Introduction
This paper has been organized on China as a selective country along with an assumed company ‘XYZ Company’ to prepare this country report integrating. The objective of this paper is to prepare a report with two broad portions- country profile report and the project description part. The fictitious company of the paper, “XYZ Company” is primarily an electronic device manufacturing company and a distributor of its products and services. In order to accomplish the company goals here also integrated necessary strategies and environmental factors or variables, strategy evaluation and implementation, SWOT analysis of the company, recommendation and a conclusion of the project portrayal.
Country Report Project
Including both positive and negative aspects of environmental forces country profile part integrated here in following aspects:
Physical and demographic profile: Formal name of China is- “The People’s Republic of China”. People of China are termed as Chinese and its capital is stayed at Beijing (North capital). China is diverse into four large municipals included urban and rural areas- Chongqing, Shanghai, Beijing and Tianjin. 1st October 1949, China was officially established as “People’s Republic of China”. There have four major official holidays during a year.
Form country profile of China (2008), it can be found that flag of China presents the Chinese Communist Party leadership. Their flag is red and which a large yellow star surrounded by four small stars in a vertical arc. Their spirit of revolution reflects through their red color flag and unity among people showed by the five stars.
Geography: Geographically, China is a part of East Asia. Mongolia and Siberian landmass is located at the south part of China, Korean Peninsula and insular Japan are at West, Southeast Asia is at north and at the East Central and South Asia is stayed. Library of Congress (2006) provides the relevant data such as it has 9,326,410 square kilometers of land and 270, 550 square kilometers of island lakes and river aggregate 9,596,960 square kilometers of the entire area. With 14 different countries Chinese land boundaries are almost 22,117 kilometers. There have 50,000 rivers in China and most of them flow from west to east and finally fall into the Pacific Ocean. Climatic circumstance is too complex here in summer temperature is 40° C but in winter, it turns to – 30° C.
Resources: World’s largest mineral reserve is in China that produces- antimony, tungsten, natural graphite and zinc. World’s largest hydropower potentiality is also in China. Other major minerals- bauxite, coal, gold, diamonds, crude petroleum, iron ore, natural gas, lead, mercury, phosphate rock, magnetite, manganese, molybdenum, tin, uranium, and vanadium.
Population, literature and health: Centuries most populated countries of the world. The total population of China was 1,313,973,713 but officially China recognized its total population is 1.3 billionths apart from Hong Kong and Taiwan. Form country profile of China (2008), it can be found estimated population growth was 0.59 % and population density was 135 persons per square kilometer.
Now China faced a high urbanization and according to census 2000 within 2035, 70 % of people will be under urban areas. Library of Congress (2006) argued that per 100 people, migration rate is 0.39 %. Amongst total population 70 % are under (15 – 35) older. Male and female ratio per 1000 people is- 20.6 and 25.9 respectively, per 1000 people death rate is 6.9 and birth rate is 13.3. there have 55 other nationalities termed as ethnic groups against the majority Han Chinese and number of this ethnic group is about 105 million persons.
Based on Beijing dialect official language of China is Mandarin. Other major dialects are- Yue, Wu, Minnan, Xiang, Minbei, Gan and Hakka. All of the major dialects use a common written form and there are 85 thousand alphabets for this. A significant point is that several minor dialects are only spoken because of their multiplicity of ethnic groups.
Major religions are: Buddhism, Confucianism and Daoism. Other than these there also have 4 % and 2 % Islam and Christianity respectively and 0.4 % is patriotic sponsored by government, (0.4 – 0.6) percentage Vatican affiliated but not recognized by official, (1.2 – 1.5) percentage is Protestant by registry.
Library of Congress (2006) also expressed that government officially recognized that about 100 million different sects of Buddhism attract tourism all over the year. Not only have these there also had 600 Daoist temples, 16,000 temples and monasteries. Approximate literacy rate is 90.9 %. Health report of China presents the fertility rate of the nation. In rural areas, more than 100 million people live and they do not get proper medical assistance. In 2005, almost 650,000 people were infected with HIV.
