Introduction
Today, air transportation is one of the most versatile and fastest modes of transport. Their main advantages are the transportation of passengers and cargo over particularly long distances. With the process of improving the material condition of the population and the development of its mobility in connection with the development of international relations, this means of transportation is prevalent. Thus, the analysis of one of the operating airlines will help form a complete picture of what a modern organization for the provision of air transportation should look like. Emirates company was taken as the basis of this study, as one of the most influential representatives of this field.
Emirates is an airline company based in Dubai. The prosperity of the organization is since it is developing in the UAE, a country characterized by rapid and efficient economic development (Simmons, 2020; Almarri and Abu-Hijleh, 2017). Emirates is also the fourth in the ranking of all airlines globally (O’Connell and Bueno, 2018; Redpath, O’Connell, Warnock-Smith 2017). A distinctive feature of the airline Emirates is the fact that the only means of transportation in its arsenal are wide-body aircraft manufactured by Airbus and Boeing (Figure 1).
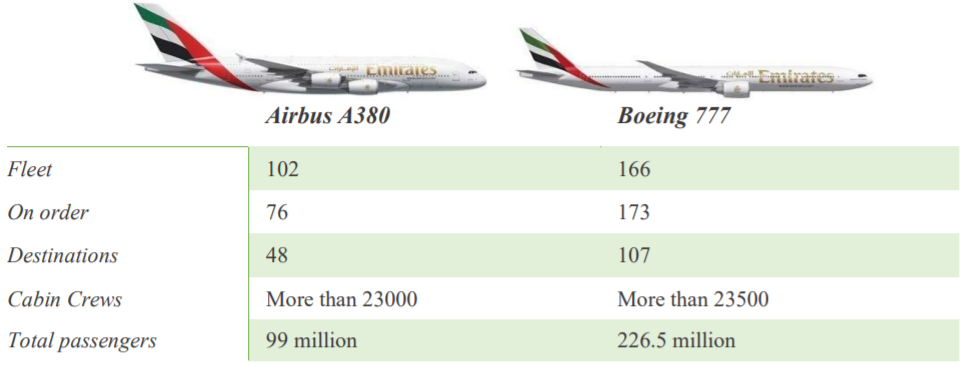
Before proceeding to the analysis of Emirates Airlines, it is necessary to highlight several positive aspects of the business of air transportation. Literature states that “airline companies are customer-centered and seek a better understanding of customer’s needs and wants in the different stages of the provision of their service” (Wafik, Abou-Shouk, and Hewedi, 2017, p. 1). The main advantage is the high speed of transportation, which allows a significant saving of customers’ time (Shanjeevan and Divassini, 2016; Shaw, 2016). This aspect also includes the expeditious organization of routes and a shortened route, which also reduces the duration of services rendered. Another aspect that plays into the airline’s side is the relatively low capital investment of the business.
The main goal of an airline, like any other business, is to make the most considerable profit, which is the difference between income and expenses. The primary sources of income for an airline are:
- Income is formed from profits from the transportation of passengers, paid luggage, and cargo, taking into account discounts and specific tariffs.
- Revenue generated from the sale of scheduled flights and charter flights.
Organizational Culture
The organizational structure of Emirates Airlines is characterized by a reasonably high hierarchy. The chairman is the head of the organization, followed by the vice president, executive secretaries, managers, heads of departments, and other employees occupying lower positions. The ownership structure in this company is characterized by narrowness, which is determined by the fact that the President controls the entire business.
The employees of the organization report not only to the head of the company but in some cases also to the vice president. The President also has the responsibility of directing the central transportation business, which also includes freight. Moreover, this boss oversees the maintenance and provision of services at airports and the hotel and holiday business.
This organizational structure facilitates faster and more efficient development because it facilitates better communication between all company levels and thus more productive decision-making. Furthermore, constant innovation, adoption of new technologies, and adjusting business strategy to all trends and currents contribute to an improved team structure (Alanezi and Al-Zahrani, 2020; Abdul-Kadir, Sadat, Sadick, 2020). Developing the team aspect of work helps the company respond more quickly to external and internal changes while suffering as few negative consequences as possible.
