Company profile
McDonald’s is a leading food retailer in the world. The company has more than 36,000 outlets. It is also listed on the New York Stock Exchange. McDonald’s establishment happened in 1940. It has more than 1.5 million workers distributed across different parts of the globe where the firm has operations. The company’s global presence makes it synonymous with globalization (McDonald’s 2015).
Products and customers
The company serves about 70 million customers around the world, who are located in the more than 100 countries where it has operations. The company serves the core features of its world famous fries and seeks to be the primary place that customers choose to eat and drink. It offers four main service types to customers as described below: First, McDonald’s has a front area service that caters for people who walk in and order fast foods. People can eat on the premises or take away their food. The service is open throughout the day and most of the night.
The second service type is drive through, which caters for customers who are going to buy food, but do not want to leave their cars. These types of clients give orders and get their food within a few minutes. There is also the McCafe type of service, where McDonald’s has a coffee outlet type of business. Here, it offers the cafe experience with coffee and other beverages and bakery items. The last service type is back area. This is the service that supports the other three services. It is the section where food components are made for subsequent delivery to customers (Walton 2015).
Prime business processes
McDonald’s has to process millions of transactions daily. In addition, it has to make several decisions at the outlet and country levels as well. Thus, it has store managers and line managers to supervise the delivery of services to customers. Managers also support business operations of procuring raw materials and employee services. The main business processes are retailing and customer care.
Product pricing
The prices of McDonald’s vary slightly from restaurant to restaurant. Prices can vary based on a number of reasons. The main reasons are the cost of input and the existing marketing promotion carried out by a restaurant (Froelich 2014).
Capital investment in IT and related infrastructure
McDonald’s has invested in a transaction processing system, which collects all data about transactions. It also stores, modifies, and retrieves stored transactions to help in answering routine questions. In addition, the system is beneficial for conducting normal business operations, such as payroll and employee record keeping tasks. It ensures that the company has reliable data to use when paying employees and when analysing the costs of operating the business or its revenue stream (Bloch 2015).
Performance measurement approach
At McDonald’s, performance management covers learning and development, succession planning, leadership and development, compensation, training and planning, sourcing and recruiting (Jurevicius 2015).
Current IT and E-business usage
The company is using a number of e-business strategies in different parts of the world. It partners with local and regional service provides to develop custom built systems that power the e-business strategy of McDonald’s. The company has implemented an online ordering and payment system that works as a technique for generating traffic and directing the traffic to its restaurants. The company is using the “Web to Store” concept as a way of simplifying its interaction with customers and boosting its relationship with the clients. Other than just capturing basic transaction information, it also obtains the identities of customers and a history of their orders for use in planning service delivery (Computer Business Review 2007).
SWOT
Strengths
McDonald’s understands that its core business is to deliver fast foods to its customers’ premises in the most convenient way. Therefore, it partners with reputable IT companies to provide IT needs and enhance its business performance. It can tap into the capacity and experience of global players in payment and transactional services so that there is a high turnout of smooth delivery solutions for the customers.
Customised e-commerce solutions for McDonald’s capture the growing trend in the use of mobile devices as the main communication gadgets. This allows the company to tap into a significant and growing market. McDonald’s allows its franchisees to enter into platform service arrangement with local companies to deliver their e-commerce strategies.
This allows the parent company to concentrate on expansion, while particular franchises handle the details of the expansion. This ensures that growth momentum remains high (Kłapeć 2014). Customers from China, Singapore, Australia, and Malaysia are among those that are enjoying the convenience of the online ordering system. In addition, the company is launching home delivery to selected markets across the world (Kłapeć 2014).
Weaknesses
McDonald’s is not in the business of buying and supplying technology. Therefore, it is ill-equipped to come up with the most innovative products for sustaining its e-business strategy. The company has to work with third party providers, which introduce risks in delays or misinterpretations of the intended designs and plans for the use of a particular system.
Opportunities
McDonald’s is in a good position to increase its presence without relying much on physical expansion, given the growing reach of consumers that is provided by its e-commerce platform. Customers have technology at their fingertips and are increasingly demanding that companies such as McDonald’s engage them using the technology. Therefore, if the company can come up with a good implementation of the existing and future technologies to increase its customer relationships, then it can increase loyalty and its brand reputation (Baldwin 2013).