Workforce characteristics
- Agriculture, forestry and fishing: China has to move violently to feed its people. Considering food crisis and large population, they concentrate their workforce on agricultural production. However, weather is the prime constraint of it. 46.9 % of total national workforce involve in agriculture, (include forestry and fishing). Sequence of an image world’s third-largest economic power chief crops is- rice, corns, wheat, sweet potato, potato, sugarcane, barley, millet, buckwheat, rye, sorghum, oats and triticale. On the other hand, vegetables are – peanuts, soybeans and rapeseed and sugar beets. It is producing highest array of leaves such as cabbages, tomatoes, cucumbers and dry onions. Fruity items are- watermelons, cantaloupes, apples, citrus fruits, bananas, mangoes and other melons over the year. Being a country of numerous smoker 18.1 % of the world’s production of tobacco leaves are produced in China. With the acceding into WTO, they are the world’s second-largest cereal producer. Poultry, fishing and livestock products are – pork, poultry eggs, cow’s milk, poultry meat, beef, veal, mutton, lamb, goat, cattle hides, sheepskins, goatskins, honey and raw silk. In case of forestry, China is the third-largest wood supplier in the world. Fishing is also under their grasp and per year, they harvest about 28.8 million tons of fish. Among them 36.7 % are collected from rivers, lakes, and the sea.
- Mining and minerals: Prime mineral resources of China are – coal and iron ore. These are adequate for meeting the demand for industrial minerals. Other than these, world’s fifth-largest gold producer in China. Storage of mining and minerals items are the source of industrial revolution, employment opportunity and producer of rare metals in high-technologies industries in local and around the world.
- Energy, industry and manufacturing: China has abundant resources of energy and 934.2 million tons of oil had produced by China. Most of them were consumed by North Korea, one-third of them by Hong Kong and a small portion by Asia. Most demandable product is coal-burning plants used in electric power generation. Both domestic and international mostly western coal demand is fulfilled through China’s self-competence. Petroleum, oil, natural gas and hydroelectric potentiality are also rich in variety and quality. Entire energy sector proof its efficiency and growth excluding any doubt and expand the scope of utilizing workforces.
- Construction: At the end of 1980s a significant change held in China’s construction sector. Therefore an important part of workforce area is under construction. Beginning of 21st century, per year investment percentage in contraction has enormously increased and in 2003, it reached 30 %.
- Services, banking and finance: Service is another important area of cultivating workforces and 40.3 % of China’s GDP was come out from the services sector. Services of China are attributed by state-operated shops, regulated prices, rationing, individual entrepreneurs, private markets, comparatively freewheeling commercial sector, Western-style retail shops, fast-food chains, nightclubs, trendy restaurants, suit, the retail sector, joint-venture hotels etc. For banking and finance, in China there have 70 foreign banks and 140 of their branches.
- Tourism: As one of the major tourism destinations China has 9,751 tourism hotels with hospitability facilities and this is a valuable source of workforce.
- Labor: About 791.4 million workforces engaged in diverse working activities. Most of them are involved in agriculture, fishing and forestry, another major part of work at mining.
Cultural and socio-political profile
- Political system and political risks: China is reformed through Marxist-Leninist model replete. That is the reason for their mixed economy. Risks of this process- revolution of the society against that and this would be a great threat for its economical progress.
- Legal and economic profile: Based on purchasing power parity (PPP) in 2005, China became the world’s second-largest economy. Their vision is to turn their per capita GDP (Gross Domestic Product) into double within 2020. Since 1978, government wins through the tool of widespread market economy mechanisms. Economic system of China is termed as “Market Economy with Socialist Characteristics.” This economic concept enveloped through centrally planned economy and socialism. Technological advancement and productivity amplification labeled the industry.
