Abstract
The world of business is in the midst of a revolution in which the key ingredient is control and Management. Every company that wants to move forward must embrace Information technology-based
The purpose of businesses is the maximization of goals especially in this era of corporate sustainability and to achieve this company will need to move with technology otherwise the train of existence will leave them. Companies in countries like Kuwait need to develop the capacity to utilize Information Technology to improve product and services choice among customers to give pleasure and satisfaction. This independence, pleasure, and satisfaction will be determined by the individual perception of the chosen product or service and the preference in the choice of the same.
Therefore, to accommodate the rapid changes occurring in the business world, and information technology web-based inventory system should be utilized in the management of stock. This case study describes the role of IT and the implementation of a prototype IT developed by a student at the University aiming to help DDD to develop technology-based inventory control. Collaborating with the management, investigated this tool in the context of managing stock control. The main purpose of stock control is to ensure the company has the right quantity of stock. This will be determined by the number of sales made during a period and the customers’ period.
I conclude that the Information technology system enhances companies managing of stocks and inventory, increases collaboration and sharing sock information among employees, and increased profitability by reducing the cost of stock control and loss due to employees stealing. I have also learned that the management DDD appreciates the system as a tool for successful stock control has described effective methods to be implemented. Finally, I was able to evaluate the usability of the information system and am using this feedback to continue the iterative process of developing the Information technology-based system.
Problem statement
Introduction
This paper describes the perceptions & opinions of The Development of an Information system for Inventory Management Study factors affecting their drives & examination.
Background of the project
Inventory management is the active control program, which allows the management of sales, purchases, and payments. It is involved in maintaining the appropriate level of stock in a warehouse. It also includes a retailer seeking to acquire and maintain a proper merchandise assortment while ordering, shipping, handling, and related costs are kept in check. On the other hand, Information System (IS) is the system of persons, data records, and activities that process the data and information in a given organization, including manual processes or automated processes. So the application of Information System for Inventory Management Study gives dynamism to a company. Thus, the study along with information systems focused on why and how technology can be put into best use to serve the information flow about the stock level within an organization.
Background of the Organization Chosen
DDD is a medium-size business located in Kuwait It was established in 1994 by owner Mohammed, and ever since has been involved in the retail and wholesale of oil. At present, DDD has a permanent staff of twenty employees and from time to time, a temporary staff is hired on contract to work on site.
The company’s major difficulty of operation deals with the stock inventory management of oil products. The stock inventory process was based on a traditional and manual process which was done using stock cards for recording and monitoring stock levels. Sales were used to be recorded in a general bill or stock book.
Therefore, this situation presented several troubles. The manual process of stock-keeping was very lingering and complicated to perform since to carry out the process only one person was assigned. In addition, stock cards that were used to store information about items were sometimes be damaged, distorted, or misplaced. Another problem was that no computerized database system was present to support the data entry, storage, and referencing of the large volumes of stock items, to provide for data timeliness, accuracy, integrity, and security. There was also no network available for more than one user to share data, applications, and hardware to improve the efficiency and productivity of business processes. Lastly, all these matters increased the lack of motivation in employees because of the rising workload.
The rationale of the Research
In traditional Inventory Management, orders are the only information that the firm exchange, but the information system now allows firms to share demand and inventory data quickly and inexpensively. It has a substantial impact on inventory management. The application of this system, especially in the growth-oriented industries, has significantly lowered the time and cost of keeping records about inventory stock and control over them. Because of this success story, there is now a general belief within industries that capturing and sharing real-time demand information is the key to improved management of inventory.
So, the need stimulated analysis of the impact of Development of an Information System for Inventory Management Study. The purpose of this dissertation was to test this belief by rigorously measuring the value of information systems in the field of inventory management, which contributes to the reduction of lead times and shipment frequency, by reducing the time and cost to process orders.
Objectives of the Research
Considering these matters in view, my dissertation paper broadly aims to provide a synopsis of the key developments, to reflect on emerging trends, and to address some frequently asked questions about this literature. I attempt to keep the technical aspects of the Information System in check and focus instead on the key implications of this literature for Inventory Management.