There are opportunities for using gamification techniques in the technology approach as a way of enhancing the usefulness of the information system at McDonald’s. The company has experimented with the concept in its mobile applications to increase its marketing campaign reach and collect valuable consumer insight about new menu items that it launched. There is an opportunity of using information from the tests to rapidly deploy new service improvement strategies across its global operations and minimize time taken to serve customers or to make recommendations more appealing to customers (Baldwin 2013).
Threats
Failure to make the technology integration experience good and seamless will cause customers to miss the value of the service. The company has to carry out its technology integration in a holistic way. The company is dependent on the big players in the IT industry, who introduce solutions to the market that may not have passed adequate fraud testing procedures. The solutions can expose customer information and business secrets to unintended parties when they are compromised. An example is the e-payment solutions that the company relies on to enhance its service delivery to customers who book meals online (Mills 2010).
ANSOFF Matrix
The ANSOFF matrix is supposed to help companies develop a strategy that can improve their marketing position. It provides four ways of achieving the objective. Firstly, it involves the penetration of the market, which is followed by developing the product. Thirdly, there is diversification, which is followed by developing the market. Market penetration will focus on selling existing products or services to existing markets as a means of achieving growth in terms of market share when applying the tool to McDonald’s. Developing the market entails making novel markets and segments to enable them sell more of its products. This is where the development of the e-commerce strategy by the firm is found. The company is using various platforms of its information systems to launch new categories of its market, where it can provide the same services or introduce new services for new customers and the current customers.
The other option is product development, which is about the development of new products that can go into the existing market. McDonald’s has also embraced this strategy, but not in the e-business strategy. The last option of diversification concerns the development of new products to sell to new markets. It is a strategy that McDonald’s has not used as part of its e-business agenda.
McDonald’s is embracing the product development strategy based on the four options. Here, it is introducing new products that offer incremental value to its existing products. The company is increasing its offers of e-payment solutions and allowing customers to decide their preferred way of purchasing meals. It offers them the convenience of an e-commerce platform and allows them to access the platform from the comfort of their phones through the mobile app (Hernandez 2012). McDonald’s has also opted to embrace product development in selected markets as it evaluates the results.
The different characteristics of the markets are the main factors that affect the testing (Carbone, Moatti & Vinzi 2012). For example, for its payment system, the company opted to test the solution in France based on its existing market features, which include a high population of customers who have access to e-payment solutions on their phones (Hernandez 2012). In Japan, the company entered into a partnership with a mobile communications company to promote an e-wallet service that would allow customers to pay for meals through their mobile phones in all McDonald’s outlets in Japan (Computer Business Review 2007).
McFarlan
The McFarlan grid is an analytical tool for evaluating business strategy. It consists of four quadrants that help to analyse the importance of a company’s information system. The analysis covers the past and the future. Therefore, the insights obtained from the analysis are useful for planning. The four quadrants are support, turnaround, factory, and strategic.
The company has an alert system for transactions made on its online platforms and its retail point of sale terminals. Information systems are linked to provide transaction support. The company relies on its phone app, its website, and its equipment to ensure that its e-business strategy has sufficient support to function optimally. In the McFarlan grid, support relates to the elements that enhance daily operations. It would be impossible or difficult for the company to achieve its operational objectives without the elements (Doole & Lowe 2012).
Under the strategic quadrant, the McFarlan uses the criteria of operations that are essential for the improvement of daily operations. These are activities that increase the business survival options. In the case of McDonald’s, an online ordering form for customers and a customer management portal provided by the phone app are some of the strategic opportunities used by the company. In addition, the company implements a customer relationship management by capturing customer information and using the data to interact with customers when they are visiting stores or making subsequent orders online. The company is relying on the decision support system to make the right decisions, based on the information that it is capturing every day from the customers who frequent its stores (Dabholkar & Abston 2008).
The company considers customers and employees as the most important people in its management information system. It gathers daily data for making performance reports on expenses, hours worked, meals ordered, customers served, and many other parameters that help in delivering the strategic goal of being profitable.
The turnaround quadrant represents the systems that are crucial to the business in the future. Under this category, McDonald’s looks at its employee training program as the most critical resource for the future. The company is also betting big on the use of technology through smart kiosks and smartphones, as well as wearable devices to sustain its market share in the business. Therefore, it is developing its IT strategy to take advantage of any emerging technologies that are relevant to its business case (Lutz 2015).
