Introduction
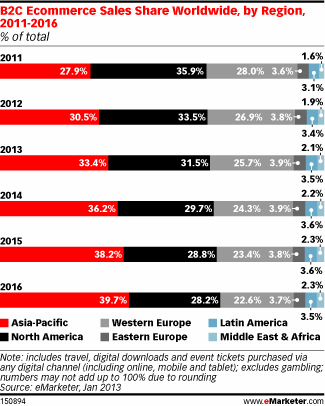
The growth in Internet technologies has facilitated e-commerce significantly. The industry has grown to include online services related to electronic funds transfer, Internet marketing, sales, data collection, and inventory and supply chain management among others. The notable trends in e-commerce are mainly innovation in products and services by using technologies, rapid growth, fierce competition, and mergers and acquisitions or takeovers. The main competitors of Alibaba are mainly Amazon.com and eBay. Nevertheless, there are also other emerging small players like OnlineAuction.com, eCrater, iOffer, uBid, and others (Chu 1; Lukoff 1). According to data from eMarketer, the E-commerce industry has grown tremendously with sales reaching one trillion USD in 2012 (eMarketer 1).
Alibaba Background
Alibaba Group consists of Internet-based businesses, which aim to promote buying and selling of anything across the globe via the Internet. Jack Ma and his 18 associates founded the company in 1999. Today, Alibaba has grown with over 20,000 employees in 70 offices mainly in the Asian region, the US, and the UK (Alibaba Group 1). Moreover, the company has several affiliates, which deal with different E-commerce products and services. In 2002, the company became profitable. Alibaba Group is the leading E-commerce company in the Asian region. It has made significant mergers and acquisitions. Given the rapid growth of the company, it is vital to understand its strategic information and management processes.
Strategic Information needs
E-commerce relies on strategic information for growth. The focus for any E-commerce business should be on operational, financial, and strategic systems. Operational systems are critical in managing the day-to-day processes of the company. The company needs operational information to control inventory and costs to create competitive advantages. Financial systems would help the company to conduct effective accounting, budgeting, and finance operations. The system would control all operations, and show data for progress through financial analysis. Finally, strategic needs help to link E-commerce strategies and effective technologies.
E-commerce firms can create a business prototype and use information technologies (ITs) to realize the business model. The company may introduce new computer systems and use IT to integrate the system to realize competitive advantages. Such initiatives are critical in overcoming E-commerce challenges and creating competitive thrust when companies use them in innovative ways (Thompson and Pian 78).
Strategic information has effects on the cost leadership of an organization. Alibaba strives to reduce costs on conducting e-commerce globally. As a result, the company has been able to grow fast in the Asian region. Alibaba also uses strategic costs to achieve economies of scale. The company has several affiliated businesses that generate substantial revenues.
Over the years, Alibaba has evolved as a different service provider in the E-commerce industry. Alibaba products and services differentiate it from other E-commerce firms. It has unique features, which are competitive in the E-commerce industry. Customers can visit Alibaba and find several E-commerce solutions for their needs. Alibaba has made many consumers believe that they receive value from its E-commerce sites.
Innovation is another effect of strategic information. IT can support or shape E-commerce products and services. For instance, Alipay is an online third party payment solution, which is innovative and relies on information technologies. The service is popular in China. The company must respond fast to market opportunities to create competitive advantages and be successful. For instance, Alibaba has formed strategic alliances with Visa and MasterCard to facilitate online payments across China and other regions. In these processes, it must account for potential risks inherent in the E-commerce business. However, the final product transforms aspects of business and introduces new ways of conducting business.
Alibaba has focused on massive expansion and acquisition. The major advantage of strategic information need is to enhance growth and promote expansion across geographical regions. Alibaba has managed this process through extensive diversification in different areas of E-commerce. IT and strategic information systems have created favorable conditions to facilitate rapid growth in a decade. Alibaba has also focused on strategic alliances to achieve competitive advantage. The company aims to grow, differentiate its products and services, create cost advantages, and enhance sales volumes and revenues, and marketing strategies.
The major responsibility of strategic information at Alibaba is to help the company to create sustainable competitive advantages. E-commerce evolves rapidly. Hence, only firms, which have sustained competitive advantages, may thrive in such environments. The company will exploit low prices, unique features, innovation, and effective customer service to maintain its growth strategies. Alibaba must use such advantages to create products and services, which are difficult to imitate.
