference that characterizes modern business is the deep integration of information systems.
It is hard to imagine a modern enterprise that does not use computers. In fact, the involvement of digital technology in business management simplifies and optimizes a number of critical tasks. For example, computer technology can be used at simple levels, which includes sales management or an online cash register, as well as at more complex ones. Forms of such advanced digitalization can be represented by complex databases with the integration of deep learning mechanisms or deep market analytics systems with the automatic development of ready-made strategic solutions based on critical evaluation of indicators. In any case, it is evident that modern business, in general, has much more developed management mechanisms and thus more potential opportunities for their use.
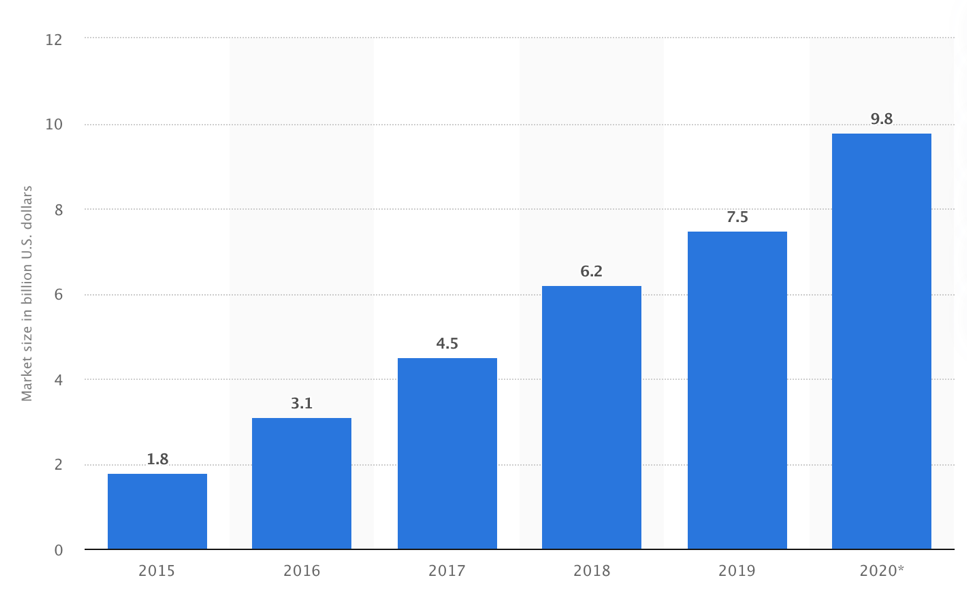
In view of the technological orientation of businesses, the market industry of e-commerce attracts particular attention. It is fair to admit that this term is somewhat ambiguous and expanded, so there is still no unified definition for this sphere in the academic community. Nevertheless, e-commerce can generally be understood as any solution aimed at generating profits in the context of the global network and online technologies. This includes online sales, online banking, ticket and hotel reservations, transactions in payment systems, online marketing, and advertising. As one can see, this spectrum is very diverse, and therefore it is appropriate to emphasize that modern society cannot exist effectively without the profound use of e-commerce. In fact, the life of the contemporary individual has become so dependent on digital technologies, including banking, transportation, entertainment, or professional aspects, that abandoning e-commerce would have a severe hindering effect on progressive social development. Specifically, according to Kemp (2021), more than 90 percent of the local population in Saudi Arabia had constant access to the Internet. Moreover, according to SRD (2021), the e-commerce market is experiencing a megatrend state, with a marked increase in its size each year. The graph in Figure 1 clearly shows the linearity of this growth, on the basis of which it is possible to forecast an increase in the size of this market sector in the foreseeable future. Thus, by now, there is no doubt about the incredible importance and profound relevance of this sector of the market.
Project Concretization
For the academic objectives of this group project, Zid, one of Saudi Arabia’s market leaders in providing e-commerce services to small and medium-sized businesses, was chosen. Zid has no extended brand history but instead is a young company formed by local entrepreneurs in 2017 (About Zid, 2021). Today, the company provides services to the retail sector in more than sixteen different sectors of commerce. The company’s total customer base includes more than four thousand active retailers with whom it works on an ongoing basis. At the same time, the company’s offerings are not limited to providing technical equipment for companies to do commerce. On the contrary, the range of services provided by Zid is noticeably more extensive and provides any solution that allows it to reach the market effectively. More specifically, this includes the use of online store systems, the development of ecosystem networks to provide more streamlined interaction between stakeholders, and even training and corporate communities for quality employee development and experience sharing. To put it another way, today, Zid is a significant industry player that provides a variety of services unified by the idea of horizontal integration.