GAP analysis
Gap analysis is a comparison of the actual performance of a company and its potential performance when all the internal and external factors are conducive. This works by helping the firm maximise its resources and perform optimally. There is an unserved and an unstructured market around the current McDonald’s market. The company’s task is to find out this market and develop the right strategies that will enable it to capture the market.
Moreover, the company has to embrace innovation cautiously because relying so much on technology that is market pioneering and futuristic may cause the company to develop products and services that customers are not willing to pay (Jarrett 2003). Therefore, the right strategy would be the one that has a balanced value and innovation attribute.
The current success of McDonald’s is found in its value proposition. The company has a different value curve compared to other restaurants, and the graph below illustrates that fact.
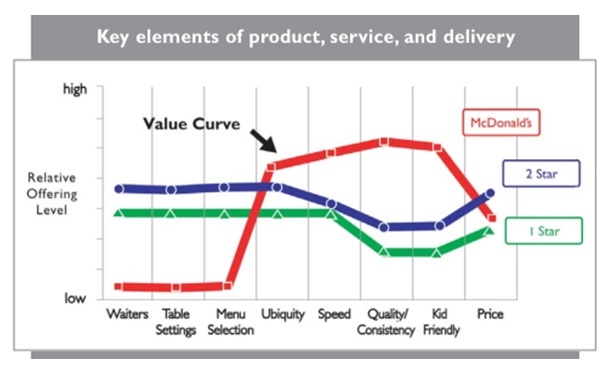
McDonald’s is not purely a restaurant because its competition is not happening directly with other restaurants. Instead, the company competes with the practice of making meals at home. Its value proposition is that customers do not have to prepare meals at home (Patton 2014). They can obtain fast, affordable, and tasty meals from any McDonald’s outlet. With its e-commerce strategy, the company is extending that value to include any location served by its delivery network. Additionally, customers can make online orders in advance so that they limit the service time when they visit a McDonald’s restaurant to take their food (Lasher 2005).
Currently, McDonald’s lags behind in implementing smart technology solutions for customers to enhance the utility of its information system. The company needs to increase the speed of implementing its plans for developing new technology solutions (Sablok et al. 2013; Wang & Tzeng 2012). For example, the firm needs to consider strategies used by other online retail companies like Amazon that are allowing customers to purchase goods and services in diverse ways, depending on the technologies that are most convenient for them (Lutz 2015). McDonald’s also falls short in the spread of its information systems, where some systems are restricted to particular areas. The company has not implemented the systems in its entire chain of restaurants across the world.
Business Technology Audit Analysis
The primary rule of technology application to business systems is that automation enhances the efficiency of an already efficient system. Therefore, the first role of a business is to make its processes efficient. For McDonald’s, the current gaps between the existing and the required technologies include the identified need to embrace smart kiosks and a holistic approach to the use of mobile communication and interaction technologies. Currently, the business has not made its digital strategy as part of its overall strategy (Jones 2014). Although it is implementing a number of digital solutions, McDonald’s still needs to train its staffs on how to use the solutions to increase productivity and enhance customer value (Peter & Olson 2010).
It is necessary for the reporting formats presented by the various technologies used by the company to remain relevant to the current business operations. For example, the kiosks that allow customers to self-order must use the existing menu items, the right prices, and the appropriate time so that workers can interact with the technology with ease. Currently, the existing dependencies in McDonald’s e-business strategy are as follows.
The use of mobile apps depends on the current platform by the company to handle the information collected and fed to the apps for use by customers and employees. In addition, the company depends on third-party payment and information system service providers to manage its solutions, although it has an internal resource for coordinating the developments in IT. The company has established a digitally focused office that will coordinate the development of new initiatives. It is also expected to enhance the brand (Frost 2015).
Reach – competition, customers
To reach out to customers and the completion, McDonald’s has to continue focusing on the emerging personal consumer technologies, especially smartphone apps and wearable devices. They can enhance the application of the company’s digital strategy, and they also provide constant access to consumer activities. Thus, the company can gain increased information about the target customers and be able to make a better decision concerning its strategies to defeat the competition. Apps can become intuitive and allow the company to use customers as crowdsourcing agents to gather information from its competitors when customers are buying or interacting with the competition (Mendoza et al. 2007).
