Introduction
There has been increased investment with the technological environment. This is due to the increased demand for technology by various organizational and individual consumers. The high level of demand has made the technology sector a viable investment sector amongst the investors. Amongst the sectors that have witnessed rampant growth include the information technology sector. This has resulted into intense global competition within this sector. The growth has also been enhanced by firms in the information technology sector investing heavily in research and development. This is due to the high volatility characteristic of the technological environment.This has resulted to innovation of divergent competing products. Competition has also been intensified by firms entering into mergers and acquisition. The discussion of this paper entails an analysis of International Business Machines incorporation. The aim is to illustrate how the firm can develop a high competitive advantage within the market.
Organizational background
International Business Machine Company (IBM) is a firm in the information technology industry. It was established in 1910 by Thomas, J. Watson (.Its headquarter is located in Armonk, New York. The firm operates as a public limited company. Its shares are publicly traded within the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol IBM. The operations of the firm are divided into various segments. These include software, system and financing and services. The various products that are offered by the firm include printing systems, mainframe and personal computers, servers, and integrated circuits. The firm has heavily invested in human resource. It has a total of 398,455 employees (Suresh, 2)
Mission
In its operation, IBM incorporation is aimed at ensuring it provides the most reliable and efficient computer technology to its diverse consumer categories that are globally distributed.
Vision statement
The management of IBM is committed at ensuring that the firm is the leading firm in the creation and development of the most advanced technologies within the information communication technology industry.
Objectives
From the analysis of the past financial year, there was a decline in the level of revenues with a margin of 12%. This resulted into total revenue of $. 44.96 billion. This has made the management to formulate a strategy aimed at boosting the firm’s level of revenue with a margin of 20% within the next financial year (Suresh, 3)
Strategies
In order to achieve this level of revenue growth, the firm will invest heavily in research and development. This will enable the firm innovate new products such as the software to meet the market demand. The innovation of the new software will entail the research and development department undertaking a comprehensive market research. This will enable the firm identify the most appropriate market to venture.
The management has also formulated a strategy aimed at adding value to its products within the market.
Firm’s external opportunities
The business environment presents numerous opportunities for the firm. For instance, both the large and the small business organizations are integrating the concept of e-commerce within their operation. The industrial and individual consumers are also integrating technology in their buying process; for instance the use of credit cards. This means that the firm can benefit from the increased demand for the various electronic commerce technologies by developing the relevant technologies to meet this demand.
External threats
The technological environment is characterized by increased volatility resulting into uncertainty. This means that the firm has to continuously involve itself with research and development. This is costly for the firm since huge amount of financial and human capital is required. There is also an increase in insecurity with regard to software products such as increased cases of data software hacking.
Firm’s SWOT analysis
Competitive profile matrix (CPM)
In the recent past, information technology environment has been characterized by emergence of new firms. This has resulted into an increase in the level of competition. The major competitors of IBM incorporation include the Hewlett- Packard and Electronic data system. The table below illustrates the competitive rating of these companies.
The ratings in the CPM indicate that IBM has got a higher rating at 2.07 compared to the ratings of Hewlett- Packard and Electronic Data Systems companies which are 1.35 and 1.15 respectively. This indicates that the IBM has a high competitive position.
Internal evaluation matrix
External evaluation matrix
Strategic Position and Action Evaluation Matrix (SPACE)
The average score of the X axis is 2.55 while that of the Y axis is 1.25. This shows that the firm is in a good competitive position within the information technology industry that is experiencing a high rate of growth. In order to effectively exploit the market benefits effectively, the management of IBM incorporation should pursue an aggressive strategy by developing its internal strengths (“Strategic method”, 6)
Boston Consulting Group Matrix (BCG)
IBM incorporation has got different departments that are involved in diverse business operations. These include the computer system, financing, services such as consulting, software, storage devices, networking systems, printing systems, servers and microelectronics. Through the use of the BCG matrix, these operations are considered as strategic business units (SBU) (Tutor2U, 11).This is due to the fact that they are unique from each other. This means that they can be classified as cash cows, star, dogs or question mark using the BCG matrix. The table below illustrates the classification of these business units.
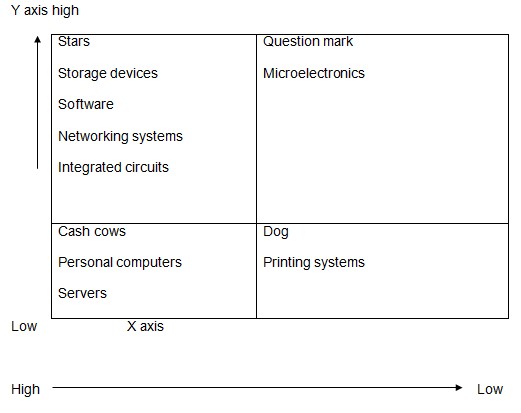
X axis represents the market share.
Y axis represents the rate of growth.
