Introduction
Many organizations understand that they need to embrace change to remain competitive (Cummings & Worley, 2008). Change management has emerged from this development and it involves processes undertaken by an organization to improve the success of adopting new systems or procedures (Hammoud, Bizri, & El Baba, 2018). The Islamic banking sector has experienced similar change patterns through the introduction of e-banking, which is a virtual tool for facilitating business transactions (Allied Market Research, 2019).
Although the growth of e-banking in the Middle East financial sector is undisputed, few Islamic banks understand how the virtual platform influences their bottom-line performance. Relative to this gap in research, this paper seeks to investigate the impact of online banking on the Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB). This financial institution will be a case study for understanding how digitization in the banking industry affects Islamic banking. The research question guiding this analysis aims to investigate the effects of online banking on DIB. Three objectives will guide the discussions. They focus on finding out the impact of online banking on the service quality, customer satisfaction standards, employee workload, and operational efficiency of DIB. Other researchers have used these objectives to study the impact of digital banking on their financial sectors. For example, the above-mentioned objectives are adapted from the investigation done by Dinh, Le, and Le (2015) to understand the impact of e-banking on the Vietnam financial sector.
Theoretical Framework and Topic Statement
As highlighted above, e-banking has affected different areas of new business development in the financial sector. However, no other industry has been significantly impacted by this change like the banking industry(Hammoud, Bizri, & El Baba, 2018; Siyal et al., 2019; Allied Market Research, 2019; Dinh et al., 2015). The change has seen the emergence of online banking as a major platform for facilitating business transactions. Most pieces of literature define e-banking as an electronic payment system, which allows for instantaneous transactions and the borderless flow of capital (Hammoud et al., 2018; Siyal et al., 2019; Allied Market Research, 2019; Dinh et al., 2015).
This definition has been supported by recent events, which have seen online banking grow by at least 22% annually to become a significant part of total global financial transactions (Allied Market Research, 2019). It is expected that if this growth will be sustained up to the year 2023, it will represent a 500% increase in banking operations compared to 2016 statistics (Allied Market Research, 2019). Sophisticated customer interfaces and the convenience of completing financial transactions are some of the primary drivers of growth in the online banking sector (Hammoud et al., 2018; Siyal et al., 2019).
Globally, the evolution of the banking industry has seen financial institutions provide goods and services, relative to their geographical profiles and banking services (Allied Market Research, 2019; Dinh et al., 2015). For example, retail, corporate, priority, and investment banking products have emerged from this change (Hammoud et al., 2018; Siyal et al., 2019). Figure 1 below shows that the growth of the online banking sector has primarily been informed by an increased interest in new financial products.
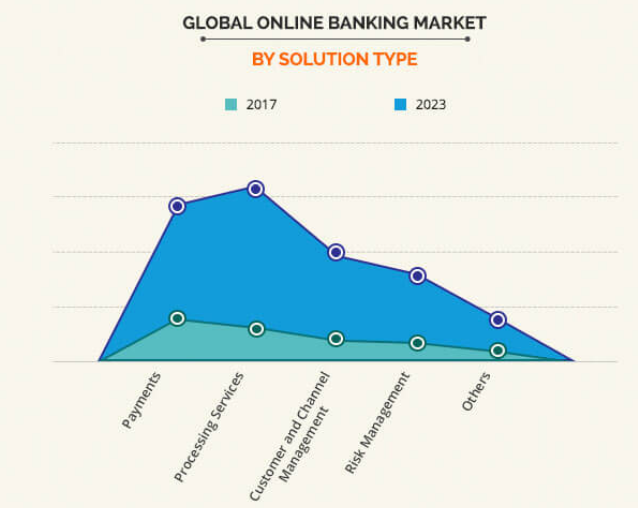
Financial payment is deemed the highest contributor to the growth of e-commerce globally. For example, in 2017, it accounted for $2.866 billion in revenue for e-commerce companies (Allied Market Research, 2019).
Islamic banking is one key segment of the online banking industry that has been poorly explored. It is estimated that the total value of this banking sector is $2.05 trillion (Research & Markets, 2019). The growth of this industry has attracted different players who have subdivided the market to increase their profitability through the provision of specialized electronic products and services (Research & Markets, 2019).
Alternatively, the global Islamic banking market has encompassed different aspects of Muslim-based financial products, including Islamic Insurance (Sukuk), Islamic bonds, and Sharia capital markets (Research & Markets, 2019). Although there have been moderate growth rates reported in the Islamic banking sector, online banking has shown promise in increasing the flow of investment capital across key industry segments(Research &Markets, 2019).
