Introduction
Royal Dutch Shell PLC
Shell PLC was established in 1907. The headquarters of the company is located in the Netherlands. However, the company is registered in the United Kingdom. Further, Shell PLC has a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange. The secondary listings are on the New York Stock Exchange and Euronext Amsterdam. The current daily production capacity stands at 3.2 million barrels of oil equivalent. The company is a component of the FTSE 100 index. Besides, it is a public entity that operates in the oil and gas industry. The key products of the company are petrochemicals, natural gas, and petroleum (Royal Dutch Shell PLC 1).
BP PLC
BP PLC was established in 1908 initially as an Anglo-Persian Oil Company. The company is a key player in the world oil and gas industry. BP PLC is headquartered in London. Further, it has a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange. The secondary listings are on the New York Stock Exchange and Frankfurt Stock Exchange. At the end of 2013, the company had operations in more than eighty countries, while the daily production stood at 3.2 million barrels. The key products of the company are Petroleum, natural gas, aviation fuel, petrochemical, and motor fuels (BP PLC 1).
Industry trends
The oil and gas industry is experiencing a free fall in prices. Since June 2014, the price of oil has dropped drastically. The current price per barrel stands at $43 and it is expected to drop further due to the market dynamics (The Telegraph 1). The drop in price has created disequilibrium in the industry because supply exceeds demand. If this condition persists, then the oil-producing companies are likely to run out of storage space. This will cause a further drop in the price per barrel. During the last decade, the demand for oil exceeded supply, and the price per barrel was expected to increase to more than $110 (The Telegraph 1). The dramatic shift in the oil market can be attributed to an increase in production over the past ten years and an increase in the use of renewable energy.
The current trend in the oil and gas industry has impacted negatively both the companies operating in the industry and the overall economy. In order to cope with the recent trends, the two companies are downsizing. For instance, in the US, BP PLC laid off 550 workers. Further, the company reduced the total annual spending by $23 billion (The Telegraph 1). These stringent measures were put in place to ensure that the bottom line and dividends are not affected by the market trends. In the case of Shell PLC, the company laid off more than 600 workers in the United States. Other regions where the company operates were also affected. Further, the company announced an aggressive restructuring plan that will save the company more than USD800 million. The industry trends have an impact on the financial performance of the two companies. The oil and gas industry is quite competitive and is made up of large players across the globe. The table presented below shows a summary of sales for major players.
The data show that Shell PLC and BP PLC rank second and third respectively in terms of sales. The pie chart presented below shows the proportion of sales for each of the companies.
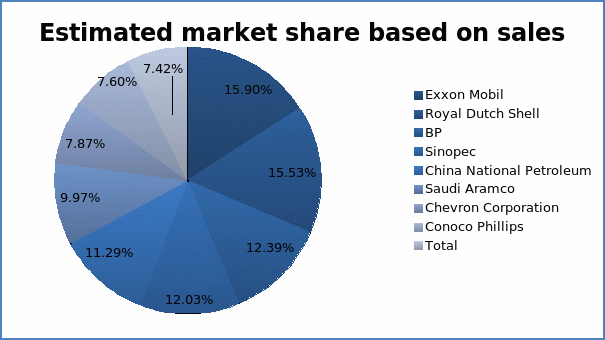
Importance of the study
The study lays a foundation for understanding how ratio analysis can be used in making investment decisions. Specifically, it gives an understanding of how ratios are estimated and interpreted. Finally, the study shows how ratio analysis can be used to select a company for investment.
The objective of the study
The paper seeks to carry out a comparison of the financial performance of Royal Dutch Shell PLC and BP PLC. Specifically, ratio analysis will be used to analyze the financial performance of the two companies. At the end of the paper, a recommendation will be made concerning which company to invest in.
Analysis and comparison
Ratio analysis
The reported financial statements of the company do not give a comprehensive analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the company. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out an in-depth analysis of the financial statements so as to have a better view of the company (Brigham and Michael 26). Further, analysis of the company helps in making an informed decision. Ratio analysis breaks down the financial data into various components for a better understanding of the financial strengths and weaknesses of the company. Ratio analysis will focus on the profitability, liquidity, efficiency, and gearing level of the company from 2010 to 2014. A comparison of the ratios for the two companies will be made. Besides, graphs will be drawn to show the trend of the values.
