Introduction
“The history books will record 2020 as the aviation industry’s worst financial year, bar none,” stated Alexandre de Juniac, the Director-General, and CEO of IATA(International Air Transport Association), in a recent interview in Jan 2021.
While the Covid-19 pandemic’s impact can be seen globally in almost every industry, aviation, together with the tourism and hospitality industry, had been the hardest hit. According to ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organisation), Airlines revenues were down by USD370 billion in 2020. As the Covid situation continued to deteriorate, it forced almost every country globally to close their borders and impose tight inter-country movement control. As a result, approximately 60% of the worldwide fleet of aircraft were grounded.
The chart below shows Year-on-year change of weekly flight frequency of global airlines from January 6 to January 4, 2021, by country. The number of scheduled flights dropped by 43.5 percent for the week starting January 4, 2021 compared to the week starting January 6, 2020.
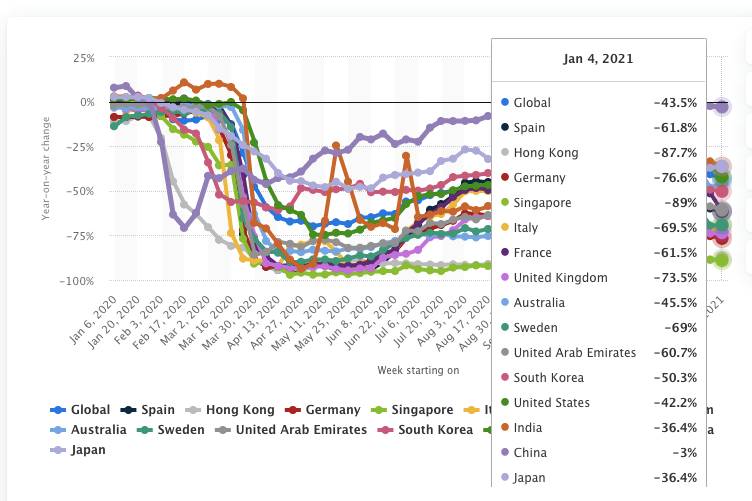
Furthermore, this has hit not only the Airlines but also the manufacturers of aircraft as well as MRO (Maintenance Repair & Overhaul) companies as well.. These industry players are all aggressively reducing costs, taking substantial credit to manage liquidity and sustainability, and continue to struggle to generate revenue.
Notably, Boeing is one of the world’s largest aircraft manufacturers in the world. Boeing’s reputation as an expert in fighter jets and military helicopters goes back to its founding in 1917.The introduction of Boeing’s commercial aircraft, the 707, in 1958 was a great success for the company since the company continued leading in the entire industry. Boeing is well-known for producing various aerospace products like commercial airplanes, jets, and military aircraft. E-cigarette product variety will increase and profit from its expanded customer base.
Airbus is a European company headquartered in Blagnac, France, and founded to compete with American companies (Hayward, 1995). In contrast to the American companies, most European companies were small-scale, and a competitor company was required in the US. The first Airbus aircraft was the Airbus 300. The A300B was designed to be able to carry more than 300 passengers. Airbus had the goal of increasing competition for its product. The company has managed to design new aircraft that can beat the competition. Today, Airbus is known for its international reference in the aerospace sector specializing in designing, manufacturing, and delivering high-quality commercial aircraft, helicopters, military transports, satellites, and launch vehicles.
Despite supplying more than 90 percent of the world’s commercial aircraft, the duo players Boeing and its competitor Airbus do not have much leverage when nearly all their airline customers fight for survival. In April 2020, the article “Steer From Crisis to Recovery” by Financial Times stated;
“As international air travel grinds to a halt in the face of the coronavirus pandemic, the global aerospace industry is being forced to confront some hard truths about a future it once believed was secure for at least the next decade. Record order books, built on a decade of booming demand and worth more than $1tn at list prices, are looking less certain by the day as airlines push back deliveries and even cancel orders to survive the worst crisis in aviation history”
This paper analyses the various roles played by Boeing and it’s performance through financial analysis and reviewing Boeing’s Balance Score Card and it’s strategic planning with his competitor Airbus.
Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
The balanced scorecard is a tool used to design the company’s strategy in a manner that takes all of its objectives into account. Per Kimmel et al. (2018), its purposes include combining financial and nonfinancial measures, creating communication linkages, providing measurable nonfinancial objectives, and avoiding excessive focus on any specific goal. To that end, it consists of four different aspects: financial, customer, internal business processes, and learning and growth. The first oversees financial performance, the second takes customers and other stakeholders into account, the third considers the quality and efficiency of performance, and the fourth and final objective oversees items such as human capital and infrastructure. By analysing all of these items, the company can determine what actions need to be taken to ensure future success.
Role of Stakeholders in Performance Measurement System
Boeing is a global corporation that works with clients worldwide, both public and private ones. As such, it has a large number of stakeholders that it needs to take into account and whose concerns it has to address. Examples of essential stakeholders include employees, suppliers, customers, shareholders, business partners, and various governmental and non-governmental agencies. All of these groups have varying requirements and some degree of power over Boeing, which they can exercise to achieve their purposes.
Additionally, for optimal performance, Boeing is incentivized to minimize the friction present in its operations, for which purpose the goodwill of all stakeholders is required. With that said, satisfying all of the stakeholders will likely be impossible due to their conflicting goals, and the company needs to actively communicate with each group and facilitate conversations to create an understanding of what can be done.
The group that is typically considered the most influential for a company is its shareholders, who expect it to display consistent growth and a strong future outlook. With that said, customers, both private and public, also exert a substantial amount of influence, as, while they need the company to service airplanes they have bought from it, they can choose to source new ones from Boeing’s primary competitor, Airbus. Suppliers are also essential, as it is expensive to make design changes to accommodate parts changes for the company’s planes, and it needs access to replacement components for planes that have already been built. Ganesh et al. (2020) highlight Boeing’s propensity for involving the last two categories in projects such as the design phase of Boeing 777. As such, the company likely values and collects feedback for performance management purposes, as well.
Strategy Map Aligning Balanced Scorecard Perspectives
The strategy map begins with learning and growth, continuing into internal business processes, customer orientation, and financial objectives. In terms of learning and growth, the company intends to enhance the quality of its human resources through education and training of its employees. Additionally, Boeing aims to further improve its knowledge gathering and retention, improving the base of learning from which workers can draw to innovate and propose improvements.
These suggestions translate into improvements in efficiency and quality, which are among the strategy goals listed in the internal business processes category. With dramatically reduced revenues and an uncertain recovery timeframe, Boeing needs to minimize its costs while remaining capable of providing a competitive, high-quality product in a timely manner. For the same reason, despite the reduced budget the company can put into its research, it needs to continue developing new concepts at the same or higher pace.
These strategies help Boeing maintain its customer-perspective agenda items, such as delivering excellent aircraft in a timely manner. One particularly vital target is modifying the Boeing 737-MAX fleet so that the flaws in it are addressed and it can be returned to service (Boeing, 2020b). The forced grounding of the aircraft following the discovery of the flaw has hurt Boeing’s buyers dramatically, and it needs to recover their goodwill. Additionally, as Boeing (2020a) notes, a significant part of its strategy is to become more environmentally friendly due to pressure from customers and other stakeholders. Lastly, in terms of financial objectives, the company’s primary goals are to increase revenue and profitability.
Due to COVID-19 and the associated airline shutdowns and closures, demand for Boeing planes has dropped substantially, and objectives such as growth and increased dividends cannot be feasibly achieved. Currently, the company will be pursuing cost reductions and trying to deliver its outstanding orders while also attracting new ones wherever they emerge.