Several key investors who are willing to deploy vast amounts of cash to remain competitive dominate Islamic banking. Some of the main players include Kuwait House Finance, Bank Al-Rajhi, and DIB (Research& Markets, 2019). Most of these financial institutions are using online banking as a tool for achieving their objectives. Consequently, the research question guiding this investigation is premised on understanding the effects of online banking on DIB, which is the case study.
Methodology
According to Creswell (2014), the two main types of research approaches in research development are either qualitative or quantitative. The qualitative approach is used in research investigations that have subjective variables, while the quantitative technique is mostly applicable in studies that have measurable variables. In this document, both approaches were used together to create a collaborative mixed methods framework. The justification for using both techniques was to investigate the research topic from multiple perspectives. In other words, the investigation was not limited to the type of data available.
The mixed-methods framework allowed for the collection of primary and secondary sources of data. The case study findings provided primary data, which were obtained by carrying out interviews with some of the DIB staff. The informants were asked different types of questions relating to the organization’s experience with internet banking. Discussions involved a review of the impact of digital banking on customer satisfaction, service quality, operational efficiency, and employee workload.
The justification for asking these types of questions was to get a proper understanding of the impact of online banking on DIB’s key operational programs. The informants were selected using the snowball sampling method because one team member was familiar with some of the bank’s employees. The initial group of employees was used to contact other informants. Interviews were done virtually and the participants comprised of middle-level managers of six DIB branches in the UAE. The views of management were sought because the team had a broader understanding of the impact of e-commerce compared to lower-ranking employees.
Secondary data was the second source of information used in the report. Data was gathered from a literature review of existing studies that have investigated the research topic. This data collection method was instrumental in gathering theoretical pieces of information for addressing the change problem (impact of digital banking on DIB’s operations). Lastly, the data was evaluated by developing key themes that emerged from the interviews. The themes were generated from identifying patterns of analysis that related to the study objectives. Creswell (2014) defines this technique of analyzing data as the thematic method.
Results (Primary Data)
Organizations that aim to improve their performance through a reorganization of their operational processes often use change management to optimize results (Cummings & Worley, 2008). Although change often involves all subsets of an organization’s processes, people are the main change agent. Therefore, to achieve the best results, change management has to be integrated into a firm’s leadership structure. This is true for Dubai International Bank because the digitization of its banking platform represents one of the most significant changes in the organization. As highlighted in this document, respondents were asked to give their views regarding the impact of digital banking on DIB through elaborate interviews. The findings are presented below.
Effects of Digital Banking on Service Quality at DIB
One of the questions posed to the respondents was the effect of online banking on the quality of services offered at DIB. Consequently, it was established that digital banking helped to increase service quality at the bank by minimizing the time and effort taken to deliver services. It also allowed DIB to collaborate with third-party agents to improve the quality of services offered. For example, the bank has collaborated with an outside entity to improve its billing system – a process that has contributed to the increased quality of banking services at the financial institution. The respondents also pointed out that digital banking helped to reduce the number of errors reported in banking transactions. They argued that virtual banking improved the speed of financial integration between different agents of DIB’s service model. Furthermore, the respondents said that the above-mentioned benefits were easily realized because the bank had a good user interface on all its banking platforms.
Another respondent pointed out that digital banking helped to improve the quality of banking services offered to customers through increased planning, coordination, and control of banking services. This benefit was also linked with minimal delays and increased efficiency in processing transactions. More importantly, the positive contribution regarding the adoption of digital banking on DIB’s operations aligned with the bank’s goal of digitizing banking services. Consumer behavior also changed with the implementation of e-banking at the institution. Based on the above changes, DIB has decided to use digital banking to meet customer needs.
The scope of e-banking use at DIB includes the development of different virtual-based financial products, such as t-banking (telephone banking), e-banking (electronic banking), and m-banking (mobile banking). Contactless cards, auto teller machines, and point-of-sale services are alternative financial services offered on the same platform. The bank’s online banking portal also supports the provision of better quality customer services because of increased efficiency and speed of providing customer services. The convenience offered by e-banking products has also played a key role in improving customer experiences when banking. Overall, these findings highlight the importance of understanding how e-banking has improved the efficiency of banking services at DIB.
How e-Banking affects the Efficiency of DIB Operations
The increased efficiency of DIB operations, which has been occasioned by the introduction of e-banking services, has been supported by the integration of indirect services into the company’s major online banking platform. For example, the simplicity of updating customer data on the bank’s records has helped to simplify loan approval processes and augmented varied transactions because of the easy identification of customers’ characteristics.
