Introduction
Spectacle Hut is one of the largest optical chains in Singapore. Founded about 20 years ago, the firm has grown and it currently has 36 outlets across the country (Lin, 2016). When it started its operations, the marketing unit was keen on strengthening the brand as one that offers the best quality eyewear to meet a wide range of needs. Traditional marketing strategies were the only means of reaching out to the targeted audience during that time. Advertisements placed on television, radio, and newspapers were effective in enabling the company to reach out to its targeted customers. However, technology has been transforming marketing. As Giles (2018) observes, traditional marketing has been going through a transformation in the digital world.
Companies such as Spectacle Hut that had been using traditional marketing strategies are finding it difficult to maintain these methods of communicating with customers. As competition gets stiffer in this industry, these firms are forced to find ways of remaining sustainable in their operations (Burgess and Burgess, 2020). Although some of the traditional marketing methods are stiff effective in modern society, these firms have to find ways of transforming their communication strategies to ensure that their messages reach the targeted audience. In this paper, the focus is to explore Spectacle Hut’s traditional marketing transformation in a digital world.
Findings
When Spectacle Hut was launched, the digital age was yet to take shape. The dot-com bubble had just created disillusionment among many firms around the world that had speculated about the rapid growth of the internet and its benefits (Siikala et al. 2014). As such, emerging companies during that period, such as Spectacle Hut, had to rely on traditional marketing platforms to reach out to their targeted audience. As emerging technologies continued to create new communication platforms, marketers realized that they could not afford to ignore change. Numerous challenges started to emerge when a firm used purely traditional methods of communication (Davis and Gourdji, 2019). It became necessary for this firm to transform its marketing practices and thinking in response to changes in the technological and social environment.
Challenges Faced by Spectacle Hut’s Marketing Unit in the Digital Era
Spectacle Hut achieved rapid growth in the market during its first decade of operation. The massive success was partly attributed to its unique marketing strategies. The firm was mainly using television, radio, and newspapers as the main platforms for reaching out to its customers (Van, 2019). The use of billboards in strategic locations within the country also enabled it to strengthen its brand and promote its products. However, changes in the marketing environment have forced the firm to redefine its marketing approach. The impact of technology on consumer behavior, especially on the ease of access to information they need has meant that the firm has to be as accurate as possible in its promise to customers during promotional campaigns. The data-driven marketing intelligence has also made it possible for the firm to understand what customers need, develop a product that meets such needs effectively, before developing a promotional message that explains to customers how the product meets their needs.
Segmentation, targeting, and positioning (STP) have become important steps when developing a product and a promotional message. A firms has to start by identifying a specific segment of the market whose expectations it can meet in the best way possible. It then has to target the segment with the right products and a promotional message. The last step is to position its products in a way that reflects the needs and expectations of customers. The digital transformation that became entrenched over the past decade has created numerous challenges to the marketing unit of this firm.
One of the biggest challenges faced by those responsible for marketing Spectacle Hut’s brand in the digital era is the reduced popularity of traditional media platforms. In the past, the firm was sure that it could reach its targeted audience through any of the platforms it used (newspapers, television, radio, or billboards) daily. However, that is no longer the case in modern society. Amelie (2019) observes that the number of those who rely on radio and television for entertainment has significantly dropped. Newspapers are no longer the preferred platforms for disseminating news in the country and around the world. The younger generation prefers using social media to meet various needs. YouTube has become one of the most preferred platforms for entertainment, replacing television and radio. Facebook and WhatsApp are popular platforms of communication and sharing news. Those responsible for promoting the brand of this company can no longer rely on the traditional media platforms to reach out to the targeted audience because of these changes.
Making a radical shift from traditional marketing to digital marketing has also been a major challenge, especially because of the generational disconnect. At the helm of management of Spectacle Hut are baby boomers and generation X. This older generation trusts traditional marketing methods as being the most effective ways of reaching out to the customers. However, this company targets a wide segment of customers based on age. Generation Y and millennial are no longer using these platforms as regularly as would be desirable for marketers (Schaffer, 2020). Convincing the older senior managers that it is necessary to transform from traditional methods to digital platforms has been a challenge. Cornwell (2014) says that most of these senior members of society still view social media platforms as being too informal to be used for important official communication. In such cases, they will not allocate enough resources for digital marketing.