- Special and Open Economic Zones: At the beginning of free-market economy China instituted its special and open economic zone (SEZs) in (1980 – 1984)- Xiamen in Fujian Province and Shantou, Shenzhen, and Zhuhai in Guangdong Province including another 14 coastal cities from north to south. These areas are categorized into- 15 free-trade zones, 53 new high-tech industrial development zones, and 32 state-level development zones (both economic and technological).
- Level of development: when China acceded into WTO (World Trade Organization) in 2001, it flexible the restraints on foreign trade. The coastal special economic zones are especially encouraged for joint ventures as well as open coastal cities. In 2004, a report identified that within two years increase of millionaires is 12 % (236,000 persons) which is the symbol of affluence escape from the reformed economy. Regional integration and globalization of the world are two major trends that greatly affect the China’s future development and market economy. Relation between these trends also repair and reform relation between China and USA.
There have many challenges for the Chinese leaders’ future economic development of the nation. Challenges are- preserve a high growth rate, effective management of rural workforce, promote productive private sector, financial system development, social security system formation, continuous development of the state-owned enterprises, scientific and educational development expansion, revise economic system and role of government in it, better international cooperation endorsement. In spite of these restraints after 2004, China becomes the third trading nation in the world against United States and Germany and now international market reconciled with China.
The factor of dynamics is- get improved economic returns fulfill the required demands, widen profitability through sufficient effort and within 2010 reduce 20 % energy expenditure by preservation of resources. Their new economic friendly arrangements also consider and focus coordination among urban, rural and regional development. In addition, approximate growth rate of GDP was 9.9 % for the year 2005.
- Inflation: From 1990 to 2002, average yearly annual inflation rate was 6 %. In 2003, it was increased by 1.2 % though, in 2002, consumer prices trim down by 0.8 %. After two years in 2005, an approximate inflation rate was 1.8 %.
Trade, investment and foreign policy profile
- Foreign economic relation: A tradition of Chinese government, China’s foreign trade has decided to compose. Since 1978, after the reformation, private partnerships have increased and developed dramatically and market place is under primary dedication of trade. United States was the largest export partner through a enlarge trade practices and these two countries finally agreed to alter the design of economic improvement China to private and foreign investment. On the other hand, in 2000 US Congress granted China as the most favored nation permanently.
- Imports and exports: 36 % import increased in 2004 that amounted 561.4 billion (in US $). As well as imports, in 2004 China’s exports have also increased by 35.4 % that amounted 593.4 billion (in US $). Major components of imports and exports are- machinery and equipment, plastics, mineral fuels, steel and iron, footwear, textiles and clothing. China’s trading partner are – 16.8 % Japan, 11.1 % South Korea, 11.4 % Taiwan, 8 % USA, 18.8 % UK and 23 % Canada. This trend of increased imports during the seven years is reflected in the amount of revenue in 2004. For instance total import amount was 138.8 billion (in US $) whereas it was about 225 billion (in US $) in 2000. on the other hand,
- Trade balance: During 2004 a favorable trade balance of 32 billion (in US $) whereas it was 38.7 billion (in US $). It was a reflection of at least eight years of favorable trade’s general course.
- Balance of payments: China’s current account balance was about 68.7 billion (in US $) in 2004 and among that 54.9 billion (in US $) was in FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) officially recognized and overall balance of payments was 206.1 billion (in US $).
- External debt: US census 2001 circulated that amount of 91.7 billion (in US $) from viewpoint of long-term debt, publicly guaranteed or external and public. In 2004, their international reserve account was 618.5 billion (in US $) the equivalent to 98.6 % from the source of foreign exchange that excludes foreign exchange holdings china’s Bank.
