Introduction
The paper will discuss a possibility of a Merger between Hospital Corporation of America (HCA) Holding Inc. and Tenet Healthcare. Both hospitals own centers in the South Carolina. HCA holding Inc. was formed in 1968. HCA owns approximately 163 hospitals and 110 freestanding surgery centers in 20 states and England. It operates in London and the United States. The health care facility employees about 199,000 people. Further, it has a market share of between 4% to 5% of inpatient services. HCA is a publicly held health institution that trades on the New York Stock Exchange with a ticker symbol denoted as ‘HCA’. Finally, HCA is audited by Ernst & Young (Hospital Corporation of America, 2013). On the other hand, Tenet Healthcare Corporation, founded in1967, is a publicly held healthcare institution based in America. The health center owns 49 hospitals, 117 outpatient centers, 14 conifer services centers, and conifer client locations in 39 states. Further, the health center engages more than 59,000 employees. In the year 2012, the center recorded 4 million outpatient visits. Both hospitals are major providers of health services in the US. They rank among the top five health providers in the US. Finally, Tenet Healthcare Corporation is audited by Deloitte & Touche LLP (Tenet Healthcare Corporation, 2013).
Aim of the paper
The paper will carry out financial statements and operating indicator analysis so as to assess the financial condition of the two Health care facilities. Further, it will analyze the debt, equity financing and capital structure of the two companies. Also, it will analyze the cost of capital for the two companies. Further, the paper will conduct a risk assessment with regard to the merger. Finally, the paper will carry out a review of management of current receivables.
Analysis of the financial statements
The reported financial statements of the health center do not give a comprehensive analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the companies. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out an in depth analysis of the financial statements so as to have a better view of the company. Further, financial analysis of the company helps in making informed decision such as the viability of a merger analysis. Ratio analysis breaks down the financial data into various components for better understanding of the financial strengths and weaknesses of the company. A key tool for financial analysis is the ratio analysis (Holmes & Sugden, 2008). This section will carry out an analysis of the financial statements of the two companies. The table below summarizes the key statistics of the two companies for the year 2012.
From the table above, it is evident that the HCA earns a more revenue than Tenet. Further, the total assets for HCA are greater than that of Tenet. Both companies have not reported losses for the past three years.
Profitability ratios
Appendix one gives the profitability ratios for the two companies. Three profitability ratios are computed these are net profit margin, return on equity and return on total assets. The profitability of HCA is higher than that of Tenet. The trend for the ratios have been erratic for the three years.
Liquidity ratios
Appendix two shows the liquidity ratios. The current ratios for both companies are quite favorable. They are above one. This implies that they are able to meet their current obligations. However, the quick ratios for the two companies were quite low. This implies that the company may not be in a position to pay current debt using quick assets.
Solvency ratio
Solvency ratios measure the ability of the company to repay the long term debts. A commonly used ratio that is used to measure solvency of a company is the times interest earned ratio. Appendix three shows the times interest earned ratio. The ratios indicate that the two companies can pay their interest expense using earnings before income and taxes.
Analysis of operating indicators
Analysis of the operating indicators reviews the internal data so as to establish the factors that contribute to the reported financial position of the health centers. The operating indicators are commonly used by the management to shape the future of an organization. A commonly used tool is the economic value added (EVA). The tools estimate the ability of the management to generate or destroy wealth of the institutions. It is an effective way of assessing the ability of the management to provide value for shareholder’s wealth (Holmes & Sugden, 2008). Appendix five shows the computation of EVA for 2011 and 2012. The EVA for the two companies were negative for the two years. This implies that the two companies are not economically viable.
Debt and equity financing
From the review of the financial statements of the two health centers, it is apparent that they use both equity and debt financing though in different proportions. The tables below summarize the debt amount of debt and equity financing for the companies.
Debt and equity for Hospital Corporation of America (HCA) Holding Inc.
From the table above, it is evident that the company has a negative total amount of equity financing. This can be attributed to the large amount of retained deficit amounting to ($10,960) and accumulated other comprehensive loss which amounted to ($457) that outweighed the total amount of issued shares. This generated net shareholder’s deficit amounting to $8,341. The implication is that shareholders of the health facility owe the company money. The total debt of the company amounted to $28,930. This comprised of senior secured second lien notes and senior unsecured notes.
