Executive Summary
Being a leader is a challenging task, especially in the context of the contemporary global economic environment. The need to address numerous external and internal factors, so that a sustainable approach could be designed is truly devastating. However, after a closer look at the evolution of leadership and management, as well as the primary principles on which the two concepts are based, one will be able to define an appropriate leadership framework for a specific organization.
It should be borne in mind that the concepts of leadership and strategic management are related to each other on several levels. Thus, it is necessary to consider the existing leadership styles from the managerial perspective, the communication process, the effects on the production quality, etc., to design an impeccable strategy. Even though the principles of the Transformational Leadership are currently viewed as the most efficient, a more flexible method of managing the company’s processes may be required.
Furthermore, the leader of an organization must promote professional and personal growth as a crucial value among employees and managers. As soon as the idea of lifelong learning is implanted into people’s minds, they will be able to approach every problem from a unique perspective. Furthermore, they will view conflicts that are an integral part of the production and organizational processes as an opportunity to acquire new knowledge and skills. Therefore, the progress of the company will remain continuous, and the levels of loyalty among the employees will grow exponentially.
Strategic Management and Leadership: Link
Although it used to be a common misconception to view leadership and management as synonyms, nowadays, the two are rarely confused. By definition, the idea of leadership concerns primarily addressing the issues associated with planning, inspiring, and creating the principles according to which employees will carry out their decision-making processes and solve ethical dilemmas. Management, on the other hand, is usually restricted to controlling the processes that are supposed to help a company achieve a particular goal, typically a production-oriented one (Walker 2014).
Introduction
Manager
However, the connection between the two ideas might not seem as obvious to the leaders and managers of an organization as it should be. Although there is an obvious line between the roles of a manager and a company leader, the former may also assume the responsibilities of the latter. Particularly, based on Mintzberg’s interpretation of the managerial roles, the following ones must be considered: a leader, a disseminator, a figurehead, the promoter of liaison, and the monitoring figure (Cox, Bachkirova & Clutterbuck 2014) (see Fig. 1).
Strategic Leader and Manager
However, the connection between the two ideas might not seem as obvious to the leaders and managers of an organization as it should be. Although there is an obvious line between the roles of a manager and a company leader, the former may also assume the responsibilities of the latter. Particularly, based on Mintzberg’s interpretation of the managerial roles, the following ones must be a considered: a leader, a disseminator, a figurehead, the promoter of liaison, and the monitoring figure (Cox et al. 2014) (see Fig. 1).
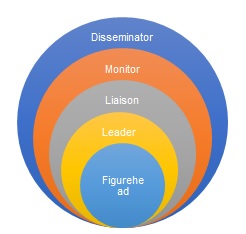
Nevertheless, the role of a company leader is more complex than the leadership responsibilities of a manager. While the latter is supposed to sustain the created environment, the former considers the ways of improving it and promoting change. A leader determines the course of the company’s development relying on the data provided by the manager. Thus, the staff is empowered to contribute to the company’s success, and the decision-making processes are based on corporate values. As a result, an increase in the firm’s popularity can be expected.
As stressed above, different leadership and management approaches have a variety of effects on the decision-making processes in the organization. Particularly, the use of strategic leadership and management allows differentiating between short- and long-term objectives, thus, maintaining the focus on what is important for the company.
Impact of Management and Leadership Styles on Strategic Decisions
At this point, the phenomenon of visionary leadership needs to be mentioned. Being future-oriented, the framework helps define the patterns for the strategic choices to be made in the future. Furthermore, a strong and efficient leader is likely to create the environment in which the staff members will develop a commitment to the company and its goals, thus, excelling in their performance. The acquisition of new skills and the active promotion of corporate values among the participants, primarily, the concept of Corporate Social Responsibility, are likely to serve as the foundation for increasing the firm’s margin profits and developing a tremendous competitive advantage (Eweje 2014).
Therefore, the opportunities to motivate, direct, and control the staff members can be deemed as the essential characteristics of strategic management and leadership in the context of the contemporary business environment. It should be noted, though, that different leadership styles have different effects on the employees. For instance, the authoritative one may restrict the staff’s options yet make them feel secure, the transformational one will encourage them to change yet may exhaust them, the laissez-faire one will give them more room for decision-making yet detach them from the company and its values, etc. (see Fig. 2). Therefore, it is crucial to make sure that a flexible strategy is applied.
Adapting Leadership Styles to Different Situations
Designed to be used in different situations and business scenarios, leadership styles should be used based on the environment in which one operates. Different leadership approaches have different goals, are aimed at different audiences, and lead to different outcomes. Therefore, it is imperative to determine the source of a specific conflict before locating the leadership framework to be used in the identified scenario.