Evaluation of Balance Score Card (BSC)

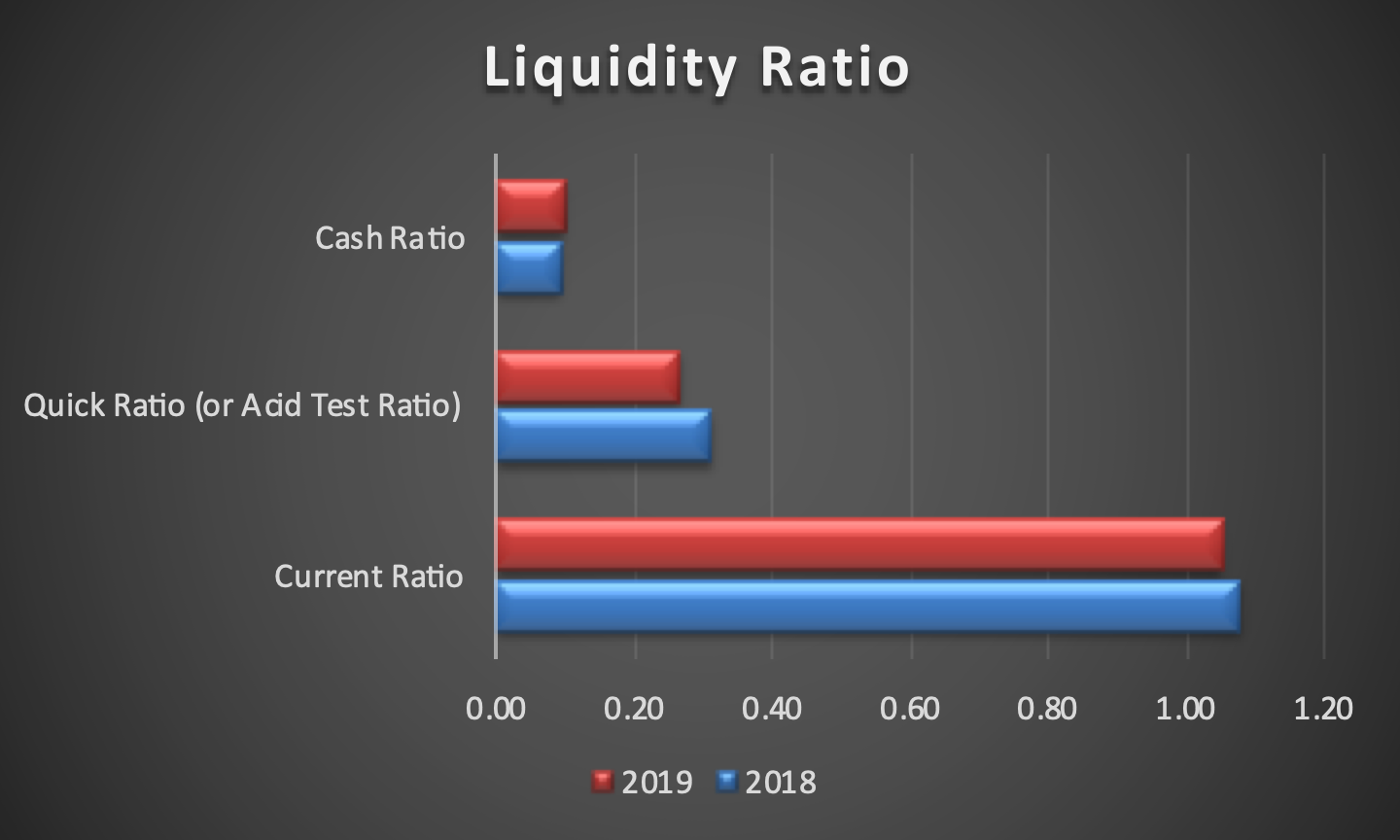
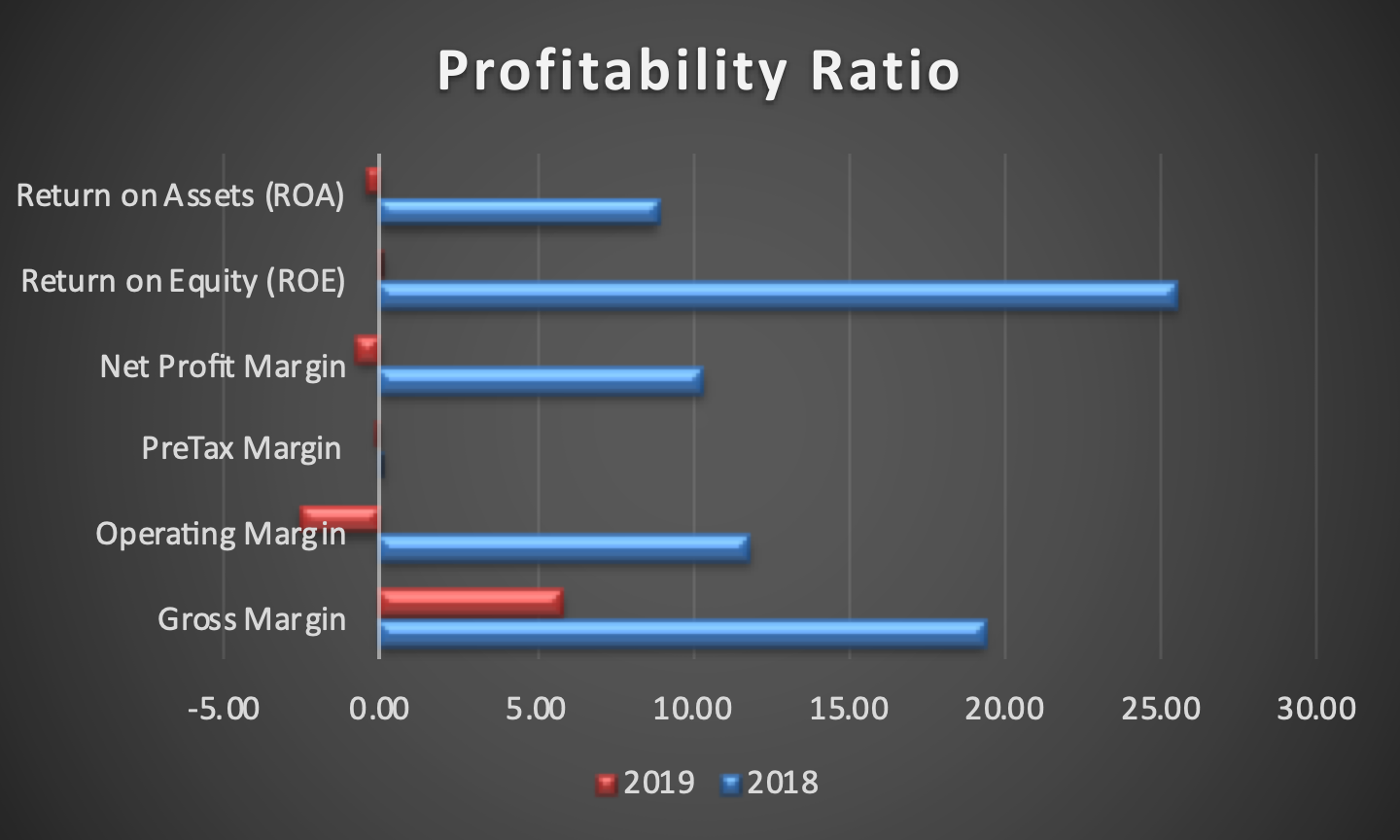
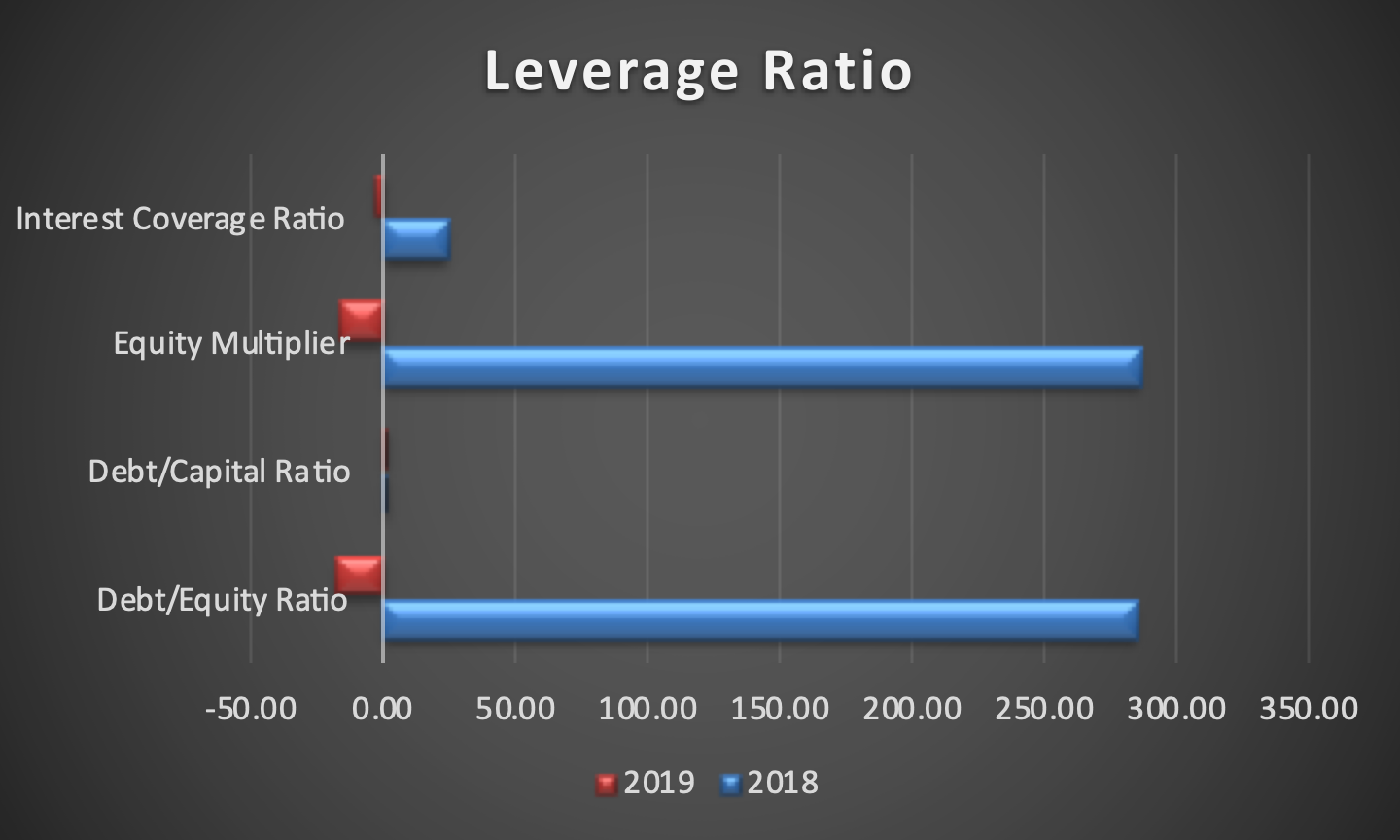
