Central Case Facts and Background
There is a colossal clash of competitors involving recognizable and big brands within the streaming content category of entertainment provision. This has been exacerbated by several anecdotal factors within the industry, with the increased demand for readily available home entertainment and increased leisure hours with the recent outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the entry of notable brands within the streaming sector. Currently, Netflix, which is undoubtedly the biggest player within the content-streaming home entertainment sector, is competitively up against a plethora of tech giants with the revenue and resource capabilities to implement the best technology, talent, and carve out a significant share of the market as well.
However, the world market for entertainment video is also expanding, driven in large part by consumer access to high-speed internet connections, the proliferation of mobile devices, and the entry of notable brands within the streaming content sector. It is, therefore, essential to assess Netflix’s competitive strategy and determine its effectiveness now, and in the long-term, factoring in scalability and flexibility gave the rapidly evolving market conditions. The primary concern for Netflix would be reasonable, the rapidly changing market for entertainment video, as well as the influx of notable and recognizable brand names in the sector, including Apple, HBO, Amazon Prime, Walmart, and, more recently, Disney. It, therefore, raises the question of whether Netflix’s strategy and business model are sufficient to ensure the firm’s operational effectiveness and bolster the competitive advantage of the corporation.
Stakeholders and Organizational Structure
Netflix Inc. features a rather hierarchical organizational structure but with inherent modifications that promote business responsiveness and flexibility. The company can, in theory, continually evolve, adapt, and offer original entertainment and an on-demand media streaming service to its target consumers. The organizational structure supports the achievement of Netflix Inc.’s corporate vision statement and mission statement, pointing to a strategic leadership goal in the entertainment domain.
Overall, Netflix Inc. implements a U-form organizational structure that involves a hierarchical approach to maintain a sense of direction and administrative control. This corporate structure is, however, rather flat as all primary business executives report directly to the CEO (Hadida et al., 2020). The inherent advantage of this structure is that it reduces the bureaucratic levels needed to escalate issues up to the directorial levels considerably. This is, however, in line with Netflix’s corporate culture, which highly promotes open cooperation and communication, despite the hierarchical nature of its corporate structure.
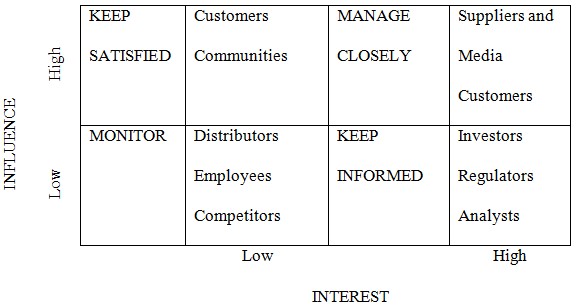
On the other hand, the company features a diverse selection of stakeholders. Institutional investors, however, do hold and control the majority ownership of Netflix through 83.05 percent of outstanding shares that they own (Daidj & Navarro, 2018). This interest is also higher than any company within the Cable and Satellite TV industry. The other notable stakeholders can be outlined as the consumers and communities, suppliers and media, distributors, employees, competitors, analysts, and regulators. Netflix’s responsibilities towards them are outlined graphically in the stakeholder analysis matrix in Table 1 below.
Communities within Netflix Inc.’s context can be taken as all people who want a Netflix account but have not subscribed to the service and those who watch the media on a borrowed account. They are of mild importance as they have a high influence on the company’s reputation, despite not contributing financially. Netflix is a consumer-oriented company, and if its consumers are not satisfied, their bottom-line will suffer. Their suppliers are also quite essential as the company arguably prevails due to superior content, including Emmy award-winning shows and their selection of branded original content.
As a result, suppliers are of high interest and strong influence as well. Distributors include not only the devices used to stream but internet service providers, given the business model of Netflix Inc. They also have analysts who monitor the shows and movies being watched and save money on licensing agreements, therefore streamlining their content to that which is popular and on-demand.
SWOT Analysis of Netflix
Netflix’s growth may be attributed to specific business strengths that facilitate an extensive expansion and dominance plan. In the SWOT analysis framework, the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats are a reflection of the corporation’s internal situation and external environment. This provides insight into the company’s market position as well. Netflix continues to strengthen its multinational operations and develop innovative solutions to secure its dominance against its primary competitors, including Apple, Disney, Walmart, Amazon, Google, HBO, and other related networks and content producers. Continuous improvement can, however, be secured by examining the factors outlined in the SWOT analysis to ensure seamless and competitive service delivery of on-demand media streaming.
Netflix Internal Analysis
The company’s strengths comprise the core competencies and competitive advantages accrued throughout its doing business. They include the following:
- A large, versatile platform of content consumers and producers
- An increasing inventory of original content.
- High brand equity.
Its weaknesses, on the other hand, comprise:
- A highly imitable business model.
- Dependence on internet service providers and content producers.