- Foreign Aid and Foreign Investment: China is considered as the recipient from view of official development assistance of bilateral, multilateral, and individual recipients of official aid and such disbursements received 1.3 billion (in US $). Forms of foreign capital are foreign direct investment (FDI), foreign loans and additional investment provided by foreign business. More than 170 counties and regions’ joint-venture enterprises have integrated their foreign businesses in China since 1980. Among 500 top transnational companies of the world 300 invested in China and in China’s economic development they are the significant capital source.
- Currency and Exchange rate: Currency of china is termed “renminbi” (RMB) or Yuan that refers to “people’s currency”. August 1 2006, interbank change rate was 1 (in US $) = 7.98 RMB. 100 fen or 10 Jiao made up RMB. In market, available denominations coins are- 1, 2 and 5 fens, in terms of Jiao 1 and 5 and 1 RMB. In terms of banknote denominations issued of 1, 2 and 5 Jiao and 1, 2, 5, 10, 50 and 100 RMB.
- Positive aspects of the environmental variables: Satisfactory source of huge natural resources is flourishing its economy dramatically.
- Negative aspects of the environmental variable: Major negative aspects are war, climate flood, and politics. Among them flood is much harmful to them.
Project Evaluation Standards
Definition and Scope
Definition of the project: Define the project here propose a company “the XYZ Company” fictitiously. XYZ Company is an electronic devices manufacturer and distributes globally their products and services. Product line of the company includes- a set of different categories cell phones, memory cards, portable music players, portable FM radios and computer chips, LCD televisions, CDs and DVDs, video cameras, PC, radio and so on.
Purpose: Today, people want to make the communication easier and the world becomes smaller in appearance of global concept. Cell phone is the most demandable product that has the competence to meet up recent communication decisive factors. Regarding this, XYZ made up its mind to be an electronic company that concentrated on cell phones.
Assumption or hypothesis of the country research: Now China is the most promising country for all categories of business purposes. There has abundant source of natural resources like- oil, coal, petroleum, gold and natural gases etc. that flourish their business opportunities indefinitely. Choosing China for the project is appropriate in practice. On the other hand, labor adequacy is another factor to choose China.
Description of the company: Following are the factors that provide a narrative outline of the company in all aspects-
Nature of the business: the company is both manufacturer and distributor of electronic devices especially varieties of cell phone items. Other than these their goal is to expert in probate music players such as portable FM radios, memory cards, computer chips, portable music player with multimedia feature- camera for video and still photo, movie storage, song storage etc.
Demographics: Demography of China is enough friendly for business operation. There have satisfactory land areas as well as waterways. Geographically, China consigns in East Asia.
Operational strategy: Field level or operational strategies of the company are shown below. These strategies take charge by supervisors and applied in-plants, department-wise functional areas and sales areas.
- It is a narrower form of strategic approach. It evaluates daily accountability of inventory control, material purchasing, shipping, advertising campaigns and maintenance.
- Overall business plan from the viewpoint of functional strategy requires more details and completeness that would be congregated only through proper continuation of operating strategy.
- Front-line managers entrusted all obligatory information and the higher ranking managers approved that.
- In decision-making, tool of formulating new strategy and database management XYZ employs their operational strategies as a source of precious support.
Structure of the firm
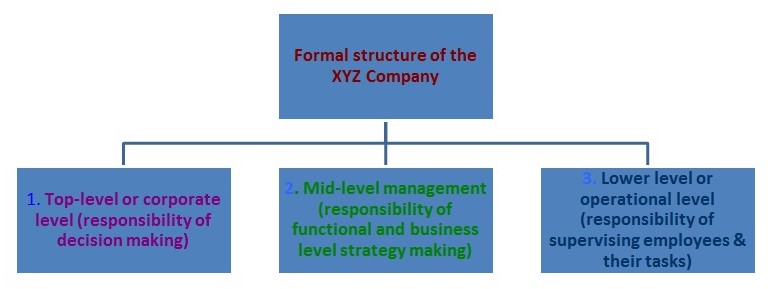
Formal structure of XYZ divides into three broad categories- top level management or corporate level, mid-level management or executive level and lower level or supervisor level. Top of the corporate level termed as CEO (Chief Executive Officer) and under his or her supervision head of different department- CFO (Chief Financial Officer), head of marketing and sales, heads of admin or HRM (Human Resource Management), head of IT would decide on their own resignation. Managers or mid-level executives work under the head of department’s supervision. Lower level workers or supervisors are worked out under supervision of mid-level executives and all the labor of the firm works under the supervisors.