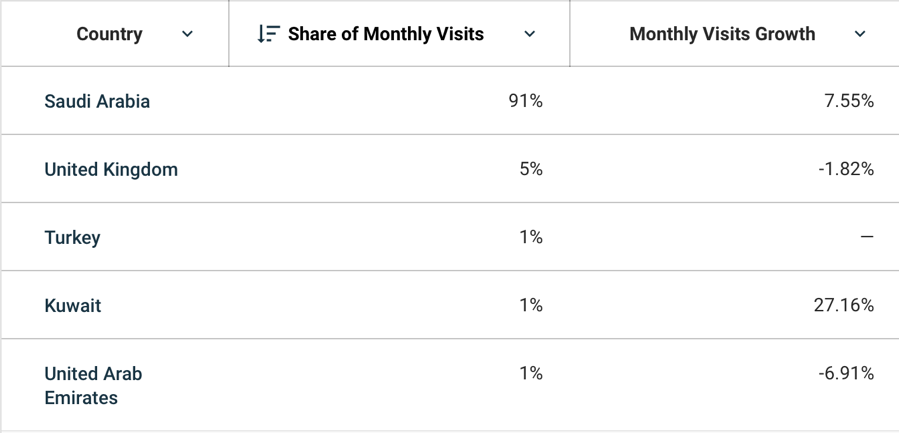
The best pre-examination strategy for a company is to identify and critically evaluate its micro-economic metrics, which will provide a better understanding of the business’s place in the current industry. Specifically, the company has total funding of $8.9 million, with six key investors (Zid, 2021). The company reportedly has over 150 employees, with an executive board represented by three managing employees (Zid overview, 2021). Analyses of the company’s technology capabilities show that Zid uses at least 16 technology products, including Google Analytics, HTML5, and jQuery, in its daily work practices (Zid, 2021). In terms of accessibility and compatibility, the company offers digital solutions for clients that can be used both on desktops and through mobile applications, which means business management becomes simplified. The company’s official website, Zid.sa, is viral mainly among regions in Saudi Arabia but is also visited monthly by users from the United Kingdom, Turkey, Kuwait, and the UAE, as shown in Figure 2. In addition, as shown in this figure, Kuwait and Saudi Arabian regions are characterized by high monthly growth in visits.
Notably, according to official data from the company’s LinkedIn profile, the average employee’s employment time does not exceed one year. More specifically, employees at Zid, on average, do not stay with the company for more than 0.9 years (Insights on Zid, 2021). Such information could be evidence of a poor corporate culture, poor working conditions, or high employee turnover in the e-commerce industry as a whole. The latter hypothesis can be justified by the high dynamism of the enterprise in this market area and thus by the increased economic competition between companies for hiring employees. Summarizing all the results together, it is possible to conclude that Zid is an average company in the e-commerce industry in the Saudi Arabian market. The number of employees, size of share capital, and a number of critical stakeholders discussed above confirm the relatively average size of the company. That said, it is essential to emphasize that the company is popular in the Gulf region and beyond. For this reason, the group project discussion of the selected company has increased educational value, as it is recognized that Zid has a high potential for strategic growth in a more digitized business environment.
Goals and Objectives of the Project Report
The central academic goal of this project is to discuss the selected company in detail to explore the known concepts of marketing strategies. Thus, the overall goal of the paper should be called an in-depth study of strategic marketing through the lens of Zid. This will not only summarize the known theoretical knowledge but also explore their practical implementation. Consequently, the work is valuable and relevant material not only for the student community but also for all persons interested in the study of marketing strategy ideas using specific corporate examples.
SMART Objectives
For the strategic development of the company and attracting more profits and investment attractiveness, Zid management should take a closer look at the following management objectives formulated according to SMART ideology. The goals are listed in priority order, in which the first is the most important, while the fifth may not be realized immediately.
- To increase the number of active customers by increasing from 4,000 current by to 8,000 by the end of 2022
- To increase the number of average years of employee employment from 0.9 years to at least three years over the next decade.
