Nature of product and service
The Apple Company is widely recognized, and one of the leading companies in developing and distributing advanced information and communication products. Apple has been at the forefront in terms of developing new products. This is the reason why the company manages to emerge as one of the most competitive players in the information and communication industry. There are three key areas in which the company manages its operations. These are designing, manufacturing, as well as the marketing of technological products. Apple deals in a number of products, which include personal computers, mobile communication and media tools, and portable digital music players. The company also develops and markets a wide range of software used to support the functioning of the media and other communication tools that are manufactured in the company, besides developing and distributing periphery products for servicing the communication tools (Markoff, 2013).
The Apple computers form the first line of products that were produced and distributed by the Apple Company in the early years of its operation in the global information and communication industry. The mobile devices have come out as the new set of products that are at the center of focus as far as the competitiveness of the company in the new markets is concerned. Apple has also concentrated on the development of software used in the communication devices and tools that are produced and distributed in the market (Markoff, 2013).
Apple has been proactive in terms of adapting to the changes and demands of technology in the broader industry, which is the reason why the stability and successful operation of the company in the market are guaranteed. Technology adoption is the key defining factor of differentiation in the diverse generation of products that are released in the market by the company. Due to its continued investment in research, Apple manages to release new technologies in the market at close intervals, a factor that keeps other competitor companies like Samsung on toes as far as competition for the global markets is concerned (Lee, 2013).
The difference in pricing is one of the factors of competitiveness in the industry in which Apple operates. It has been noted that pricing is not only determined by the level of technology that is applied in the manufacture of products or the nature of services that are provided by the company but to a greater extent the external forces in the market. This affects the propensity of consumers to consume technology products. On this basis, it can be said that other competitor companies in the market like Samsung have managed to gain a wider market share through the utilization of pricing as a factor for accessing the market. The prices of Samsung products, such as tablets, are far much lesser than the prices of iPads (Lee, 2013).
Market trends
The marketing environment in information and communication technology is highly dynamic. The level of dynamism in the industry is dictated by the number of players in the industry and the demand for information and technology products in the market. There is a resounding rate of shifting demand in consumption trends in the personal computer and information technology industry due to the quick pace at which technological changes take place in the industry. Consumers often keep seeking for new products with new technological features. The consumption of goods in the technology industry is mainly shaped by the level of utility and the prices of goods and services in the industry.
The demand for products that deploy a high level of technology keeps rising. However, the issue of prices keeps pressure on the consumers in the sense that they cannot easily afford the highly technological products, such as the ones produced by Apple at the prices that they can afford to offer. However, in certain markets, there are indicators that the demand for Apple iPhone 5, which is one of the latest technological products that have been released in the market by Apple, is quite high. The demand does not match the supply, meaning that the market equilibrium is set higher on the demand and supply curve. This can be explained by the demand and supply curves below (“Lack Supply of Apple iPhone 5”, 2012).
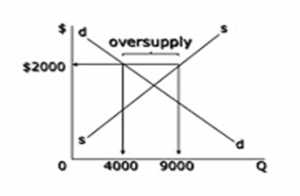
The increased demand for the supply of iPhone 5 results in the rise in the prices, which in turn attracts more supply of the iPhones. This results in the oversupply of the product in the market.
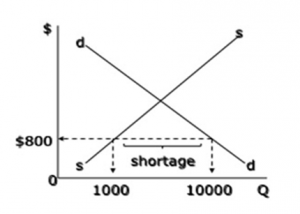
Figure 1.1 denotes the shortage in demand, which works for the rise in the price of the commodity in the market.
The general trend in the market denotes the likelihood of reduction in prices of products of Apple as the company seeks to reduce the pressure that mounts on its performance due to the high prices that are attached on its products. However, the demand in the market will remain to be a key factor in the determination of the rate at which Apple adjusts the prices of its new inventions in the market.