- Other relevant information of the company: For continuous product improvement and new product and service innovation there has a research and development (R & D) department. Under this department there also would have a promising and intense researchers work hard and soul.
- Mission statement of the company: After establishment, within next five years XYZ like to imprison their global market arrangement as a market challenger with a strong brand image and cost effective.
- Inclusiveness of variables: Variables that are combines both external and internal forces of the country. Inclusiveness of variables is economic forces and economic system, technical support, social forces, political and legal forces, changing consumer test.
- Relevancy and saliency of variables: Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Hoskisson, R. E. (2001), expressed that saliency variables deal with the environmental forces that are essential to foster any business activities in any country. This category of variables includes- financial position, product and service position, product and services quality, marketing capability, research and development capability, human resources, storage of logistics and raw materials, organizational structure and previous and recent objectives and strategies.
Identification and Analysis of Country Variables
Country variables would divide into two major general term-external environmental forces and internal environmental forces. As the requirement of this paper, following are the terms that analyze the country variables for the business purposes of XYZ.
Strategic Recommendation and Implementation
Alternative propositions
Four strategies: To be a global company XYZ would need to involve in- direct investment, joint ventures and licensing, franchising, exporting, turnkey project and management contract. Considering this procedure four strategies are:
- Direct investment and joint ventures are a source of funding and expand business connectivity around the world especially in developed countries.
- Kotler, P. (2006), argued that franchising would be another way that permits dealing business abroad with own technical and management support especially in developing and under-developed countries.
- Licensing and exporting are inter-related to each other and this strategy would also bring financial benefit and develop foreign trade relationships for the company,
- Turnkey and management contract is cooperative only for a short time. It just allows any specific project execution.
Merit of the strategies: Fruitful benefits of the strategies are:
- Strengths the financial positions,
- Develop relationships among companies that provide similar products and services.
- Develop marketing capabilities that boost sales volume.
Demerits of the strategies: Following are the disadvantages of the above strategies:
- Make financial dependency that could slow down the business activities.
- Change of political environment obstructs the business operation in abroad.
- Recent financial recession would be another barrier that reduces investment abroad.
Criticism and reason of logical synchronized: Though there have many opportunities in FDI and joint venture but there have time boundaries or lead-time in completing the operations. This confine could be a reason for financial and image drop.
Identify, select and analyze the best strategy: Foreign direct investment and joint venture is the best strategy for the company. Financial support, technical support exchange, product innovation and development, develop foreign trade etc are the reason behind choosing the strategy.
