Introduction
The global steel industry is highly competitive as large multinational corporations struggle to expand their market share beyond their national borders. According to Lynch (2015), the massive growth in the global steel industry is directly attributed to the growth of various related industries such as real estate, transport, and automotive. The United States, European Union, China, and Japan are some of the largest global markets for companies in this industry. The management of Severstal has been keen on expanding the firm’s operations beyond national borders. The United States is one of the foreign markets that the firm has often considered exploring.
It is important to note that the industry has some challenges that it has to address when planning its expansion strategy. The slowing demand means that finished products sometimes stay in the warehouses of the company for longer periods than would be necessary, increasing the overall cost of operations (Peng & Peng 2014). The players in the industry are keen on finding ways of overcoming this problem in order to ensure that they remain sustainable in their operations. Thriving in a highly competitive industry require unique strategies that would make a firm’s brand and products more appealing to customers than that of its competitors.
Addressing the Topic
The global steel industry plays a critical role in the growth of other industries. According to Lynch (2015), the construction industry remains the leading consumer of products from the steel industry, using about 50% of the total amount of steel produced in the world. The transport sector also consumes a significant amount of steel in making cars, trucks, rails, shipbuilding and the aviation sector. It is estimated that the machinery industry also consumes about 14% of the amount of steel produced globally (Piekkari, Welch & Welch 2014). It is evident that the steel industry plays a pivotal role in the growth of other sectors of the economy. It means that slow growth in any of these sectors may have a significant implication in the global steel industry. The case study demonstrates that when there is an imbalance between supply and demand, in which case supply exceeds demand, then the industry will be affected negatively. In this section, it is important to conduct a thorough analysis of the global steel industry based on the case study provided.
Industry Analysis
The case study shows that some of the major concerns of the leading companies in this industry are uncertainty and volatility. Predicting the global demand is becoming increasingly difficult for the players in the industry, especially in an environment where numerous Chinese firms consider exportation as the best way of eliminating their dead stocks (Mueller et al., 2017). Although the industry has registered growth in the past three years, competition remains one of the biggest challenges in the current market. It is important to analyse this industry using appropriate models to understand these market forces and ways in which a firm can achieve a competitive advantage over its rivals.
Porter’s five forces
This model makes it possible to understand specific forces in the industry that would have a direct and indirect impact on the operations of a firm. One of the main concerns, as shown in figure 1 below, is the threat of new entrants. Although Severstal is operating in the global market, Russia, European Union, and North America are its main markets. The ease with which new firms can enter these markets is a major concern. The United States has created a business environment that makes it easy for firms to enter and exit the market with ease. Any possible entry of a new market would mean that the competitive rivalry would stiffen as they struggle to win the loyalty of the existing customers. This company has been keen on dealing with such challenges by exploring new markets around the world. The emerging economies in North Africa and the Middle East (MENA) region offer one of the most attractive growth opportunities in the global market.
The threat of substitute products, as shown in the case above, is significantly low. Steel products are important in the construction, transport and machinery industries. It is almost impossible for these industries to replace steel with other alternatives. Ojo (2018) argues that steel provides strength to structures, and it may not be possible to replace it with alternative products. The emergence of prefabricated low-cost housing structures may be seen as a major threat, but Lokkesmoe, Kuchinke and Ardichvili (2016) explain that the popularity of such houses is low because they cannot last long and may not withstand adverse environmental forces. These structures also use light steel, which means that they cannot eliminate the use of steel. As such, Severstal does not have to worry about the existence of substitute products.
The bargaining power of buyers is a major issue. The case study shows that the global steel industry is still reeling from the effect of the Great Recession of 2008. The slowing real estate industry in North America, Europe and some of the emerging markets is another major concern. As the number of suppliers continues to increase while the demand remains unchanged, customers have various options to choose from every time they want to make their purchases. They know that companies in this industry are desperate to make sales. Morrison (2016b) explains that in such a situation, buyers would want the best quality products in large quantities at the least price possible. They know that if one firm is not willing to offer them the best deal that they desire, they can easily switch to a rival firm and get what they need. Most of these customers are organisational buyers with immense negotiation power. A firm such as Severstal cannot afford to lose such important customers. As such, the only option is to give in to their demands, which would mean reducing the profitability of the firm.