Lack of proper regulation of digital media platforms has been a major challenge for large corporations seeking to make a shift from traditional to digital marketing strategies. According to Iansiti and Lakhani (2020), unlike mass media where companies have the moral and legal obligation to ensure that they publish true information and that their publications do not unfairly harm others, social media has no such restrictions. Individuals can publish anything they want without considering the consequences of their actions. Domino’s Pizza was a victim of such reckless actions of individuals at a time when it was making a transformation into the digital world.
On April 13, 2009, two employees of Domino’s Pizza filmed a prank in the kitchen of the restaurant where they handled food in an unhygienic way and then proceeded to serve it to an unsuspecting customer. They then uploaded the video on YouTube, which at that time was gaining massive popularity around the world (Mehta and Pickens, 2020). The video soon became viral and customers started to avoid the food chain. At first, the top management thought that they could ignore the issue because it was only on social media. However, within two days, the firm was on the brink of collapse as customers opted to purchase products from rival firms. The chief executive officer had to use the same platform, and mass media as well, to clarify the issue and to assure customers that its products are safe for consumption (Hacioğlu, 2020). Such unethical practices still pose a major challenge as Spectacle Hut considers shifting to the digital platform.
The cost is another challenge that the marketing unit at Spectacle Hut has to deal with in this transformation. As mentioned above, some of the top managers of the company still trust traditional marketing as the most effective way of communicating with the targeted audience. As such, they would give it a priority when budgeting. Social media marketing has become expensive as these platforms continue to gain popularity. There has been a challenge in balancing the budget in a way that ensures that the firm uses both traditional and new platforms to reach out to customers (Whatmough, 2018). Favoring one platform at the expense of the rest would mean some of the targeted population may not be reached.
Spectacle Hut’s Traditional Marketing Transformation in a Digital World
The marketing unit of Spectacle Hut has been keen on ensuring that the brand of the company remains as conspicuous in the market as possible. It has been necessary to find ways of overcoming the challenges discussed above to ensure that strategies used to promote the company’s brand and its products are as effective as they were in the past (Smith and Zook, 2020). In this section, the focus is to discuss the actual transformation of the firm’s marketing practices and thinking that are occurring in response to the changes in the technological and social environment. The section also discusses the theoretical model that the firm embraced to ensure that the transition process is as smooth as possible.
Theoretical Analysis
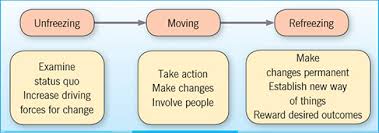
Introducing change in an organization is a challenging process. As Cunningham and Craig (2019) observe, in some cases, specific stakeholders may resist change when they feel that it may affect them negatively. Shareholders of a firm may resist change when they fear that it may affect their profitability in the market. Managers may impede change when they believe their position in the firm can be compromised. Similarly, employees may resist change when they feel that they may be rendered jobless or even demoted when the change is implemented. Others may reject change for the fear of the unknown. Every time a section of stakeholders in the firm resist change, they can frustrate the implementation process to ensure that it fails. As such, Cordelli (2020) advises that it is often critical to ensure that the process of transitioning from one system to another is conducted with caution. It is necessary to use a specific change model that can ensure that the process is conducted seamlessly. Kurt Lewin’s model of change was considered the appropriate theory that explains the path that Spectacle House took when transitioning from a traditional to a hybrid marketing approach.
The model identifies three stages that should be taken when effecting change. The first stage, which Lewin defines as unfreezing, involves preparing all the stakeholders for change. This important process involves explaining why the current strategies are no longer effective, the dangers of rejecting change, the benefits of the new system, and how it will be implemented in the organization (Ingrassia, 2020). It is critical to train employees on how to operate under the new system. Concerns of all stakeholders should be addressed at this stage. The second stage involves taking action to introduce change. In this stage, the management should guide the rest of the team in introducing the change. Further training may be needed when weaknesses among employees are witnessed. The last stage, defined as refreezing, involves making the change permanent. It has to be entrenched in the organizational culture to ensure that it becomes standard practice. Figure 1 below shows the model. The main benefit of this model is that it adequately prepares all the stakeholders for the change and minimizes cases of resistance as much as possible.