Production/Supply Process and Costs
Efficiency in supply and production is critical in sustaining the operations of a company in a competitive market. Apple has been at par with changes and the demand in the industry and the market due to its strategy of enhancing diversification of production and the formulation and execution of a supply chain that favors the operations of the company in the competitive market. It has been noted that the company has chosen to expand its production capabilities in other regions as a way of minimizing the cost and time of production. This ensures that products are developed and availed in the market at the required time, and that customers do not miss out on the products that they demand for in the market.
Most of the raw materials of Apple are acquired from countries in Asia. The company has, therefore, established a network with its suppliers, which ensures that quality and patterns of delivery are sustainable. The company has also established several production plants in the Asian region, which help in reducing the cost of transporting materials to the mother plant in the United States. The company, instead, enhances production in areas that have a relatively closer proximity to the raw materials (Bibey, 2013).
The other important factor to note is that Apple has established retail stores in all the regions in which it advances the marketing of its products. The Apple stores are quite critical as far as stocking of products in the distant markets are concerned. The stores also aid in giving extra services to the customers; for instance, advising the customers about the best way to make use of the products. The Apple stores also help in responding to the needs and concerns of customers. Besides the real stores, the company has also developed online or digital stores that help in the marketing of its products (Farfan, 2013).
Structure of the industry/ Market
The global information and communication industry is an industry that is highly concentrated in terms of the wide range of technologies that are demanded for in the market. The industry is broad and has a lot of players who have proven to be competitive. In the personal computer industry, which is a sub industry in the larger information and communication technology industry, the Microsoft Corporation and Apple are deemed to be the main competitive firms.
However, there are a substantial number of players when it comes to the broader industry. These include Google, Motorola and Samsung among other companies. Players in the industry keep coming up as the demand for technology keeps rising. The rate at which the industry attracts other players, who become competitors to the main firms in the industry like Apple, is quite high. The upcoming companies in the industry keep venturing in specific technologies, unlike the giant companies in the industry like Apple who ventured in the diverse segments of the industry, a factor that increases the scale of their competitiveness (Hill & Jones, 2010),
According to Hill and Jones (2010), competition in the information and communication industry is driven by two factors. These are the forces that originate from the industry and the external forces that keep molding in the market. The internal forces in the information and communication industry come from the deeper seated competition in the industry. Firms in the industry often compete by virtue of technology change and adoption. Apple, for instance, has managed to remain a vital competitor in the industry due to the rate at which it has been able to invest in research and development, which enabled it to come with a new ray of innovative technologies in the market.
A similar thing is happening to other firms in the market, which are striving to match the rate of innovation that has been attained by Apple. The development of new and more advanced software and hardware is determined by the scale at which the competitiveness of firms in the industry. The value attachment to any company by customers is often judged by the level of innovation that is attained by the company in the nature of products and services that are produced and marketed by a given company in the industry.
According to the trends in the market, which denote a lot of dynamics, it can be argued that there is no firm in the industry that has been able to attain absolute competitiveness. However, a certain level of oligopoly has been attained by dominant companies in the market like Apple, Microsoft and Samsung. These companies deploy several strategies. A close comparison of prices by the key players reveals a state in which the key competitors keep adjusting their prices relative to the prices of other competitors. An example is the adjustment of the prices of iPads due to the adjustment of the prices of Samsung galaxy tablets, which had gained dominance in terms of the sales in the market (Lee, 2013).
Government Role
The modern economy, especially in the developed countries like the United States, has seen the reduction in local and international barriers in order to enhance the production capacity of industries. As has been observed in the contemporary times, governments are increasingly seeking to liberalize the information and communication industry because it is seen as one of the most critical industries in the prosperity of the 21st century economy. The role of the United States federal government in the economy is to ensure that the economic policies are favorable to business companies because it is the business companies that drive economic growth (Thierer, 2012).
It can, therefore, be said that the Apple Company finds a favorable environment in the United States. However, the globalization of the economy has resulted in the liberalization of the trading environment and the need for the company to enhance its competitiveness through venturing in the external markets. This makes the company to be exposed to critical aspects of regulation in the external market, which put a lot of pressure on the company. These factors include the exorbitant taxation regimes in the developing world, which forces Apple to adjust the prices of its products.