The threat of the bargaining power of suppliers is another issue that this firm cannot afford to ignore. The main raw materials used in the manufacture of steel include iron ore, coke and limestone (Gaspar 2016). The unique strategic advantage that Severstal has over most of its global market rivals is that these raw materials are readily available in the local Russian market. It means that the company can easily have a strategic partnership with the leading suppliers of this product locally to ensure that it can acquire the materials at the lowest price possible. The case study also shows that this company has embraced the strategy of vertical integration. It has been acquiring firms involved in the mining of iron ore to help it cut the overall cost of operation. The strategy means that this firm does not have to rely on suppliers to have the materials needed for production. The reduced power of suppliers means that Severstal can afford to set competitive prices in the global market without compromising on its profitability.
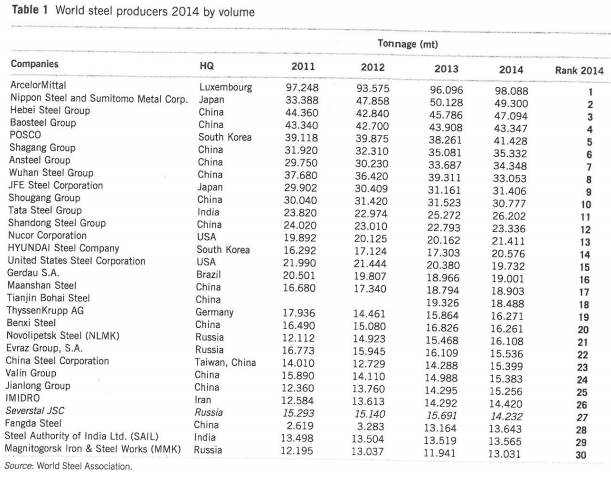
Competitive rivalry is the main issue that firms in this industry face, as shown in the case study. Severstal achieved market dominance through the acquisition of smaller market rivals. However, the emergence of numerous Chinese firms in the global market has been a major concern. The case study shows that there is an imbalance between the global supply of steel products and the demand. As new firms continue to enter the industry, the level of competitiveness continues to be stiff. As shown in Table 1 below, the global steel market has numerous players. ArcelorMittal S.A. is currently the world’s largest producer of steel products. Other top global brands include Nippon Steel and Sumitomo Metal Corp, and Hebei Steel Group in that order (Lokkesmoe, Kuchinke & Ardichvili 2016).
Other dominant players include POSCO, Shagang Group, Ansteel Group and Wuhan Steel Group. It is important to note that out of the top ten largest steel producers, six of them are Chinese firms. Lien (2016) explains that one of the biggest advantages that these Chinese firms have over their global rivals is cheap labour. It lowers their overall cost of production, making it possible for them to lower their prices and still make attractive profits. Severstal was ranked position 27, behind two other Russian firms, Nevolipetsk Steel ranked position 21, and Evraz Group S.A ranked position 22 globally. It shows that competition is not just stiff in the global market but also locally within the Russian market.
Objectives of Severstal’s Acquisition Strategy
The case study shows that Severstal has an ambitious integration strategy as a way of lowering the cost of operation and increasing its profitability in the market. The company acquired many firms in the United States and Europe as one of the best ways of entering these lucrative markets. According to Glowik (2017), when planning to enter a new market, it is critical to find the best strategy that would be suitable to the firm based on its financial capacity, human resource capacity and the level of competition in the market, foreign government policies and any other factors that the management may find relevant. The following were the objectives of Severstal’s acquisition strategy:
- To expand the market share of the company beyond the local Russian market and increase its profitability;
- To reduce the level of competition in the new global market that the company explored;
- To tap into the local market’s pool of experienced and talented employees by acquiring firms already in operation.