Reaction – customer feedback
Currently, the company relies on social media and other electronic forms to collect feedback. However, the feedback options rely on customer triggers. It is also very easy to miss customer feedback when there is no absolute deviation from the norm in service delivery. However, with smartphone apps that are always on, the company can enhance its feedback collection by providing customers with an easy to tap feature that does not require too much investment. The internal systems can then collect the location and consider other details of the customer automatically, such as meals ordered and the history to help in making the report on the performance of a particular restaurant or menu item. The company needs to collect the information passively (Ferrell & Hartline 2011).
Responsiveness – concepts into products
The strategy used by McDonald’s is to focus on the customer at all times. This implies that any strategy that the company uses to gather customer intelligence will first have to correspond to the demands and expectations of the customer. The preferences of customers at a particular market shape the decisions that the company makes concerning its product and service delivery. The central component of collecting information about customer feedback and transaction goes on to inform the customer response strategy at all interaction points in the company.
Refinement – responding to customers
Customers are increasingly picky about the fast food restaurants that they frequent. The business has to bring speed and energy into the business by being more vocal about its values and meeting customer expectations at its restaurants (The Associated Press 2013). As cultures change, the company also makes inroads to different types of business. For example, its McCafe concept is a refined idea of meeting the needs of customers who have been seeking a McDonald’s experience, combined with a coffee outlet ambience (QRSWeb.com 2010). In addition, the company uses its online platforms to provide sufficient feedback to customers on a personal basis. The concept allows the company to take care of empty tables during low traffic times. It allows customers to stay on the premises and increases the opportunity for the company to collect additional information on serving customers better (Fancourt, Lewis & Majka 2012).
Reconfiguration – re-engineering & restructuring
The company has been re-engineering its menu and product services in its markets. It also allows its IT frameworks for some operations to be provided by local companies. This allows the overall product to depict the needs of the market. McDonald’s frequently introduces new menu items to reflect tastes and preferences of customers. It does this based on information gathered from the competitors and customers with regard to its products. The company can retain ensure that customer needs are always using a robust management information system that can provide localised reports for the different market segment, met.
Redeployment – financial, physical and human
A fundamental attribute of the McDonald’s success is the integration of product development, market research and human resource management. It also includes financial control and operations management to ensure that there is the consistent creation of products and services that meet customer needs in the restaurants around the world. With a functional digital strategy office, the company dedicates physical, human, and financial resources to the development of useful strategies. Moreover, it coordinates the development function with real practice in various markets where it tests and implements its solutions, such as the McCafe and e-payment online ordering options.
Reputation – quality and service
Marketing and public relations activities of the company rely on the existing intelligence on market segments and target customer. The constant collection and analysis of information allows the company to learn of any customer dissatisfaction early so that it can make remedial steps (McDonald’s 2014). It also updates its training programs for staffs to reflect changes in its operating environment. Training ensures there is standardisation of service provided. Transaction processing information between customers and the company or between suppliers and the company plays an important role in the making of daily operations decision. It also informs the top executives on the direction the company is taking on its quality and service reputation so that it can make necessary adjustments through worker changes and product developments (Prajogo & Sohal 2006).
Recommendation for improving the performance
Knowledge of the McDonald’s business and its customers is essential for the realisation of organizational, profits, and other objectives. Therefore, the company has to focus on the need to access data about all its operations and interactions with employees and customers at all levels of the business. Given that the company has a dominant global presence with millions of customers, it needs to find strategic partners to handle the information that it collects on a daily basis. Already, there are solutions that favour the food industry with regards to the large amount of data that companies have to deal with in their marketing and operation strategies. Data firms like IBM are providing solutions for major food-related companies as they can collect large magnitudes of data and make better decisions about the strategic choices that should work (Thusoo 2015).
Therefore, the task ahead for McDonald’s is to open up its information system to make it easy to integrate the existing public and private information platforms. The aim is to attach the system to others that can significantly boost the intelligence of the business in its market place. Here, the company can be able to tap into the solutions provided by advanced systems that rely on computational technology to go through a large pool of data on the relationship of ingredients, reaction of customers, health details of components, ergonomic features of restaurant seats, and the population demographics of particular areas. These information sources end up providing insights of why a particular product or promotional strategy will work in a particular type of market. The outcome of the information system integration with the publicly available data using established global data companies should lead to improved efficiency at all levels.