In this SWOT analysis case, the brand name of Netflix allows the company to maintain popularity and penetrate current and new markets. Furthermore, its large platform of consumers and content producers present strength and allow Netflix to maximize its service attractiveness, as well as operational efficiencies and overall business growth. The company’s overall value proposition is achieved by exploiting these strengths within a unique online streaming value chain.
On the other hand, Netflix has a highly imitable business model, which is an intrinsic business factor that weakens the business. For instance, any other competitors can viably copy and implement the Netflix business model to their own on-demand online media streaming platforms as none of the technology is patented. Furthermore, dependence on content producers is an inherent weakness that makes the company susceptible to producers’ strategies. Finally, the company depends on internet service providers who, in turn, determine connectivity speeds, which is essential in consumer satisfaction with the service rendered by Netflix. These weaknesses present the strategic challenge of making the company less vulnerable.
Netflix External Analysis
The external analysis outlines opportunities and threats within the streaming company’s unique market scenario. The opportunities available for Netflix’s exploitation may include:
- Expansion of the company’s product mix.
- Business diversification with entry into other industries.
- Penetration into new markets.
The accompanying threats facing the company include:
- Imitation and competition.
- Content piracy
- Cybercrime.
The SWOT analysis outlines Netflix’s opportunities that would facilitate growth. These include the expansion of the company’s product mix, whereby the corporation can develop diverse entertainment content availed on its mobile applications or website. This can be leveraged directly within Netflix’s competitive strategy, as well. Penetration into new markets would also be a viable opportunity, especially due to the marked deficiency of on-demand streaming services in notable markets such as China. The business model, which is primarily online, also offers an opportunity for diversity, which can be accomplished by acquiring a complementary firm to improve strategic success and positioning.
Conversely, business imitation and competitors are a significant threat to Netflix’s operations. Competition is a strategic factor, but in the specific context of a SWOT analysis, it provides an obstacle towards maximizing company revenues and profitability within the streaming industry. Furthermore, content piracy threatens the corporation by allowing consumers to pirate content, rather than consume the available content on Netflix’s platforms. Considering the resource-based approach, cybercrime is also an inherent threat due to the information technologies employed by Netflix.
Competitive and Growth Strategies
In response to the opportunities and threats facing Netflix and its quest to dominate the on-demand streaming media market, its generic competitive strategy highlights the competitive advantages of a high level of operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness of information technology. The company has an aggressive growth strategy, based on marketing to expand its streaming operations on an international scale and cost minimization whenever the latter can be supported (Dias & Navarro, 2018). This is a rather generic approach, but one that has been anecdotally proven efficient in the corporation’s domination of the streaming media market.
The online company’s business framework also implies strategic support for the management of information technology for efficient global expansion and operations. Inherent strengths within the online business framework also bolster Netflix’s competitive advantage, including cutting out the middleman in a straight-to-consumer delivery system whereby any intermediaries are non-existent on its streaming service. This has allowed the streaming giant to reach target audiences around the globe and directly transact with potential and existing consumers.
Several features of the company’s competitive strategy are also apparent, such as an obvious cost leadership approach. The corporation can provide frequently minimized selling costs, allowing the service to be affordable for the plethora of content that it provides, without necessarily being the lowest or best-cost provider. Netflix acquires customers broadly in the online market segment, without focus strategies that would concentrate on specific markets and alienate others (Daidj & Egert, 2018). This is especially apparent in contrast with some of its competitors, who are often region-locked and unavailable in specific parts of the world.
Recommendations, Alternatives, and Conclusion
A recommendation to the company’s competitive approach would be to embrace the differentiation of its operations. Despite mainly implementing a cost leadership approach the company’s fundamental strategy of acquiring and maintaining competitive advantage, differentiation would ideally involve developing its online platform and the offered services and products in a way that makes it distinct from its competition. From simple cues such as a highly recognizable logo to further production and domination of originally produced and appropriately branded content from local and diverse content creators. This would be a platform to support aggressive growth strategies and the expansion of its online operations.
Overall, the strategies that Netflix has implemented against earlier competitors such as HBO and Hulu have, from anecdotal and scholarly evidence, been largely successful. However, with the influx of colossal competitors, including Disney, with their highly famed and successful cinematic universe, it would be sound to revise or assess their competitive approach and consumer culture perspectives. With the scalable and flexible organizational culture that Netflix employs, however, the corporation is poised to adjust, and only time would tell if it would remain prominent in the shaping of media consumption across the globe.
References
Daidj, N., & Egert, C. (2018). Towards new competition-based business models? The case of Netflix on the French market. Journal of Research in Marketing and Entrepreneurship, 20(1), 99-120. doi.org/10.1108/JRME-11-2016-0049.
Dias, M., & Navarro, R. (2018). Is Netflix dominating Brazil?. International Journal of Business and Management Review, 6(1), 19-32.
Hadida, A. L., Lampel, J., Walls, W. D., & Joshi, A. (2020). Hollywood studio filmmaking in the age of Netflix: a tale of two institutional logics. Journal of Cultural Economics, 1-26.