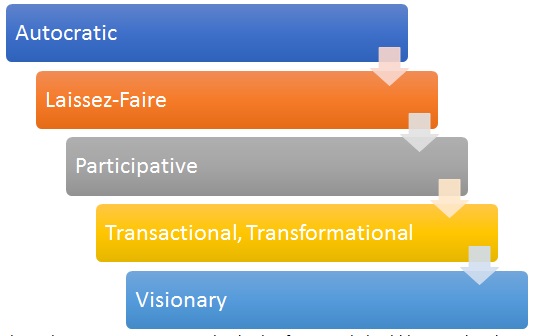
The authoritative, or autocratic, leadership framework should be considered in case the opinions of the employees do not have any lasting impact on the outcome.
The laissez-faire tool should be considered as a possible method in instances when the employees are qualified enough to make their own choices regarding workplace processes.
The participative leadership framework is crucial when there is a necessity to reinforce the process of cooperation among staff members.
The transactional style needs to be deployed when the motivation and engagement rates among the personnel must be increased fast.
The transformational approach has to be applied when a company suffers changes in its vision and needs to promote specific values to the staff.
The visionary style should be viewed as an option for a future-oriented company with the leader’s mind being set on making a difference in the target industry.
Therefore, the choice of framework depends on the situation. As soon as the primary factors affecting the firm are determined, and the stakeholders are identified, a sustainable approach will have to be developed.
Impact of Management and Leadership Theories on Organizational Strategy
The phenomena of leadership and management have been studied extensively since the dawn of time, which has led to a plethora of theories about how leadership works. While some theories are subverted and new ones emerge regularly, each has had an undeniably vast impact on the design of organizational strategies.
Great Man Theory
Assuming that leadership qualities are intrinsic, GMT helped build a rigid organizational hierarchy.
Trait Theory
Although often viewed as the extension of GMT, the trait theory (TT) suggested that leadership qualities can be fostered in people. Thus, it provided an opportunity for designing new organizational behavior (OB)
Behavioral Theories
BT provided a chance to evaluate the effect of leaders’ behaviors on the performance of the staff members. As a result, the assumption that leadership qualities can be fostered was confirmed
Contingency Theories
CT assumed that using a uniform leadership framework is unreasonable and that a leader must be flexible in the choice of strategies. As a result, opportunities for taking the needs of the staff members were created.
Transactional Theories
The theories facilitated a connection between leaders and staff members. As a result, the communication process in the workplace could be improved.
Transformational Theories
The theories considered the means of altering the staff members’ behavioral patterns to encourage them to accept the corporate values. Thus, the premises for focusing on the significance of motivation and learning in the workplace could be built.
Innovative Theories
In the wake of the IT era, modern theories shed light on how the future progress of the company and its stakeholders can be facilitated by using the available data and information management tools (McCleskey 2014).
Leadership Strategy That Supports Organizational Direction
As explained above, there is a need to make sure that the values and the goals of the company align with the leadership strategy and the management tools that were chosen to implement the identified practices and meet the corporate goals. In other words, the direction in which the company evolves needs to coincide with the strategy for leading its members. For this purpose, a situational approach should be used.
Operating in the environment of the global economy implies having to be ready for any change in the target market. Therefore, a flexible framework needs to be adopted. The situational approach, which permits shifting between different leadership strategies and at the same time keeps the focus on what is important, should be viewed as a possibility.
For instance, the visionary leadership style should be interpreted as the foundational framework that will guide the leaders and the managers toward success. It should become the foil for building the environment in which the company members operate. The transformational approach will serve as the support for the staff members at the stage of accepting new values, principles, and ideas. The laissez-faire tool should be used as the basis for promoting independence among the personnel, which will be especially important when branching out to different markets and creating new affiliates that will be self-guided. The transactional approach, in its turn, will promote the idea of consistent learning and new skills acquisition among the employees. As a result, the company will be able to build a team of trusted and loyal employees, who will contribute extensively to the company’s progress (Bodenmuller 169). Thus, the company will be able to evolve in the global economic environment.
Recruitment and Future Development for a Specific Leadership Role: Changing Employees’ Ethical Standards
Current Leadership Requirements: A Review
Leading change management is an admittedly difficult task. Indeed, change initiatives are very common in the contemporary business and economic environment, yet the success thereof is underwhelmingly little: only 55% of cases can be deemed as successful (Nielsen & Randall 2012). The identified phenomenon can be attributed to the unwillingness of companies to accept the idea of change as the foundation for their leadership framework so that the person could be encouraged to acquire new skills and knowledge regularly, thus, adapting to the demanding environment of the global economy. Indeed, the current requirements for transformational leadership and the people promoting it are admittedly challenging. Nevertheless, meeting them is possible as long as the organization gets its priorities in line.
Among the essential requirements toward transformational leaders, the ability to adapt to the iSixSigma framework deserves to be mentioned first. Being a comparatively recent approach, the iSixSigma concept implies that changes must be administered in the target environment based on either the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control) or DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify) model (Pyzdek & Keller 2014).