The efficiency of the bank has also been improved through e-banking by reducing the number of people who visit physical branches to make transactions. The speed of information exchanges between the bank and outside parties has also contributed to the improved efficiency of DIB’s operations. Although improved efficiency has been supported by the increased integration of information technology tools, some banking transactions at DIB still demand the physical presence of the customer.
The bank’s cost management department has also reported an increased efficiency of e-banking services on DIB’s operations because of a decline in operating expenses. These advantages have reduced the turnaround time for processing financial transactions and minimized human errors. The effects of e-banking on DIB’s operations have also helped to improve the company’s profitability and efficiency. This outcome has been supported through improved financial indices, such as the cost-to-income ratio and an increased return on investments. Therefore, improved financial performance is linked with a reduced level of reliance on manual processing when reviewing financial transactions or making periodic performance evaluations.
Broadly, the findings generated from this investigation show that digital banking has helped to improve the efficiency of DIB’s operations based on an increase in the turnaround time and quality of services offered. The percentage of transactions involving the physical presence of customers has also declined due to an increase in e-banking usage. This reduction in physical bank visits was largely attributed to the minimization of financial transactions of a utility nature, such as the payment of water and electricity bills because of automation.
The efficiency brought about by e-banking services has also been linked with the provision of updated information and live updates of financial transactions. Broadly, based on the above-mentioned advantages of digitization, the respondents affirmed that there has been an increase in the volume of online transactions undertaken by different departments of DIB. Consequently, this surge in numbers has contributed to the total volume of transactions undertaken by the bank. For example, one of the informants estimated that up to 70% of all corporate banking transactions are done online.
Impact of e-Banking on Customer Satisfaction
Many factors contribute to the success or failure of different types of businesses and customer satisfaction is one of them. Online banking has been reported to have a positive effect on customer satisfaction at DIB. This outcome is partly linked with the increased efficiency and productivity associated with the bank’s e-banking products and services. These views suggest that customer satisfaction has surged through the increased adoption of digitization services. Particularly, the development of easy-to-use interfaces has increased the ease of navigation of the e-banking platform, thereby improving customer satisfaction. Relative to this discussion, some of DIB’s bank’s customers are hesitant to embrace online banking and find the need to physically visit the bank’s branches to gain access to the bank’s financial services. However, some of the informants projected that this trend will stop as people learn and trust online banking.
Customer awareness about online banking was deemed one of the most important factors driving the increased adoption of e-banking services at DIB. Key attributes of the bank’s digital banking services are largely responsible for the surge in customer satisfaction standards that have been reported at DIB. Particularly, the bank’s products have assimilated important attributes, such as perceived quality and functional value, which influence how customers rate the quality of services offered at the bank. Service speed, employee-customer engagement, brand trust, and innovation are other attributes of the bank’s online banking platform, which have contributed to an increase in customer satisfaction standards.
Overall, DIB has started to accept digital banking as a standard way of conducting banking business. This is why the organization has developed many digital-based banking products. Comparatively, one of the respondents said that some of their competitors use digital banking as a separate entity for undertaking specific financial transactions. Nonetheless, there is little contention that the bank’s customers are becoming more aware of digital banking and are willing to try out new products, relative to the efficiency and convenience offered on the platform.
Effects of Digital Banking on Employees
In many organizations, employees are often under pressure to complete specific tasks within set timelines. DIB is no different because the staff is contractually required to perform well. However, digital banking has impacted its performance by affecting how they complete their tasks and obligations. As mentioned in this document, the automation of many banking processes has led to a reduction in the time taken to complete financial transactions. Consequently, the financial system has become efficient as human errors have been reduced and more information about customers acquired.
AT DIB, the digital banking model has had a positive effect on the bank’s employees by reducing their current workload. This outcome has been linked to increased automation because such systems carry out most of the tasks in the organization. However, the respondents noted that the quality of inputs integrated into the automation process should be carefully reviewed because it is a risk factor for the bank, in the same manner as human error is. Some of DIB’s employees pointed out that the use of digital systems to complete tasks was easier and faster than manually completing the same duties. They also said that physically attending to customers was a difficult task because of communication barriers. These advantages were not only limited to employees because some of the bank’s clients preferred to use automated systems to complete their financial tasks, as opposed to contacting employees.
A reduction in the number of clients who come to the bank was also cited as an indicator of a reduction in employee tasks because the staff only has to attend to a few employees, as most of them would be undertaking their financial transactions online. The free time created could be used to complete other tasks, such as innovating to boost the company’s performance. Therefore, the digital banking platform has made it easier for both employees and customers to understand how to accomplish more with minimal interaction from other people. This approach to operations management is a source of competitive advantage for DIB because its customers can easily understand the safeguards created to complete financial transactions without unnecessary contact with banking employees.