Moreover, the team structure that characterizes an airline ensures the development of leadership within the organization. In this case, the probability of internal problems related to such an essential resource as human resources is reduced. It is also worth noting that in such a structure, heads and team members can communicate directly with each other and increase the operational efficiency of the organization. At the same time, an important aspect is the constant encouragement of work and initiatives and the timely response to team needs.
Analysis of the Effectiveness and Operational Metrics
The leading metrics of the operational effectiveness of any business, including air transportation, is such an important economic indicator as profitability. It represents a breakdown of the revenue that a company receives in the provision of services for the transportation of passengers and cargo in relation to how much the organization has spent on these activities.
Profitability was chosen as the primary operational metric because the profit from air transportation makes it possible to set a lower level of flight load at which the airline will have a financial advantage. In addition, this economic indicator helps to identify the necessary reserves to reduce the cost, thereby finding the most profitable transportation routes to optimize the route network. In this case, the airline can also form a more effective future policy. In addition, in this analysis of services provided, the organization determines a more productive system of tariff policy and sales strategy of air transportation.
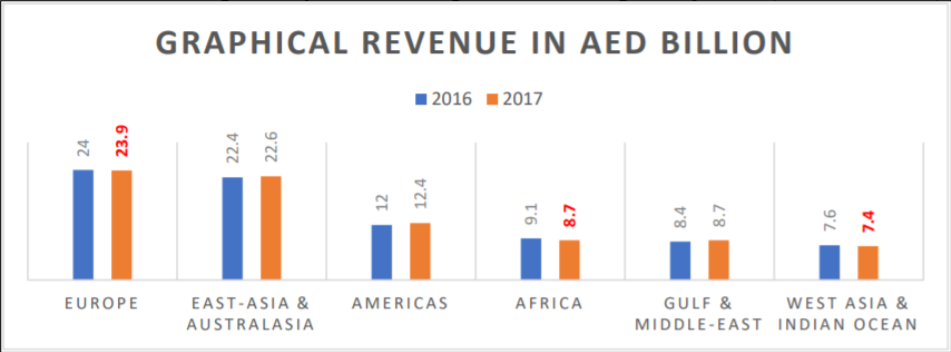
By analyzing and examining the economic indicator of the profitability of the company, the organization receives the necessary information on the main and more minor financial metrics about the effectiveness of its operation. These indicators can include revenues and expenses for different types of flights, their profitability, and financial results. The profitability as operational metric of Emirates Airlines presented in Figure 2 helps not only to assess the efficiency of its services but also to identify other important ways to optimize its performance. Thus, profitability analysis can be a productive tool for economic diagnosis. It can show possible deviations in the company’s operations that need to be changed and help make informed and balanced strategic decisions.
Emirates is characterized by a fairly extensive number of business units. Among them, there are many in related industries and sectors. Thus, such units as airport service, engineering, event management, catering, and tour operator activities can be highlighted. All these parts of the company are closely cooperating and are operated by a well-thought strategy. Moreover, this number of business units has a positive effect on customer loyalty and increased profit levels.
The airline’s tour service is called Emirates Holidays, which specializes in destinations such as Dubai, Indian Ocean, Southeast Asia, Australia and South Africa. The peculiarity of this business unit is that it provides premium, individual tours with escorted flights on award-winning Emirates. Emirates Engineering, which provides repair services from the organization, also plays a significant role in making a profit. Thus, this unit is considered technologically advanced in the field of aircraft maintenance enterprises.
