Introduction
Under normal conditions, the human body releases insulin from the pancreas to regulate blood sugar levels. However, if this function is impaired, patients have to manually regulate their glucose levels because if left untreated, the condition could have a debilitating effect on patients by damaging their eyes, kidneys, nerves, and blood vessels (Tate et al., 2017). Nonetheless, diabetics find it difficult to manage blood sugar levels because of resource limitations and the unavailability of reliable gadgets (Tonyushkina & Nichols, n.d.). Therefore, there is a need to use a reliable device for monitoring blood glucose levels to give patients adequate data to make their medical decisions.
Several products in the pharmaceutical industry are available to help diabetic patients regulate their blood sugar levels. However, depending on market dynamics, most of them are ineffective or inaccessible to a majority of patients because of various reasons including high prices, product unavailability, and the lack of proper knowledge on how to use them (Tate et al., 2017).
Alternatively, companies that sell invasive glucose test devices have received negative feedback from customers who are uncomfortable poking their skin to get a blood sample. Consequently, there is an increased preference for the use of non-invasive devices to read blood sugar levels. In line with this development, MediCorp has introduced a non-invasive blood sugar testing device called iGluco that is easily attached to a patient’s arm to relay blood sugar levels periodically.
This document is a marketing plan to launch iGluco in the Chinese market. The Asian economy is selected for this review because it is the second-largest healthcare market in the world (Lu, 2015). Furthermore, there is a high prevalence of diabetes in the country, which heightens the need to provide a reliable device in the market to accurately measure sugar levels without interfering with the patients’ lives. Key sections of this report will discuss the main characteristics of the target market, the impact of cultural differences on the business plan, the appropriate mode of market entry, and the governance standards that will be observed when implementing the proposed recommendations.
Marketing Analysis
Market Analysis
Many medical devices for managing diabetes have been designed to manage hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic disorders. MediCorp’s product, iGluco, could carry out the same function because the device is attached to a patient’s arm to periodically indicate the blood sugar level. The readings could be relayed to a patients’ smartphone and additional information on the appropriate medical actions to take provided. The device is different from other products in the market because of its pain-free nature. Therefore, the product’s main purpose is to help people change the way they manage diabetes and improve the quality of their lives in the process.
iGluco’s use in the market is defined by its NAICS classification code of 325413. This index was assigned by the North American Industry Classification System, which sets manufacturing standards for new product development in the United States, Canada, and Mexico (Census.gov., 2012). Based on this certification, MediCorp is ready to launch a new product that will improve the way people manage diabetes in China. To differentiate it from substitute products in the market, iGluco will be marketed as a lifestyle brand that is aimed at making the management of diabetes more bearable to patients.
This statement inspires the main slogan that will be used in the product’s promotion plan, which is, “Whatever pace you live your life at, iGluco is with you all the way”. The key message here is to make customers believe that the product will simplify their lives, as it will allow them to live normally without worrying about the need to stop and conduct a medical check of their blood sugar levels.
The product’s success in the market will be largely dictated by the pricing model. Most pricing policies are dominated by cost and profit considerations (SIS International Research, 2020). However, MediCorp will have a flexible pricing strategy that will be informed by income disparities across different parts of China. Broadly, the company’s main competitors, which include Shanghai Pharmaceuticals, Sinopharm Group, and Huadong Medicine, sell medical devices for managing diabetes online at an average price of between $3 and $5 (Alibaba, 2020). For the low segment of the market, which includes tier 2 cities like Tianjin, Suzhou, and Hangzhou, iGluco will be sold at $3 because of their lower per capita income of $6,043 (Center for Strategic and International Studies, 2020).
In tier 1 cities, which include Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen, the product will be sold for between $5 and $7 because they have a higher per capita income of $30,000 (Center for Strategic and International Studies, 2020). This flexible pricing plan should accommodate the varied income disparities across China.
MediCorp’s place strategy will be based on the integration of the company’s product distribution network with an existing one domiciled in China. This strategy is justified by the enhanced role of globalization in shaping contemporary product distribution systems (Tabrizi & Kabirnejat, 2015). Therefore, the company’s place strategy will be designed to fit this digitized distribution system. In line with this assertion, the SIS International Research (2020) suggests that companies should highlight unique value elements that align with the digital space. Therefore, the company’s place strategy will be based on the effectiveness of integrating the company’s supply chain system on the virtual platform.