Critical appraisal of strategic information systems and business planning
Strategic information systems (SISs) are “systems that support or shape a business unit’s competitive strategy” (Callon 6; Neumann 36). The critical aspect of SIS is to change the business process in order to create a strategic advantage for an organization. Strategic information systems support critical business activities. They help in enhancing efficiency, control, and business process effectiveness. SISs may not lead to profitability. Instead, they help a firm to run smoothly and formulate strategic directions.
Key success factors in strategic information are numerous, but it depends on the type of industry under review. First, innovative applications help firms to achieve strategic advantages by using IT solutions to serve customers. Second, firms use IS as a competitive weapon for enhancing superior customer services. Third, IT systems promote changes in organizational processes. Firms that have effective enterprise planning systems use their systems for cost-savings and nationwide management (Davenport 121). Fourth, IT connects firms with their business partners in different locations. Fifth, companies use IT to reduce costs. For instance, Alipay has reduced the cost of money transfers in China while other online services also have low costs. Sixth, IT has improved the relationship between business and customers and suppliers. Firms use IT to lock in and retain their associates. In addition, they have also used the system to make it hard and expensive for clients or associates to move to rival businesses. Seventh, Alibaba has used IT to develop new products and services that are in high demand in the Asian region. These are mainly online buying and selling of products. Finally, IT provides competitive intelligence to its users. Firms use IT applications to collect and analyze data related to products, competitors, economic conditions, and external changes.
Information system strategy affects business strategy and organizational strategy. On the other hand, both business and organizational strategies also affect information system strategy. One can use the Information Systems Strategy Triangle in order to “understand the relationship among IS, business strategy, and organizational strategy” (Pearlson & Saunders 23). According to the triangle, all these three aspects of the triangle have complementary roles. Hence, organizations must align these strategies to support each other. Business Strategy is at the top of the triangle. According to Pearlson & Saunders, “business strategy starts with a mission and is a coordinated set of actions to fulfil objectives, purpose and goals and serves to set limits on what business will seek to accomplish” (Pearlson & Saunders 23).
The organizational strategy focuses on operational processes, employees, organizational structures, hiring culture, and other practices that would allow the business to achieve its goals. Information systems strategy helps firms to deliver information services to their partners. The direct or inferred assumptions regarding strategy from the triangle include the following.
- “Successful firms have an overriding business strategy that drives both organizational and information systems strategy” (Pearlson & Saunders 23).
- IS affects “business and organizational strategies, and it is affected by organizational and business strategies” (Pearlson & Saunders 23). This implies that any “change in the IS strategy should have complementing organizational and business strategies” (Pearlson & Saunders 23).
- IS strategies may yield both intended and intended outcomes, which involve both business and organizational strategies.
eBusiness planning
Time
Alibaba is an Internet-based firm that conducts its business throughout the year without time restrictions. The company has managed its business processes efficiently and effectively with its Internet-based business models.
Distance
The company overcomes challenges related to distance and geographical locations because sellers and buyers can transact from any location in the world.
Relationships
Alibaba uses online platforms to manage all relationships with customers and partners. This is also the main form of interaction that Alibaba uses with the aim of creating “an open, collaborative, and prosperous e-commerce ecosystem that benefits consumers, merchants and the economy as a whole” (Alibaba Group 1).
Product
The company develops e-based products and services in order to serve expansive China and Asian region markets. These are mainly products and services, which consumers need in order to solve their problems.
There are different types of planning in an organization. Strategic planning focuses on initial stages, which ensure that all business, organizational, and information strategies complement one another. The planning supports both internal and external processes and accounts for the use of technology and information systems with an organization. Technology planning is also important in a strategic plan.
Tactical planning requires organizations to understand their strategic goals and formulate a course of action required to achieve organizational strategic goals. Operational employees formulate tactical plans in order to execute business strategies.
Operational plans focus on organizational services and products. Such plans develop strategies for maximizing market share, sales, and financial performances. Operational plans account for personnel, production processes, inventory, and other business processes.
The nature of planning at Alibaba is a continuous and ongoing, goal-oriented, integrated, flexible, and intellectual process. The fundamental concept of strategic planning at Alibaba is that it focuses on the organization as a single unit and not on its individual parts. The purpose of planning at the organization is to ensure effective and efficient processes, which result in the realization of strategic business and organizational objectives. Strategic planning focuses on all areas of the organization and yields a corporate strategic plan for the long-term performance of Alibaba.