Partnerships
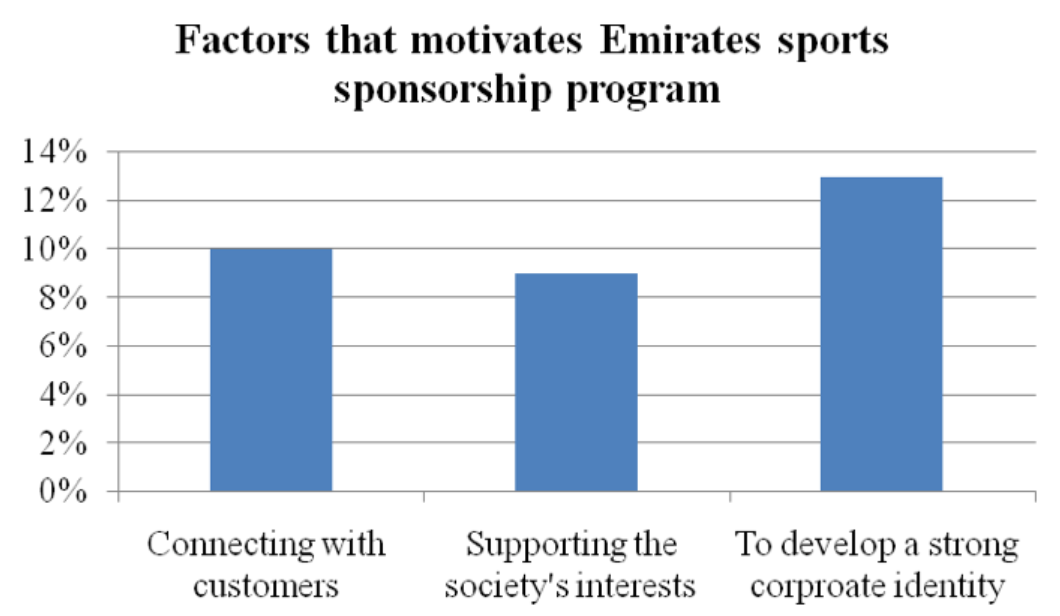
Emirates Airlines has a sufficiently large number of partners because of its impeccable reputation and excellent performance. The organization has a unique partner program, which is to accumulate Skywards miles. Users can accumulate and spend these bonuses when using the services of the airline and its partners (Alshubaily, 2017). Figure 1 shows the main factors influencing Emirates’ sports sponsorship program. As can be seen the primary one is gaining a strong corporate identity which can be particularly beneficial for the airline company.
Among the main partners of the program are Air Mauritius, Alaska Airlines, EasyJet, and Japan Airlines. Among the partners, customers can also find services that provide accommodation services in different parts of the world. The use of such policy helps not only to improve relations with other companies but also greatly increases client loyalty and adherence, which directly influences company’s profits in the market (Saleem, Zahra,Yaseen 2017; Vilkaitė-Vaitonė and Papšienė, 2016).
Research shows that “partnership program changes including increasing reward tier requirements or even discontinuing the program are likely to increase consumer defection from the firm” (McCall and McMahon, 2016, p. 111). Furthermore, the partnership with other companies provides the organization with free advertising, which takes place through the appearance of various materials on the websites of partners. In addition, there is a simultaneous formation of the company’s image through greater outreach.
Insourcing and Outsourcing
Before starting the discussion about how outsourcing and insourcing are done at Emirates Airlines, we need to take a closer look at the concept and rationale behind these two phenomena. Thus, these concepts are relatively new in today’s business industry. They arose because even with the most rational and correct approach, there may be situations in which the company needs outside assistance. In this case, outsourcing specialists are involved who can provide considerable assistance in solving one or another problem (Letica, 2016; Stamenovic and Dobraca, 2017). Luhtala defines insourcing as “delegating a function within a company” (2021, p. 10). Furthermore, insourcing is used by companies in cases when there is no need to resort to additional costs and when the company can provide itself with specific resources.
Interesting is the fact that outsourcing was first noticed in the aviation industry and is still in demand in this area of activity of society. Because the process of firing, finding, and hiring new employees is not only costly financially but also time-consuming, organizations turned to a less costly method like outsourcing (Nyameboame and Haddud, 2017; Globerman and Vining, 2017). This type of outsourcing is beneficial when several people need to be involved in solving a particular problem.
Emirates Airways is taking many different balanced decisions to optimize its business and satisfy not only the main stakeholders but also the customers themselves. Due to the constant growth of competition and the development of innovative technologies, the company has to take new measures in order to keep up with current trends. One such change is a change in sourcing strategy. This step was taken after the company’s management realized that it had sufficient capacity to create its own workforce. This decision made the airline one of the leading airlines in the world.
However, the one aspect that bothered the company the most was the fast growth of IT sphere and its state within the company itself. The problems that arose as a consequence were problems in the booking process, which led to the need to take measures to improve the system in order to increase efficiency. This was the reason for turning to insource and the creation of a specialized program that would be able to provide significant improvements in internal communication and general communications within the company. To make this innovation more effective, outsourcing was called for because of the apparent lack of personnel to streamline operations. Thus, there was a situation in which the internal forces of the company were in productive interaction with outsourced specialists.