Debt and equity of Tenet Healthcare Corporation
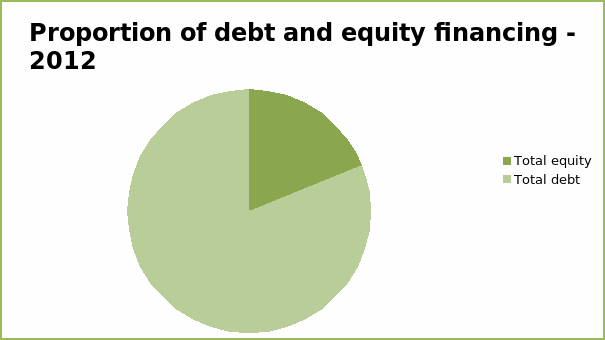
From the table above, the total amount of shareholder’s equity amounted to $1,218 million. While the total debt amounted to $5,252. The total debt amounted to comprised of various senior notes maturing on different dates, senior secure notes, credit facility due 2016, capital leases and mortgage notes, and unamortized note discount and premium. It is evident that the the amount of debt financing is about 4.3 times the amount of equity. This could be an indication of high leverage (Holmes & Sugden, 2008). The pie chart below shows the proportion of each amount of financing.
Evaluation of the capital structure and cost of capital
Analyzing the capital structure of the two health care centers is of utmost importance because it determines the rate at which a company grows. Further, it also dictates the amount of working capital that is available in the centers and the amount they can spend on investments. The management of the companies needs to maintain an optimal mix of various sources of funds because the mix has an impact on the profitability, cash flows and amount attributed to shareholders. The capital structure that a company decides to use depends on the market the company operates in. The tables below show the proportion of the amount of each type of financing in the amount of capital structure.
Debt and equity for Hospital Corporation of America (HCA) Holding Inc.
From the table above, it is evident that the health center is highly levered. The amount of debt in the capital structure is more than 100%. This debt level affects the profitability of the company since the company paid an interest expenses amounting to $1,798. While the net income amounted to $2,006. It is evident that the interest expense is about 81% of the amount of net income.
Debt and equity of Tenet Healthcare Corporation
From the table above, it is evident that the health center is highly levered. The amount of debt in the capital structure is 81.17%. This debt level affects the profitability of the company since the company paid an interest expenses amounting to $412. While the net income amounted to $133. It is evident that the interest expense is about 309.7% of the amount of net income.
Cost of capital
Determination of optimal capital structure is a vital decision on financing options to use. Optimal level of debt is the level at which the cost of capital is minimized. It is the level beyond which a firm should not borrow. Computation of optimal debt, cost of debt and cost of equity will be based on the Damodaran model thus, the amount of debt has an effect on the capital structure of the firm. First, the cost of debt and cost of equity for the health centers will be calculated. Thereafter, the weighted average cost of capital will be computed. The weighted average costs of capital approach will be used to calculate the required rate of return.
Determination of cost of debt
A number of firms consider it as a cheap source of finance. It is based on the fact that debt attracts predetermined rate of interest which is payable at a fixed period of time. A company’s cost of debt is based on the cost of bonds. The cost of debt is the rate a company pays for its debt. The cost of debt of the company is determined by a number of factors these are, the rate at which the company can borrow long term today (risk free and a default spread) and the tax rate. The cost of debt is computed as shown below.
Cost of debt for Hospital Corporation of America (HCA) Holding Inc.
Cost of debt = (risk free rate + default spread) (1 – t)
Risk free rate = 4.5%
Default spread = 5.3
Tax rate = 34% (corporate tax in the US is 34%)
Substitute the values
(4.5% + 5.3) 0.66 = 6.468%
Cost of debt of Tenet Healthcare Corporation
Cost of debt = (risk free rate + default spread) (1 – t)
Risk free rate = 4.5%
Default spread = 6.1
Tax rate = 34% (corporate tax in the US is 34%)
Substitute the values
(4.5% + 6.1) 0.66 = 7%
The high cost of debt can be attributed to high leverage.
Determination of cost of equity
Cost of equity shows the amount of return that shareholders expect to receive from their investments. The return investors expect at the end of the year comprises of two elements these are, the fluctuations (positive or negative) on the market price of the shares and the dividends paid by the company. It is worth noting that the amount of debt in the capital structure has an impact on the cost of equity. High amount of debt increases risk of equity thus increasing the risk premium that shareholders will require for their investment. The capital asset pricing model is commonly used to compute the the cost of equity (Weiss, 2008).