When analysing these objectives, Yip’s theory of internalisation would help understand the strategy that the company was using and why it needed to achieve the above goals. According to Lien (2016), Yip’s theory identifies four categories of drivers of internalisation. The first category is market globalisation drivers (Tuleja 2017). One of the main factors that motivated the management of Severstal to explore new markets was the level of attractiveness of some international markets in Europe and North America. The booming automotive industry in the United States, parts of Europe and East Asia meant that this company had a huge market in these countries (Ahmed & Alam 2017). It was convinced that exploring these new markets would improve its competitiveness in this industry and increase its revenue streams.
Yip’s theory identifies cost as another major globalisation driver. According to Glowik (2017), some companies consider exploring new markets because of the desire to lower the overall cost of operation. Severstal was keen on tapping into new skills and innovation in the United States and Europe. Bringing these highly talented individuals from their home country to work in a foreign country, which in this case would be from North America or Europe to Russia, can be expensive (Lien 2016). It is more cost-effective for the company to open up new plants in these foreign countries to tap into the pool of talented workers. As the case study shows, the company retained employees of its acquired companies in the international market as a way of maintaining continuity and improving the overall performance.
The third driver of globalisation is government incentives and policies in both the home market and foreign countries. Glowik (2017) explains that incentives are given by foreign governments to attract international investors may compel a company to explore the new market. In other cases, the local government may give incentive such as tax holidays to companies exporting the local products into the international market (Ahmed & Alam 2017). At the time when Severstal considered entering the American market, the United States government had created a favourable environment for foreign investors. The government was keen on fighting unemployment, and that meant foreign companies did not have to struggle to open up outlets in the country (Tuleja 2017). The management of this company made the decision to take advantage of the opportunity in this market.
The last driver of globalisation, as identified in Yip’s theory, is competitiveness. Glowik (2017) believes that one of the best ways of overcoming competition in the market is to consider exploring new global markets. The Russian steel market has been expanding over the years, and some foreign companies have already started operations in different cities in the country. As the competition becomes stiff, the company is forced to find new markets that can enable it to compensate for the lost market share locally and assure it of continued growth. Competing at the global level also makes this firm embrace best practices that would lower the cost of operations and enhance profitability (Tuleja 2017). Brands such as HBIS Grou, POSCO, and Shagang Group are an example of some of the top global competitors that this firm will face in the market. The management knew that the only way of ensuring that it remains sustainable in the current competitive industry is to explore new markets.
The strategy’s suitability as an International strategy in the strategic environment of the world steel industry
The strategy of Severstal in exploring new markets is effective in managing stiff competition in the steel industry. The choice of the country was particularly suitable for a company seeking to achieve global dominance in the market. The United States has one of the most robust automotive industries in the world (Piketty & Goldhammer 2017). It is one of the leading countries in the manufacture of vehicles, aeroplanes and various machines that use steel as raw material. The growing construction industry is another major market for steel manufacturers (Denson 2014). The internalisation strategy meant that this company moved closer to its customers, making it easy to negotiate for better long-term business deals (Glowik 2017). It is important to conduct an external environmental analysis of this market to determine the capacity of this firm to achieve the desired success. PESTEL analysis would be effective in examining the external forces in the United States that would have a direct and indirect impact on the firm’s operation.
The economic environment in the United States is suitable for Severstal as it seeks to expand its operation to the global market. According to Keller (2016), the United States is the largest economy in the world in terms of gross domestic product (GDP). It has large companies from the real estate sector to the automotive industry that heavily relies on steel. The purchasing power of these companies, such as Boeing, which is the largest aeroplane manufacturer in the world, is also high (Ahmed & Alam 2017). Domestic consumption of products made from steel such as cars, aircraft and housing structures is also high (Mooney 2017). It means that from the economic angle, the decision of this firm to explore this market was suitable.