Additionally, the airline reservation problem mentioned earlier was solved. Emirates thus improved the customer experience by allowing people to purchase tickets in advance on the online portal (Becker and Jaakkola, 2020). Jain, Aagja, and Bagdare state that “customer experience is an interactive process, facilitated through cognitive and emotional clues, moderated by the customer, resulting into unique and pleasurable memories” (2017, p. 624).
It is noted that the need for such an innovation is due to the weakness and ineffectiveness of the previous system, which over time would have ceased to bring even the slightest positive results. Outsourcing was a productive solution because it improved the firm’s IT environment. Moreover, the new booking system was designed to allow all the ticket offices at the airports to have instant communication between them and their customers.
Stakeholders
Stakeholders are actively involved in all aspects of operating a business. They have as much interest in the development and success of the company as its parent bodies (Boaventura, et al., 2020; Lehmann-Willenbrock et al., 2017; Voinov et al., 2016). Emirates Airlines’ main stakeholders appear to be the government, direct customers, suppliers, service providers, potential customers, the press, the public, and the community. It is also worth noting that despite the active position of these business stakeholders, they have different influences on the functioning and strategic decision-making process of the business (Hutahaean, 2016).
The most influential of these are those who are particularly important in the management of the company. This is because their level of power and interests concerning the organization is exceptionally high (Tobisová et al., 2017). This type of stakeholder for Emirates Airlines is direct customers because their interests and satisfaction are the highest priority.
Moreover, the company has those stakeholders whose satisfaction plays an important role, but their interest is lower than that of the more powerful stakeholders. This group of stakeholders includes the company’s suppliers, whose power is still relatively high and includes, for example, airports. However, the government of Dubai and the authorities of the United Arab Emirates must first obtain the necessary information about the functioning of the aviation industry, its progress, and its success.
What is more, the stakeholders who must constantly receive information about the airline are potential customers and the public. This is because increasing the level of dissemination of knowledge about the company, and direct customer loyalty will have a direct impact on the profits and the number of services provided by the organization (Mohamad et al., 2017; Al Saed, Upadhya, Saleh 2020). Less influential stakeholders are the media, especially the press.
Recommendations for Improvements
One of the problems that could become a severe threat to Emirates in the recent past could be poor productivity. This problem can have a substantial influence on the company’s performance and profitability of the business (Thurow, 2019). In the case where it is observed that the results are significantly lower than planned, timely decisions must be made to rectify the situation. Notably, this aspect relates to the poor or incomplete performance of the airline’s employees. Thus, a strategy to improve personnel performance may include bringing more specialists, such as outsourcing, to the support division. This is because it is this department that has the highest demand, and the percentage of successfully processed tickets is the lowest.
In addition, ensuring a higher level of productivity comes with additional training for old employees and more detailed briefings for new employees. As noted, the low efficiency of a company’s personnel can significantly negatively affect its complete and successful operation. The next possible step may be to restructure the workflow and reorganize the teams. This decision should be made after carefully examining the performance of employees and calculating those that show the least satisfactory results.
It should be noted that these measures should be applied on an ongoing basis, not only when a specific problem arises. Specialized key performance indicators, formed for each department of the company, are taken into account in this case. Such an individualized approach to performance management is vital to identify employees whose work negatively affects the organization’s performance. It is also essential that when a weak link is found, personnel can be reassigned to perform other tasks that match their skills, and termination is only applied in special exceptional cases.
The following recommendation for the airline under consideration is an improved performance evaluation system and performance management policy. This requires, firstly, a complete analysis of the company’s performance and key performance indicators. Consequently, it is necessary to introduce innovative technologies to improve the performance metrics of the employees and give them a competitive advantage (Benjamin, 2019; Abeyratne, 2016).
Great emphasis is placed on the company’s personnel, as human resource management is the most important in the work of any successful and competitive company. It is also worth noting that the Emirates airline is exceptionally flexible and up-to-date in its decisions despite the need for some changes. Thus, an optimization of the data collection process in collecting individual performance information can be suggested.
Key Operational Metrics
Emirates Airlines uses a tailored approach to measure and analyze critical operational metrics. Among the areas that are included in this study are response quality, quality of operations, and time to resolve problem situations. With the help of special software, specialists conduct the necessary research and provide information to the company. Then, the managers directly make the necessary decisions on changing the functioning of this or that department and on the need to review and update the company’s activities.
