Executive Summary
Virgin Blue Holdings is one of the largest airlines in the Eastern hemisphere. This company owns and operates other companies, united by the Virgin Blue brand name. These companies are V Australia, Pacific Blue and Polynesian Blue Airlines. Virgin Group is the main shareholder of the Holdings. The company was shaped within the frames of Virgin Group headed by Sir Richard Branson in 2000. In 2003 Virgin came to agreement with Patrick Corporation on investing the Virgin Blue Holdings in order to let it grow into the national airline company. Thus, Patrick achieved 50% return share investing $AU260 million. Moreover, the company could benefit from new political connections with Howard government and had an opportunity to become the leader in Australian market of airline transportation.
The purpose of this report is to analyze the financial performance of the Virgin Blue Holdings basing on the annual information provided by the company and on the external data which may be found in open sources. Originally, in spite of the decline of the airline transportation because of the world crisis, the Virgin Blue Holdings managed to overcome the difficulties and stay among the leaders of the air transportation market. Thus, the diversified approach towards business running, applied by Virgin Corporation requires particular attention, as Virgin Blue Holdings’ future prospects look rather perspective and beneficial, as innovations and professional strategic and financial management will help the company to develop its success independently on the world financial situation.
Introduction
The start of the company from the perspectives of financial operations was the investment of the Patrick company into Virgin Blue Holdings. Later, in 2006, Patrick Corporation started the joined business activity with Toll Holdings, and the partnership relations with Virgin Blue Holdings continued, which helped the company to expand its business activity and achieve the immense success.
Originally, VBA is the constantly growing company with the immense achievements in the sphere of marketing management and financial flow management. In accordance with the annual report (2009), the incomes of the company 12.9% increased, and totaled $2 635,4 million. The net loss is 263.8% of the previous reporting period loss and totaled $160.0 million. Additionally, it should be stated that dividends were not registered for this period, which defines the disastrous position of the company on the market at the moment.
As for the fleet, which the company owns, it should be stated that initially the company was acting on the basis of leasing approach, nevertheless, a lot of planes have been purchased lately, by the company. Thus, the company ordered 9 Boeing 737-800 planes using the previously purchased options. Moreover, the company owns 19 Embraer ERJ-190 and ERJ-170 planes, with an option of purchasing five more planes. In accordance with the information on the official website, it is stated that VBA has been recognized with numerous awards for the IT innovations, and for the third year in a row, the company is winning the prize of the ‘Best National Airline’ national award ( Godfrey, 2010)
Business Analysis
Virgin Blue Holdings is often regarded as the second largest Australian Airline company. The fact is that, the company uses the widely known business model implemented by Southwest Airlines and Ryanair, which allows to decrease the cost of the transportation at the expense of free on board meals and the use of paper tickets. The sale of meals, beverages, as well as on-line and phone ticket booking were implemented instead. At the beginning of its activity the company managed to decrease the technical service expenses by using the planes of the only type – Boeing 737. The planes of the other type were purchased in order to recommence the transportation along the route Sidney – Canberra and other routs with low passenger traffic. Thus, as it is emphasized by Crawford (p. 51):
VBA through its three airlines namely Virgin Blue Airlines, Pacific Blue and Polynesian Blue, is providing domestic air services across 24 Australian cities and centres and international services to eight destinations which are New Zealand, Vanuatu, the Cook Islands, Fiji, Tonga, Samoa, Papua New Guinea and Bali. At present the Company has a modern fleet of 68 Next Generation Boeing 737-700 and 800 series and Embraer E-190 and E-170 aircraft. Virgin Blue operates more than 2100 flights per week with in excess of 15-million travelers using Virgin Blue Airlines’ air services each year.
In 2003 VBA announced that her affiliate company Pacific Blue started an airline between Australia and New Zealand in accordance with the same business scheme. Originally, Pacific Blue is positioned as the low-cost competitor of the Air New Zealand and Qantas on this direction.