The social environment of a country is another factor that Lasserre (2017) believes a firm should not ignore when planning to enter a new market. The ease with which a firm can integrate its diversified workforce defines its ability to achieve success in the market. The United States is one of the most socio-culturally diversified countries on earth (Ahmed & Alam 2017). The country has been dealing with the problem of discrimination over the past decades, but Kim and Mauborgne (2015) report that the current workplace environment in America is accommodating to people of diverse backgrounds. It means that this firm will not struggle to integrate parent country nationals and host country nationals in its operations.
The model identifies the political environment as another factor that a company cannot ignore in its normal operations. According to Busse et al. (2016), large corporations in India have accused politicians of direct interference with their operations during the electioneering period. Such issues where the political class interfere with the business operations of companies are rare in the United States (Glowik 2017). The country has an advanced socio-political system where the political class do not get engaged in operations of private businesses with the aim of paralysing their operations. Politicians focus on legislating laws that improve the workplace environment and promote foreign investment. As such, it was suitable for Severstal to consider opening up new plants in this country.
Technology is another critical environmental factor that defines the ability of a firm to achieve success. Using modern technologies helps in reducing cost, improving efficiency and productivity and lowering the time that it takes to make products available in the market (Lien 2016). A firm can be motivated to enter a new market because of the desire to take advantage of existing technological opportunities. The United States is one of the most technologically advanced countries in the world (Ahmed & Alam 2017). The government has been investing in education and innovation over the past several decades (Lien 2016). Some of the largest technology companies are headquartered in this country. It makes it easy for the company to find the right talent for its production and marketing strategies. The company is also able to collaborate with these technology companies to enhance its operations. As such, Severstal made the right move to come to this country.
The legal environment also plays a pivotal role in the success of a firm in a foreign country. According to Sainidis (2017), laws and regulations define how a firm can relate with its customers, suppliers, competitors, government agencies and the public. As a foreign firm, Severstal would be relying on legal systems and structures to protect it from unfair business practices. The United States has laws that protect the intellectual rights and needs of both local and foreign companies (Tihanyi et al., 2015). This company will not find it challenging to operate in the market because the legal system protects all firms irrespective of their nationality. The management should ensure that it understands these laws to avoid facing litigation because of failing to observe them.
Environmental concerns should not be ignored when analysing the external environment of a foreign country. According to Lewis and Mckone (2016), the global society is getting increasingly concerned about global climate change, global warming and general environmental degradation. The environment is one of the three main pillars of sustainability. In the United States, the government has enacted tough laws to regulate the number of greenhouse gases a company can produce within a given period (Reeves, Haanaes & Sinha 2015). The country also has strict laws that define how industrial effluent should be managed at a company level to avoid devastation to the environment. The management of Severstal should come up with its own internal policies to protect the environment and avoid any illegal pollution of air, land and water bodies. Figure 2 below identifies the six environmental factors that a firm has to consider when scanning the environment of a foreign country.
Conclusion and Recommendations
The global steel industry has been growing rapidly over the past decades with the growth of automotive, construction and related industries. The case study analysis shows that the steel industry has been facing various challenges such as uncertainty and unpredictability of the demand. It is evident from the case that some of the leading companies in this industry have registered net losses in their most recent financial statement. However, this firm has managed to make profits over the past years despite these challenges. Its top management unit has come up with unique strategies of lowering its production costs through vertical integration and increased mechanisation of its operational activities. When planning an internationalisation strategy, it is important for a firm to understand the forces that it will have to face. The management should consider the following:
- The marketing unit of Severstal should conduct thorough market research of any market that it plans to explore to understand forces that it would face in its operations.
- The firm should consider developing strategic partnerships with some of the leading consumers of its products in the global market. Toyota Corporation, Ford, Mitsubishi and Mercedes Benz are some of the leading vehicle manufacturers. Having a strategic partnership with these companies would ensure that the demand for its products remains high.