Characteristics of Potential Customers and International Cultural Differences
The main target market for iGluco is patients who suffer from diabetes and are living or residing in China. Diabetes is a lifestyle disease affecting millions of people around the world. It is estimated that about a third of the world’s population that suffers from the disease resides in China (Lu, 2015). If contextualized within broader statistics showing the incidence of diabetes in China, the proportion of people who suffer from the condition in the Asian nation reflects an increase in the incidence of the condition within the country in the last 30 years.
In 1980, it is estimated that the incidence of diabetes in China was 0.67% but this number has since increased to 10.3% today (Jia et al., 2019). The majority of people who suffer from the condition in China have type 2 diabetes. Reports suggest that the incidence of type 1 diabetes is only 5% (Jia et al., 2019). Although there is a disproportionately high number of people who suffer from type 2 diabetes in China, iGluco will be useful to both sets of patients by helping them to know their blood sugar levels.
Since communications, teamwork, and organizational hierarchy are important aspects of international business management, it is important to understand the cultural differences between China and western countries that may affect the proposed marketing plan. Culture refers to a system of norms or values that employees subscribe to when performing organizational tasks (UMGC 1).
Linguistically, the Chinese people speak Mandarin and Cantonese and the executives of MediCorp speak English. MediCorp is aware of these language differences and will develop two types of marketing strategies for Mandarin and Cantonese audiences. The implications of these cultural differences to the implementation of the proposed marketing strategy are highlighted by the need to develop cross-cultural literacy across the two cultural groups to promote synergy in the organization (UMGC 1).
Hofstede’s cross-cultural framework has been used to analyze cultural differences across many countries as a lever for developing effective marketing strategies. It ranks countries according to their performance on six cultural dimensions, which include power distance, individualism vs. collectivism, masculinity vs. feminism, uncertainty avoidance index, long vs. short-term orientation, and indulgence vs, restraint (UMGC 1). According to figure 1 below, China ranks highly in terms of power distance and a long-term orientation, where it scores 80/40 and 87/26, respectively (Hofstede Insights, 2020). Comparatively, the US has higher rankings in the areas of individualism, indulgence, and uncertainty avoidance (Hofstede Insights, 2020).
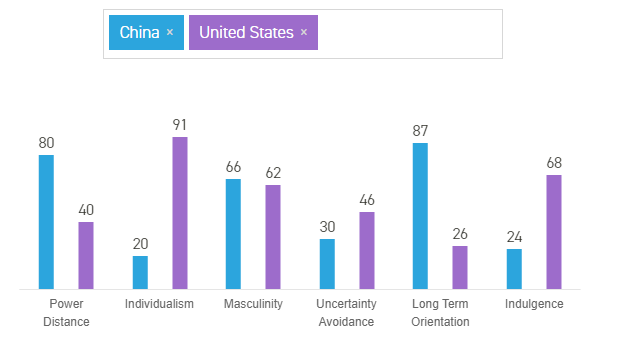
The above-mentioned rankings have significant ramifications on the proposed marketing plan because they should influence the administrative and governance styles of the new venture as well as help managers predict how the market would respond to iGluco’s launch.
For example, the long-term-oriented nature of the Chinese people would make the market more receptive to the long-term benefits of using iGluco. Similarly, the low level of individualism in Chinese society would lead to the development of marketing strategies that have a collectivist appeal. For example, consumers could be encouraged to buy iGluco for an ailing relative or sibling, thereby expanding the product’s market beyond the primary patient group. The cultural differences highlighted above will also have a significant impact on the product’s marketing mix as described below.
Use of Web Networks and Social Media for e-Marketing
MediCorp’s promotion strategy will be based on electronic marketing techniques such as social media. These platforms will be used to educate people about the uses of iGluco. Social media platforms, such as Twitter and Facebook, will also be used to increase awareness about complications that may arise from diabetes, including their signs and symptoms. This strategy will be implemented to establish a 24-hour diabetic control unit that will highlight the importance of gestational diabetes and the need for its control during pregnancy. All of these factors, if properly integrated into a broader web network, would greatly improve the value of iGluco to the customers and justify the pricing strategy highlighted in this report.
The main goal of adopting the social media marketing plan is to make consumers more aware of the value they would be getting from purchasing iGluco because the device has new technological features that are not available in other gadgets. Therefore, technology will be the main value offering for the product. Its success is pivoted on the integration of these value elements in the company’s design, marketing, and delivery functions to generate a significant competitive advantage over rivals that adopt a superficial integration of the same value elements in their marketing strategies. To monitor the performance of the above-mentioned promotion strategy, MediCorp will assess the efficacy of the marketing plan based on key performance indicators that will be contingent on effective product engagement and positive market feedback.