Competitors Analysis
The key competitors of the VBA are Air New Zealand, Hawaiian Airlines, Qantas, Singapore, Emirates and Cathay Pacific. Thus, it should be emphasized that the competition environment is rather high; nevertheless, these companies aim to conquer the same market with different prices. The diagram reveals the market share of these companies and provides the comparison for the pricing strategies. Thus, Virgin Blue is the company with the lowest prices, consequently, it has achieved its main aim to lower the prices, and become one of the most successful companies in Australia. Originally, the diagram reveals not only Australian market, that is why Virgin’s market share is lower in comparison with some other companies.
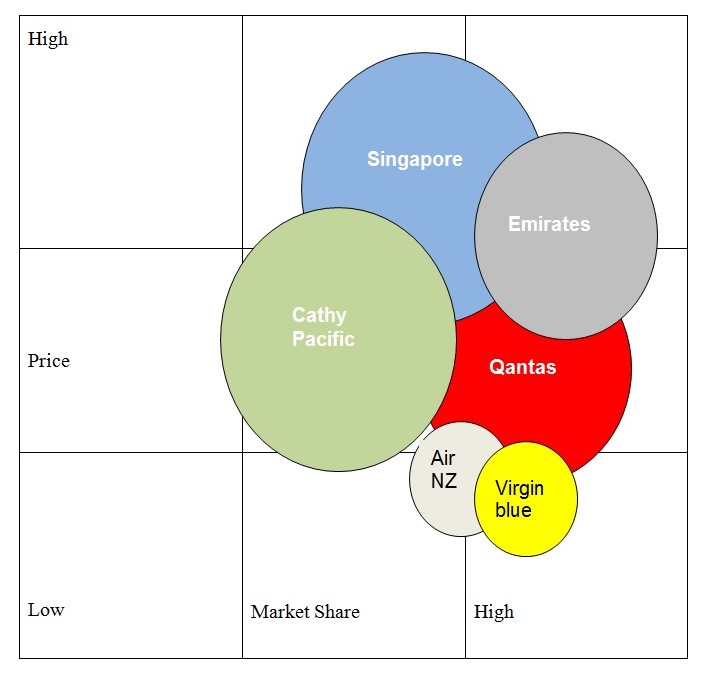
The fact is that, Air NZ had to terminate the low-cost department, which has been acting under Freedom Air brand, and Qantas arranged several routes to New Zealand with its affiliate company Jetstar Airways, which was founded in 2004 as a response for the low-cost VBA.
Both, Qantas and Air New Zealand continue flying in these destinations, and Virgin Blue revealed the strong determination to start inner airlines in New Zealand. The flights between Oaklend and Wellington, as well as Christchurch and Wellington started in October 2007.
Valuation
The fact is that, VBA, in comparison with other low-cost airlines is not highly dependent on the business method, which it uses. It should be emphasized that the means, which allowed the company to decrease the costs appeared to be effective and promising, as the company is intended to develop this strategy of low-cost flights. The value of equity model reveals the fact that the company’s shares are evaluated in 0,58 AUD per share. The market cap is 1,568,479,460, the amount of the outstanding shares is 2,209,126,000, and the amount of the closely held shares is 60,078,826. In accordance with the report by Virgin Blue Holdings Limited, the valuations of the VBA shares are the following:
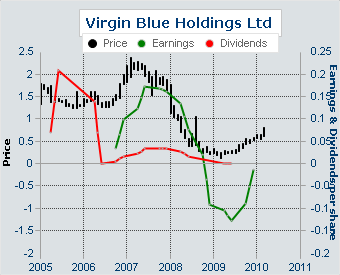
Earnings and dividends per share have fallen recently because of the financial crisis and the decline of the airline transportations allover the world, nevertheless, the latest tendencies reveal the steady growth of the dividends. The recent stock performance is the following:
- 1 Week 2.2%
- 4 Weeks 20.3%
- 13 Weeks -5.3%
- 52 Weeks 166.3%
Technical Analyses
The analyzed 2008-2009period revealed the confident market share increase after the rapid fall, caused by the financial crisis. Originally, the total revenue of the company totaled $ 2,600.3 million ($ 2,321.7 million in 2007 – 2008 period). Additionally, the operating expenses have also increased. Thus, in 2008 – 2009, this amount totaled $ 2,664.5 million, while the expenses of the previous period were $ 2,183.8 million.