Planning and control relate to each other and are often used interchangeably, but they have different meanings in the business world. Control focuses on actual organizational performance against set objectives. It also provides strategies to correct any deviations in order to realize the required outcomes. The planning process begins at the initial stage of setting organizational goals, but control comes in the last stages.
The strategic planning process entails several stages at Alibaba, which are often lengthy and iterative. Some scholars have noted that the planning process has five stages (Piccoli 159).
- Strategic business planning at Alibaba acts as a way for systems planning and defines future objectives, mission, targets, and specific execution strategies
- The planning process also involves information systems assessment in which a review of the current IS resources and their effectiveness takes place
- The company also uses a strategic planning process to set its information systems vision to allow it to use IT resources effectively
- Strategic planning at Alibaba also accounts for information systems guidelines. These are sets of guidelines, which define how Alibaba uses its IS resources and technical skills.
- Strategic initiatives provide long-term IS strategies for organizational new initiatives
Alibaba’s knowledge management and customer relationship management activities
Knowledge management (KM) involves “strategies and processes formulated to identify, capture, structure, value, leverage, and share an organization’s intellectual assets to enhance its performance and competitiveness” (Botha, Kourie, and Snyman 13). The focus of KM is to “capture, document, and disseminate individual’s tacit and explicit knowledge in a firm” (Smith 309).
The explicit and tacit knowledge of Alibaba
Tacit knowledge is cognitive or technical knowledge, which consists of “mental models, values, beliefs, perceptions, insights, and assumptions” (Smith 313). Alibaba mainly relies on technology to facilitate the development of its tacit knowledge as employees share their experiences and learn. The company also manages its explicit knowledge through training, seminars, providing manuals, and protecting such knowledge through patent. Technology has helped the firm to personalize information, capture and share tacit knowledge, and manage social relations and conversations.
Alibaba uses both IT tools and non-IT tools and techniques to capture, store, and share knowledge among its employees. The aims of these tools and techniques are to ensure that the company creates, shares, and organizes its knowledge base in order to fulfill its goals. Some of the technology tools include document libraries, document management systems, intranet and extranet, and decision support tools. In addition, there are also content management systems, social network services, collaborative virtual workspace, knowledge portals, and video sharing. Non-IT tools and techniques include brainstorming, knowledge worker competency, collaborative physical workspace, and mentor programs.
KM has critical impacts on a firm’s productivity, shareholder value, management, and control. Alibaba has used KM to get solutions for achieving increased productivity. KM has facilitated sharing and instilled cultures of change in the company. As a result, employees have the right information and the correct time. KM has brought best practices to the company. Besides, KM offers collective knowledge of the firm for the management team to utilize in running and control the processes of the company.
A firm generates new knowledge from KM best practices, and then applies such knowledge to increase productivity. High productivity results in increased shareholders’ values. A firm reacts promptly to changes in the market when it has the right information. Moreover, advanced knowledge can allow a company to develop improved services and products. This creates an edge against competition as a firm offers alternatives to customers’ challenges. KM offers productivity, shareholders’ value, and management and control efforts in several ways to a firm.
KM creates competitive advantages for Alibaba. Alibaba has captured valuable knowledge from its employees and used it to develop nearly 25 business models. The company has created new knowledge of new products. As a result, the company has competitive advantages over its competitors in the region. KM allows Alibaba to respond quickly to competitors and demands in the market. Hence, it has been able to develop online products and services, which many consumers require. KM has ensured that Alibaba has an edge against its competitors. The company considers its products and services as solutions to customers, which create great customer delights and high retention. KM has been able to make the company productive in several ways.
Customer Relationship Management
According to Robert, Customer relationship management (CRM) is “a platform for managing a company’s interactions with current and potential customers” (Shaw 57). Technology provides organized, automated, and coordinated sales, marketing, relationship management, and technical support. Customer relationship management is critical for any organization. CRM aims to facilitate customer experiences through automated processes. Moreover, organizations use customers’ information to create a competitive edge by offering personalized services to their customers. In addition, CRM has become a major tool for competing among firms (Pepper and Rogers 67).
CRM enhances advertising and marketing for Alibaba. Alibaba uses its CRM data to track and target potential customers with its marketing strategies and activities. Hence, it can effectively use social media, e-mails, and online advertising to the right customers.
The company has CRM for promoting its business activities and providing discounts to customers. The company shares data on promotion through its online channels, which customers use to make informed decisions before purchasing products.