Scope and Limitation of the project
My focus is on the Management Information System (MIS), which has been used extensively by both empirical and theoretical researchers. I aim to explain the driving forces for using information systems for inventory management. Here I have discussed major developments concerning customer requirements, Stock level, shortage or surplus of stock, and networked inventory management. Reviews some decision systems for inventory management, and compares traditional inventory management to information systems for inventory management. Summarizes the results of the study, and provides an outlook on further research.
This project will only focus on the design and implementation of a stock inventory database, graphical user interface, and peer to peer network for use only by the staff and management at DDD Furthermore, such a system would only deal only with the stock inventory process of managing transmission parts for the industrial chemical and lab equipment.
Detailed Gantt chart
Relevant literature review
Overview of the Topic
Inventory is more than a substantial investment; it is usually a company’s largest asset. Smart companies have found that the ability to manage this asset is a key factor in their ultimate success or failure. The major types of Inventory Management solutions are as follows:
Barcodes
A barcode is an encoding tag or label that is placed on all merchandise that allows computers to track and ring up products much faster and more accurately than if it were to be performed by hand. Using barcodes can reduce the amount of training time needed for employees. A scanner is fairly simple to operate, and automatically does the computation for you.
Max Patel described the use of barcoding and barcode scanners have transformed operational efficiencies of a phenomenal number of businesses both large and small.
John Schreibfeder also states that bar codes can help your business by providing value-added services to customers, also improving inventory accuracy, and making employees more productive. There are many more advantages including operational efficiency, better customer service, and improved visibility of key business information to management.
But there are also disadvantages of using barcodes such as you have to be able to see them, the bar code cannot be written on or defaced, you cannot change the data once they are printed and also they take up space on the object they are printed on.
Barcodes today are becoming outdated as newer technologies exist and there is a lot of fierce competition out there in trying to bring in the customers.
RFID
Radio Frequency Identification allows a business to identify individual products and components, and to track them throughout the supply chain from production to point-of-sale.
As Charles Atkinson as said in his article, instead of using technology to track inventory as it is moved, RFID counts inventory automatically from a remote location. This is superior to perpetual inventory tracking or perpetual inventory for a couple of reasons. Most notably is that RFID accounts for shrinkage. RFID counts what is there, and it can tell you exactly where it is.
Mark Henricks and Mark Roberti state that RFID is an innovative technology similar to the Internet and how it has revolutionized and many businesses today are introducing RFID to better solve inventory management solutions.
There are many advantages of RFID, there is inventory efficiency because the line of sight is not required to read RFID tags, return on investment although the cost may be high at first, the total cost of ownership should go down over the years and provide a return on investment, vulnerability to damage minimized barcodes can be damaged in many ways.
But there are also disadvantages to RFID, there are dead areas and orientation problems there may be certain areas that have weaker signals or interference. In addition, poor read rates are sometimes a problem, security concerns because RFID is not a line of sight technology like barcoding, additionally, when RFID is used for high-security operations such as payment methods, fraud is always a possibility and there are many more to name such as proximity issues, high costs, etc.
Online Inventory
By using the internet to store your valuable inventory information, you will realize several significant advantages over traditional paper or home PC-based solutions.
The Internet Advantage: access anytime, anywhere, internet access can now be found in even the farthest reaches of the world, which means you can get to your information from home, work, or even across the continent, if and when you need it, offsite storage of the actual inventory data which means that no matter what happens to your computer, your property, or even the surrounding community, you’ll still have your complete inventory information to assist you, no special software to install or upgrade, all that’s required is a web browser. You can access it from any computer that has a web browser and an Internet connection.
But here are some disadvantages of online inventory as it more relates to drop-shipping. The first is inventory, your supplier may not have an accurate online accounting of inventory and you may end up selling an item your supplier cannot send to your customer, the second disadvantage is timing and control, your supplier may be slow to ship for various reasons and you have little control over the speed of shipping or the accuracy of the shipment itself.
