Executive Summary
This paper presents two analytical techniques on an industry and firm level which allow a firm to create its competitive strategy according to its strengths and weaknesses. Though these tools are based on a micro level, they allow the industry and the firms to evaluate and compare it with the forces in order to build its own market position. The five forces model was presented in detail along with a conclusion regarding its effectiveness. The value chain model was shown to be an effective management device that allowed firms to deal with competition head on in heavily competitive markets.
This paper would analyze and discus analytical techniques which are used by corporations’ world wide in order to achieve their corporate aim. These analytical techniques can be defined as competitive forces which allow these businesses to manage their positioning and competitive strategies. The industry tools which would be analyzed by this paper would be an industry level tool and a firm level tool such as Michael Porter’s five forces model and the value chain. In order to evaluate these two tools; their origins and their implementation would be presented in the following paper.
Porter’s models
One of the most famous models: Porter’s five forces model, was introduced in Michael Porter’s book in 1979. The model was derived from the economic concepts based on the industrial organization dynamics. These forces are a component of the microenvironment and are used to compare and contrast against the external environmental forces. These forces allow a company to predict its profitability and to evaluate its market capabilities against other organizations. A change in one of the forces results in an overall reevaluation on the behalf of the organization’s management.
This model consists of five forces which are viewed as external to the industry itself but deal with those competitive forces that are internal to the industry. In order to compete in an effective manner, the management has to understand the way the industry and the market operate. Competition is created by the interaction of these five forces which interact differently for every industry. These forces can be defined as the threat of substitutes, the intensity of competitive rivalry, threat of new entrants, bargaining power of supplier, and lastly the bargaining power of customers (Porter, 1996).
Functional Qualities of Business Models
In order to make a qualitative evaluation of the strategic position, this model is used as an effective tool. This form of competitive analysis can be used for an industry level analysis in which a single industry develops and competes with each other. The first form of competitive force; the degree of rivalry, allows the firm to determine the value which is created by an industry is met head on through competition. Though it normally perceived as one of the most valuable of the five forces model, it allows the analyst to consider several other forces which are at work. (Porter, 1996).
This force is used by existing industries in order to figure out the extent of competition existing in the market. In the case of the software industry, after realizing the rising extent of the power of a rival, Google and Yahoo, Microsoft made attempts to take over Yahoo while at the same time coming up with newer versions to compete with Google.
By analyzing the extent of rivalry, firms seeking to enter an industry can decide whether it is in fact profitable to do so. This force is therefore, clearly an important tool in deciding the extent of the strength that one has in the market and the extent of competition that exists in the industry.
Strategic Forces
Some factors which decide the extent of competitive rivalry are the existence of barriers, brand equity, access to distribution, absolute cost advantages, government policies etc. In certain countries, the government themselves try to create monopolies on order to prevent certain unfair practices. This is normally done for the energy producing companies which have to ensure equitable distribution and private companies only seek to make profit at the expense of the customer. (Porter, 1996).
Another force which is a component of the five forces model used by strategists is the threat of entry force. This force allows the potential and the existing firms to influence the average industry profitability. This is based on the amount of barriers to entry that exist in the market- the more the barriers, the lower the threat of entry.
In case of monopolies, the case is of unusually high market barriers. This is normally true for the energy industries where the government producing companies are virtually monopolies in this particular sector.
The most common type of barriers that exist today is economies of scale, costs of entry, distribution channels, government legislations and lastly differentiation. These make entry into a particular industry difficult depending on their strength. The higher these barriers are, the more difficult is the entry.
Microsoft has been accused of being a monopoly due to certain factors which had made it virtually impossible for other companies to enter. However, after certain legislations Microsoft had to remove certain barriers in order to make it more feasible for other companies to enter the industry. (Porter, 1996).
However, if there are no barriers to entry, than that would result in a perfect competition position. This is normally in the case of a homogenous product which has many suppliers and hence, that drives down the price to a level which s the same for all.
However, perfect competition is not considered to be a viable market position and industries themselves try to maintain some level of barriers to entry in order to have some bargaining power over the customer.
A fourth force, the bargaining power of suppliers can exist in a number of ways such as where the switching costs are high, high power of brands such as McDonalds, Burger King, Pepsi Co, possibility of forward integration of suppliers and lastly the fragmentation of customers with a limited bargaining power.
