Introduction
Today’s business environment is characterized by its rapid globalization, contributing to the overall changeability of the landscape. The case of the Vapiano chain of restaurants is representative of the entire industry in that it shows how a company can be affected by external forces. The sphere of hospitality and restaurants entered a phase of intense turbulence amid the Covid-19 novel coronavirus pandemic, which posed new challenges while revealing the underlying issues of the industry.
The Covid time has become an appropriate background, which allows researchers to analyze the agility and management capabilities of global companies faced with new barriers. The purpose of this paper is to examine the case of the Vapiano restaurant chain in terms of its competitive environment and strategy while providing recovery recommendations.
Vapiano Restaurant Profile
The development of the chain under review corresponds to the general trends of the global industry. Vapiano is a Germany-based company, owning Italian restaurants across the globe. The first Vapiano venue was opened on October 22, 2002, in Hamburg, but the headquarters of the organization remain in Cologne (Our story, n.d.). Following the creation of its first restaurant, the company’s management made a decision to launch a franchise, aiming at the global market. Subsequently, Vapiano continued its expansion, and the chain has reached the level of over 200 venues in 33 countries dispersed across five continents (Our story, n.d.).
According to the CEO, further worldwide growth will remain one of the company’s priorities (Everke, 2019). Therefore, it appears possible to state that the chain is aiming at a global presence, which would allow it to retain a considerable customer base within the broad geography.
It is natural for a global company to expect all its franchisees to exhibit a unified vision and approach to business. Vapiano’s leading principle is “if you have an easy-going and relaxed approach to life, you’ll live more healthily and longer” (Our story, n.d., para. 1). Accordingly, the company’s objective is to provide its customers with a positive atmosphere in which they will feel comfortable enough.
As can be inferred from the name and the concept, the chain focuses on the Mediterranean, namely Italian cuisine. From the culinary point of view, Vapiano offers pizza and pasta, as well as traditional sauces and dressings (Our story, n.d.). The company’s idea was to make the choice of meals as easy as possible so that it does not distract visitors from communicating with one another (Our Vapiano design, n.d.). All venues are decorated with fine materials and designed with an emphasis on the social aspect of restaurants. Such an environment prompts the guests to abandon the daily routine and concentrate on enjoying themselves, as long as they stay on the premises of Vapiano. As established prior, the chain aims at a global presence, and all its locations are expected to adhere to the general strategy.
Competitive Environment of Vapiano Restaurants
Restaurant Industry
Vapiano remains an important part of the global restaurant market, which is often viewed in the broader context of the entire hospitality industry. Evidently, this field demonstrates particular features, which are conditioned by the direct nature of customer interaction. The recent development of technology and transportation has to lead to stable growth of this industry, as more people choose to travel globally (Baltescu, 2020). Daries et al. (2018, p. 125) state that restaurants, being an integral element of the hospitality industry, have become “key assets in the economies of many countries and are often considered attractors of tourism in themselves” (p. 125).
In fact, the restaurant industry amounts for about four percent of the Gross Domestic Product of the United States, the world’s leading economy (75 Significant Restaurant Statistics, 2020). At the same time, the market’s size in Europe has passed the level of 500 billion dollars, and this segment is projected to grow in the following decade (The restaurant industry — a global perspective, 2018). Naturally, many companies, including Vapiano, opt for a worldwide presence, following the development of the industry and the increasing stream of revenues.
There is a large number of foodservice companies, which maintain their presence across the globe. However, research suggests that the leaders of the market with the best numbers in terms of capitalization and profits operate in the fast-food sector (Reiff, 2020). For example, Reiff (2020) states that Starbucks and Mcdonald’s occupy the highest positions on the list of the largest restaurant chains worldwide. Despite the evident profitability of fast food, Vapiano aims at conquering higher tiers of the market, offering high-quality Italian cuisine. On the other hand, this segment appears equally popular, attracting major players, such as Jaimie Oliver and his Jaimie’s Italian. Accordingly, the organization in question has been operating in an industry in which the rapid expansion is balanced by intense competition.
Critical Forces
It appears possible to examine the competitive environment of Vapiano from the standpoint of Porter’s Five Forces model components: new entrant threat, bargaining powers of suppliers and buyers, current competition, and substitute product threat. First of all, the threat of new entrants in the restaurant business is quite high, as opening a dining venue is a moderate investment. Vapiano is an international business, meaning that it has to compete with new rivals both globally and in each particular location. The bargaining power of buyers imposes additional restrictions on the company.
Considering the amount of competition in the industry, unwise pricing policy will quickly push customers toward competitors, also increasing the threat of substitute products. Next, the bargaining power of suppliers is not as significant, as Vapiano is a mid-range Italian restaurant. This segment is quite developed globally, meaning that the selection of suppliers is also broad. Finally, as discussed earlier, restaurant business is highly competitive, and Vapiano faces rivalry in each location it is represented from both local and other global players.