Transformation in Marketing Practices
When this company started its operations, traditional media were its primary platforms of advertisement. Radio, television, and newspapers were effective in enabling the firm to promote the brand. Figure 2 below shows a newspaper advert promoting the brand and products of the firm. The company also used billboards to promote the product in the local market. Within the first decade of its operation, these platforms proved effective in communicating with customers in the market. Most of the youths would be targeted through radio and television adverts. On the other hand, newspapers and magazines were used to target the elderly. Billboards were meant to target travelers.

The marketing unit realized that in the digital world, the firm could no longer afford to rely on traditional platforms to promote the brand and products. Newspapers and magazines were no longer as effective as they traditionally were because the number of those who used them regularly reduced. It started making a gradual transition into other forms of communicating with its customers. One of the new platforms that the firm started using actively were flyers. Figure 3 below shows a flyer used by Spectacle Hut to promote its products. Flyers were used in densely populated places such as schools, places of worship, or during major sporting events (Chang, 2018). It was particularly effective when the firm was targeting a specific geographic location. The top management was convinced that the new world order could not allow the firm to rigidly embrace traditional methods of communication.

The marketing unit had to find a way of dealing with the threat of increasing competition in the local market. The firm’s response to the increasing competition was to explore new markets around the world. The strategy meant that its marketing strategies had to focus on the global market. Although the firm did not completely abandon traditional marketing strategies, it had to embrace digital platforms to reach out to customers. The fact that the majority of major competitors such as Nanyang Optical, Eyecare Studio, Owndays, and Four Eyes were using these emerging platforms meant that this company had to rethink its marketing strategies (Christensen, Ojomo, and Dillon, 2019). The firm has been using pricing as a way of attracting customers, but that does not replace the need for it to embrace effective marketing strategies (Moon and Baer, 2018). It had no option but to integrate online platforms into its marketing strategies.
Facebook was one of the first digital platforms that the firm embraced. The platform was particularly effective in its international promotion campaigns. It was widely used whenever the firm was opening a branch. Figure 4 below shows an example of a Facebook advert that Spectacle Hut used when making an entry into the South African market. Before it considered making major investments in traditional media in South Africa, the company considered using Facebook as a way of communicating its presence to the target audience (Publishers, 2020). The decision was made after an initial market survey. The firm established that a significant majority of youths in South Africa, especially those who are in institutions of higher learning, are regular users of Facebook (Fryrear, 2020). As such, the platform offered the firm a perfect opportunity to reach out to them

YouTube has also become a major platform that the company is using in its international promotional campaigns. One of the benefits of YouTube over television is that a single commercial can be used to reach out to a global audience as long as the issue of the language barrier is addressed (Roth, 2020). In the current globalized society, the reasons why Singaporeans purchase spectacle is relatively the same as those that Americans, Britons, French, Germans, Chinese, and South Africans have. The global social environment has gone through integration as needs, especially of the youth, continue to converge. Instead of developing television commercials for each television station in different countries, a single commercial can be used widely through YouTube. Other platforms that this firm is actively using include Instagram and Twitter.
It is necessary to note that the firm’s current state in its traditional marketing transformation can be described as being a hybrid. The company has fully embraced digital marketing as a way of promoting the brand and products that can no longer be ignored (Guerra, 2019). A substantial budget is often set aside for the same. At the same time, the company still believes that traditional media also offers an effective means of reaching out to a specific segment of the market. Traditionalists, baby boomers, and generation X still prefer television, radio, and newspapers as reliable means of communication (Charan, Barton and Carey, 2018). They also form a significant number of those who need glasses for medical reasons (Batat, 2019). As such, the company is still using these traditional platforms to promote its brand and products.
