Executive Summary
Total quality management is a tool used by firms to enhance their production efficiency. This tool was developed in the 1970s in North America and it spread to Europe and other parts of the world.
A number of quality management methods have emerged since then, but total quality management still remains very popular. A firm may need to use this tool alongside other tools in order to have superior outcome in quality management. Emergence of information technology has enhanced the application of this tool because of the ease with which information can be shared within a firm.
Introduction
Total quality management has been in use for the last forty years as a tool which helps companies manage quality of their production (Chary 35). This tool seeks to ensure that an organization maintains quality at all stages of production. According to Besterfield, the term total was used to emphasize the fact that quality is a process, not a stage in the production process (19). This means that to have quality products, a firm must ensure that all processes of production embrace quality.
This starts with the first stage of sourcing for materials. It is almost impossible to have high quality products when raw materials are of poor quality. Total quality management demands that a firm should start by sourcing for high quality raw materials that are to be used in the production process. When this has been sourced, the next step is to have quality production system that is based on modern technology.
Chary says that in the past, production took an inward-out approach (35). This meant that firms paid less attention to the needs of their customers during the production process. Competition was very low hence customers had to accept what was presented to them. However, this is no longer the case. Total quality management promotes an outward-in approach of production.
This is a customer-centric strategy where a firm produces what a given market demands. The storage and transportation of the product must also focus on just-in-time strategy to ensure that customers get their production in time. Finally, the process of delivering the products to customers in the market must also be done in a proper manner. This research will focus on total quality management and how it is used in the modern business society.
Discussion
Total quality management emerged in North America and spread very fast to the European countries in the 1970s. According to Morfaw, the United States and Europe was concerned about the emergence of Japan as a dominant player in production of plants and equipment (33).
For a long time, this had been an industry dominated by the United States and European countries. However, Japan had mastered the art of producing machines in a unique way using various quality management tools. Japan’s quality management tools helped firms to lower the cost of production without compromising on quality. This alarmed the West as Japanese firms such as Toyota became dominant players in the motor industry.
The United States commissioned US Navy to come up with a quality management tool that will not only enhance quality of production but also lower cost of production. US Navy came up with the concept of total quality management.
This concept seeks to embrace quality in the production process from the time of sourcing for raw materials to the time of delivering finished products to the customer. It is a continuous quality management process that seeks to cut cost of production by limiting time of delivering products to the market while enhancing quality of the products which come to the market.
Meeting customers’ expectations
According to Chary, the concept of total quality management is focused on meeting the expectations of customers in the most unique manner (47). The expectations can never be universal because of the differences in living standards and socio-cultural background. Total quality management tool is used to identify these unique customer needs and coming up with strategies through which they can be met. A firm can only achieve success in the market if its products meet expectations of customers.
In many cases, customers are always at liberty to choose a brand they believe offers the best value for their money. That is why American firms such as General Motors and Ford embraced this tool as soon as it emerged. Hill notes that this tool helped many Western companies to compete favorably with Japanese firms (11). It helped them lower the cost of production while enhancing the quality of products delivered in the market.
Is total quality management enough for competitive advantage?
Many firms have embraced the concept of total quality management as a way of enhancing efficiency in production process. However, the main question that many firms struggle to answer is whether or not total quality management can be used as the only tool in managing quality. The market is getting increasingly competitive and firms are under pressure to find ways of managing this stiff competition. Using quality management tools that enhance efficiency in the production process is the only way of managing such competition.
Total quality management is one of the tools that have proven to be effective in enhancing production efficiency. Many firms are still using this concept to manage their production systems and the result has been good.
However, other new quality management tools have emerged in various parts of the world. This tool gained massive popularity in the 1990s. Large firms such as General Electric, Verizon, and IBM have been using Six Sigma in managing production processes. This does not mean that total quality management has been rendered irrelevant in the production process.
According to Besterfield, despite the emergence of other quality management tools such as Six Sigma, the concept of total quality management has remained relevant among firms in the modern society (53). The major challenge that firms face is how to integrate these quality management tools in the production process.
This is so because in most cases, one will realize that one of the tools is superior in one area of production but weak in another area compared to other existing tools. For instance, total quality management may offer superior strategy when it comes to sourcing for quality materials and delivering high value to the customer. However, this tool may be inferior to Six Sigma in the actual production process.