- To increase monthly growth of site traffic by reaching 30% user activity by six months.
- To expand the geography of customers from the Persian Gulf to the European continent over the next three years.
- To expand the range of e-commerce services from sixteen to twenty by the end of 2021.
For the generated goals, it is advisable to use a table with critical performance parameters, which will be used by the analytical department, management, or audit in a critical evaluation of the results achieved. For this purpose, each of the five goals was fragmented to establish the most critical metrics.
Table 1. Key Performance Characteristics for each of the Five SMART Strategic Management Objectives in Zid
Marketing Recommendations and Key Reasons
First SMART Goal
This goal focuses on building a customer base, which means known growth strategies can be applied. This includes improving advertising campaigns, including the promotion of contextual and targeting offers, social media marketing, and the implementation of subscription pages or mailing correspondence and email announcements. In addition, expanding the customer base should be realized through offline activities, including the company’s participation in panel business shows, cold and hot calling platforms, and creating a loyalty system for recruiting new employees.
Second SMART Goal
The second strategic goal has a focus on employees, as the implication is that a better customer experience and a supportive corporate environment are possible if the work environment is suitable for employees. For example, in order to increase employee retention by more than three times, Zid management should develop a system of loyalty and performance rewards, as well as establish intra-corporate competition (Dibyo et al., 2021). Moreover, it is advisable to develop a training program that will not only qualitatively increase the intellectual weight of employees but also engage them in corporate values. Finally, salary increases, bonuses, and incentives for personal engagement can be practical tools for employee retention.
Third SMART Goal
The focus of the third goal is built around the need to increase user engagement on the company’s official website. The justification for this vector of marketing development is that the company receives most of its traffic via direct link, which means increased website traffic has the potential to lead to an increased customer base and, therefore, sales (Shukla et al., 2018). Critical recommendations for development in this context are the use of contextual advertising, promotion of advertisements on major search engines, both local and global. In addition, management can use available marketer analytical tools to increase traffic.
Fourth SMART Goal
Perhaps the fourth goal is the most abstract because it is not quantitatively measured but instead has a qualitative focus. The deliberate avoidance of quantification is justified by the impossibility of accurately following the objectives of the geographic context due to the multiplicity of influencing factors. Therefore, Zid should enter the European market within three years, and both advanced marketing tools and the establishment of company branches in local communities can be used for this purpose. In addition, the company should actively participate in European professional fairs and conferences to make itself known to local companies. Finally, attracting foreign investment can be an effective solution to bring the Saudi-Arabian company closer to the European market.
Fifth SMART Goal
Although this goal was chosen as the lowest priority, this decision does not at all imply disinterest on the part of the management in implementing a broader range of services. In fact, in order to make the range of b2b offerings more complete, the company should conduct an initial analysis of the current market, including through a study of competitive forces: for example, according to Porter’s five forces model. At the same time, expansion involves severe organizational risks, and therefore a third-party audit to assess the robustness of the transformation is critically necessary before this goal can be realized. Finally, the expansion must be performed according to current market needs and, just as importantly, foreseeable scenarios.
Target Market
The analysis of the target market structure provides sufficient information for the organizational transformation of the company with the goals of both gaining more profits and implementing all of the previously planned SMART objectives. Thus, the composition of the target market for Zid has been tentatively broken down into three branches, listed below in order of priority:
- Small businesses interested in entering the branch market but not equipped and competent enough to use e-commerce systems. Data from the Saudi Ministry of Labor and Social Development determines that small businesses are represented by more than 1.5 million firms, representing 97.6% of the entire private sector (Mubasher, 2020). Consequently, this vector is key for the Zid.
- Medium-sized businesses that already have channels of communication to enter the market but are interested in strategic development. More specifically, such enterprises already have a client base and generally have stable activity at the market, but have the potential to grow professionally. The Department of Labor and Social Development indicates that such companies have about a two percent share of the total private sector, therefore, the priority for this market is lower than for small businesses (Mubasher, 2020). However, medium-sized businesses often need third-party assistance to improve technical equipment and optimize available resources, so Zid as a provider of such services may be relevant to this market.
- Finally, the third target market profile for Zid is companies that outsource and hire businesses as secondary service providers. More specifically, such companies may be engaged in auditing, promoting corporate services, or implementing strategic business objectives and thus are intermediaries between the provider and the businesses. Such intermediaries often need e-commerce services both for personal use and to implement corporate objectives of b2b clients. It should be noted that this direction is the least prioritized for Zid, as it actually creates additional challenges in establishing effective communication between the company and its target customers.