Alibaba has several services and distribution channels. CRM has allowed it to identify its key partners, target markets, and streamline information to these groups. In addition, it provides personalized information, notes customers’ needs, and understands its distribution networks.
CRM is a major tool for cost reduction. Alibaba uses CRM to make business partners rather than customers. Alibaba’s clients do their own order entry through its online platforms. The company offers information related to the pricing of products and services through its CRM platforms so that customers can make informed decisions. Pricing influences how customers visit online stores.
Further, CRM is an important tool for promoting new product features. CRM gathers useful information from customers. Alibaba uses such data to promote new product features to specific customers. These are critical advantages, which the company has exploited to remain competitive in China and other countries in the Asia region.
CRM has several effects on customer retention. One must recognize that customer retention can only take place when such customers have delightful experiences with the company. CRM has created improved customer service for the company. The company has managed to integrate all data from customers to improve customer service. This makes information available when needed. Moreover, customer service departments provide information, which customers need or lead customers to the information they require. CRM is an effective tool for retention because customers can navigate the system and find their own solutions, which enhance their experiences at Alibaba.
Customer satisfaction leads to customer retention. CRM makes customers feel that they are a part of the company, particularly through personalized services. This leads to enhanced customer retention. CRM cannot improve any poor products. However, Alibaba must meet the expectations of its clients anywhere in the world. Customer satisfaction can predict repeat business and customer retention. This creates maximum value for the company from a single customer (Berger and Nasr 67). Hence, CRM leads to customer loyalty. CRM platforms impress customers and create loyalty. Loyal customers may use Alipay on several occasions. This is how effective CRM creates customer loyalty.
A loyal customer also has a high total value as an individual customer to the company (Berger and Nasr 17). This increases customer lifetime value with the company. This has allowed Alibaba to focus on its long-term strategies by expanding its services in the entire Asian region, the UK, and the US. As a result, Alibaba can focus on acquiring new customers and expand to other regions.
Conclusion
Alibaba relies on a strategic information system to drive its business processes, control costs, differentiate itself, and develop innovative online products and services. As a result, Alibaba has 25 online services and products. The company relies on a business model to provide services without time or geographical restrictions. Strategic planning in business accounts for organizational strategy, business strategy, and information system strategy. These strategies work together in order to realize strategic organizational objectives. Strategic planning helps the company to set short-term and long-term goals for growth. Alibaba uses Knowledge Management to manage processes, enhance shareholders’ value, and increase productivity through competitive advantages. Customer relationship management facilitates customer experiences, retention, product features, and customer loyalty and retention. This creates value for the company.
Works Cited
Alibaba Group. Company Overview. 2013. Web.
Berger, Paul, and Nasr Nada. “Customer lifetime value: Marketing models and applications.” Journal of Interactive Marketing 12 (1998): 17–30. Print.
Botha, Antonie, Derrick Kourie, and Retha Snyman. Coping With Continuous Change in the Business Environment: Knowledge Management and Knowledge Management Technology. Chicago: Neal-Schuman Publishers, 2008. Print.
Callon, Jack. Competitive Advantage Through Information Technology. New York: McGraw Hill, 1996. Print.
Chu, Lenora. EBay rivals circle vulnerable auctions kingpin. 2008. Web.
Davenport, Thomas. “Putting the Enterprise into the Enterprise System.” Harvard Business Review 76.4 (1998): 121-32. Print.
eMarketer. E-commerce Sales Topped $1 Trillion for First Time in 2012. 2013. Web.
Lukoff, Kai. Alibaba and eBay: More competition than cooperation, despite a show of friendship. 2010. Web.
Neumann, Seev. Strategic Information Systems—Competition Through Information. New York: Macmillan, 1994. Print.
Pearlson, Keri, & Carol Saunders. Managing and Using Information Systems: A Strategic Approach 4th ed. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2010. Print.
Peppers, Don, and Martha Rogers. Enterprise One to One: Tools for Competing in the Interactive Age. New York: Currency Doubleday, 1997. Print.
Piccoli, Gabriele. Information Systems forManagers: Text & Cases. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2008. Print.
Shaw, Robert. Computer Aided Marketing & Selling. London: Butterworth Heinemann , 1991. Print.
Smith, Elizabeth A. “The role of tacit and explicit knowledge in the workplace.” Journal of Knowledge Management 5.4 (2001): 311-321. Print.
Thompson, Teo, and Yujun Pian. “A contingency perspective on internet adoption and competitive advantage.” European Journal of Information Systems 12.2 (2003): 78-92. Print.