Firms always struggle to find out how they can use different tools at different stages in order to get the best results. This may be very challenging at times. Total quality management has its specific stages that must be followed in order to achieve the best results. Six-Sigma also has its own steps that a firm must follow when using it.
Getting to know the stage at which one should switch from using total quality management to Six Sigma is the biggest challenge that firms face. The main fear is that the whole system may fail to work if the shift from one tool to another was not done correctly or at the right stage.
According to Chary, no single tool of quality management can be considered sufficient in the modern competitive business environment (62). In order to manage market rivalry, firms need to embrace a number of quality management strategies suitable. Total quality management is a good concept that has helped many firms in Europe and North America achieve success in the market. However, Hill warns that firms should avoid using it as the only tool in managing quality (72).
This is so because it also has its own weaknesses that can be eliminated in case it is used alongside other strategies. Many other quality management tools have emerged in the recent times which are very effective. This does not mean that other tools developed in the 1970s are no longer effective. What firms need to determine is how these tools can be used in an integrated approach without disrupting the production process.
Evolution of quality: First fifty issues of production and operations management
The concept of quality management was introduced by large manufacturers when they started facing competition in the market. Before that, many firms did not put much emphasis on quality because they dominated the market.
However, this changed soon after the end of the Second World War when many companies started emerging not only from Europe but also parts of Asia. Erickson says that the journey of quality management has been a long one (71). What started as a simple way of ensuring that goods are of the right standards has evolved into a computer-based strategy where the entire production process is systemized. The figure below shows the stages in the evolution of quality
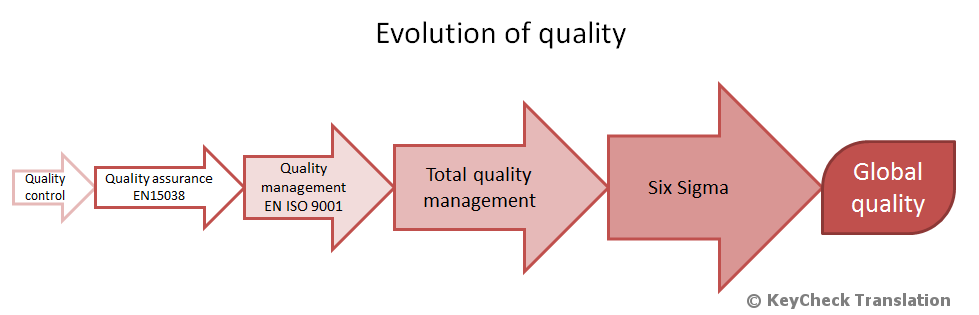
As shown in the figure above, the concept of quality management started with simple quality control measures. This was a basic inspection of the production process that focused on limiting defects in the production process. Quality control focused majorly on supervising the employees involved in the production process to ensure that they did their best to ensure that final products were of high quality. Little attention was paid to most of the stages used in quality management processes in the modern society.
As Erickson observes, the main focus of quality control was the actual process of production done by the employees (88). This evolved to quality assurance where firms focused on how to maintain a continuous flow of high quality products in the market.
The term assurance was used to reflect a customer-centric approach that this strategy was taking. The strategy offered an assurance to consumers that they shall get high quality products consistently. This evolved further into ISO 9001. It is at this stage that firms started looking at quality management from a holistic perspective.
Many firms realized that to achieve the best results in quality management, a firm had to go beyond employees in the production department. The management had to focus on the employees, machines, time, raw materials, and time invested in the production process. All these factors played a role in quality management. When any of these factors is ignored, then achieving the desired results may be almost impossible.
Since the inauguration of management and operation issue in 1992, researchers have made massive contribution in the field of quality management. First fifty issues of production and operations management looks at these contributions and how they have enhanced the application of TQM. When total quality management was introduced, firms had already realized that efficiency can only be achieved by taking a holistic approach in the entire supply chain.
This tool went a little further than tools that had been used previously. It started by paying attention to the quality of raw materials and how they are delivered to the production facilities within a firm. The entire process of converting raw materials to finished products and then delivering them to the customers is also covered in this tool.
The term total was used to emphasize the fact that this tool looks at the entire supply chain in order to ensure that products that customers get are of the right quality. Six-Sigma is one of the latest quality management tools used in the modern business environment. It minimizes variability in business and manufacturing processes (Gattorna 32).
The tool has become very popular in the modern business environment where standardization is of critical component in the production process. A firm that delivers products which are not standardized cannot win trust of customers in the market. A customer wants an assurance that what a firm delivers today is what will be expected of it tomorrow.