Having analyzed the composition of the target market for Zid, it should be emphasized that all subsequent discussions will focus only on the first two vectors. This decision is justified primarily by the need for a concise and technically accurate project report, while the intermediary market is ambiguous and contradictory. Thus, all the conclusions and findings described below are only true for small and medium-sized businesses, which together form 99.7% of Saudi Arabia’s business.
The Service Offered
Since the needs of SMEs are to set up e-commerce systems and platforms, launching an online store creation service from scratch is an effective strategy to meet this need. More specifically, the company offers clients the to bring their business ideas to life even if they have no knowledge of information systems and technology. Thus, the entire responsibility for creating a website, optimizing traffic, and establishing communication channels falls on the service provider company, while the client business provides only a formalized idea and vision of the final result.
It should be emphasized that this service is not only the realization of the goals of creating a website but, on the contrary, represents the whole range of services for the creation of software architecture. In more detail, this service includes tasks such as designing, developing, and integrating client design, web layout, setting up communication channels, setting up online banking systems, domain registration, and building capacity for network expansion, including scaling traffic (Carmichael, 2021). Moreover, for the client business, such service starts with an application to create an online store and ends with a finished product, in which all the changes are approved and implemented, and all the expectations of the parties are met. In addition, such work implies full involvement of clients — with their desire — which means that at all stages of multifactorial and consistent work of the provider, recommendations and wishes of the client should be taken into account.
The list of crucial advantages of such service from Zid includes full responsibility of the provider for the architecture creation, which means that the client business does not need to have any competence in the field of information technology. In addition, an active discussion of the implementation of ideas is also a significant advantage, as it allows for effective communication throughout the project. Finally, another advantage for customers may be the relatively low cost of the service, as it is understood that the price for the creation of an online store will not be higher than competing offers.
Positioning Strategy
Positioning Slogan
Zid focuses on providing affordable and high-quality idea services to create an online store as an e-commerce solution for small and medium-sized businesses in the Saudi Arabian market.
Positioning Strategy Description
As it is known, a competitive positioning strategy is aimed at achieving the company’s competitive advantage in the market segment. For this reason, the development of such a strategy is necessary to realize the goals of Zid’s advertising activities or, to put it differently, to develop or maintain a particular image of a product or brand in the minds of customers. Since the target market has been defined, it is necessary to provide a complete description of the chosen positioning strategy in known aspects.
First and foremost, it is necessary to ensure that the points of differentiation of the service that is provided to the client business are fully followed. First of all, customers may not be satisfied with the long waiting time when developing an online store platform. According to the review, the average wait time ranges from two to fourteen weeks, with this period directly depending on the complexity of the project (Field, 2014; How long does it take, 2020). For Zid, it is necessary to ensure that waiting times are minimal in order to achieve this point of differentiation clearly. Other points of differentiation include modern design solutions, broad basic functionality and responsiveness, and simplified interface interaction. Thus, all of the aspects described will create the image of a successful and highly developed enterprise that is strongly interested in solving customer business problems.
Summarizing this section, it should be emphasized that the positioning strategy has been chosen by service attributes so as to achieve coverage of key competitive advantages. This includes price, speed, optimization, and efficiency of the service. In this way, Zid will be able to integrate the service sold with its attributes, which will have a positive impact on the recognizable image of the Saudi-Arabian brand.
Pricing
Similar to most modern businesses, Zid offers a subscription-based mechanism where the client business pays a subscription fee depending on the scheme chosen: monthly or annually. This form of payment has a number of key advantages for both the provider and the client business. On the one hand, Zid does not receive a one-time payment but forces customers to pay monthly — or annually — for services, which is known to increase overall company profits (Fontanella, 2021). On the other hand, by paying a subscription fee, the client receives a guarantee of support for the effective operation of the platform during the reporting period, and including the implementation of edits, updates, and fixes for technical errors. Moreover, the cost of a subscription varies depending on the breadth of functionality. For the service of creating an online store, this cost ranges from $61 to $122 per month or from $613 to $1227 per year. As it is possible to see, the customer can get a discount of up to twenty percent when paying for a yearly subscription. In addition, if a customer sets up multiple online stores at once — for example, for different regional markets — the business can expect a discount for bulk order placement, although these terms are negotiated individually. The basic subscription version includes a set of standard functionality, including the creation of a custom domain, attaching key e-commerce features, and customizing CSS. Alternatively, the extended subscription provides the client business with full consulting services for running an online store, integration with well-known search engines, storage and database management, and employee training capabilities.