These result in the reduction of the prices tagged on Apple products. This implies the reduction of the levels of anticipated profits due to the regulations that are imposed on the operations of the company in the foreign markets. On the other hand, it can be argued that the liberalization of the trading environment acts as a basis on which governments pacify the regulatory environment as a way of promoting international trade. Regulation is, therefore, bound to be a less critical barrier in as far as the enhancement of the operations of Apple is concerned (Thierer, 2012).
Business environment
Information and communication is the most important sector in as far as the advancement of the modern economy is concerned. Both the domestic and international economic environments are volatile in terms of the level of competition and the interplay between the operation of the company and the factors of production in the economy. As one of the most economically advanced economies in the world, the essence of technology is quite critical as far as the sustainability of the economy of the United States is concerned. The main challenge of the company is the mounting competition from other companies in the domestic and international market, as well as the external forces in the economy like inflationary pressures and issues of environmental sustainability. This results in the crush of the market outcomes, thereby impeding production.
The Apple Company bases its operations in the United States. However, as part of leveraging the complex supply chain and its implications in the business outcomes of the company, Apple has diversified its operations in the sense that the company no longer centers on a centralized production. The company has opened production plants in several markets that seem promising like China, which helps to expand its productive capacity besides helping the company to easily access new markets in the international economy (Gitman & McDaniel, 2009).
The issue of economic globalization remains critical to the advancement of operations by firms across the world. Economic globalization has opened up the market to an extent that Apple has successfully penetrated external markets in Asia, South America and Africa, besides North America and Europe which have been the main markets for the company. However, there is also a negative side to the issue of economic globalization and the liberalization of trade in the information technology industry. The liberalization of trade enables other firms to access the markets that have been dominated by Apple in Europe and North America. These companies use other comparative marketing features like pricing to take advantage of the prevailing conditions in the economy to win customers (Linden, Kraemer & Dedrick, 2007).
Firm/Industry Location
Owing to the prevalence of massive competition in the contemporary economy, location factors play resoundingly in the competitive operation of a firm in the contemporary industry and markets. Location factors are determined by several factors that are drawn from the specific area in which the economy is located. For instance, the location of the Apple plants in China have been attributed to the fact that ethical considerations in the Chinese economy are far much less considered compared to other countries in the region. This is an attractive factor in the operation of the company productive facilities in the region. However, several unethical practices have been reported in the Apple plants in China, which have attained the reputation of the company in the market (Sawayda, 2011).
The optimal operations of Apple are based on parent country operations, which form the largest market for the company’s products and services. The United States offers a number of economic incentives to the company. Among the factors is the protection of the local firms from liberalization of the international economy through economic policies. This gives Apple a competitive edge over the foreign information technology companies that operate in the parent market. Location factors keep changing with the changes in the external and internal economic derivatives in the given location.
However, business incentives are highly derived from the localized operations. This is the reason why the company gives a greater preference to the United States as the key operating market, irrespective of staging other operations in other regions of the world. The question of the advancement in technology and the nature of quality that is embedded in the products of the company is another explanation for the reasons why the activities of the company are highly concentrated in Europe and North America. Income inequalities in other regions of the world make it harder for the company to fully access other markets in the developing regions of the globe (Gitman & McDaniel, 2009).
Business and pricing strategies
Each company in the industry keeps coming up with strategies that can help it position its activities in the information and communication industry because of the nature of competitiveness that prevails in the industry. Apple is a successful company in the industry and its success is attributed to the ability of the company to be strategic in its operations. One of the key business strategies that perhaps fully define Apple Incorporated in the information and communication industry is investment in innovation and focus on litigation as a way of protecting its innovations (Mourdoukoutas, 2012). Innovation is, therefore, one of the main defining factors of business positioning in the company.
