Challenges of Apple’s Supply Chain
Changes in the Global Economy
Recession, price increase, and other economic challenges that affect the globe pose as challenges to Apple’s Supply Chain. Supply Chain Risk Leadership Council (2011) state that since the supply chain is a composition of all the processes right from supply of raw materials to delivery of the products to the consumer, changes in global economies have a direct influence on the performance of the supply chain. For instance, inflation affects the operations of Apple and other industries in the globe by increasing the prices of commodities. Inflation, recession, and boom are changes that characterise global economies and lead to fluctuations in the cost of goods produced, supplied, and delivered by companies. Therefore, it is clear that a change in the global economy is a challenge that affects Apple’s Supply Chain.
Poor Management of Inventories
Since Apple Company operates internationally, it at times experiences challenges related to the supply of products, which emanates from poor inventory management. When employees and suppliers working with the company underestimate supply or overestimate demand, the company experiences the challenge (Asamoah & Chovancová 2010). Issues associated with bullwhip and order batching arise when employees or suppliers of Apple Company engage in poor inventory management practises. The implication of the practises is increased costs in operations such as storage and transport. It is important to note that poor management of inventory is a challenge that stakeholders and human resources working with Apple Company cannot downplay.
Limited Supply of Components
For effective delivery of its services, Apple Company needs a sufficient amount of components, which are useful in the manufacture of finished products. When the amount of components supplied is minimal, the products released by the company reduce. As such, the demand in the market becomes dependent on the quantity of supplied materials. In effect, the challenge concerning the limited supply of raw materials has various negative outcomes that include losing of consumers, reduced attitude from the clients, and inefficiency of the supply chain (Supply Chain Management Faculty 2014). In addition, the challenge linked to the limited supply of components affects the rate at which the company supplies its products to distribution points globally, and hence, affects the number of products available in its stores.
Reliance on Outsourced Partners
Outsourced partners have several negative effects, which make outsourcing a challenge that requires effective systems of redress from Apple Company. Since outsourced partners are third parties, who work for the company as affiliates, they can fail to adhere to codes of conduct stipulated by the company or supply products of competing firms. In the explanation provided by Sodhi and Lee (2007), outsourced partners can, at times, demonstrate limited obedience and loyalty. The implication of failure to abide by the code of the company and obedience from outsourced partners leads to a poor reputation, which affects the overall image of the company in a destination.
Solutions
Employee Training and Control
Employee training and control helps Apple Company address challenges that affect its supply chain. When the company trains its employees, it equips them with knowledge on the essence of a chain that utilises timely production, supply, and delivery of products. Since training helps employees manage their inventories and practise teamwork, issues relating to high or low supply reduce. Moreover, by training its employees, Apple Company addresses the challenge associated with the limited supply of components. When the company develops a productive environment where creativity and innovation thrives, employees advance ideas that foster the supply of raw materials used in production. Therefore, training and controlling human resources is an outstanding solution that Apple Company can utilise in addressing challenges that affect its supply chain.
Risk Management and Its Importance in a Supply Chain
Risk management is a major element that Apple Company needs to utilise in its quest to improve the performance of its supply chain. Practically, several companies are increasingly employing the concepts and theories that are useful in addressing uncertainties that affect supply chains. In the assertion of Asamoah and Chovancová (2010), contingency theories are useful and companies can utilise them in minimisation of the effects advanced by risks that affect its supply chain. As such, Apple Company should undertake measures and employ theories and models, which address the challenges posed by uncertainties.
Examples of the Companies
Notably, Samsung is one of the companies that employ the concept of risk management in an organized manner. Since the company understands the essence of risk management, it undertakes measures that address risks associated with poor inventory, uncertainties, and changes in global economies. Therefore, Samsung provides a practical case study of companies that are in the forefront in application of risk management concepts, theories, and models. In addressing issues regarding risk management, Samsung has developed a supply chain that not only matches consumer requirements, but also helps the company achieve its objectives in the competitive marketing environment.
Customer Service Gaps Scenario
IKEA Company
IKEA Company manufactures and sells furniture to consumers globally. Based in Sweden and established in the 1950s, the company has grown and currently serves consumers from international markets. The increasing number of consumers in need of its products compelled IKEA Company to develop more warehouses and distribution centres in various points where its potential clients live. To satisfy the wide consumer requirements, which are trendy and dynamic, the company provides furniture designed in orientation with the Swedish culture, a factor that makes the furniture appealing and increases demand. It is fundamental to assert that the company has also taken exceptional strides in making its supply chain flexible and convenient for its consumers. Convenient supply chains play an integral role in addressing consumer gaps that characterise organizations, which fail to match their products with consumer expectations.