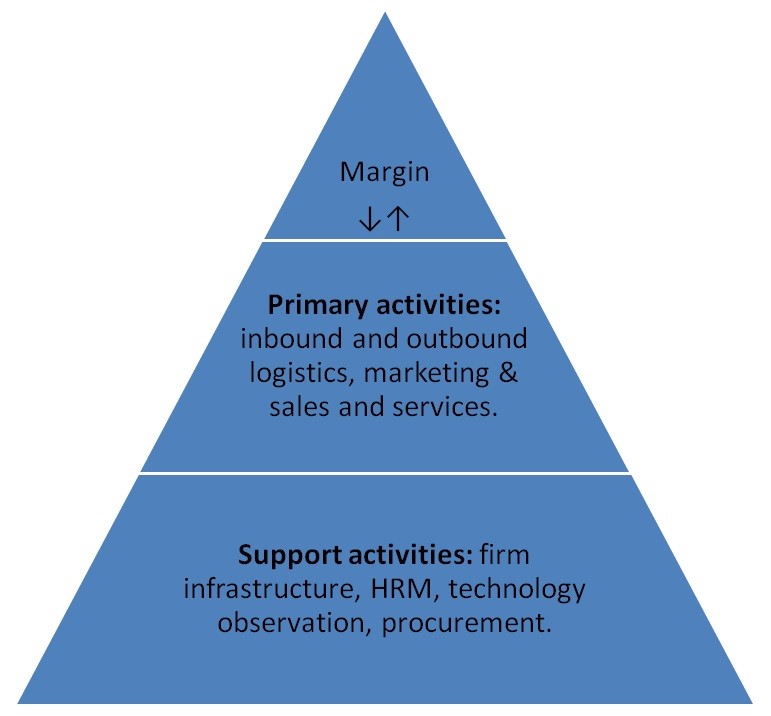
Pro and con approach to demonstrate the strategy is best for the company: Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Hoskisson, R. E. (2001), argued that pro and con approach is a combination of two classes of activities- primary activities and support activities. Primary activities involve in-inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing, sales, and services. On the other hand, support activities are- firm infrastructure, human resource management (HRM), technology development and procurement. All of these movements would efficiently turn into practice throughout the chosen strategy of foreign direct investment and joint venture.
Strategic Implementation
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Hoskisson, R. E. (2001), argued that following are the steps that should be taken to implement the recommended strategy:
- Logistical considerations: All of the equipment that needs in operating manufacture, database management, communicating tools like- telephone, Internet, machinery that manufacture products, building and proper land spaces for both official and manufacturing operation, safety and security for the personnel, first aid tools, canteen with hygienic food, toilet and pure drinking water.
- Government policies: China is a country of mixed economy and there has both capitalistic and socialistic coordination. On the other hand, government policies are friendly in foreign direct investment (FDI).
- Marketing and distribution concerns: Personal selling, retail store, shop in supermarket, online selling, sell-by post, advertisement by posturing, electronic media, print media, on Internet etc. are the process of marketing and distribution.
- The export process and export intermediaries: By road, sipping through waterways, by air using plane are process and export intermediaries,
- Core competencies of the company: Both local and international firms, which produce similar products and services,
- Corporate culture: Corporate couture is influenced by the culture of the nation and the society. Recent corporate culture for both domestic and transnational involves in- policies, motivation, relations, change agent, quality consciousness as also will reflect on the XYZ Company.
- Leadership view: Kotler, P., (2006), argued that among three leadership style- ethnocentric, polycentric and geocentric, geocentric is the ideal view. This has the competency to control the accountability and transparency of the entire company.
Strategic Evaluation
According to Lind, A. D., et al (2005, p.441), following are the steps that evaluate the strategic implementation:
- Trade relation between China and Americans: With the acceding into WTO (World Trade Organization), trade relation between USA and China has changed dramatically. In 2008, China export about 23 % of their total foreign trade to USA. Not only USA, most of the European countries depend on China in foreign trade and also Canada and Japan.
- An export diversity strategy: As the placement in a significant geological spot of China, XYZ gets advantageous of export diversity strategy. All of the modes that could be used for export all are available in China.
SWOT analysis
SWOT analysis of XYZ Company considering all of its business plans and procedures are as bellow:
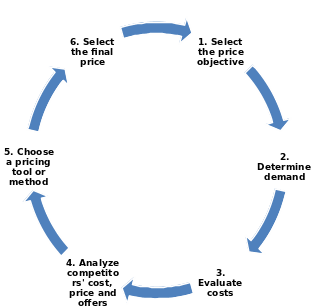
Diagram: In strategy formulation, execution and evaluation following figures illustrate the techniques are obligatory.