It is important to state that there is no need for Zid to create a high perceived value targeting the premium market segment since the key target market vectors are aimed at small and medium-sized businesses. Thus, the above-mentioned subscription pricing allows for a favorable environment in which the cost is perceived to be average but fully justified. It can be seen that Zid does not emphasize the creation of low perceived value because the brand value is known to be positively related to customer trust. More specifically, if a company were to make the perceived value too low, it would negatively impact the company’s business image. In this case, the compromise is average pricing, in which the value of the service does not seem extremely overpriced or suspiciously underpriced.
Distribution Channels
An effective marketing strategy for promoting a product or service implies the development of distribution channels so that the product reaches the end consumer unhindered, but at the same time, the cost of intermediate costs is not too high. Such channels can be long or short, and there is no universal formula for evaluating their effectiveness: the correctness and optimization of the distribution system are critically examined on a case-by-case basis. In the case of Zid, it should be understood that customer business tends to ask for the service of creating an online store in a targeted and targeted manner. That said, it is wise not to create channel redundancy, as in this context, it will only create additional costs but not an effective solution. Thus, omnichannel for the Zid case does not seem to be a viable strategy since the delivery company should not be interested in all aspects of customer business workflows. On the contrary, distributing the service through multichannel schemes seems to be a more intelligent solution.
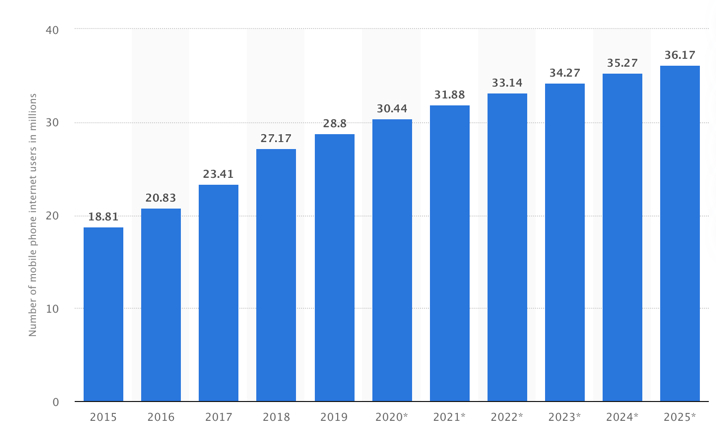
First of all, marketing multichannel allows creating an extended network of interaction with the customer, which leads to increased engagement. Thus, the client business can learn about the service being implemented by the Zid through various communication channels, which include the use of social networks, targeted queries in search engines, the use of target advertising, or word of mouth. Multichannel, on the other hand, means that customers can be found through a variety of electronic devices. More specifically, while most office workers typically use desktops or laptops to access the Internet, the use of mobile network data is increasing rapidly, as the statistics in Figure 3 confirm. In fact, a growing number of Saudis are using mobile Internet in their daily practice, which means it is very likely that key employees will be able to learn about Zid services through this channel.
It is fair to emphasize that search engines and display ads among inquiries should not be viewed as service retailers, as the delivery company creates its own ad campaigns. Thus, multichannel distribution for Zid includes the use of a variety of electronic devices, whether desktop or mobile, as well as a variety of platforms for the promotion. It is not hard to see that the current marketing strategy does not involve the use of retailers. In fact, an approach that uses resellers does not seem appropriate for an online store creation service. The reasons for rejecting such a strategy are to deliberately complicate the interaction between the customer and the direct performer, even though the company’s competitive goal is to reduce production time. Summarizing the above-mentioned reasoning, the following distribution channels seem appropriate and the most effective for Zid company:
- Official Website: This implies direct sales, where customers themselves go to the website and leave a request to perform a service.
- Cold and Hot Calls: This channel is aimed at expanding the customer base, in which the company makes calls to potential clients from the database to tell about the services and increase engagement.