Slow shipping is one of the biggest complaints of customers online, shipment accuracy brings us to the third problem with drop-shipping: returns, making returns of drop-shipped items, for whatever reason, is a huge hassle for the seller – especially if that retailer wants to hide the fact that he/she is drop-shipping to the customer.
The biggest of the disadvantages to drop-shipping is pricing. Drop-shipped items are usually at a higher price-point compared to true wholesale pricing (pricing based on bulk purchases). So many sellers may find themselves out-priced by those who inventory instead of drop-shipping.
While for many retailers online, drop-shipping is the way to do business most effectively, many find that it has too many problems for their particular situation.
Stockless Inventory (Just In Time)
The term “stockless inventory” implies the elimination of inventory. In a stockless system, virtually no space, inventory, or staff members remain in a storeroom because storage service is contracted to a distributor.
Rene T. Domingo talked about the stockless operation and how it is necessary for a competitive environment, also talking about the negativity of inventory.
Too much money is tied up in inventory that is still waiting to be used (LaPlante, 1992).
JIT is every component in the manufacturing system arriving just in time for it to be used. Since the products arrive just in time there is no need for stock holding facilities of any kind.
Since JIT is a stockless production and does not allow room for defects or error having trustworthy reliable suppliers is an important factor.
Just-in-time manufacturing can be a positive influence on a company. However, there are many risks associated with attempting to implement JIT manufacturing techniques. When looked at it appears to be a very simple, quick, and easy thing to do. In reality, it is a very complicated technique that takes long-term commitment and an initial cost with no guarantee of success. If implemented successfully it would eliminate waste, make the company more productive and more efficient.
Advantages of stockless are decreased inventory costs throughout the value chain, rolling out a true build-to-order system will lead to stockless inventory solutions and stockless suppliers, decreased production costs throughout the supply chain with sophisticated collaborative planning and execution processes, and real-time information provided throughout the supply chain, production can be better planned and capacities optimally streamlined and there are many more including increased customer orientation, shortening vehicle production and reliable delivery lead times allows for higher product individualization, quality relationship with suppliers, no downtime, possible increase in profits and increased flexibility for suppliers. (but each will differ in each company)
As with the others, there are disadvantages of stockless, although the advantages outweigh the disadvantages, the disadvantages can hurt the company. The disadvantages are a long-term commitment, possible large initial cost with no short-term returns, problems with a supplier that can cost the company large amounts of money, and the risk of never successfully implementing JIT.
In this research study, we will try to analyze how inventory management can impact an organization through these major solutions with the help of an Information System. For this purpose, this literature review includes writings, research, and scholarly opinion concerning the description, measurement, and evaluation of “Information Systems for Inventory Management”. It provides the background needed for managing and controlling inventory in a firm through an information system and how its factors most significantly influence organizational success.
The views and opinions of the contemporary business world concerning inventory management, relevant Information technologies, and Models, organizational strategies, and productivity are discussed. Together, the historical theories and modern techniques form a solid basis upon which to design a research study to further refine the causal relationships affecting Inventory Management.
Literature Review
Inventory Management that is based on an information system has brought many scholars to give their valuable opinion about it. Some mentionable quotations about this literature have been discussed below.
“Inventory accuracy starts with an understanding of the conditions under which errors occur and ends with error-resistant processes, intelligent use of information technology, a well-trained and highly motivated workforce, and an ongoing process of continuous improvement. In between, there’s cycle counting, root cause analysis, process evaluation, user interface design, procedures, employee training, accountability, control methods, process checks, audits, exception reporting, transaction techniques, measurement, counting methods, bar codes, RF systems, speech-based technology, light systems, and software.”
Inventory control is concerned with minimizing the total cost of inventory. This term is often used as stock control also. The three main factors in the inventory control decision-making process are:
- The cost of holding the stock (e.g., based on the interest rate).
- The cost of placing an order (e.g., for row material stocks) or the set-up cost of production.
- The cost of shortage, i.e., what is lost if the stock is insufficient to meet all demand.
The third element is the most difficult to measure and is often handled by establishing a “service level” policy, e. g, a certain percentage of demand will be met from stock without delay.