Liquidity
Liquidity ratios show the ability of an entity to sustain positive cash flow while satisfying short-term obligations, that is, the availability of cash to pay short-term liabilities. It is necessary to maintain optimal liquidity ratios since either low or very high liquidity can be detrimental. The current ratios for the two companies fluctuated during the period. The values of liquidity ratios rose between 2010 and 2012. Thereafter, the two companies reported a decline in 2013 and an increase in 2014. Further, it can be noted that the current ratios for BP PLC are higher than those of Shell PLC. The values of the current ratio were greater than 1for the two companies. This implies that the companies are able to meet current obligations using current assets (Brigham and Michael 67). The value of quick ratio for Shell PLC followed a similar trend as the current ratio. In the case of BP PLC, there was a general increase in the values of quick ratio. Further, BP PLC had a slightly higher value of quick ratio than Shell PLC. The quick ratios for both companies were less than one. This implies that they cannot meet the current obligations using liquid assets. A company with a sound liquidity position should be able to meet short-term obligations using both the current and liquid assets. Thus, it can be noted that the two companies have a weak liquidity position. However, BP PLC has a slightly higher liquidity level than Shell PLC. To an investor, the liquidity position of the two companies shows that they may be facing liquidity management problems. The graph presented below shows the trend of the liquidity ratios for the two companies.
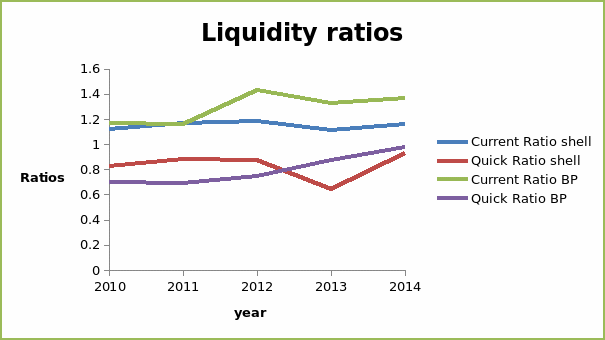
Leverage
A company’s leverage is explained by the amount of debt financing it holds. The ratios are significant because they give information on the extent of exposure of equity financing. A high leverage ratio is not favorable because it reduces the amount of profit attributed to the shareholders (Brigham and Michael 66). On the other hand, very low ratios are not favorable because they show that the management is not willing to exploit the potential of the company. Therefore, a company needs to maintain an optimal leverage level. The total debt ratio for the companies fluctuated during the period. In the case of Shell PLC, the debt ratio declined between 2010 and 2012. Thereafter, the company had an increase in the value of the ratio. In the case of BP PLC, the total debt ratio remained fairly constant during the period with a slight increase in 2014. Further, it can be noted that BP PLC has a high total debt ratio. This implies that it has a higher leverage level than Shell PLC.
The interest coverage ratio gives information on the long-term solvency of the entity. Solvency shows the ability of the company to service long-term debt. Between 2010 and 2012, Shell PLC had a zero value of interest coverage ratio. This can be attributed to the fact that the company did not have debt in the capital structure during that period. Between 2013 and 2014, the value of the ratio dropped significantly. This shows that the ability of the company to pay interest expenses dropped. In the case of BP PLC, the value of the ratio improved between the years 2010 and 2012. Thereafter, there was a significant drop in the value of interest coverage ratio. The interest coverage ratio is highly dependent on the operating profit of an entity. Thus, there is a direct relationship between the operating profit of the company and the interest coverage ratio. For the two companies, the decline in the interest coverage ratio can be attributed to the drop in the amount of operating profit and an increase in the amount of debt. The results show that Shell PLC has a higher level of solvency than BP PLC. Therefore, based on this criterion, an investor should select Shell PLC for investment. The graph presented below shows the trend of the leverage ratios.
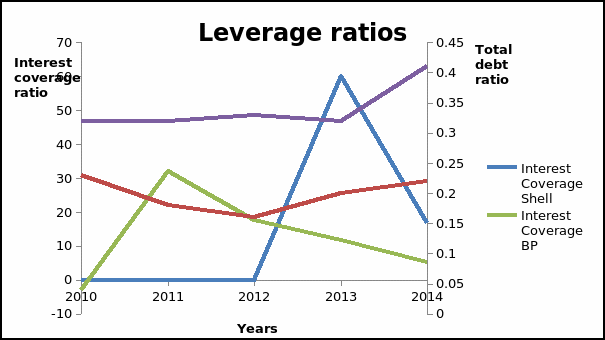
In the graph, the values of the two ratios fluctuated during the period. The interest coverage ratio had a sharp increase followed by a sharp decline for both companies while the total debt ratio fluctuated.