McDonalds is on the right path and should continue to actively pursue a data-driven culture. The c must enhance its trend-analytics so that it can effectively by relying on hiring out the service, instead of limiting itself to company based solution. This approach can make the company more responsive to trends without posing a significant capital expenditure risk that can jeopardise other business operations. In addition, relying on specialised service providers for its information system also needs allows the company to manage country-specific needs and challenges with ease. It can have different service providers working jointly to cover different market segments, such as the fast food business and the coffee house business segment.
Reference List
Baldwin, C 2013, McDonald’s to engae with tech-savvy customers in restaurants, Web.
Bloch, H 2015. Statistics and facts on McDonald’s. Web.
Carbone, V, Moatti, V & Vinzi, VE 2012, ‘Mapping corporate responsibility and sustainable supply chains: An exploratory perspective’, Business Strategy and the Environment, vol 21, pp. 475-494.
Computer Business Review 2007, McDonald’s and DoCoMo enter into Japanese e-payments JV. Web.
Dabholkar, PA & Abston, KA 2008, ‘The role of customer contact employees as external customers: A conceptual framework for marketing strategy and future research’, Journal of Business Research, vol 61, pp. 959-967.
Doole, I & Lowe, R 2012, International marketing strategy, Cengage Learning, Stamford.
Fancourt, L, Lewis, B & Majka, N 2012, Born in the USA, made in France: How McDonald’s succeeds in the land of Michelin stars. Web.
Ferrell, OC & Hartline, M 2011, Marketing strategy, 6th edn, South-Western, Cengage Learning, Mason, OH.
Froelich, A 2014, This shows exactly how much McDonald’s costs, Web.
Frost, P 2015. McDonald’s CEO Easterbrook sees digital as key to turnaround. Web.
Hernandez, BA 2012. McDonald’s tests PayPal hot on heels of Starbucks-Square deal. Web.
Jarrett, M 2003. ‘The Seven Myths of Change Management’, Business Strategy Review, vol 14, no. 4, pp. 22-29.
Jones, A 2014. McDonald’s to focus on digital and marketing strategies. Web.
Jurevicius, O 2015. McDonald’s SWOT analysis 2015. Web.
Kłapeć, A 2014. McDonald’s quickly improves its e-commerce presence. Web.
Lasher, RL 2005, ‘Blue ocean strategy: Book review’, CSC World: Putting innovation to work, pp. 38-40.
Lutz, A 2015, McDonad’s is plotting to copy Amazon’s strategy. Web.
McDonald’s 2014, McDonald’s Newsroom. Web.
McDonald’s 2015, Better, not just bigger. Web.
Mendoza, LE, Marius, A, Perez, M & Griman, AC 2007, ‘Critical success factors for a customer relationship management strategy’, Information and Software Technology, vol 49, pp. 913-945.
Mills, E 2010, McDonald’s warns customers about data breach. Web.
Patton, L 2014. McDonald’s profit drops 30% as U.S. sales slump. Web.
Peter, JP & Olson, JC 2010, Consumer behavior and marketing strategy, 9th edn, McGraw-Hill Higher Educatio.
Prajogo, DI & Sohal, AS 2006, ‘The relationship between organization strategy, total quality management (TQM), and organization performance – the mediating role of TQM’, European Journal of Operational Research, vol 168, pp. 35-50.
QRSWeb.2010, Skinner: McDonald’s to launch oatmeal, more differentiation. Web.
Sablok, G, Bartram, T, Stanton, P, Burgess, J & Mcdonnell, A 2013, ‘The impact of union presence and strategic human resource management on employee voice in multinational enterprises in Australia’, Journal of Industrial Relations, vol 55, no. 4, pp. 621-639.
The Associated Press 2013. McDonald’s sales gain kept in check by slack U.S. demand. Web.
Thusoo, A 2015. How big data is revolutionizing the food industry. Web.
Walton, E 2015, McDonald’s offers ‘special perk’ to teachers on Teacher Appreciation Day. Web.
Wang, Y-L & Tzeng, G-H 2012, ‘Brand marketing for creating brand value based on a MCDM model combining DEMATEL with ANP and VIKOR methods’, Expert Systems with Applications, vol 39, pp. 5600-5615.