Conclusions
The global eyewear industry has been growing gradually over years and Spectacle Hut has emerged as one of the players. As competition gets stiffer, the firm has been under pressure to find ways of ensuring that it maintains a strong brand and creates a pool of loyal customers. Besides pricing as a strategy of expanding its market share, the firm has understood the need to have a traditional marketing transformation in a digital world. The discussion above shows that the firm faced various challenges as it planned the transition process. However, the marketing unit finally settled on a hybrid model. Although digital marketing, especially through platforms such as Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram, was introduced, the firm did not completely abolish some traditional platforms such as television, radio, and newspapers.
Reference List
Amelie, K. (2019) Corporate language in online campaigning: candidate trump’s tweets in the 2016 presidential election campaign. London: McMillan.
Batat, W. (2019) Digital luxury: transforming brands & consumer experiences. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Burgess, C. and Burgess, M. (2020) The new marketing: how to win in the digital age. Los Angeles: Sage.
Chang, A. (2018) Lean impact: embracing innovation to deliver radically greater social good. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.
Charan, R., Barton, D. and Carey, C. (2018) Talent wins: the new playbook for putting people first. Boston: Harvard Business Review Press.
Christensen, C., Ojomo, E. and Dillon, K. (2019) The prosperity paradox. New York: Harper Business.
Cordelli, C. (2020) The privatized state. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Cornwell, T. B. (2014) Sponsorship in marketing: effective communication through sports, arts and events. New York: Routledge.
Cunningham, S. and Craig, D. (2019) Social media entertainment: the new intersection of Hollywood and Silicon Valley. New York: New York University Press.
Davis, S. M., and Gourdji, J. (2019) Making the healthcare shift: The transformation to consumer-centricity. New York: Morgan James Publishing.
Fryrear, A. (2020) Mastering marketing agility: transform your marketing teams and evolve your organization. Oakland: Berrett-Koehler Publishers.
Giles, S. (2018) The new science of radical innovation: the six competencies leaders need to win in a complex world. Dallas: BenBella Books.
Guerra, G. A. (2019) Organizational transformation and managing innovation in the fourth industrial revolution. Hershey: IGI Global.
Hacioğlu, U. (ed.) (2020) Digital business strategies in block chain ecosystems: transformational design and future of global business. Cham: Springer.
Iansiti, M. and Lakhani, K. R. (2020) Competing in the age of AI: strategy and leadership when algorithms and networks run the world. Boston: Harvard Business Review Press.
Ingrassia, L. (2020) Billion dollar brand club: how dollar shave club, warby parker, and other disruptors are remaking what we buy. New York: Henry Holt and Company.
Lin, M. (2016) ‘New vision for optical shops to stay competitive’, The Straight Times, 3 May, p. 1.
Matsui, A. (2019) Economy and disability: a game theoretic approach. Singapore: Springer.
Mehta, N. and Pickens, A. (2020) The customer success economy: why every aspect of your business model needs a paradigm shift. Hoboken: John Wiley and Sons.
Moon, G. and Baer, J. (2018) 10X marketing formula: your blueprint for creating ‘competition-free content’ that stands out and gets results. London: CoSchedule.
Publishers, V. (2020) Digital marketing essentials you always wanted to know. New York: Vibrant Publishers.
Roth, L. (2020) Digital transformation: an executive guide to survive and thrive in the new economy. Bloomington: Balboa Press.
Schaffer, N. (2020) The age of influence: the power of influencers to elevate your brand. London: HarperCollins Leadership.
Siikala, A. et al. (2014) Creating diversities: folklore, religion and the politics of heritage. Helsinki: Finnish Literature Society.
Smith, P. and Zook, Z. (2020) Marketing communications: integrating online and offline integration, customer engagement, and analytics technologies. London: Kogan Page.
Spectacle Hut Optometrists South Africa (2021) [Facebook] Web.
Spectacle Hut. (2021) About us. Web.
Van, B. (2019) The marketing bible for a digital world. Leuven: Lannoo Campus Publishers.
Whatmough, D. (2018) Digital PR. London: Emerald Group Publishers.
Yuen, B. (ed.) (2019) Ageing and the built environment in Singapore. Singapore: Springer.