Capital asset pricing model
The capital asset pricing model is a model that is used to ascertain the required rate of return of an asset. The model takes into account risks arising from the market in which the asset trades. The systematic risk is represented by the beta factor. The model computes the price of a single portfolio. The capital asset pricing model that will be used to compute the cost of equity is shown below
Cost of equity = risk free rate + Beta * Risk premium
Risk free rate
Risk free rate is the rate of interest that does not have default risk, no reinvestment risk and are in the same currency. It represents the rate of interest for an investment that does not incur any losses.
Asset Beta
Asset beta is used in the capital asset pricing model. It measures the volatility of a company’s stock relative to the market changes. Computation of asset beta is founded on historical returns which may not give an estimate of the firm’s future share prices. A number of factors can make the value of asset beta to fluctuate. Some of the factors are risk of the business, operation risk, financial risk, and sales risk.
Risk premium
Risk premium can be denoted as the incentives for investing in a risky asset. The risk premium is the amount over and above the risk premium. An investor will demand for compensation for the risk element in securities which are risky. Risk premium measures the market risk in which the group operates in. Calculation of cost of equity is shown below
Cost of equity for Hospital Corporation of America (HCA) Holding Inc:
Cost of equity = 4.5% + 2.2 * 4.468% = 14.33%
Cost of equity of Tenet Healthcare Corporation:
Cost of equity = 4.5% + 2.2 * 3.4% = 12%
The cost of equity for HCA is greater than the cost of equity for Tenet. This can be attributed to the high leverage in HCA.
Weighted average cost of capital
Weighted average cost of capital is neither cost of debt nor equity. It is an average rate that a company should pay to fund its assets. Alternatively, it is the rate of return which a firm must make from the assets to satisfy the people who provide funds to the company, there are the shareholders and creditors. The weighted average cost of capital takes into account the relative weights of each component in the capital structure of the firm. This shows that one must have required rate of return for each component of the capital structure. This facilitates the calculation of the weighted average rate cost of capital. In most cases, the individual firm’s weighted average rate cost of capital is different from that of the industry (Weiss, 2008). However, over time the weighted average rate cost of capital for all firms in the industry tend to converge to the industry weighted average rate cost of capital.
Hospital Corporation of America (HCA) Holding Inc:
The weighted average cost of the capital = cost of equity * proportion equity the capital structure + cost of debt * proportion debt in the capital structure.
Weighted average cost of capital = 14.33% * 40.51% + 6.468% * 140.51% = 14.89%
The calculations above can be summarized as shown in the table below.
From the table, the weighted average cost of capital for the company is 14.89%. The value can be considered to be relatively high.
Cost of debt of Tenet Healthcare Corporation
Weighted average cost of capital = 12 * 18.83% + 7% * 81.17% = 9.82%
The calculations above can be summarized as shown in the table below.
From the table above, it is evident that the WACC for HCA (14.89%) is greater than that of Tenet which is 8%. This might cause a challenge during merger since the investor for HCA requires higher return than those of Tenet.
Risk assessment
A major risk that the two companies are likely to face during merger is compliance with the various regulations requirement. The two companies must comply with the antitrust laws. These laws prohibit mergers and acquisition that are perceived to eliminate competition in the market thus creating a monopoly. Thus, before proceeding with the merger, the two companies must review the possible impact of the merger on the market. This reduces the penalties that may arise from noncompliance with the antitrust laws (Weiss, 2008). Another challenge for the company would be the inability to raise the amount of capital for expansion. This can be attributed to the nature of the capital structure of the two companies. Finally, another challenge for the two companies during merger would be merging the policies of the two companies.
Management of receivables
Management of receivables focuses on the cost of collection of the debts, average collection period, the amount of bad debts and sales. The total amount of reported receivables for HCA amount to $4,672. The provisions for doubtful debts relate to the uninsured amount due from patients directly. Write offs are carried out on specific accounts identified. This requires adjusting accounting entries. This comes after several failed attempts to collect the debts. The day’s revenue in accounts receivable was 52 days in 2012 and 53 days in 2011. This implies that it takes the company an average of 52 days to collect receivables. On the other hand, the total amount of accounts receivables for Tenet amounted to $1,345 million. The company’s policy is to collect all amounts due from their clients. Exceptional cases such as during emergencies the policy do not apply.
References
Holmes, G., & Sugden, A. (2008). Interpreting company reports. Harlow: Financial Times/Prentice Hall.
Hospital Corporation of America. (2013). Investor relation. Web.
Tenet Healthcare Corporation. (2013). Annual report – 2012. Web.
Weiss, L. (2008). How to understand financial analysis. France: Insead, Fointanebleau.