Relative to the above assertion, one of the respondents cautioned that it was important to design the online banking platform properly because the failure to do so would frustrate customers who would then pile pressure on employees to address the issue. An internal study conducted by the bank, which involved 200 customers, highlighted the importance of increasing awareness about existing banking products because it was difficult to realize meaningful growth without increasing awareness about banking products to provide the best customer experience. Nonetheless, when employees experience reduced pressures from their work, they are likely to be satisfied and innovative.
Lastly, DIB employees also suggested that digital banking increases their ownership of tasks, thereby improving production efficiency. The demanding nature of the modern customer has forced the bank’s management to demand increased performance from their staff, but this strategy has had to be supported by the use of robust information communication tools, which have reduced employee workload. For example, the use of digital banking services has allowed DIB to delight its customers by creating instant channels for accessing banking services. Furthermore, it is established that some of the most effective banking employees are those who interact with their employees because they are the strongest link in service delivery. The respondents reported this outcome in the general banking operations department and the provision of Ahlan banking services.
Discussion
The terms “e-business” and “e-banking” stem from a larger concept of “e-commerce,” which emerged in the mid-1990s (Siyal et al., 2019). These concepts are often used interchangeably to represent the adoption of internet-based tools to complete financial transactions. According to Nadler and Tushman (1980), it is common to find resistance to change in organizations that have deeply entrenched systematic ways of conducting their operations. However, this is not the case for DIB because the bank has effectively integrated change as a standard operating procedure. Indeed, established in 1975, DIB has grown to be one of the most sharia-compliant financial institutions in the Middle East (Dubai Islamic Bank Inc., 2019).
The technology acceptance model (TAM) could be used to explain the impact of digital banking on DIB’s firm performance. It explains the effect of technology on the banking industry because researchers have used it to evaluate the impact of computer applications on the industry’s performance (Al Shbiel& Ahmad, 2016). This theory suggests that a user’s perceived ease of using digital banking is likely to influence his or her acceptance of the technology (Al Shbiel& Ahmad, 2016). This is why the respondents pointed out that the ease of using digital banking significantly affected how customers perceived services.
Schein’s management theory could also explain why DIB has successfully adopted online banking with significant success because it highlights the role of culture in adopting change (Schein & Schein, 2019). If applied to the context of this study, this theory suggests that a strong innovative culture at DIB has largely contributed to the success of online banking. Schein’s management theory contends that for this outcome to happen, change has to be felt at the “surface” level (involving superficial aspects of communication, such as employee dressing), value level (where a company’s mission, vision, and objectives reflect the change) and at a subconscious level where employees’ beliefs influence how they adopt change.
The last two levels of change management largely characterize DIB’s management practices because the bank is keen on making sure values and beliefs guiding employee operations should be accommodative of new changes. Indeed, being champions of morality, equality, and transparency, the bank has developed a brand as a trusted financial partner for individual and corporate customers in the UAE. The adoption of the digital banking platform and its potential effects (as highlighted above) also aligns with the bank’s overall vision, which is to be the most progressive Islamic institution in the world (Dubai Islamic Bank Inc., 2019). The organization’s online banking strategy also aligns with its mission, which is to improve the firm’s positioning as a leading Islamic bank through innovation (Dubai Islamic Bank Inc., 2019).
Lewin’s change model is another applicable theory for understanding the effects of the digital revolution on DIB’s operations. The model suggests that change occurs in three phases: freezing, unfreezing and refreezing (Bert, 2010). Proponents of this theory contend that effective change management can only be realized when there is a perceived need for change, an alignment of organizational behavior towards this change, and embracing the outcome as part of organizational norms (Bert, 2010). Based on the responses provided by the informants, DIB is in the refreezing stage where digital banking is increasingly regarded as a standard way of undertaking banking transactions. Overall, it is believed that internet banking would soon change the firm’s conventional investment model because it threatens the existence of physical bank branches and undermines the need to have paper-backed financial records.
Lastly, Argyris’s maturity theory could be used to explain DIB’s online banking success because it explains the best balance for achieving management and employee effectiveness. The theory suggests that this optimum level of output can be best achieved when management practices meet mature employee behavior (characterized by independence, self-confidence, and self-control) (HRF, 2019). The successful adoption of online banking at DIB shows that the bank’s digital banking products meet mature employee behaviors manifested by the bank’s customers. In other words, the products offered to provide a good balance between management, employee, and customer needs.