- Social Networks, SMM: This channel allows finding new clients with the help of social platforms’ tools — Facebook, Instagram, Twitter — and negotiate cooperation through local chats. In addition, this is an excellent opportunity for creative advertising of the service, increasing brand recognition not only among customers.
- Word of Mouth: The most effective type of distribution in which information about services is spread by the company’s customers (Huete-Alcocer, 2017). To increase the likelihood of word-of-mouth radio, Zid can develop a referral system in which current customers receive a discount if new ones are invited.
- Search Engines: Displaying contextual advertising on user search queries greatly increases the index of recognition and boosts profits. Zid can pay for advertising campaigns so that potential customers receive offers for the service when they make thematic inquiries.
Evaluating the effectiveness of distribution channels must meet the criteria of systematicity and criticality. In other words, the scenario in which one of the channels spends resources but does not generate any profit should be ruled out. The evaluation of KPIs for distribution channels is performed by the marketing analytics department and includes a comparative study of the balance of input and effort and output response. At the same time, it is not only the cost-to-profitability ratio that is an essential criterion for evaluating performance. The degree to which customer expectations are met, the level of competition, accessibility and manageability, and long-term perspective should underpin the selection of relevant channels. As a consequence, Zid will have a strategic plan based not on an intuitive understanding of distribution mechanisms but on a comprehensive and comprehensive assessment of strategic prospects for each of the channels, taking into account the market orientation of the company.
Marketing Communications
There are several different ways in which a brand can interact with the public. Primarily, it should be recognized that the term “marketing communications” is ambiguous, but in general, it includes the totality of all levels of interaction between a company and a consumer. Thus, it includes advertising campaigns, distribution channels, sponsorship, and other sales tools. Consequently, the discussion of marketing communications in this section is inextricably linked to the comprehensiveness and integration of all forms of such interaction, from the business idea to the processing of feedback from the client. This section includes a brief description of the communications used and some recommendations for making their implementation more optimized.
Branding
Branding should be understood as a relatively long process of creating an attractive image of a commercial product in the eyes of the consumer. The service of creating an online store is not innovative for a client, so the task of Zid is to use such a marketing strategy, in which this service will be perceived as unique and competitive in comparison with its analogs. To do this, the company can emphasize the advantages of services such as speed and quality of execution, comparably lower cost of work, and feedback from current customers. The target audience for this communication will be the spectrum of all potential customers, i.e., small and medium-sized regional businesses. In addition, the urban community as a whole is also a secondary target audience, as building a high brand awareness index can be an excellent foundation for word-of-mouth radio. The cost of this type of marketing communication is calculated on a case-by-case basis, but as an example, the average cost of branding ranges from $1,000 to $30,000 for small businesses depending on the range of work performed (Maurer, 2020). For medium-sized businesses, these amounts may be higher depending on the technical complexity of the tasks to be performed.
Advertising
Advertising is the most effective marketing communications tool to spread the effect of public awareness of the brand. To promote the service of creating an online store, Zid must address advertising through offline and online platforms. This includes both the use of city billboards and posters as well as placing digital ads and video content on social media and search engines. Separate advertising budgets are used for this type of communication, with the cost of online and city billboard advertising varying wildly by location, traffic, and size. The target audience for advertising is both the urban community and the pool of potential customers for whom targeted advertising is set up.
Public Relations
PR mechanisms are responsible for creating a favorable image of the company in the minds of consumers, and this type of communication is conditionally free. In particular, through participation in conferences, barter agreements with partners, or interviews with the city press, Zid can inform the community practically for free about the benefits of its product and the qualities that distinguish it from its competitors. In addition, it should be recognized that PR can be dishonest, in which the provider implicitly or explicitly flaunts compromising information about competitors in a way that reduces their attractiveness in the eyes of potential customers. So, this communication will require little or no material investment from Zid, but it does require intellectual resources. The key audience for this marketing communication is small and medium-sized businesses interested in the service offered, i.e., leads.
Publicity
This mechanism stems in part from public relations tools, as it involves the use of the media and celebrities as platforms for posting commercial information. This type of communication is sharpened to create long-term relationships through openness, transparency, and credibility of published information. In today’s marketplace, publicity is a frequently used strategy as more and more users follow prominent bloggers or publications who are advertising persons or company ambassadors. With this method, Zid can collect feedback and process it effectively. Cooperation is also conditionally free since the media is often interested in exciting content, and bloggers can use the company’s services on a barter basis. The target audience for this type of marketing communication is readers of local media and subscribers of prominent bloggers, including small and medium-sized businesses.