Microeconomics Theory
Microeconomics theory explains the importance of understanding consumer behaviour in addressing consumer gaps in organizations. From the explanation of Larkin (2002), consumers usually purchase products that give them high levels of satisfaction and pleasure. Therefore, the theory substantiates the relevance of initiatives undertaken by organizations such as IKEA. Initiatives like convenient supply chains and personalised products undertaken by companies like IKEA enhance the relevance and the link that the theory of microeconomics has on consumer behaviour and risk management. The relationship that is evident between risk management and effectiveness of the supply chain emanates because when companies like IKEA execute consumer oriented initiatives, risks associated with poor demand and low revenues reduce. Therefore, the theory of microeconomics is very practical in the study of consumer gaps, development of effective supply chains, and risk management.
Recommendations for Improvement
Increasing the Number of Distribution Outlets
For IKEA Company to continue enjoying its market share and consumer base, it needs to add more stores and distribution points in regions where its potential clients live. The need to increase the number of distribution outlets transpires from the rising number of consumers, who love and purchase its products. When the number of consumers in need of services from IKEA increases, the company should respond by adding the number of distribution points, which supply its products. By providing several outlets that supply its products, the company develops a supply chain, which is efficient and convenient. Efficient and convenient supply chain comes into existence because by increasing the number of outlets that offer its services, IKEA Company reduces the challenges and costs that its consumers encounter in the process of purchasing its furniture.
Preparedness for Challenges
Preparedness for Challenges is a solution that IKEA Company can use in addressing consumer gaps and risks that can affect its supply chain. The company needs to adopt solutions, which incorporate aspects such as agile and lean supply chains, minimised middle players, or supply partners, and use of customer oriented supply chains. While agility refers to the level of responsiveness to consumer dynamics, lean supply chains imply chains that accelerate product delivery. According to Larkin (2002), IKEA Company focuses on increasing the speed at which products reach their potential consumers. To implement the focus, the company has to ensure that its supply chain is agile, lean, and has minimal number of middle players. When a company’s supply chain has several middle players, the prices of its products are likely to increase as opposed to companies that have minimal number of supply partners. Therefore, to develop products that follow an effective supply chain customised in relation to client requirements and sustain its present progress, IKEA Company should employ strategies that enhance its level of preparedness.
Plan and Risks
A Project Plan to Improve the Supply Chain and Risk Management Strategies of IKEA Company
Present State of the Supply Chain and Risk Management in IKEA
Currently, the supply chain of IKEA Company incorporates a well-connected network of suppliers and distribution points all over the world. The company has also developed measures that cushion it from the effects advanced by uncertainties or risks. IKEA Company has stores in various parts of the world as it strives to meet the amplified consumer demand. Furthermore, the company operates in countries such as the United States, Sweden, Paris, and others parts of the world. The design of the stores is in a manner that minimises problems that consumers experience in disorganized and complex warehouses. Some of the outstanding features that make the distribution points and supply chains of the company effective include the presence of child playgrounds, clearly indicated sections and items, and skilled human resources, who provide the required information to the consumers.
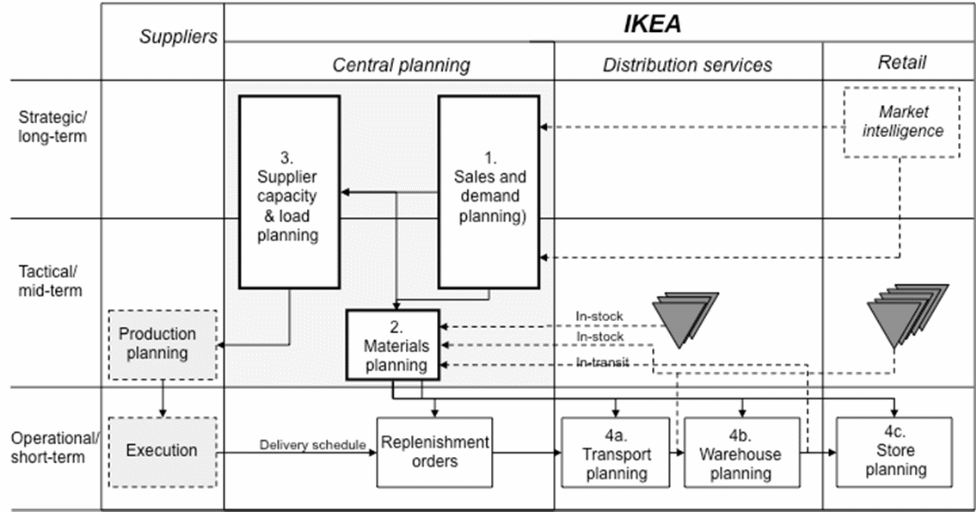
From the diagram, it is clear that IKEA Company has a good supply chain that facilitates timely delivery of products. The diagram elaborates the fact that the company understands the importance of a good supply chain that is free from delays. It is fundamental to explain that when customers experience delays, their loyalty, and willingness to purchase products of a given organization reduces. Therefore, the presence of a well-designed supply chain as demonstrated by the diagram compounds the application of Just in Time (JIT) concept and speeds up the process of product delivery.