The ABC Classification: The ABC classification system is to grouping items according to annual sales volume, in an attempt to identify the small number of items that will account for most of the sales volume and that are the most important ones to control for effective inventory management.
Reorder Point: The inventory level R in which an order is placed where R = D.L, D = demand rate (demand rate period (day, week, etc), and L = lead time.
Safety Stock: Remaining inventory between the times that an order is placed and when new stock is received. If there are not enough inventories then a shortage may occur.
Safety stock is a hedge against running out of inventory. It is an extra inventory to take care of unexpected events. It is often called buffer stock. The absence of inventory is called a shortage.
To have a strong command and control over all these facts of inventory management, an organized Information system (IS) is mandatory. Information systems (IS) make it possible to improve organizational efficiency and effectiveness, which can provide a competitive advantage.
An autonomous information system design for inventory management is proposed for the efficient supply chain management. By using rewritable RF-ID tags instead of popular bar codes as a job ID, which represents a manifest of an item, each processing system directly communicates with the tag information of each item, and autonomous item management can be realized. The following four basic functions are designed, to introduce new items, link each item to processes, update item information, and acquire process records. The prototype systems, which handle RF-ID tags as processed items, selecting correct items and processes according to a production plan, are confirmed. (Itsuki, R.; Shibata, H.; Ikkai, Y.; Komoda, N.: the autonomous information system design for item management using rewritable RF-ID tags in the supply chain)
Inventory control software eliminates the need to individually change prices one inventory item at a time. Through a global price change window, one can set rules and conditions for inventory categories that require price updates. Utilizing pricing methods (like Markup and Margin percentages), one can quickly do mass changes to inventory without the tedious effort of manual data entry.
Discussion on Literature Review
From the above discussion on the literature review, we can spread our analysis highlighting two important issues.
- Why online inventory is the best choice?
- How inventory management can impact an organization?
By establishing an online system an organization can maximize its inventory investment to meet its unique business requirements. So it can be termed as the best choice for inventory management, as this online inventory system provides the organization with the following advantages.
- Identify a wide range of inventoried and non-inventoried items.
- Define the inventory calendar of their own choice.
- Set up multiple price lists (in multiple currencies), multiple companies, and multiple warehouses.
- Cross-reference part numbers with customer part numbers for quick reference during order entry and inventory processing.
- Define buying authority thresholds for specific buyers.
The Impact that Inventory management has on an organization is stated below:
- Complete control of inventory.
- Complete information about the value of the inventory
- Complete visibility on Quantities on hand, Quantities committed and Quantities sold
- Response time to demand changes reduced
- Increased sales
- Knowledge of the exact size of merchandising inventory
- Frequent analysis of purchases, sales, and inventory records.
- Removal of unnecessary use of warehouse space used by unneeded parts of inventory.
- Reduction in excess merchandise stock.
- Taxes and insurance premiums paid on excess merchandise inventory avoided.
- By providing timely accurate information about inventory location, movement, and valuation, receipt of goods, sale, and return of goods and profits an organization can make sure that its inventory is visible throughout a network.
With inventory management, you can set your product catalog to hide products that are not in stock, or change prices based on the number of products available in the warehouse. The quantity available can be displayed to the shopper and this can prevent unnecessary confusion when the shopper adds items not available to a shopping cart. The store buyer can be automatically notified about low inventory levels.