Practices of TQM in today’s environment
According to Morfaw, today’s business environment has become very sensitive to the products that firms deliver in the market (54). Image is everything in such a sensitive market. When the image of a firm is tainted through the delivery of substandard products, then customers will develop mistrust towards it. Its products will always be associated with the poor products that it once delivered in the market.
This explains why it has become critical for firms to embrace quality management tools which will ensure that a firm’s products are of very high quality. Total quality management is still in use as a method of enhancing production efficiency. As mentioned above, a number of new quality management tools have emerged. However, many firms still find it relevant to use total quality management. General Motors is one of the multinational corporations that have used this tool for a very long time.
Charantimath observes that General Motors has started using some of the new quality assurance methods alongside total quality management (62). Some of these methods were developed based on the concepts of total quality management. This makes it easy for firms to continue using the processes that were previously applied with TQM. Such a firm will only need to adjust its systems to be in line with the new approaches of managing quality.
Ford Motors is another firm that has been using total quality management in its production process. The company’s international market was affected by the emergence of Toyota Motors as a major manufacturer of the low-cost vehicles. In order to protect its market share, Ford Motors started using Total Quality Management in its production strategies.
The strategy enhanced the efficiency of the firm’s production methods. Since then, Hill says that the management of Ford developed trust in this tool (96). Many other firms in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia are still using this tool in managing the quality of their products.
TQM: influence of information technology
According to Charantimath, information technology has had a major influence in the application of TQM as a tool of enhancing production processes (21). Technology has revolutionized the strategies that firms use in their production process. Information plays an important role in the normal operations of a firm. Gattorna says that firms have invested heavily in research (83).
The only way of remaining relevant in the current business environment is to engage in research in order to understand the changing environmental forces. Information technology plays an important role in conducting research.
A firm can engage its customers in an online research due to the emerging technologies. For instance, Apple Inc uses its interactive website and social media to engage its customers. Through the engagement, a firm gets to know the changes taking place in terms of quality that customers expect and the best approaches that should be used in delivering products.
Such pieces of information help in determining how to apply the concept of total quality management. Through information technology, researchers can share their findings and come up with a conclusion over an issue under investigation. Once the team involved in research has come up with its finding, the information must be shared among the relevant departments. In many cases, market research is conducted by a team of marketing experts.
However, the information these experts gather is more important to the production department than it is to the marketing unit. For that matter, Nersesian suggests that this information should be processed and made available to all the stakeholders (21). Information technology makes this possible. Using an integrated communication system, such information will be available from the database where all the relevant stakeholders in the supply chain can access.
The logistics unit, production department, the marketing unit and finance department can access the information and know how they need to interact in order to achieve the desired outcome. Information technology has had a positive influence on how TQM is applied as a tool of enhancing quality of production processes.
Conclusion
In the current business environment, quality management has become a critical issue that a firm cannot ignore. The competition in the market is very stiff and it is only those firms which offer superior value that can manage to stay operational. Various tools of managing quality have come up over the past fifty years. Total quality management is one of the tools that have been in use for the last forty years. This tool emphasizes on the need to manage quality in the entire supply chain system.
This means that a firm will need to ensure that its raw materials are of the right quality, the logistics and production processes are standardized, and the marketing team understands how to deliver products to target customers. With the emergence of information technology, TQM has become even more relevant to firms because it is easy to put into application.
Works Cited
Besterfield, Dale. Total quality management. Delhi: Dorking Kindersley, 2011. Print.
Charantimath, Peter. Total quality management. New Delhi: Pearson Education, 2006. Print.
Chary, Samson. Production and Operations Management. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill, 2004. Print.
Erickson, Gary. Advertising Competition in a Dynamic Oligopoly with Multiple Brands. Operations Research, 57.5 (2009): 1106-1113. Print.
Gattorna, John. Gower Handbook of Supply Chain Management. Aldershot: Gower, 2008. Print.
Hill, Andrew. What makes total quality management work: A study of obstacles and outcomes? New York: Cengage, 2008. Print.
Morfaw, Jones. Total quality management (TQM): A model for the sustainability of projects and programs in Africa. Lanham: University Press of America, 2009. Print.
Nersesian, Roy. Trends and Tools for Operations Management: An Updated Guide for Executives and Managers. Westport: Quorum Books, 2000. Print.