Recommendations
The use of internet banking at DIB is still at its formative stages and the following recommendations should be considered for implementation:
- Sensitize customers about the benefits of e-banking, including why they have to pay extra fees and safeguard their confidential information.
- Formulate a campaign to increase people’s awareness about digital banking to reach the maximum number of users.
- Constantly improve the user interface to enhance customer experience and give information about services offered beyond the traditional banking products.
- Increase management support for change management (digitization) as it can influence most departmental activities.
- There should be more follow-up activities to understand clients’ views and experiences about new products or services offered on the online platform.
- There should be more resources allocated to communicate changes to the banking process before they are implemented. This strategy is aimed at increasing stakeholder buy-in.
Conclusion
The findings of this study suggest that digital banking helped to increase access to banking services at DIB because customers could access financial services virtually and on a 24-hour basis. Furthermore, clients could see their account balances from wherever they are and this unlimited access to their accounts increases their level of satisfaction with banking services. In this regard, digital banking helps DIB to deliver services smoothly and seamlessly. The availability of virtual banking services helps to alleviate the workload imposed on banking customers because clients can carry out their financial transactions easily and without necessarily seeking the input of banking employees. Consequently, employees have more time to undertake other tasks. This outcome improves their level of job satisfaction and signifies the important role of digital banking in boosting the firm’s performance. Overall, based on the case study findings highlighted in this report, we learn three items relating to change management.
- All stakeholders if communicated and executed well can easily embrace change.
- A change could fundamentally alter the banking structure and operational dynamics of banks.
- There is a need for constant review in change management processes.
Abstract
Change management is an inevitable process that organizations have to endure as they try to adapt to the fast-paced developments of the modern world. One of the most significant changes to have occurred in the Islamic banking sector is digitization. The concept of e-banking has emerged from this development but few banks understand how it influences their bottom-line performance. Relative to this gap in research, this paper investigated the impact of online banking on the Dubai Islamic Bank (DIB). Given that this research project was goal-oriented; three objectives guided the discussions. They focused on finding out the impact of online banking on the service quality, customer satisfaction standards, employee workload, and operational efficiency of DIB.
Data were obtained from two sources: primary and secondary research. Primary data was received by interviewing six employees of DIB, while secondary data was computed from reputable and published materials. The findings of this report suggest that digital banking helped to increase access to banking services at DIB because customers could access financial products virtually and on a 24-hour basis. Besides, online banking allows customers to see their account balances from wherever they are and this access increases their level of satisfaction with banking services. In this regard, digital banking helps DIB to deliver services smoothly.
The availability of virtual banking services also aids in alleviating the workload imposed on employees because clients can carry out their banking tasks easily and without necessarily seeking their input. Consequently, employees have more time to carry out other tasks. This outcome improves their level of job satisfaction and signifies the important role of digital banking in DIB’s performance.
References
Allied Market Research. (2019). Online banking market overview. Web.
Al Shbiel, S., & Ahmad, M. (2016). A theoretical discussion of electronic banking in Jordan by integrating technology acceptance model and theory of planned behavior. International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences, 6(3), 272-284.
Bert, S. (2010). Implementing organizational change: theory into practice (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Creswell, J.W. (2014). Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. New York, NY: SAGE.
Cummings, T. G., & Worley, C. G. (2008). Organization development and change (9th ed.). Mason, OH: Thomson/South-Western.
Dinh, V., Le, U., & Le, P. (2015). Measuring the impacts of internet banking to bank performance: Evidence from Vietnam. Journal of Internet Banking Commerce, 20(1), 98-103.
Dubai Islamic Bank Inc. (2019). Our role in tomorrow. Web.
Hammoud, J., Bizri, R. M., & El Baba, I. (2018). The impact of e-banking service quality on customer satisfaction: Evidence from the Lebanese banking sector. SAGE Open, 8(3), 112-121.
HRF. (2019). Argyris theory explained. Web.
Nadler, D.A.,&Tushman, M.L. (1980). A model for diagnosing organizational behaviour. Organizational Dynamics, 9(2), 35-51.
Research & Markets. (2019). Global Islamic finance markets report 2019: Islamic banking is the largest sector, contributing to 71%, or USD 1.72 trillion. Web.
Schein, E. H., & Schein, P. A. (2019). The corporate culture survival guide. London, UK: John Wiley & Sons.
Siyal, A. W., Donghong, D., Umrani, W. A., Siyal, S., &Bhand, S. (2019). Predicting mobile banking acceptance and loyalty in Chinese bank customers. SAGE Open, 9(2), 1-10.