Results and analysis
Quality Management
During project design, quality management was taken into consideration. This involved quality planning, product description and is a plan
Quality Planning
According to Sommerville (2004), “Quality planning is the process of developing a quality plan for a project. The quality plan should set out the desired software qualities and describe how these are to be assessed”. A quality plan should therefore offer options and avenues for improving and assessing the quality of the proposed system. The following is the quality plan developed for the project:
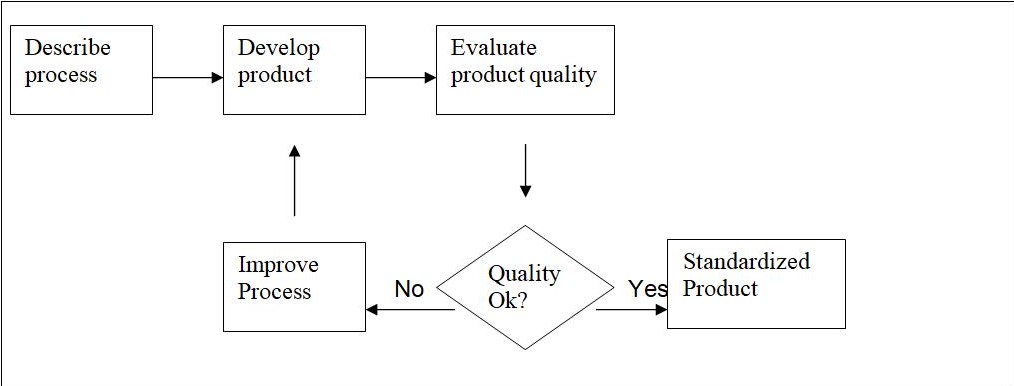
Product Description
A computerized database inventory system, which will be used by the permanent staff at the company, is termed a stock inventory database. This product aims to offer a faster, accurate, and easier method of keeping stock. In addition, the Graphical User Interface (GUI) grants a simple method of navigating through the database whereas the peer-to-peer network should allow for evident concurrent access and manipulation of data.
Product Plan
A critical release date set for the entire proposed system was set since successful implementation would mean allowing time for staff to be trained and become more acquainted with the new system.
The manager explained that the current stock control system was not good and it only provided information that was not inadequate manager stock. the system provides stock levels and how much was in store for each item. He further explained that it took a long time to ascertain the actual stocks in stock. Apart from stock level reports the current system was providing reports on obsolete, stock slowing moving stocks and other reports but it failed to give information period which the stock was being held in store.
The manager felt that the current system needed to be upgraded to a networked system with software that generates reports daily. He taught of web-based but realized that it was expensive to maintain it.
In a nutshell, the proposed system by both the manager and employees indicated that they wanted a system that will as in the following ways:
- Enter, edit, and cancel orders; track them. Provide flexible pricing and customer discounts and handle additional miscellaneous charges such as freight, handling, and shipping. Specify order types to control the flow of orders through the IT system.
- Generate and track backorders when there is insufficient stock allow to quick purchases. Automatically release backorders when purchases arrive or release backorders manually. Monitor inventory levels and conduct inventory inquiries. Receiving sales orders and inventory adjustments and reporting. Be able to do inventory costing and valuations. Be able to create relationships between products for selling and offering replacements for obsolete and other out-of-stock items and maintain reports on quantities of all products.
- Print transactions summary reports of all products when needed in the shortest time possible.
- Summarize all stock activities; account for all stocks, the period stock is held and Graphical reports, analyze financial, production, and performance data comparative Analysis reports. Be able to analyze sales and forecast stock requirements.
From their responses, I visualized a system that has the following diagram
Configuration Management
Configuration management deals with “the development and use of standards and procedures for managing an evolving software system” Sommerville (2004). Requirement changes may take place during the development and operation of the system. So it is important to originate a consistent plan for the inclusion of such new requirements into the new system versions.
Certain specific items will be managed for the development of the stock inventory database, GUI, and peer to peer network, which are as follows:
- Risk Plan.
- Project Budget.
- Feasibility Report.
- Requirements Specification Document.
- Logical Systems Design Specification.
- Test Plan (White box and Black box).
- Implementation Plan.
- User Documentation.
- Backup Plan.
Risk Management and Plan
To define Risk Management, Sommerville (2004) said “the process of identifying risks, assessing their severity, planning measures to put in place if the risks arise and monitoring the software and the software process for risks”. In this sense, risk must be identified, analyzed, and dealt with by putting in place countermeasures to deal with any potential threat to the project objectives. This fact of risk management is an essential matter for all projects as they can be vulnerable to potential risks. So I have tried to identify all the possible threats and plan contingencies to avoid and deal with possible risk factors. A risk plan is needed to be formulated to assist in such management of risks.