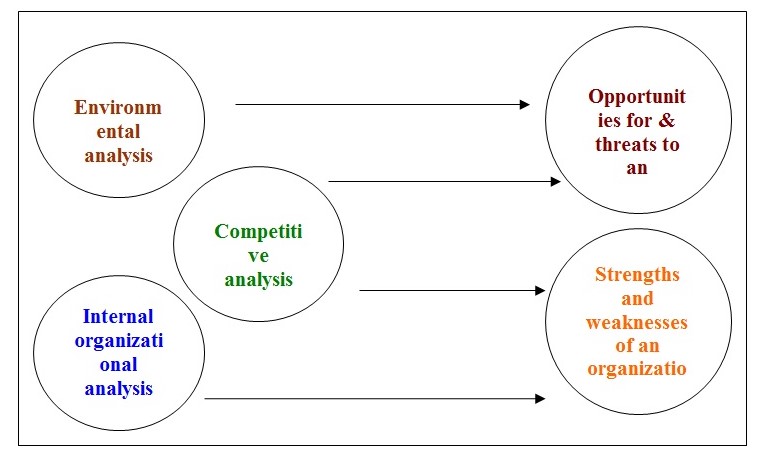
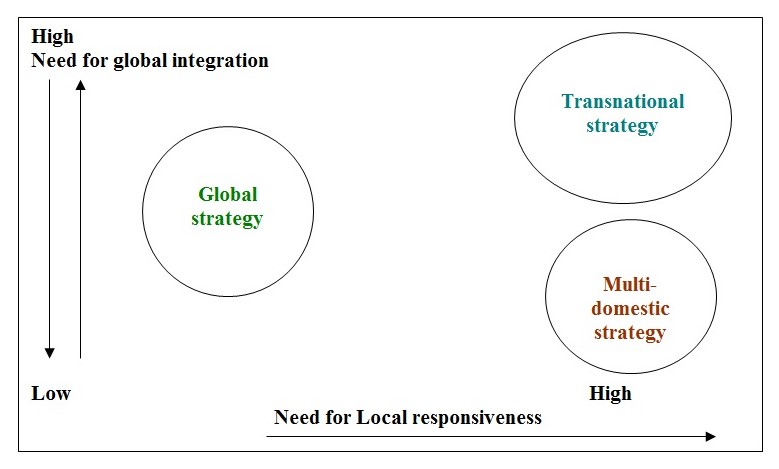
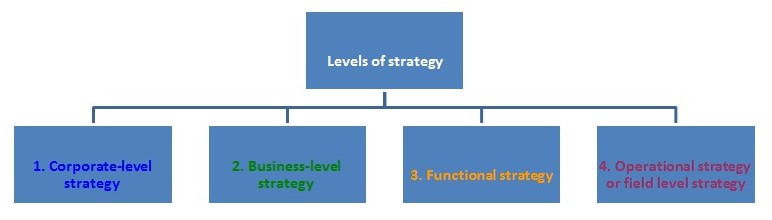
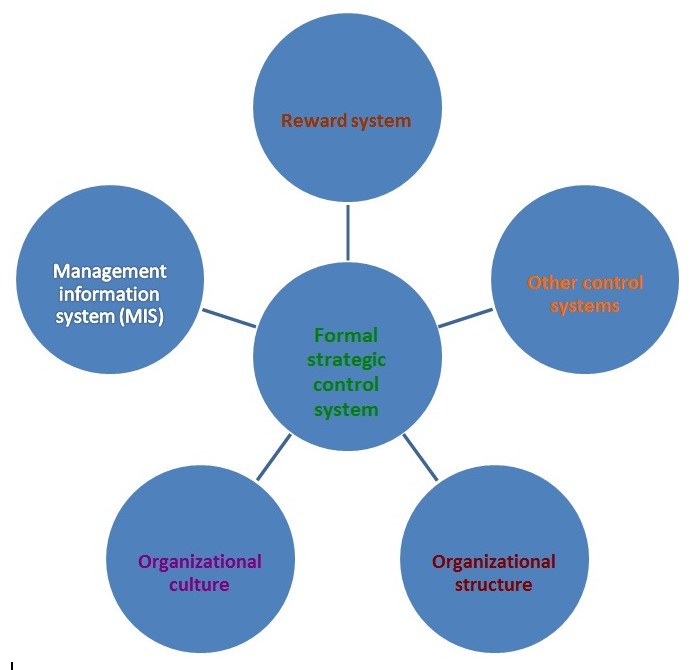
Recommendation
Considering above all discussion, following is the recommendation for “the XYZ Company”:
- For the period of market segmentation, it would be better for XYZ to target the young generation studying in graduate or higher level education, business and service holder who deal with latest information in any view.