Sponsorship
As another type of effective marketing communication, sponsorships should be singled out to help a brand gain the trust of its core audience. In particular, Zid can sponsor e-commerce-related events and activities, conferences, or exhibitions to not only build brand awareness but also to increase the trust of visitors. In this way, sponsorship works for brand image and requires a significant financial investment to achieve results in the long run. The target audience for this marketing method is interested individuals who attend themed events and thus are looking for the best e-commerce solutions.
Direct Marketing
This type of company interaction with the public consists of direct communication with potential customers through hot and cold calling systems, emails, meetings, and communication at thematic exhibitions. For Zid, this type of communication can be highly effective because it allows for the management of leads throughout the sales funnel, as well as expanding the customer base. Thus, the target audience is the leads, and the funding for this referral depends on the customer’s readiness to buy.
Loyalty Programs
Loyalty programs have a focus on developing a long-term relationship with the customer, which qualitatively increases the level of trust in the brand. In the context of Zid, loyalty programs can be aimed at creating referral systems of inviting new customers or receiving preferential terms for bulk purchases. Though, in this case, the company receives less profit from the client, this vector is instead aimed at creating the company’s image. The target audience of loyalty programs is current customers.
Conclusion
To summarize, it should be emphasized that the marketing analysis of strategies and is managed is a comprehensive and comprehensive procedure that evaluates the company from different perspectives. For the purpose of this report, Zid, a Saudi-Arabian company specializing in the e-commerce industry, was chosen. It was shown that this sector of the Arab market has become increasingly important in recent years, with Zid holding a strong position as a middle marketer. The service under discussion was the mechanism of creating an e-shop for a client business from scratch. It was shown that the key target market is small and medium-sized businesses, which was the focus of the report. Pricing policy was also discussed and why the subscription mechanism is a priority for e-commerce companies. In addition, the report analyzed the marketing distribution channels and communications that could be used to attract a customer base. Moreover, the paper includes an illustrated example of print advertising for the service in question, as well as a rationale for the relevance of such studies through research on trends in the surrounding social and political environment. Finally, key financial metrics for the service were summarized, and competitive and SWOT analyses were conducted. Thus, this paper is a comprehensive and extensive marketing research document.
Appendix A
Features and Benefits
Features or characteristics of the sold service are not only descriptive elements of the commercial product but also allow for highlighting the key competitive advantages that qualitatively distinguish this service Zid from counterparts in the industry market. The following characteristics are relevant to the service of creating an online store for small and medium-sized businesses:
- Creation of the platform from scratch;
- Full responsibility for the creation of the online store;
- Speed of production;
- Simplicity of interaction with the client;
- Consistency with the terms of reference;
- Ability to perform work of any complexity and depth of layout;
- Reasonable cost;
- Appropriate level of cybersecurity and online banking security;
- Ongoing support by technical specialists;
- No need for the client to have IT competencies;
- Customization of business analytics tools;
- Availability;
- Beautiful design or custom design;
- Interactivity.
The advantages of this service are:
- the relative cheapness of the project compared to competitors’ offers,
- full support throughout the work and even beyond,
- the high speed of platform production,
- complete consistency with the terms of reference,
- the provision of consulting services when purchasing a complete project,
- full responsibility for the site development, with no need for the client to have specialized knowledge.
Appendix B
Print Advertising
A visual style of eye-catching image with critical messages on it was chosen to create the print advertisement. The following preliminary layout illustrates an example of such an advertisement, which at a glance gives a clear idea of the service to be implemented: the creation of an online store for the client. The layout includes the company’s personal trademark, corporate colors on the key brand phrase, and an additional slogan that reflects the key benefits of working with Zid. As it is supposed to be for professional advertising, the image for this ad was taken from free stock services, which means there is no conflict with copyrights.

Appendix C
Significant Factors and Trends in the Environment
- Saudi Arabia’s e-commerce market has already reached the $9.8 billion mark, and this figure will continue to grow (SRD, 2021).
- More than 95 percent of Saudi Arabia’s population uses mobile Internet in their daily practices, and this figure will continue to grow (SRD, 2020).
- 95.73 percent of Saudis use the Internet through any electronic device every day (ITU, 2019).