Comparison with other Airlines
In order to better understand which direction to take and where changes are necessary, it is necessary to analyze the competitors in the market. Due to the fact that the provision of air transportation is an integral and vital part of society, this industry is widely developed (Logothetis and Miyoshi, 2018). Despite the significant advantages of business development in this industry, it is necessary to remember that in this area, there is a lot of competition. It is also worth noting that managers should not be afraid of this aspect of the organization, as it is one of the primary motivators of company development. It also includes three key factors: the number of competing companies, the forces behind the competition, and the strategies used.
Among Emirates’ main competitors are Middle Eastern, Asia-Pacific, and European companies. The company’s first significant competitor is International Consolidated Airlines. This company was formed after the merger of organizations in England and Spain. Additionally, the company provides aircraft repair services and also provides reward program opportunities. Emirates can use such an effective tool in the company’s activities as benchmarking to maintain a competitive position (Torun et al., 2018; Oliveira et al., 2019). It provides an opportunity to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of competitors’ performance and gives an understanding of what changes should be made to improve the functioning of the company and its departments.
Another airline that is a competitor of Emirates, and with which it is often compared is Qatar Airways. Both organizations, due to their success in doing business and providing services, have raised the bar very high for other participants in the air transportation sector. It is difficult to determine exactly which company is better, since both provide a great user experience, especially in the luxury department. Emirates surpasses Qatar in that it operates flights to more than 150 destinations in more than 80 countries. The rival, in turn, performs about 130 flights. At the same time, the average rating of the Dubai Airline is four stars, while Qatar has five stars and was the first air transportation organization to receive this award.
Therefore, this study focused on an analysis of the efficiency and productivity of Emirates Airlines. In conclusion, it can be said that the company has a thriving business policy and correctly analyzes its key performance metrics. This aspect helps to understand the industry better and understand how the organization works and what changes can be made. The paper also conducted a study of the stakeholders, competitors, and gave some recommendations to optimize the operation of the passenger and cargo air transportation company.
Reference List
Abdul-Kadir, A., Sadat, A.A. and Sadick, A.A. (2020) ‘Global strategies of the airline industry: a case study of Ryanair, Emirates, NetJets, and Thomas Cook’, StudNet, 3(3), pp. 204-217.
Abeyratne, R. (2016) ‘Achieving competitive advantage through connectivity and innovation: an application in airline hubbing’, Competition and Investment in Air Transport, pp. 131-143.
Al Saed, R., Upadhya, A. and Saleh, M.A. (2020) ‘Role of airline promotion activities in destination branding: Case of Dubai vis-à-vis Emirates Airline’, European Research on Management and Business Economics, 26(3), pp.121-126.
Alanezi, F. and Al-Zahrani, R. (2020) ‘Strategic management of Emirates Airlines’, Proceedings of the 2020 2nd Asia Pacific Information Technology Conference, pp. 172-177.
Almarri, K. and Abu-Hijleh, B. (2017) ‘Critical success factors for public private partnerships in the UAE construction industry: a comparative analysis between the UAE and the UK’, Journal of Engineering, Project & Production Management, 7(1).
Alshubaily, A. (2017) ‘Exploring the key success factors for young airlines. A focus on emirates airlines and its regional competitors’ strategy for success’, Saudi Journal of Business and Management Studies, 2(1), pp.30-37.
Becker, L. and Jaakkola, E. (2020) ‘Customer experience: fundamental premises and implications for research’, Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 48(4), pp. 630-648.
Benjamin, R., et al. (2019) Captivating Technology. United States: Duke University Press.
Boaventura, J.M.G. et al. (2020) ‘Value distribution to stakeholders: The influence of stakeholder power and strategic importance in public firms’, Long Range Planning, 53(2), p. 101883.
Emirates airlines CSR application research paper. (2021). Web.
Globerman, S. and Vining, A.R. (2017) ‘The outsourcing decision: A strategic framework’, Global Outsourcing Strategies, pp. 27-40.
Hutahaean, M. (2016) ‘The importance of stakeholders approach in public policy making’, Proceedings of the International Conference on Ethics in Governance, pp. 9-20.