- Promotion and distribution strategies should be deicide by considering competitors strategies,
- The competitors such as Sony and Samsung had cut the job of their employees to prevent recessionary impact but XYZ company should cut the cost rather than the job of employees,
- It should implement corporate and international strategy,
- Give out user-friendly products, less time consuming and take care of the ethics of the society both local and international. Make a restraint in responsive issues that generate a negative collision on consumers.
- Proper exercise of corporate social responsibility activities such as concerning people of environmental pollution, remove the waste of the roadside, global warming, increase literacy of the country, eave natural resources for the next generation and also campaign for HIV protection approaches.
Conclusion
This paper discusses project planning in China of the XYZ Company. In this discussion, there have been incorporated two major parts country profile and project profile. As the satisfactory scale held in China XYZ decided to be a communication tool manufacturer and distributor. Another vision is to be a global competitor in this industry. From overall discussion, probability of business in China is very much profitable though there have some natural constraints and recent global economic recession. But supportive tools are greater in number- cheap and skilled labor, advantage of FDI, adequate natural resources, significant geographical placement, flourish of industry and manufacturing firm and friendly working environment. Considering all of these China is the right place to start operating business in a global view. It could be assumed that XYZ would be benefited if they start their business there.
Bibliography
Burke, R. (2003), Project Management: Planning and Control Techniques, 4th edition, John Wiley & Sons (ASIA) Ltd, ISBN: 9812-53-121-1
Doing business, (2008), Country Profile: China, Web.
Griffin, R. W. (2006), Management, 8th Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston New York, ISBN: 0-618-35459x
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Hoskisson, R. E. (2001), Strategic Management, 4th Edition, South-Western Thosmson Learning, Singapore
Hill, C., and Jones, G., (2007), Strategic Management: An Integrated Approach, 8th edition, South-Western College, ISBN: 9780618894697
Kotler, P. (2006), Marketing Management, 11th edition, Prentice Hall, NJ, ISBN: 0-13-0336297
Library of Congress – Federal Research Division, (2006), Country Profile: China, Web.
Lind, A. D., Marchal G. W., and Wathen, S., (2005), Statistical techniques in business and economics, 12th edition, Mc Graw-Hill, ISBN: 0-07-111315-0,
Meredith, R. J., and Mantel, J. S., (2008), Project management, 6th Ed., John Wiley & Sons (Asia), Inc., ISBN-13: 978-0-471-74277-7 and ISBN-10: 0-471-74277, page-2.
Shah, A., (2008), Global Financial Crisis. Web.
Stoner, J. A. F., Freeman, R. E., Gilbert, D. R. (2006), Management, 6th Edition, Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited, ISBN: 81-203-0981-2
Saloner, G., Shepard, A., and Podolny, J., (2001), Strategic Management, 2nd edition, John Wiley, ISBN: 9780471380719
Thompson, A. et al (2007), Strategic Management, 13th edition, Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company limited, New Delhi, India.
Treanor, J., (2008), What is a short position? The Guardian, Web.
ZTE Corporation (2009), Annual Report Summary and Results Announcement. Web.