- An increasing number of SMEs are receiving direct development loans from state-owned banks, which means they have the initial capital to purchase the service (OBG, 2018).
- Although a small number of GCC businesses are represented in the online environment, the percentage of presence has gradually increased over the years (Tiwari, 2021).
- Social media is gaining popularity among users, especially large conglomerates.
- Saudi Arabia, as one of the Gulf regions, is gaining increased investment appeal and becoming one of the centers of attraction for technological progress.
- 69% of Saudis bought at least one product online in the past year 2020 (eCommerceDB, 2021).
- Key e-commerce trends in the local market include fashion, electronics and media, food, toys, and furniture (eCommerceDB, 2021).
Appendix D
SWOT Analysis
Appendix E
Analysis of Individual Competitors
Elogic Commerce
- Full-range e-commerce services with a focus on creating an online store and running B2C and B2B businesses. Most of our client base comes from the U.S., but they also have European representation.
- 30,000-$135,000 depending on the size of the business and technical complexity of the project.
- Wide client base, cooperation with famous brands and, as a consequence, high reputation, favorable working conditions for employees.
- Extremely high cost of services, workload due to a large number of clients.
RIKSOF
- A company with a twelve-year history presents opportunities to develop mobile and web applications according to customer requests. The company works in different branches of e-commerce: from retail stores to the health care sector.
- N/A.
- 24/7 expert technical support, partnerships with established brands.
- No available information about the cost of services, the need to contact managers to decide the amount of payment for the project.
Magento
- Magento is one of the largest e-commerce platforms created on the basis of the famous Adobe. It offers a wide range of services tailored to the objectives of the business and also gives a simplified functionality for the client to create a unique design and manage sales.
- From $1988.00 per month.
- Has a trial subscription period, omnichannel, breadth of features offered.
- Incredibly high cost for a paid subscription; the free version has limited functionality.
Intellias
- Large local company that works with Fortune 500 brands. Has a focus on building the company’s IT and e-commerce capabilities as well as R&D.
- N/A.
- Worldwide distribution, frequent mentions in Forbes, work in various areas of commerce, advanced machine learning technology.
- No available information about the cost of services, the need to contact consultants to solve financial issues.
Appendix F
Projected Revenues, Major Costs, and Profits (USD)
Reference List
About Zid (2021) Web.
Carmichael, C. (2021) Building online stores. Web.
Dibyo, B., Mangifera, L., Putri, P.A.K. and Wardani, S.F.A. (2021) Effectiveness of customer relationship management (CRM) and customer satisfaction on shopee customer loyalty. Issues on Inclusive Growth in Developing Countries, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 31-40.
eCommerceDB (2021) The eCommerce market in Saudi Arabia. Web.
Field, J. M. (2014) Ecommerce questions. Web.
Fontanella, C. (2021) What’s a subscription business model & how does it work? Web.
How long does it take to build an ecommerce website? (2020) Web.
Huete-Alcocer, Nuria. (2017) A literature review of word of mouth and electronic word of mouth: Implications for consumer behavior. Frontiers in psychology, vol. 8, pp. 1256-1262.
Insights on Zid (2021) Web.
ITU (2019) Individuals using the Internet (% of population) — Saudi Arabia. Web.
Kemp, S. Digital 2021: Saudi Arabia. Web.
Maurer, C. (2020) How much does branding cost for small businesses? Web.
Mubasher (2020) Small businesses dominate 97.6% of Saudi private sector. Web.
OBG (2018) Saudi Arabia’s small and medium-sized enterprises fostering new job opportunities and economic growth. Web.
Shukla, P., Vyas, P.H. and Shastri, H. (2018) Investigating the mechanics of affiliate marketing through digital content marketing: a key for driving traffic. Research Essentials, vol. 219, 1-16.
SRD (2020) Saudi Arabia: mobile phone internet users 2015-2025. Web.
SRD (2021) E-commerce market size Saudi Arabia 2015-2020. Web.
Tadajewski, M. (2017) The Rotary Club and the promotion of the social responsibilities of business in the early 20th century. Business & Society, vol. 56, no. 7, pp. 975-1003.
Tiwari, K. (2021) Rising kingdom of ecommerce: post-covid online retail trends in Saudi Arabia. Web.
Zid (2021) Web.
Zid overview (2021) Web.