- The management should find a way of maintaining its good relationship with the Russian government without creating the perception that it is a major player in the country’s political arena. The current relationship with the regime should not compromise its ability to have a cordial relationship with future rulers or other foreign governments.
- The firm should continue to explore new markets through divestment. The diversification strategy can help this firm to remain sustainable when various market forces affect the steel industry.
Reference List
Ahmed, F & Alam, MA 2017, Business environment: Indian and global perspective, PHI Learning Private Limited, Delhi.
Ayden, Y, Demirbag, M & Tatoglu, E 2018, Turkish multinationals: market entry and post-acquisition strategy, Palgrave Macmillan, Cham.
Busse, C, Schleper, MC, Niu, M & Wagner, SM 2016, ‘Supplier development for sustainability: contextual barriers in global supply chains’, International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, vol. 46, no. 5, pp. 442-468.
Denson, A 2014, Cool Japan guide: fun in the land of manga, lucky cats and ramen: a comic book writer’s personal tour of Japan, Tuttle Publishing, Tokyo.
Gaspar, JE 2016, Introduction to global business: understanding the international environment & global business functions, 2nd edn, Cengage Learning, New York, NY.
Glowik, M 2017, Global strategy in the service industries: dynamics, analysis, growth, Routledge, New York, NY.
Keller, W 2016, Ultimate guide to platform building, Entrepreneur Press, La Vergne, TN.
Kim, WC & Mauborgne, R 2015, Blue ocean strategy: how to create uncontested market space and make the competition irrelevant, Havard Business School Publishing Corporation, Boston, MA.
Lasserre, P 2017, Global strategic management, Palgrave, London.
Lewis, A & Mckone, D 2016, Edge strategy: a new mindset for profitable growth, Harvard Business Press, Boston, MA.
Lien, K 2016, Day trading and swing trading the currency market: technical and fundamental strategies to profit from market moves, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ.
Lokkesmoe, KJ, Kuchinke, PK & Ardichvili, A 2016, ‘Developing cross-cultural awareness through foreign immersion programs: implications of university study abroad research for global competency development’, European Journal of Training and Development, vol. 40, no. 3, pp. 155-170.
Lynch, D 2015, Strategic management, Pearson, Harlow.
Mooney, C 2017, Inside the steel industry, Big Business, New York, NY.
Morrison, J 2016a, The global business environment: challenges and responsibilities, Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke.
Morrison, J 2016b, The global business environment: challenges and responsibilities, Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke.
Mueller, W, Silva, TH, Almeida, JM & Loureiro, AF 2017, ‘Gender matters! Analysing global cultural gender preferences for venues using social sensing’, EPJ Data Science, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. 1-16.
Ojo, M 2018, Uncertainties and risk assessment in trade relations, Business Science Reference, Hershey, PA.
Peng, MW & Peng, MW 2014, Global business, Cengage Learning, Mason, OH.
Piekkari, R, Welch, DE & Welch, LS 2014, Language in international business: the multilingual reality of global business expansion, Edward Elgar Publishers, Cheltenham.
Piketty, T & Goldhammer, A 2017, Capital in the twenty-first century, Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
Reeves, M, Haanaes, K & Sinha, J 2015, Your strategy needs a strategy how to choose and execute the right approach, Harvard Business Review Press, Boston, MA.
Sainidis, E 2017, Severstal: growth and consolidation strategies in a turbulent global steel industry, 11th edn, Pearson, Harlow.
Tihanyi, L, Pedersen, T, Devinney, TM & Banalieva, E 2015, Emerging economies and multinational enterprises, Emerald Group Publishing Limited, Bingley.
Tuleja, AE 2017, Intercultural communication for global business: how leaders communicate for success, Taylor & Francis, New York, NY.
Zajda, J (ed) 2015, Nation-building and history education in a global culture, Springer, Dordrecht.