Governance and CSR
The governance and CSR activities of MediCorp will be guided by the need to merge the shareholder and stakeholder views of management through a broader and enlightened framework of value maximization. This governance guideline stems from an ongoing debate regarding the need to maximize shareholder value as the primary objective of business existence (Value Chain, 2005), versus the desire to adopt a holistic framework of management that caters to the needs of all people or parties involved (UMGC 2).
This premise of management highlights the importance of CSR to MediCorp as it ventures into the Chinese market because it needs to demonstrate to its stakeholders that its operations are not only profit-motivated but also socially responsible. Therefore, its management philosophy will be guided by the need to have a positive social and environmental impact on the community. To this end, the company will fund health research in different areas of Chinese medicine as a contribution to the advancement of local medicine.
MediCorp will also organize free healthcare checks for Chinese patients suffering from diabetes and provide supplementary medical advice to those who may need it. These events will be organized annually across different regions of China. The aim is to reach many people and increase awareness regarding proper diabetes management. This objective is consistent with the goal of this marketing plan, which is to market iGluco. Therefore, through the implementation of the robust governance and CSR framework highlighted in this paper, MediCorp will achieve both its profit and CSR goals. This management philosophy will also provide a perfect balance between the need to uphold governance and accountability standards.
Financial Projections
This section of the report will provide the market share estimates, break-even estimation, and projected revenues for MediCorp in the next three years. The break-even analysis for the company is provided in table 1 below.
Break-Even Analysis
Table 1. Break-even Analysis (Source: Developed by Author).
According to table 1 above, the break-even sale was deduced by factoring in the total fixed expenses and the gross margin percentage of sales. With an annual break-even amount of $47,458,548, MediCorp would need to make sales worth $3.9 million monthly to break even.
Market Share and Sales Projections
The Chinese pharmaceutical industry is highly competitive because of the presence of many firms that provide substitute products. However, as highlighted in this document, MediCorp’s main competitors are Shanghai Pharmaceuticals, Sinopharm Group, and Huadong Medicine. Figure 2 below highlights the projected market share for MediCorp, relative to the above-mentioned competitors.
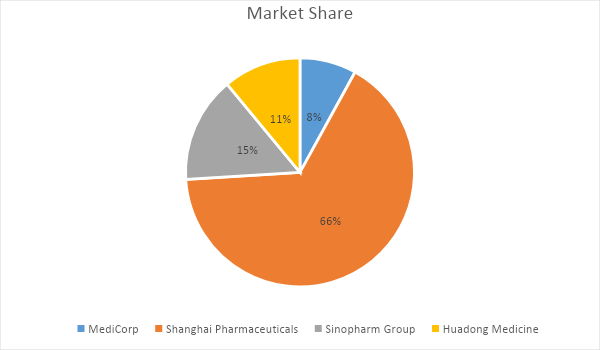
As highlighted above, MediCorp is expected to have an 8% share in the market. This proportion of representation is worth about $3.6 billion (Lu, 2015). To achieve the aforementioned market share in China, MediCorp needs to implement an aggressive sales strategy that would generate enough revenue for promoting further market expansion. The annual projections for the next three years are highlighted in table 2 below.
Table 2. Projected Sales (Source: Developed by Author)
According to the statistics mentioned above, MediCorp is expected to make $54 million and $60 million in sales within the last two years of the forecast, respectively. In the first year, the company is not expected to have any revenue but it will have a cash flow injection of $254,125 for normal operating expenses. In the second year, the organization is expected to make about $54 million, while subsequent years of operation could see this figure increase by $6 million annually.
Strategy Implementation
The above-mentioned insights regarding the market could significantly influence the market entry strategy for MediCorp. Indeed, a company’s mode of entry is an important determinant of its global success because its mode of entering the market needs to align with its key competencies to have a maximum effect on the target population (Lowe, 2019). Therefore, there is a need for companies to properly understand their strengths and apply them well in the market using balanced and effective market implementation tools. MediCorp is cognizant of this fact and its market entry strategy is informed by the need to have an entry plan that balances all market dynamics. In this regard, a strategic partnership approach will be adopted to merge the company’s key competencies and those of an existing entity in the market through a strategic partnership agreement.