COVID-19
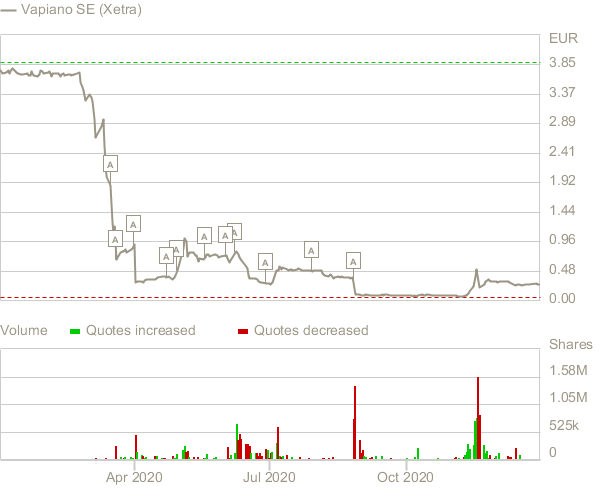
Covid-19 has had an immense impact across all industries, but it is the hospitality sector that was influenced the most. Substantial effort was made to support vital industries, but hospitality is mostly associated with leisure, which is why its uninterrupted functioning was never a priority. According to Song, Yeon, and Lee (2021), restaurant sales decreased by almost 50% in the United States during the first month of lockdown in March. Furthermore, over 3% of American restaurants had to cease their operations on a permanent basis in the fallout of the pandemic (Song, Yeon, and Lee, 2021). Figure 1 demonstrates the market rates for the company’s shares across the year between January 2020 and January 2021.
However, earlier reports imply that the company faced a crisis even before the outbreak of Covid-19. Lischtschuk (2019) writes that, by that time, the share price had already decreased by 75% percent since the moment of Vapiano’s IPO in 2017. The pandemic accelerated the process, which is why the company was unable to fulfill its financial obligations amid the crisis in 2020. As a result, Vapiano filed for insolvency in April, being unable to apply for a governmental aid program (Reuters Staff, 2020). Therefore, Covid-19 added another dimension to the already competitive landscape of the industry, aggravating existing issues and creating new ones.
Competitive Strategy and Critical Investments of Vapiano Restaurants
The Vapiano restaurant chain opted for an aggressive strategy of global expansion following its foundation in the early 21st century. According to the vision of its founders, Vapiano wanted to be available to customers across the globe (Our Vapiano design, n.d.) This idea suggests that a frequent traveler should be prompted to visit the chain’s restaurants in all locations which they visit, knowing exactly what experience they will have.
In order to attain this objective, the company’s management promoted the franchising model, actively supporting international operations. The broad geography of Vapiano, encompassing countries from Latin America to the Middle East, was expected to become a crucial element of its competitive advantage (Lischtschuk, 2019). In addition, the management wanted to make dinners at Vapiano an intense social experience. The idea behind the arrangement of spaces inside each restaurant was to promote socialization (Our Vapiano design, n.d.) In addition, Vapiano’s locations have always been characterized by a strong connection between the kitchen and the visitors, which is rarely present in other places. Guests could interact directly with cooks, placing their orders and enjoying the culinary experience of watching their meals be prepared.
Consequently, the organization continued to lay emphasis on the development in the aforementioned areas. First, Vapiano’s chefs were trained to create culinary performances and interact effectively with their customers (Lischtschuk, 2019). In other words, the work of the kitchen staff received another critical competency, aside from the direct professional responsibilities. However, this strategy was not appraised by the entirety of the customer base. According to Lischtschuk (2019), the impressive culinary experience often entailed increased waiting time for Vapiano’s guests, many of whom did not appreciate it.
This way, the chain lost the loyalty of a substantial market segment, which shared the traditional vision of food service establishments as places to eat. Simultaneously, a large portion of the company’s investment was allocated to the development of its global franchising network and amounted to 70 million euros in 2018 (Lischtschuk, 2019). Therefore, the strategy of Vapiano restaurants can be described as rather aggressive, with an emphasis on social experience and rapid expansion across countries and continents. Despite some advantages, which allowed the company to grow throughout the first decade of development, Vapiano experienced its drawbacks aggravated by the Covid-19 pandemic.
Core Competency of Vapiano Restaurants
Considering the latest development and the issues highlighted by the coronavirus outbreak, it appears possible to conclude that the strategy of Vapiano Restaurants had its flaws. Instead of pursuing extensive development on an increasingly larger scale, the company would benefit more from concentrating on its areas of core competencies. First of all, as discussed earlier, the geography of the chain was increasing rapidly, demanding considerable investments. In this regard, the management may have overlooked the core of its operations, which is located in Europe.