Implementation Plan
A parallel implementation strategy is to be used with single cutover. According to Adams, Powers, and Owles (1985), “both systems are operated concurrently for some time.” Parallel implementation will be used as both current and new systems will be operated concurrently. This will be done to allow all users already trained in the manual system to continue using the current system until the new system has proved itself.
Technical Issues
Technical issues would deal with the necessary elements to be considered to develop the proposed systems. Furthermore, technical issues are broken down into hardware and software issues.
Hardware Issues
The following is a list of important hardware to be considered while developing the physical proposed system:
- HP Dell Dimension desktop computer.
- HP DeskJet Printer.
- Crimping tool kit.
- Category 5 Cable.
- Pack of RJ45 connectors.
Software Issues
The following is a list of important software components that were used in the system:
- Microsoft Access 2003.
- Microsoft Windows XP Professional.
Project cost
The following was the project cost, clearly outlining the cost of each new component that was purchased:
Figure 1-7: Cost of New Hardware Components
Feasibility Study
According to Kendall & Kendall (2002), a “feasibility study is used to gather broad data for the members of management that in turn enables them to decide on whether to proceed with a systems study.” In this sense, this section deals with providing management with a clear indication of the nature of the project in terms of business options, costs/benefits, and return on investment. This section will form the basis of a feasibility report, which is expected to be used to initiate the project.
Business options
The company’s perception is to recover cost and gain profits by computerizing the system to minimize processes to increase efficiency and effectiveness. This should capture the various activities taking place. In this case, the company would provide auto parts (mainly transmission parts) and accessories to public customers. Furthermore, the business would re-order stock when items reach a certain re-order level. All stock must be reordered when it reaches its specified re-order level. Furthermore, all stock cards must have up-to-date stock level information.
Cost/Benefit Analysis
According to Powers, Adams, and Mills (1984), cost/benefit analysis must ensure that “Identifiable benefits must equal (or preferably exceed) identifiable costs”. So each cost should be weighed against each benefit received.
Others
We can also carry on the feasibility study through break-even analysis and calculating return on investment.
System Analysis
Requirements Specification
This stage deals with the production of a summary of the proposed system. The purpose of the design and implementation of a stock inventory database, graphical user interface, and peer-to-peer network for DDD was to improve efficiency and increase productivity while managing the stock inventory processes of transmission parts.
The stock inventory database system is projected to support staff in running their tasks in a convenient and more manageable way by minimizing processes, so that it may increase motivation and lessen the workload. It also helps the organization to earn profit and run the business smoothly.
For this purpose, a graphical user interface will be developed to assist employees in supervising the new system, thus creating a user-friendly environment to validate the effectiveness of the system. Moreover, a peer-to-peer network will be developed to permit two users to access the database, share data, and print stock reports and other documents.
Design
The design of a new system for DDD was segmented into the following areas:
Logical Systems Specification
The logical systems specification will deal with the identification of three (3) hardware and software combinations, comparison of the three, and the selection of the most suitable option
Logical Design
The logical design will deal with providing textual descriptions followed by a high-level functional design and Graphical User Interface Design. Furthermore, such a GUI design will include a logical design for screens, forms, and reports.
Physical Design
The physical design will show the design of screens and reports for specific pages. Furthermore, it would also show how the normalization of data for the stock inventory database will be done.
Test Plan
The test plan will deal with the creation of a Blackbox and Whitebox test plan. In addition, the Blackbox test plan will encompass the creation of a system test plan and an acceptance test plan. Whitebox will deal with creating Unit modules and Integration test plans.
Development
This section is concerned with the actual formation (development) of the Stock Inventory Database, Graphical User Interface, and Peer-to-Peer network for TESS. Additionally, the development would rely on the requirements in terms of feasibility, analysis, and design. It is important to note that the implementation of the system would focus on the actual setup, installation, and configuration of the network.
Testing and Implementation
In this stage, we need to test the new system and after that, we will go for implementing it. The implementation plan consists the following tasks:
- Site preparation:
- Check power outlets availability;
- Layout office furniture.