In those industries where the customers bargaining power is greater than the supplier is unable to exercise any power of his own but in those industries where the bargaining power of the supplier is high especially in Just In time manufacturing systems, the suppliers can voice their terms and conditions.
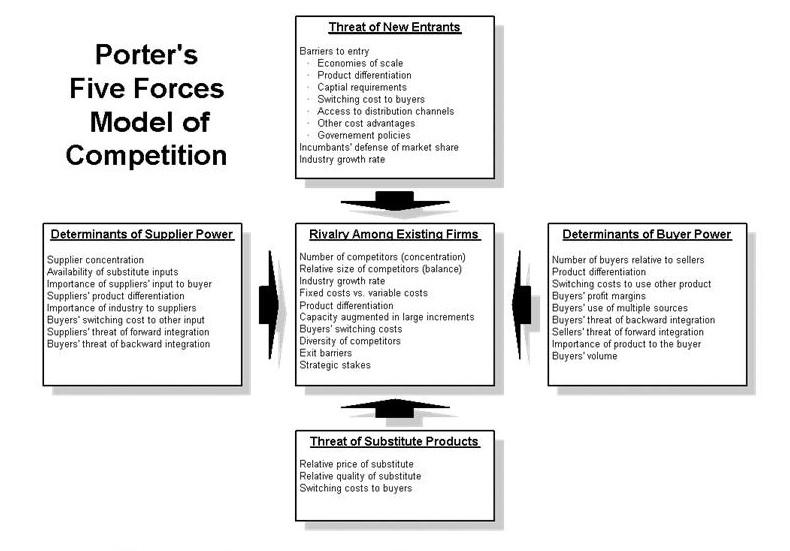
The last type of force that would be discussed would be that of the bargaining power of customers. This force can be strong in those industries where there are a large number of undifferentiated, small suppliers, such as small farming businesses.
All the above forces are therefore, to some extent effective tools used to analyze and evaluate the competitive position of the different companies in an industry. However, the strength of these forces can be insufficient if the structure of the industry is not evaluated as that can play an effective role in the competitive positioning of any industry.
These five forces emphasize extended competition for value purposes rather than amongst the already existing rivals.
It allows a firm to take advantage of the strengths that it possesses while at the same time taking measures to overcome its weaknesses. For these five forces model to be effective, the situation has to be studied in detail. All the relevant points and factors which can pertain to a specific market position should be evaluated.
However, there is a downside to this model as well. These forces are for a particular situation while the external forces are always changing. Therefore, it becomes quite difficult for the analysts to predict and foresee ahead when they are doing so with forces that are static in nature.
In conclusion and in regards to this particular model, it can be seen that by looking at the type of force and it strength in comparison to each firm and the overall industry, a certain positioning strategy can be formed which can aid an industry and its analysts.
The Value Chain Tool
The other tool that this paper would evaluate in terms of its strengths and weaknesses is the value chain tool. This is a type of approach which allows a firm to examine the development of an advantage. It was also created by Michael Porter and this china basically as the name suggests, consists of a series of events that create and add to the value. It is a type of a business approach in which various business functions are broken down into strategic activities which add utility to each product and service. This value chain is divided into two primary forms of activities-primary and support activities. A type of primary activities-inbound logistics includes the receiving, warehousing, and inventory control of input materials.
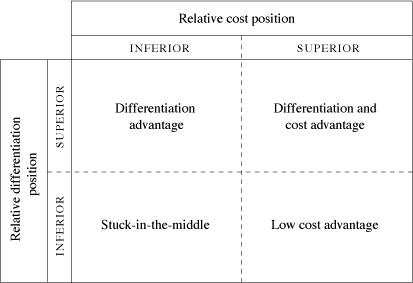
In order to survive in the fiercely competitive world of today, it has become imperative that each organization that any organization achieve some sort of a competitive advantage. It should either have a low cost/pricing strategy which aims to provide goods at a lower price to the customer in reference to its competitors or it should provide better quality goods and services at a price which is competitive and justifiable due to the quality standards.
Competitive capacity
Value chain analysis is therefore clearly an important tool which allows the competitive advantage to be identified along with the potential of the competitive advantage of an individual firm. A firm’s competitive ability is determined by its ability to produce crucial activities along the value chain in comparison to its competitors.
In order to diagnose the competitive performance, the firm has to construct its activities alongside the value chain itself.