Implementation of the Project Plan
Although IKEA Company has a superb supply chain and risk management methods that lead to development of products, which match consumer demands, it still has to continue engaging in initiatives that foster and sustain its progress. To achieve the objective, the company has to institute strategies geared towards sustained development and risk management. A project plan tailored to address issues that concern supply chain and risk management is substantial for IKEA Company as it strives to increase the market share and consumer base. In effect, some of the measures include consumer oriented supply chains, centralised ways of executing its operations, and continuous research on consumer trends. These measures are very important in amplifying the supply chain of IKEA and ensuring that its potential clients receive the best from the company..
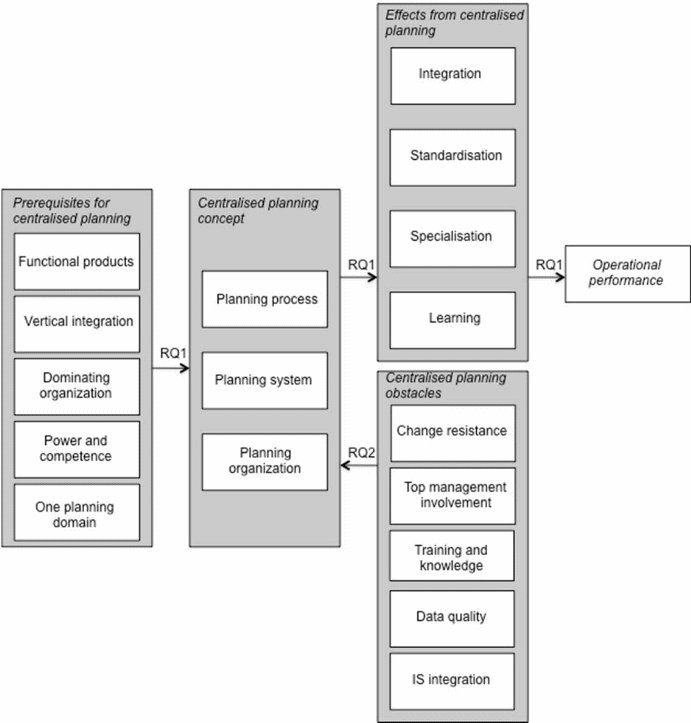
Principally, planning is one of the major strengths that lead to implementation of a workable and productive project plan. To implement its project plan and ensure that the supply chain and risk management procedures undertaken by its suppliers and human resources meet excellent standards, the company has to devise policies that focus on planning and research. From the diagram, figure 2, it is evident that organizations need to engage in planning forecasts, implementation, and an eventual survey of the effects advanced by the plan (Jonsson, Rudberg, and Holmberg 2013). The diagram illustrates that a well-designed plan is responsible for an exceptional operational performance. As such, the diagram best explains the importance of designing workplace policies and implementing them after an intensive process of due diligence.
Expected Outcomes after Implementation of the Project Plan
Exceptional operational performance, delivery of high-end products, and increased consumer base are effects that transpire after a successful implementation of a well-designed project plan. When IKEA Company follows the provisions designed in the plan and the diagrams (figure 1 and 2), the instances of achieving the best increases. Increased chances of achievement occurs because adherence to the implementation procedures leads to development of supply chains that are workable and risk management procedures that minimise unwanted costs emanating from uncertainties.
Risk Assessment Plan
Figure 3: Table of Activities
Figure 4: Grant Chart
Reference list
Asamoah, E & Chovancová, M 2010, An overview of the theory of Microeconomics (consumer behaviour and market structures) in fast food marketing, Tomas Bata University, Zlín.
Jonsson, P, Rudberg, M & Holmberg, S 2013, ‘Centralised supply chain planning at IKEA’, Supply Chain Management: An international journal, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 337-350.
Larkin, J 2003, Strategic reputation risk management, Palgrave Macmillan, Hampshire.
Sodhi, M & Lee, S 2007, An Analysis of Sources of Risk in the Consumer Electronics Industry, JORS Publishers, London.
Supply Chain Management Faculty 2014, Managing Risk in the global supply chain, Tennessee, University of Tennessee.
Supply Chain Risk Leadership Council 2011, Supply Chain Risk Management: A Compilation of Best Practises. Supply Chain Risk Leadership Council, New York.