This type of partnership is popular because it addresses market uncertainties in the global business environment (UMGC 3). MediCorp needs to adopt the strategic alliance method because it will give it the flexibility to implement market operations beyond what it could do if it adopted another strategy, such as direct entry (UMGC 3). To this end, Guangzhou Baiyunshan will be approached as a strategic partner because of its massive blueprint in the Chinese pharmaceutical industry.
Guangzhou Baiyunshan is regarded as one of the world’s oldest pharmaceutical factories. Based on its immense market experience that spans about 415 years, MediCorp’s partnership with Guangzhou Baiyunshan will mostly be limited to tapping into the latter’s distribution network, which covers most submarkets in China (Guangzhou Pharmaceutical Holdings, 2020). Therefore, the patents and copyright of iGluco will remain with the parent company to safeguard the integrity of the product. Therefore, the Chinese partner will be sought to aid in providing network distribution resources, as opposed to co-manufacturing the product. The strict laws in China restricting majority foreign ownership of local companies also inform its inclusion in the strategic partnership agreement. Therefore, the strategic alliance will cover the legal and product distribution requirement of iGluco.
The success of the marketing strategy highlighted in this report depends on the effective implementation of the broader marketing plan. To safeguard the integrity of the strategy implementation process, the balanced scorecard technique will be used to highlight four areas of strategic implementation that need to be focused on when implementing the market plan. They include business process, customer, financial, and growth perspectives (UMGC 4). Balancing these four measures of strategic development has been hailed as an effective tool for monitoring progress because it gives managers a holistic perspective on important areas of strategic focus (Dziak, 2019). Using this technique, Medicorp’s managers will set targets on how to accomplish the goals of each management perspective (UMGC 4). These objectives will act as a guide for assessing other areas of operational focus that require further strategic alignment.
Conclusion
The market opportunities that China offers MediCorp are immense because of the country’s high population and incidence of patients who suffer from diabetes. The marketing mix strategy highlighted in this paper seeks to exploit this market opportunity while leveraging some of the key competencies of the company. The marketing mix framework has been discussed with four pillars in mind: product, place, price, and promotion strategies.
As part of MediCorp’s product strategy, iGluco will be marketed as a non-invasive device that helps users to know their blood sugar levels without the inconvenience and hassle of piercing the skin to get a blood sample. In this regard, it is expected that the product will have little interruption on the users’ daily lives and it will be marketed as such. Therefore, the company’s main value offing that sets it apart from the competitors is the ease of use and its non-invasive nature because patients can simply attach the device to their arms and read their blood sugar levels at specific intervals of the day.
Overall, the proposed marketing strategy will be implemented by merging shareholder and stakeholder views to address the diverse interests of people who would be affected by the company’s activities. This strategy will be accompanied by a robust CSR plan that will center on sponsoring local health programs and providing annual free medical services to local communities. This governance model will be implemented using the balanced scorecard technique that will measure the progress made vis-à-vis business, process, customer, financial, and growth goals.
References
Alibaba. (2020). Product (blood glucose meter price). Web.
Census.gov. (2012). US Census Bureau Site North American industry classification system. Web.
Center for Strategic and International Studies. (2020). How well-off is China’s middle class?. Web.
Dziak, M. (2019). The balanced scorecard (BSC). New York, NY: Salem Press Encyclopedia.
Guangzhou Pharmaceutical Holdings. (2020). Who we are. Web.
Hofstede Insights. (2020). Country comparison. Web.
Jia, W., Weng, J., Zhu, D., Lu, J., Jhi, L., Zhou, Z., … Zhao, Z. (2019). Standards of medical care for type 2 diabetes in China 2019. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews, 35(6), 3158. Web.
Lowe, S. (2019). Driving good governance through accountability. Web.
Lu, M. Q. (2015). Approaching China’s pharmaceutical market: A fundamental guide to clinical drug development. New York, NY: Springer.
SIS International Research. (2020). Pricing market research. Web.
Tabrizi, S., & Kabirnejat, M. (2015). Management, strategies, tools, and practices in e-marketing. Journal of Knowledge Globalization, 8(2), 69-81.
Tate, M., Deo, M., Cao, A. H., Hood, S. G., Huynh, K., Kiriazis, H., … Ritchie, R. H. (2017). Insulin replacement limits the progression of diabetic cardiomyopathy in the low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research, 4(1), 423-433.
Tonyushkina, K., & Nichols, J. H. (n.d.). Glucose meters: A review of technical challenges to obtaining accurate results. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, 3(4), 971-980. Web.
Value Chain. (2005). A to Z of management concepts & models, 389-391. Web.