Asset management ratios
Efficiency ratios focus on the internal operations of the company. These ratios show the level of activity in a company (Brigham and Michael 78). Specifically, the ratios show how well a company makes use of resources to generate sales and income. For both companies, the receivable turnover grew between the years 2010 and 2013. Thereafter, the two companies experienced a decline in 2014. The turnover for Shell PLC grew from 5.84 in 2010 to 11.59 in 2013 and dropped to 8.84 in 2014. In the case of BP PLC, the turnover rose from 9.16 in 2010 to 12.04 in 2013 and dropped to 10.12 in 2014. An increase in the value receivables turnover shows that the efficiency in the collection of debts from customers has improved while a decline shows that the level of efficiency has declined. Further, a high value of the ratio is preferred to a lower value. The data show that the level of receivable turnover for BP PLC is higher than that of Shell. This implies that BP PLC is more efficient in managing receivables than Shell PLC.
The asset turnover gives information on how assets are used to generate sales revenue. The asset turnover for Shell PLC grew from 1.23 in 2010 to 1.45 in 2011. The values later dropped from 1.37 in 2012 to 1.21 in 2014. In the case of BP PLC, the asset turnover rose from 1.19 in 2010 to 1.37 in 2011. The values later dropped to 1.31 in 2012 and further to 1.22 in 2014. The ratios for the two companies show that the amount of asset turnover ratios deteriorated. This can be attributed to three reasons. The first reason is that the assets are not used efficiently. The second reason is that the company has a higher amount of current assets in the balance sheet as compared to non-current assets (Brigham and Michael 167). In most cases, sales are generated through the use of non-current assets and not current assets. The final reason is that the assets of the company are dilapidated. This implies that they cannot efficiently serve their purpose. A higher value of the asset turnover ratio is preferred to a lower value.
Efficiency is directly related to profitability. A company with a high level of efficiency is likely to have a high level of profitability. The two companies had a relatively equal level of efficiency. In terms of efficiency, an investor will prefer to invest in BP PLC than Shell PLC because it has a relatively high level of efficiency. The graph presented below shows the trend of the asset management ratios for the two companies.
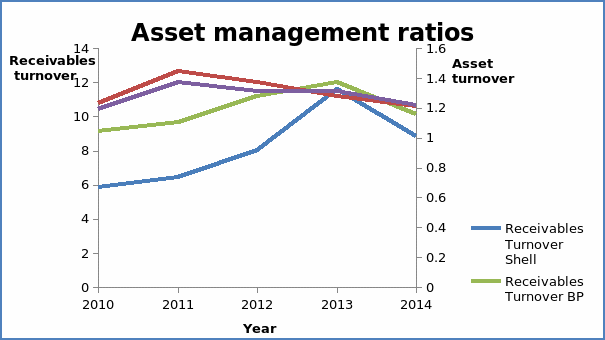
Profitability
Profitability ratios give information on the earning potential of a company. The ratios show the ability of the company to generate profit both in the long and short run. The ratios show how well a company employs its resources to generate returns. These ratios are important to a future investment because it gives the information on the number of returns they expect to earn from their investment (Brigham and Michael 56). The value of the profitability ratios fluctuated during the period for both companies. In the case of Shell PLC, the net margin rose from 5.32% in 2010 to 6.38% in 2011. The net margin for BP PLC was negative in 2010. This was caused by the heavy penalties that were imposed on the company for the oil spill. In 2011, the company recovered and reported a positive net profit margin of 6.65%. The ratio dropped to 2.98% in 2012. In 2013, the net margin rose to 5.92%, while in 2014 the value dropped to 1.05%. The trend of return on equity was similar to that of net margin for both companies.
The net profit margin gives information on the ability of the management to control the cost of running the business and pricing so as to generate profit (Brigham and Michael 59). A decline in the value of the ratio can be an indication that the company is inefficient. Even though some costs of running a business have to be incurred irrespective of whether a company makes sales or not, the management should be able to manage the costs by matching them to sales. This reduces the negative impact of unfavorable economic conditions. On the other hand, the return on equity shows the amount of profit generated from a unit of shareholder’s fund. Investors prefer to invest in an organization that generates high returns. The profitability ratios for the two companies were quite erratic. This can be attributed to the unpredictability of the oil and gas industry. The situation is caused by instability in the Middle East. It can be noted that the movement of the profitability ratios is the same for the two companies. This shows that the trends are caused by external factors that are inherent in the industry. The low profitability of BP PLC can be attributed to the penalties for the oil spill. The two companies seem to be struggling in terms of profitability. However, Shell PLC has a higher level of profitability than BP PLC. Therefore, an investor will prefer to invest in Shell PLC based on this criterion. The graph presented below shows the trend of the profitability ratios for the two companies.