Vapiano is a German company, above all, and it owes a large portion of its success to the pilot venue in Hamburg. Accordingly, one can infer that the initially positive experience of the company was conditioned by its ability to meet Western European market demands. Vapiano took the most enticing aspects of Italian restaurant culture and adjusted to the mindset of the German population. The initial design was tailored in accordance with the local public’s expectations, without taking into consideration possible expansion into other continents. Accordingly, in a time of crisis, Vapiano can benefit from what it knows best, which is the expertise in the European market.
Recommendations
Course of Action
Having examined the history, core values, and challenges of Vapiano restaurants, it appears possible to devise a set of recommendations, which will allow the company to regain market success. First of all, a comprehensive change of strategy is required to overcome the fallout of the present crisis. As stated by Lischtschuk (2019), Vapiano’s issues had begun before the outbreak of Covid-19, which implies some systemic problems.
According to Song, Yeon, and Lee (2021), market research confirms that substantial financial leverage became the primary enabler of resistance to the Covid-induced challenges for restaurants. Prior to the present situation, Vapiano willingly spent its resources on global expansion without saving enough funds for a potential crisis. The new strategy should be more economizing, allowing the management to prepare a safety net for future perturbations.
In addition, Vapiano will benefit from following modern positive trends in terms of sustainability. As discussed by Iraldo et al. (2017), green initiatives have become important factors enabling competitiveness in the sphere of hospitality. The market’s leaders utilize recycled materials in décor while making considerable effort in reducing the environmental impact of their activities. Vapiano devotes considerable attention to its environmental policies, advocating for animal welfare (Our vision, our value, n.d.).
Nevertheless, the chain may want to lay additional emphasis on these topical issues, highlighting its efforts in the sphere and supporting words with meaningful, public actions. The list of these actions can include the use of recycled materials to produce menus and other handouts. The menu itself will benefit from a broader variety of meat alternative-based products, promoting Vapiano within vegetarian and vegan communities.
Resource Allocation
Evidently, in a time of crisis, the resources of the nearly bankrupt chain are almost depleted. However, a major shift in the strategic vision will allow Vapiano to utilize the existing assets in the most efficient way. As discussed by Lischtschuk (2019), excessive expansion on other continents has become of the nurturers of Vapiano’s downfall. In today’s troubled environment, the company should cut its global expenditures, reallocating the funds to its European locations.
In fact, as controversial as this decision is, closing most of the businesses overseas will reduce the unnecessary expenditures and free enough resources for Vapiano to resume growth. Lischtschuk (2019) suggests that a more franchise-oriented model will be profitable once Vapiano continues its global development. In the meantime, the company should utilize its European resources, especially in its home area of Germany, to accumulate sufficient resources for a safety net. This way, Vapiano will be able to recover from the most recent crisis over the short term, re-entering the global competition in three to five years.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the case of Vapiano serves as an excellent example of the way in which the current Covid-19-induced crisis can reveal and aggravate the underlying issues of the business. In its pursuit of global presence and originality, Vapiano’s management was unable to provide effective distribution of resources. As a result, once the company grew on a worldwide scale, maintaining the same growth rate became a challenging task. The pandemic put Vapiano on the verge of bankruptcy, and the company should make considerable strategic changes to remain in the business. Reorienting the operations in a more localized way will enable a quicker recovery, leaving a way to resume global development in the near future.
Reference List
75 significant restaurant statistics: 2020/2021 analysis of data & market share (2020). Web.
Baltescu, C. A. (2020) ‘The relevance of online reviews for the development of restaurant industry’, Annals – Economy Series, 1, pp. 42–47.
Daries, N. et al. (2018) ‘Maturity and development of high-quality restaurant websites: a comparison of Michelin-starred restaurants in France, Italy and Spain’, International Journal of Hospitality Management, 73, pp. 125–137. Web.
Everke, C. (2019) Vapiano in Transition. Web.
Iraldo, F. et al. (2017) ‘Greening competitiveness for hotels and restaurants’, Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 24(3), pp. 607–628. Web.
Lischtschuk, A. (2019) Crisis restaurant chain: What Vapiano did wrong. Web.
Our story (n.d.). Web.
Our Vapiano design (n.d.). Web.
Our vision, our value (n.d.). Web.
Reiff, N. (2020) 10 biggest restaurant companies. Web.
Reuters Staff. (2020) German restaurant chain Vapiano files for insolvency. Web.
Share performance. (2021). Web.
Song, H. J., Yeon, J., and Lee. S. (2021) ‘Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic: evidence from the U.S. restaurant industry’, International Journal of Hospitality Management, 92. Web.
The restaurant industry — a global perspective (2018). Web.