The firms’ business units involved in manufacture of storage devices, software, networking systems and integrated circuits are categorized as stars. This is due to their high rate of growth resulting into a high market share for the firm. These business units generate high revenue for the firm (Tutor2u, 5).IBM has been dealing with manufacture of personal computers and servers for a long time. These business units are characterized by low growth and high market share. Their high and sustainable revenue generation makes them to be considered as the foundation of the firm.
The printing systems business unit is classified as a dog. This is due to its low market share and rate of growth which makes it to be less attractive. On the other hand the microelectronic business unit is classified as a question mark. This is due to the fact that they have a low market share and high potential of growth. The management of IBM should consider microelectronics as a potential investment to generate more returns for the firm.
Quantitative strategy planning matrix (QSPM)
Advantages and disadvantages of alternative strategies
Mergers and acquisitions
By entering into mergers and acquisitions, IBM would be able to effectively boost its competitive advantage. This is due to the fact that mergers and acquisitions result into synergy. This is due to merging of divergence competence from the individual firms. Considering that the competing firms are geographically distributed, the firm is able to expand its scale of international operation even in markets where there may be restrictions. These may include strict political requirements
Disadvantages
If firms entering into merger and acquisitions do not consider all the relevant factors, there are high chances of failure. This means that the acquiring firm may not meet the desired objective. Undertaking mergers and acquisitions involve a lot of financial resources. This may result into financial loss incase of a failure. On the other hand the employees may be affected by the merger and acquisition. This mainly occurs if the two firms have different corporate cultures. This may reduce their performance level resulting into ineffective performance of the firm.
Investing in research and development
Advantages
Investing in research and development can result into effective performance of a firm. This is due to the fact that the firm would be able to produce high quality products resulting into an increase in the level of sales. On the other hand, the firm would be able to develop new products to meet the changing needs of the consumers. This would result into increased competitive advantage of the firm. With regard to the already existing products, investing in research and development would enable the firm add value to these products. This results into an increase in their marketability culminating into an increase in the level of profits for the firm.
Disadvantages
Investing in research and development requires that there be efficient resources in relation to human capital, machinery and equipment. This may cost the firm huge amount of financial resources.
Strategy recommendation
The management of IBM should formulate policies related to research and development. This is illustrated from the table QSPM model where the total attractiveness score for research and development is higher than that of mergers and acquisitions. That is 4.02> 3.5.
Long term objective
Despite the fact that IBM is the leading firm in the information technology industry it has not penetrated the entire market. The long term objective formulated by the management entails the effective penetration into the global market. This will result into an annual increase in its market share with a margin of 15%. In order to attain this, the management has formulated a policy aimed at developing new products. This will entail comprehensive research and development. For instance; considering the volatility of he technology, the management of IBM has an objective of ensuring it develops products that will cope with the security threats.
Itemized cost of research and development
Strategy implementation procedure
In order to effectively implement this strategy, the management should scan conduct a comprehensive market research to identify the opportunities it can exploit. After effective identification, the management should conduct a cost and benefit analysis. If the benefits are more than the costs, the management should undertake the project. Before producing the product for market purposes, a pilot project should be undertaken to ensure that the product is successful. This will help in the elimination of chances of product failure upon it being launched in the market.
Projected financial statements
Projected balance sheet
Forecasted financial ratios
Recommendation for specific annual objectives and policies
Considering that the technological environment is characterized by intense competition, the management of the IBM should ensure that it increases its competitive advantage. In order to achieve this, the management should formulate a policy aimed at adding value to its products already in the market apart from developing new products. This means the management should increase its financial investment in research and development.Adding value to products and the development of new products should result into consistent annual increase in the firm’s market share.
Strategy review and evaluation
The management should conduct continuous review and evaluation of the research and development strategy. One of the factors it should consider is the contribution of the value addition and new product development to the firm’s financial returns. It should also conduct a consumer market research to determine their level of utility attained from the consumption of the firm’s products. Through the market research, the management of the firm should be able to identify and seal the gaps within its products. This would result into increased competitive advantage for the firm.
Conclusion
The information technology sector of the economy is a very competitive investment sector. Firms in this sector should conduct a comprehensive firm and industry analysis. This would enable them to formulate strategies and policies that would result into the firm attaining a high competitive advantage. Investing in research and development is one of the most effective policies that firms in information technologies such as IBM should incorporate. This would enable the firm innovate new products and add value to the already existing products.
Works cited
Max-pedia. “SPACE matrix: strategic management method”. Max-Pedia. 2009. Web.
Max-pedia. “Quantitative strategic planning matrix”. Max-pedia. 2009. Web.
Max-Pedia. “Internal and external factor evaluation matrix”. Max-pedia. 2009. Web.
Reuters. “Key developments for International Business Incorporation Machines.” Reuters UK. 2009. Web.
Suresh,Khumar. “IBM company profile”. Sureshkhumar.net. 2009. Web.
Tutor2U. “Product portfolio strategy: introduction to Boston Consulting Group Matrix.”. 2009. Web.