The diversification of the services offered, and the split of branding policy originated the unique approach towards running business in general. Thus, Virgin Blue Holdings unites three brand names: V Australia, Pacific Blue and Polynesian Blue. The consolidated financial statement reveals the unified strategy of the entire business performance and indicates that this branding policy is successful enough.
The earnings per share, from the perspective of the represented data, does not provide the actual trading position analysis for the Virgin Blue Holdings. Thus, the earnings ratio, achieved in 2009, is caused by the increase of the popularity of low-cost air transportations. This is explained by the fact, that people just wish to get to the destination point as soon as possible and at the lowest possible price with maximum comfort. VBA offers its customers such opportunity, consequently, the market share of the company growth. The DuPont analysis reveals the following situation:
On the one hand, it seems that the allocation of the financial resources is not effective, as the percentage is very low, nevertheless, it is the image of the steady overcome of the difficulties, associated with financial crisis.
Common Sized Statement Analysis
The general overview of the business performance is featured with the increased losses, caused by the financial crisis, and the allover decline of the passenger traffic. The financial analysis of the financial performance reveals the decline of the sales in 2009, nevertheless, starting from September 2009, the sales growth appeared to be essential and sufficient for covering the main part of the expenses and losses, caused by the rapid decline in revenues.
Global Market Place
The marketplace of the company has changed recently because of the described financial problems, associated with crisis. Originally, some low-cost airline companies had to terminate their market performance, thus, VBA had an opportunity to make the significant leap forward and increase its market share. Moreover, the company managed to avoid serious losses, and innovate the principally new approach towards satisfying customers. Currently, the company owns up o 35% of the Australian market, and now the company is the largest Australian carrier. The main competitor of the Virgin Blue Holdings is the Qantas, and both companies are fighting the market severely. Nevertheless, this competition is the powerful engine of the market development, as consumers are satisfied with the low prices ($29 per ticket), thus, the incomes of both companies grow. As it is stated by Condie (p.34):
Despite the intense competition between them, both carriers claim they are growing the market and are increasing their jet fleets, rather than taking business from each other. Jetstar is currently running 14 jets with plans to increase this by 23 over the next two years. Virgin also recently added to its fleet.
It should be emphasized that the carrier is currently planning to use the changing attitudes towards airline travelling for the further growth of the market share. Thus, promoting the consideration that airline travelling is not expensive, and may be available for everyone.
Business Strategy
Originally, the strategy of the VBA is closely linked with the notion that airline travelling should be as cheap as possible and provide maximum comfort for the passengers. The business performance and the quality of the provided services is frequently checked and verified by the managerial team. The key aspect of the successful strategic performance is the notion, that the company is the vigorous and effective competitor from the perspectives of price, customer care and innovations. Thus, as it is stated in Godfrey:
In 2008, the carrier introduced Premium Economy Class throughout its entire fleet. This involved new seating being installed in the first three rows of the cabin, which could be converted from three seats in main cabin configuration to two seats with fold-down table in the middle for premium use, with greater seat pitch and legroom. The premium product offers priority check-in, larger baggage allowance, lounge access, priority boarding, and all-inclusive in-flight entertainment and meals/beverages on board. The product is aimed at attracting more business and corporate market to the carrier.
Debt Structure
The company mainly operates with a positive cash balance, nevertheless, the difficulties, which appeared during the period 2008-2009 made the CEO originate the debt strategy, which will be helpful for overcoming the possible financial difficulties. Thus, the debt management strategy is based on selling shares. There is an information (Condie) that the company is going to issue a request for proposal for the debt financing of four aircrafts, nevertheless, the partnership with Toll Holdings will be used as the basis for solving this difficulty. Originally, the information is not confirmed by VBA, thus, the detailed data is not available. Additionally, as it is emphasized by Mornson:
The move to long term leasing of aircraft implies a debt which is not specifically recognised in the financial statements. The underlying liabilities as a result of the leasing agreements need to be incorporated into the accounts and this would dramatically impact upon the ratios and highlight the true underling poor position of the company, both in internal structure and cost settings to remain competitive in the expanding market operators.