Furthermore, a transformational leader (TL) must be capable of promoting the idea of lifelong learning and consistent acquisition of relevant knowledge and skills among the staff members. In other words, a TL must motivate the staff and at the same time make sure that they should not cease to develop professionally and personally. Once the identified goal is reached, the prerequisites for improved performance will be created. Furthermore, by showing the employees that they are valued and that the firm is ready to invest in their development, the company will facilitate a steep rise in personnel’s loyalty rates.
Development of Future Situations Requiring Leadership
Predicting every possible scenario in which leadership skills must be used is practically impossible – every company needs consistent leadership to facilitate the promotion of the relevant ideas and ethical standards, yet the scenarios in which these standards can be applied are countless. Nevertheless, basic ideas about the application of specific leadership skills to manage a common conflict can be suggested.
Conflict Management
Unfortunately, conflicts are an integral part of the workplace environment. Because of the imperfections that are intrinsic to the communication process, misunderstandings will occur. Therefore, conflicts should be viewed as opportunities for learning new skills and information as opposed to feeling personal about work-related issues. The TL framework will help transform the staff’s concept of conflicts so that they could constructively resolve them and derive essential lessons from any misunderstanding.
Negotiation
Similarly, TL should be used in the course of negotiations. Thus, the approach based on a compromise will become a possibility. As a result, all parties involved, including customers, employees, managers, leaders, suppliers, and company partners will be satisfied.
Quality Management
By focusing on the issues associated with quality, including the standards, the repeatability and reproducibility issues, etc., a leader will promote a significant improvement in the firm’s performance. Therefore, the necessity to boost the quality of the products or services delivered by the organization should be listed among the possible scenarios in which the TL leadership skills will have to be applied.
As stressed above, though, the situations mentioned above only partially reflect the multifaceted reality. The number of challenges that a company may meet in the global economy are countless. Thus, a flexible approach must be used for a company to remain sustainable
Planning the Development of Leadership Skills
Developing Leadership Skills for a Specific Requirement
When considering the list of requirements mentioned above, one must give credit to the necessity to focus on conflict management. In the context of the global business environment, where intercultural communication is a part of daily activities, it is imperative to avoid and manage conflicts in a manner as efficient and expeditious as possible. Therefore, a TL must consider acquiring conflict management skills and learn more about the appropriate techniques. For these purposes, the following plan should be viewed as a necessity:

It is expected that the specified approach will help a leader create the foil for the further development of the relevant skills and abilities. Furthermore, it is assumed that the adoption of the transformational framework will encourage the staff members to assume the suggested behaviors eagerly and follow the values designed by the company leader successfully.
The Usefulness of Planning Methods for Developing Leadership Skills
The significance of adopting the appropriate planning tool for acquiring new skills and competencies can hardly be underrated. As soon as the primary objectives are set, and the goals of the organization are identified, one can locate the means of improving the relevant leadership skills. This is even more important, the devices for monitoring the progress and evaluating it can be designed and introduced into the company’s framework. Thus, the data received in the course of the program implementation will inform the further choice of strategies used for the progress of the leader.
It is expected that the identified planning tools will serve as the foundation for the further improvement of the organization’s performance, the communication processes in it, and the efficacy of the leader’s actions. In other words, the TL framework in question will become the tool for promoting active communication between the leader and the stakeholders involved, including the staff members, customers, business partners, suppliers, etc. Thus, the possibility for both personal and professional growth will be created.
It would be wrong to assume that the approach chosen for the improvement of the leadership process is flawless. Even though the TL framework has been used for quite a while, it has its limitations. As a result, not all risks will be eliminated successfully. However, with the adoption of a sustainable framework that will allow making efficient use of the available human resources, particularly, convincing the leader to invest in the staff’s professional growth, a steep rise in the efficacy of the company can be expected.
Therefore, the adoption of the TL approach should be considered as one of the most sensible steps to take in the environment of the global economy. Consequently, unceasing progress will become an opportunity even in the challenging environment of the global economy, and the risks associated with the expansion of the organization will be managed successfully.
Reference List
Cox, E, Bachkirova, T & Clutterbuck, DA 2014 The Complete Handbook of Coaching, SAGE, Thousand Oaks.
Eweje, G 2014, Corporate social responsibility and sustainability: emerging trends in developing economies, Emerald Group Publishing, Bingley, UK.
McCleskey, JA 2014, ‘Situational, transformational, and transactional leadership and leadership development’, Journal of Business Studies Quarterly, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 117-130.
Nielsen, K & Randall, R 2012, ‘The importance of employee participation and perceptions of changes in procedures in a teamworking intervention’, Work & Stress, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 91-111.
Pyzdek, T & Keller, P 2014, The Six Sigma Handbook, revised and expanded: a complete guide for Green Belts, Black Belts, and managers at all levels, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY.
Walker, R 2014, Strategic management communication for leaders. Cengage Learning, Boston, MA.