The quality and high level of continued innovation is what brought the company, under the leadership of Steve Jobs, to the limelight. Apple competes through innovation, which is evident in the kind of business leadership of the company and the level of utility that can be derived by customers in the products and services by the company. Apple has also given a sound amount of attention to the influential management of its supply chain structure. The company gives a considerable amount of attention to the suppliers of the company owing to the fact that the suppliers of the company are drawn from different countries. This ensures that the company gets quality and timely delivery, which enables it to fulfill the demands and needs of customers in the products that are released in the market (Meyer, 2012).
The issue of pricing has come out to be one of the derailing factors for Apple, especially when it comes to the penetration of the company’s products in the developing and newly industrializing markets in the world. With a long focus on quality as a basis on which prices of the Apples products are determined, it has been discovered that other companies in the market take advantage of the pricing model of Apple in the market. The company is, therefore, considering other factors like the application of corporate strategies that can help in expanding the operations of the company in the emerging markets (Moorman, 2012).
Entrepreneurial ability of managers
Business leadership is an important quality of the leadership of any company in any given industry. The culture of innovation that prevails in Apple today is attributed to entrepreneurial qualities of the leaders of the company. One thing that has to be noted in as far as the position of the Apple Company in the contemporary market is concerned is that the company would have rarely attained the culture it has developed today without able leadership. Leadership in this sense refers to not only the ability of the chief executives of the company to model the operations of the company, but most importantly the molding of the internal operations environment of the company, which enabled the employees of the company to effectively participate in steering the operations of the company to the contemporary heights (Bhargava, 2011).
Apple has two leaders, Steve Jobs and currently Tim Cook. Steve Jobs is the molder of the innovative culture through the creation of an environment that fully backed innovation. By leading from the front, Job was able to steer the employees in coming up with the innovations that are evident in the products of the company today. Such a culture has continued to prevail and define the company even after the demise of Jobs. Protection of the company has also been a key feature of the leadership of the company in the contemporary times when there are a lot of issues of competitiveness. Steve Jobs was strict to an extent that he confronted companies that seemed to unfairly compete with Apple through infringing on the copyrights and patents of Apple. On the other hand, Tim Cook and the contemporary management team, by building on the foundation of Jobs, have centered on improving the corporate culture of the company and molding the marketing strategies to penetrate the market and minimize internal and external competitive pressures in the economy (Moorman, 2012).
References
Bhargava, R. (2011). Steve Jobs and the 4 counterintuitive business strategies of Apple: And what we all might learn from them. Web.
Bibey, C. (2013). Apple Inc. (AAPL): This supply chain bombshell may kill shares today. Web.
Farfan, B. (2013). Global supply chain challenges, rumors, disruptions for Apple, Amazon, IKEA, Nike and Forever 21 – Retail supply chain ignorance now a common defense (AAPL, AMZN, NKE, WMT). Web.
Gitman, L. J., & McDaniel, C. D. (2009). The future of business: The essentials. Mason, OH: South-Western Cengage Learning.
Hill, C. W. L., & Jones, G. R. (2010). Strategic management theory: An integrated approach. Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin.
Lack Supply of Apple iPhone 5. (2012). Web.
Lee, J. (2013). Samsung blows Apple out of the water when it comes to smartphones sold. Financial Post. Web.
Linden, G., Kraemer, K. L., & Dedrick, J. (2007). Who captures value in a global innovation system: the case of Apple’s iPod. Irvine, CA: Personal Computing Industry Center. Web.
Markoff, J. (2013). Apple Incorporated. The New York Times. Web.
Meyer, C. (2012). Apple Business Strategy 2012. Web.
Moorman, C. (2012). Why Apple is a great marketer. Forbes Magazine. Web.
Mourdoukoutas, P. (2012). Can Microsoft adopt Apple’s business model? Forbes Magazine, Web.
Sawayda, J. (2011). Apple Inc.’s ethical success and challenges. Daniels Fund Ethics Initiative, University of Mexico. Web.
Thierer, A. (2012). Regulatory, anti-trust and disruptive risks threaten Apple’s Empire. Web.