Jain, R., Aagja, J. and Bagdare, S. (2017). ‘Customer experience–a review and research agenda’, Journal of Service Theory and Practice, 27(3), pp. 642-662.
Kamarudeen, N. and Sundarakani, B. (2019). ‘Business and supply chain strategy of flying above the dessert: A case study of Emirates airlines’, 8th International Conference on Operations and Supply Chain Management, pp. 1-17.
Lehmann-Willenbrock, N. et al. (2017). ‘The critical importance of meetings to leader and organizational success: Evidence-based insights and implications for key stakeholders’, Organizational Dynamics, 47(1), p. 32.
Letica, M. (2016). ‘The effect of outsourcing activities selection on the benefits of outsourcing’, Management-Journal of Contemporary Management Issues, 21(2), pp. 77-97.
Logothetis, M. and Miyoshi, C. (2018). ‘Network performance and competitive impact of the single hub–A case study on Turkish Airlines and Emirates’, Journal of Air Transport Management, 69, pp. 215-223.
Luhtala, H. (2021). Case study: The benefits and challenges of insourcing in a technology company. Masters’ Thesis. Lappeenranta-Lahti University of Technology.
McCall, M. and McMahon, D. (2016) ‘Customer loyalty program management: What matters to the customer’, Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 57(1), pp.111-115.
Mohamad, H.A.D., Ab Yazid, M.S., Khatibi, A. and Azam, S.F. (2017) ‘Service quality, customer satisfaction and customer loyalty of the hotel industry in United Arab Emirates (UAE): A measurement model’, European Journal of Management and Marketing Studies, 2(4), pp.1-26.
Nyameboame, J. and Haddud, A. (2017) ‘Exploring the impact of outsourcing on organizational performance’. Journal of Global Operations and Strategic Sourcing, 10(3), pp. 362-387.
O’Connell, J.F. and Bueno, O.E. (2018). ‘A study into the hub performance Emirates, Etihad Airways and Qatar Airways and their competitive position against the major European hubbing airlines’, Journal of Air Transport Management, 69, pp. 257-268.
Oliveira, C., et al. (2019). ‘Benchmarking business analytics techniques in big data’, Procedia Computer Science, 160, pp. 690-695.
Redpath, N., O’Connell, J.F. and Warnock-Smith, D. (2017) ‘The strategic impact of airline group diversification: The cases of Emirates and Lufthansa’, Journal of Air Transport Management, 64, pp. 121-138.
Saleem, M.A., Zahra, S. and Yaseen, A. (2017). ‘Impact of service quality and trust on repurchase intentions–the case of Pakistan airline industry’, Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 29(5), pp. 1136-1159.
Shanjeevan, B. and Divassini, P. (2016) ‘Corporate strategies, strategic options and integration: Empirical study on Emirates Airline’, ICARE, p. 32.
Shaw, S. (2016) Airline marketing and management. London: Routledge.
Simmons, J.M. (2020) ‘United Arab Emirates. In The Forum of Federations Handbook of Federal Countries’, Cham, pp. 353-366.
Stamenovic, M. and Dobraca, A. (2017) ‘Benefits of outsourcing strategy and IT technology in clinical trials’, Acta Informatica Medica, 25(3), p. 203.
Thurow, L.C. (2019) ‘The productivity problem’, Macro-Engineering and The Future, pp. 89-102.
Tobisová, A., et al. (2017) ‘Social network applicability in air transport’, Transport Means-Proceedings of the International Conference, pp. 1040-1044.
Torun, M., et al. (2018) ‘Assessing business incubation: A review on benchmarking’, International Journal of Innovation Studies, 2(3), pp. 91-100.
Vilkaitė-Vaitonė, N. and Papšienė, P. (2016) ‘Influence of customer loyalty program on organizational performance: A case of airline industry’, Inžinerinė ekonomika, pp.109-116.
Voinov, A., et al. (2016) ‘Modelling with stakeholders–next generation’, Environmental Modelling & Software, 77, pp. 196-220.
Wafik, G.M., Abou-Shouk, M.A. and Hewedi, M.M. (2017) ‘Airline passenger travel cycle, satisfaction and loyalty: A comparison of Egyptair and Emirates airlines’, International Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Systems, 10(1), p. 1.