- Installation of Hardware:
- Crimping of cables;
- Running of cables;
- Placement of computers and printer;
- Connecting crossover cables to PCs.
- Installation of Software:
- Ensure that Microsoft Access was installed;
- Copy the Stock Inventory Database to the computer.
- Testing of Hardware:
- Test network compatibility using database;
- Test network connections;
- Printer Connection.
- Training:
- Role and Purpose of the new system;
- Rules and Regulations of system;
- Questions and Answers;
- System Demonstration;
- User/System interaction;
- User comments and evaluation;
- Distribution of User Guide;
- Conclusion of Training Sessions.
- Cut over- Covert to the new system:
- Data entry – old data copied to the system;
- Remove of parallel system.
Conclusion
Information technology systems permeate organizations, supporting almost everything–apart from managing IT items themselves. Although software-configuration-management systems can provide some management assistance, they aren’t designed to handle the totality of a distributed enterprise or to act as a management information resource. Software sources constitute major organization assets, but they can’t be treated as such until they’re inventoried. Software inventorying is one of a set of integrated technologies developed to address problems of managing constantly changing technological and business processes.
Those technologies are aspects of an evolving business paradigm called the paradigm of change. Creating an enterprise IT inventory is a complex task requiring large amounts of information, but such an investment can produce a considerable payoff.
In this paper, we have tried to develop an Information system for the Inventory Management of DDD through developing a Stock Inventory Database, Graphical User Interface, and Peer-to-Peer network. The new system allowed for the achievement of all objectives set out. This included the creation of a database with functionality providing for data integrity and security, a Graphical User Interface to provide an organized and manageable view of information, and a Peer-to-Peer network, which was configured for security and the provision for simultaneous usage.
The importance and effect of the Information System (IS) in day-to-day operations management, especially in Inventory Management has widened and explored the present dynamic and heterogeneous business environment. But these are yet to implement, operate and exploit fully formally and professionally to enable them to derive maximum business gains out of it.
References
- Adams, D.R, Powers M.J, Owles, V.H, (1985), Computer Information Systems Development: Design and Implementation, South-Western Publishing Co.
- Bolton, S., (2007), Take Real Control Over Chemical, Inventory Management, Copyright – W3 Markets, Inc.
- Buchan, J., & Koenigsberg, E., (1963), Scientific Inventory Management, Prentice-Hall.
- Copacino, W. C., (1997). Supply Chain Management: The Basics and Beyond. The St. Lucie Press/ /Apics Series on Resource Management, Publisher: CRC.
- Donath, B., (2002). The IOMA Handbook of Logistics and Inventory Management, Institute of Management & Administration, John Wiley and Sons.
- Intellisoft, (2006). Serial Number Tracking Software Solutions. Web.
- Itsuki, R., Shibata, H., Ikkai, Y., and Komoda, N., (2003), The Autonomous Information System Design For Item Management Using, Re-writable RF-ID Tags In Supply Chain, Lisbon.
- James C. EMERY, (1987). Management Information Systems: The Critical Strategic Resource, Oxford Univ Pr.
- Kendall, K.E, Kendall, J.E, (2002), Systems Analysis and Design, 5th Edition, Prentice Hall.
- Khosrowpour, M. (2001), Pitfalls and Triumphs of Information Technology Management. Idea Group Pub.
- Lucas, H. C., (1976). The Analysis, Design, and Implementation of Information Systems, McGraw-Hill.
- Michael J. Earl, (1996). Information Management: The Strategic Dimension. Oxford University Press, USA. Web.
- Piasecki, D. J., (2003). Inventory Accuracy: People, Processes and Technology. Ops Publishing, Kenosha, Wisconsin.
- Prichard, J. W. & Eagle, H. R. (1965), Modern Inventory Management, John Wiley and Sons Ltd. Web.
- Sherman C. Blumenthal, (1969), Management Information Systems: A Framework for Planning and Development, Prentice-Hall.
- Sommerville, I. (2004), Software Engineering, 7th Edition, Pearson Education Limited.
- Toomey, J. W., (2006), Inventory Management: Principles, Concepts and Techniques. 1st edition. Web.