Then, the firm would have to perform activities alongside the internally performed activities and then the linkages with the customer and supplier would also have to be analyzed. In order to ensure that customer satisfaction is achieved, the firm would have to identify activities that are crucial to customer satisfaction. The benchmarking actions would allow the firm to identify how well it is performing in comparison to its peers, and how its cost structure is in comparison to its peers.
An important aspect of this is analysis is that is allows the firm to identify the competitive advantage area of the firm so that it can target its customers and clients accordingly. After discovering the competitive position, the next integral step is that it has to be seen that how strong is the stronghold on this competitive edge.
The ranking ability of an individual firm in comparison to its peers allows it to form its unique identity and its competitive strategy henceforth. Whether this edge can be maintained or not has to be identified as well as otherwise it can create problems for the firm’s competitive capacity.
The act of ranking the competitive strength of a firm in comparison to its peers allows the firm to get an idea about the competitive strength that it has in comparison to its rivals. The costs of a value chain analysis can be done through two types of factors; structural cost drivers and the exceutional cost drivers.
The structural component includes scale economies, experience curve effects, technology effects, capital intensity and lastly complexity of product line. The other factor, executional cost driver allows the company to determine a number of aspects-the commitment of the workforce, attitudes and abilities regarding quality, cycle time in getting products to market, and lastly the efficiency of the firm and the supplier’s relationship.
These cost drivers allows the firm to analyze whether it can achieve its competitive edge in terms of the cost advantage or in terms of differentiation.
Strategic Activities of the Tool
Amongst some of the other primary activities are operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales and lastly services. Operations consist of value creating industries that transform the good into the final product, outbound logistics include the activities that were required to get the finished product to the customer, marketing and sales consist of those activities which are associated with getting buyers to purchasing the product, and lastly the service activities which maintain and enhance the product’s value.
These activities from operations to services all add to the process of creating value and to satisfying the ultimate consumer. The example can be quoted of a distributor for the logistics component while services are an integral part of the maintenance of any organization. (Pasternack & Viscio).
Support activities are those which are industry specific and include four types; procurement, technology development, human resource management and lastly firm infrastructure. Procurement includes the action of purchasing the raw material and the other inputs, technology development includes research and development activities, human resource management includes all those functions which are carried out with the management of the human resource and lastly, firm infrastructure in which activities such as finance, legal etc are included.(Tichy).
Those firms which want to have an added advantage and an extra benefit can make effective use of this support tool. In the case of those organizations which have developed an image and developed over a time period indulge in the support activities to distinguish themselves in the industry like Nestle etc.
For a value chain, the linkages have to be identified in order to see how value is created. Any firm’s value chain consists of a number of buyers and suppliers and the value system allows the firm to develop its competitive advantage.
An example can be quote of Dell which made effective use of the value chain process as it made effective of its strengths in order to develop a customer service, as well as a proper system of manufacturing. (Fingar & Smith).
Conclusion
In today’s time and age, an important part and parcel of the employee empowerment is an integral part of any organizational management in the present times.
According to Peter Drucker who mentioned in his Management by objectives, there has to be a balance between the management and the employees. A manager has to observe all the individuals in terms of their performance and evaluate them accordingly.(Porter)
Another case can be quoted is that Canon which made effective use of its employees suggestions to improve their delivery performance. (Tichy)
As Henry Ford once said:
“The man who will use his skill and constructive imagination to see how much he can give for a dollar, instead of how little he can give for a dollar, is bound to succeed.”
In order to have a high value added chain for the purposes of Product development, there has to be collaboration on product design and development amongst the entire value chain participants. It should be measured by product development cycle time and lastly, it should be enabled by web-based collaborative modeling that allows manipulation. (Fingar &Smith)
The above system is therefore an effective method of analyzing certain vital activities that allow the firm to identify and target vital development areas. However, a firm has to make sure that it has the required resources and the managerial skills required to develop itself according to the needs and requirements of that particular for both the function.
In conclusion, it has been seen that both of these tools are effective competitive techniques which an industry and firm can make effective use of positioning itself appropriately.
References
- Fingar, P. & Smith, H. (2004). Business Process Management. The Third Wave. Meghan-Kiffer Press.
- Porter, M. (1996). What is Strategy? Harvard Business Review.
- Pasternack, B. & Viscio, A. (n. d.). The Centerless Corporation. Simon & Schuster (trade Division).
- Tichy, N. (2004). The cycle of Leadership: How Great Leaders Teach Their Companies to Win. Collins Business.
- Porter, M. (1998). Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors. Free Press; 1 Edition.