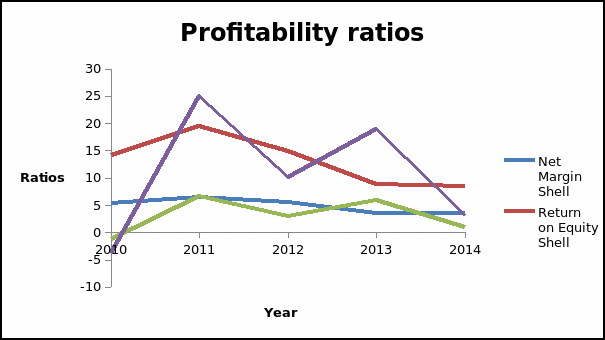
The graph shows that the two companies are trying to maintain a high level of profitability. There is a general decline in the profitability ratios.
Market value ratios
The market value ratios are quite significant to an investor because they provide information on the valuation of a company. The price-earnings ratio is a valuation measure that gives the amount an investor is willing to give out for each dollar of investment. The price-to-earnings ratio for the two companies fluctuated during the period. Shell PLC reported a decline between 2010 and 2011 and growth between 2012 and 2014. On the other hand, the price to earnings ratio for BP PLC rose in 2012, declined in 2013 and later grew again in 2014. The price-to-earnings ratio shows how a company is expected to perform in the future. Thus, if a company has a high value price-earnings ratio, then it implies that investors should expect higher returns in the future. In the case of the two companies, the values of the ratios are volatile and an investor cannot predict the future earnings. However, Shell PLC tends to have a relatively more stable price-to-earnings ratio than BP PLC. Therefore, based on this criterion, an investor should select Shell PLC for investment.
On the other hand, the price to sales ratio gives a comparison of the stock price of a company to sales. Thus, it shows how much an investor is willing to put on each amount of sales. The ratio is suitable for comparing the valuation of companies that operate in the same industry. The price to sales ratio for Shell PLC was stable during the period with a slight decline in 2012. In the case of BP PLC, the value of the ratio fluctuated during the period. Thus, Shell PLC tends to have stable and slightly higher values of price to sales ratio than BP PLC. An investor will select Shell PLC based on this criterion. It is worth mentioning that the price to earnings and price to sales ratios cannot be used individually to analyze a company. On their own, they do not give much meaning to the valuation of the company. Therefore, it is important to analyze other valuation ratios together with these two ratios before deciding on the ratio to invest in (Brigham and Michael 56). The graph presented below shows the trend of the market value ratios for the two companies.
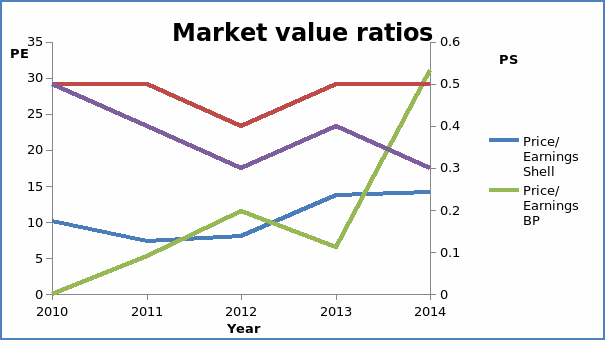
Conclusion
The paper carried a comparative financial analysis. The financial performance of Shell PLC and BP PLC was analyzed. Data for five years were used in the review. The paper focused on ratio analysis. The study shows that two companies have a high value of current assets. However, they may face difficulties when it comes to the use of quick assets. Besides, BP PLC has a relatively higher liquidity level than Shell PLC. In terms of leverage, Shell PLC has a low leverage level than BP PLC. This gives it room to grow in the future. Besides, Shell PLC has a higher solvency level than BP PLC. Under asset management, BP PLC is more efficient in handling accounts receivable than Shell PLC. Further, the two companies seem to have the same ability in managing assets. Therefore, BP PLC is more effective in asset management than Shell PLC. In terms of earning power, Shell PLC has a more stable and higher level of profitability than BP PLC. Finally, the market-based ratios show that investors should expect higher returns when they invest in the shares of Shell PLC than if they invest in BP PLC. Even though BP is a key player in the world of oil and gas and its shares are trading at a lower price, the financial standing of the company is quite unstable. Besides, the company is having a major lawsuit that is taking a toll on its performance. However, the company is having a high potential of performing well in the future. On the other hand, Shell PLC is having steady and high performance. The company is facing challenges that relate to the oil and gas industry. Therefore, an investor to purchase the stock of Shell PLC.
Works Cited
BP PLC. Annual Report and Form 20-F 2014. 2015. PDF. Web.
Brigham, Eugene and Ehrhardt Michael. Financial Management Theory and Practice, USA: South-Western Cengage Learning, 2009. Print.
Royal Dutch Shell PLC. Annual Report 2014. 2015. Web.
Technical Talent. 10 Largest Oil and Gas Company. 2015. Web.
The Telegraph. Latest Energy. 2015. Web.