In the light of this statement, it should be emphasized that the traditional approach towards debt structure management is not used, as the comp-any possesses sufficient reserve for covering the possible shortages.
Cash Flow
The cash flow of the company is generally subjected to steady decrease in the operating flows, as the expenses had to be decreased.
Additionally, it should be stated that the company had to decrease the investment outflow in 2009, because of the decreased incomes and the growing expenses. Originally, the necessity to restructure the cash flow operations and the structure of the entire financial management was originated by the situation on the airline transportation market, as the people – the target audience of the airline companies – preferred to delay their trips. Therefore, the company had to deal with the changed preferences of the consumers, and implement principally new managerial approaches.
Fixed Assets
The net asset value of the Virgin Blue Holdings totaled $ 611.8 million, which is $ 251,5 million less in comparison with the year 2008. Originally, the decrease of the assets may indicate the serious problems with the financial flow analysis within the management of the company, or the problems with keeping the existing customers’ range. If the problem is in the customer care policy, the decrease will be observed until the policy is improved. In spite of these problems, the company managed to keep the liabilities on the same level in comparison with the previous year, nevertheless, the share incomes decreased essentially (15,2 cents loss per share). The company had to lower the investment outflows, which caused the depreciation of its stock shares, which finally caused the fall of the share dividends.
Nevertheless, in spite of the decrease in incomes, the company proceeds with arranging sponsorship actions. Thus, as it is stated in Virgin Blue Holdings Limited (2010):
In 2009, Virgin Blue introduced an all new advertising campaign entitled “Now there’s an idea”. TV Commercials showing comparisons between flying in Australia in 1999 as opposed to 2009 were screened, to the tune of one of The Cat Empire songs. New billboard advertising was launched, showcasing Virgin Blue’s variety of products and on-time performance records.
Originally, sponsorship practices are often regarded as the best advertising. Consequently, the company has all the necessary opportunities to improve its business performance and achieve the necessary level in competition.
Conclusion
The business analysis of the Virgin Blue Holdings airline carrier revealed the strong competitive potential of the company. Originally, in accordance with numerous forecasts, everything that prevents Virgin Blue from becoming an Australian leader in the sphere of airline transportation is the time. This notion is explained by the statement that the company is regarded an innovator in the sphere of services and customer care. In spite of the fact, that Virgin Blue has implemented the traditional model for lowering the price of air transportation, the innovative approaches helped the company to succeed in conquering 35% of low-cost airline transportation market.
Financial analyses of the company’s operations and business performance are not favorable, as year 2009 is featured with the decrease of incomes, the growth of the expenses and decrease of the market share price. Nevertheless, the competitors analysis shows that the innovation practices within VBA are better in comparison with its key competitors, moreover, VBA better realizes the needs and requirements of the consumers. Thus, the target audience will be better satisfied and will probably chose VBA.
Works Cited
Clark, SS. ‘Viewing the Global Attack on the Global Economy from Australia.’ Defense Counsel Journal 69.2 (2008): 185
Condie, B. ‘Branson Loses Battle for Control of Virgin Blue.’ The Evening Standard (London, England) 2005: 44.
Condie, B. ‘Virgin Blue in Newalert as Branson Plan Fails.’ The Evening Standard (London, England) 2005: 34.
Condie, B. ‘Virgin Blue Walks Away from Air Macau Talks.’ The Evening Standard (London, England) 2005: 34.
Crawford, S. ‘Virgin Blue Flies in to Deliver Whitsunday Tourism Boost.’ The Daily Mercury (Mackay, Australia) 2009: 51.
E*Trade Australia ‘Virgin Blue Holdings Limited (VBA)’ E*TRADE Financial Corporation and E*TRADE Australia, 2010. Web.
Godfrey, B. ‘Welcome Message from Brett’ Virgin Blue. 2010: Web.
Mornson, J. Management and Accounting, Captain Press, New York. 2007
Virgin Blue Holdings Limited ‘Preliminary Final Report for the year ended 2009’ Web.