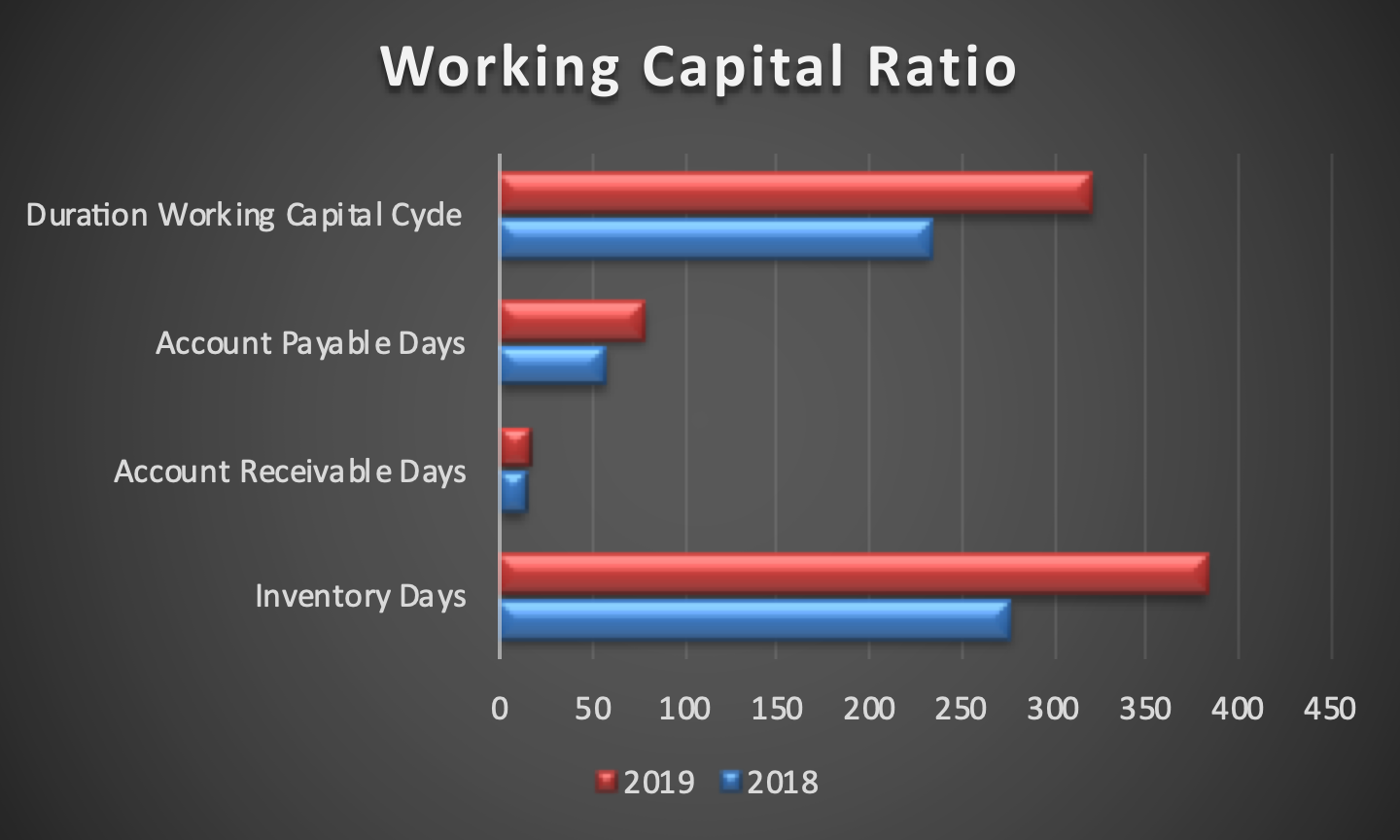
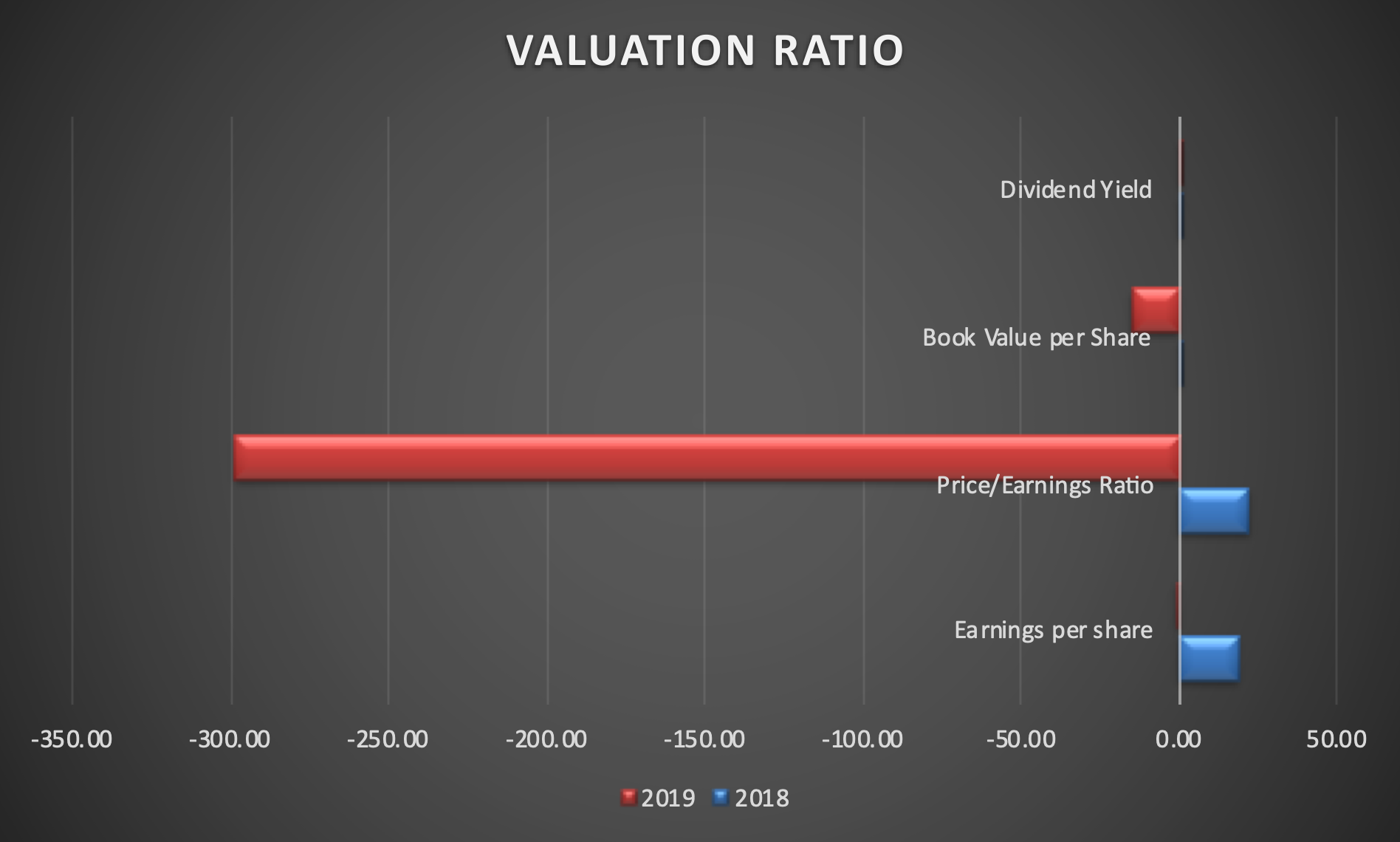
The balanced scorecard was formulated based on Boeing’s annual reports from the years 2017, 2018, and 2019. Information regarding its 2020 performance, which is of particular note due to the damage caused by COVID-19, is not yet available, limiting the analysis that could be performed on the company in that timeframe. The goals outlined in the scorecard were formulated based on the strategy map discussed above. As can be seen, financially, the corporation started facing issues in 2019, primarily due to the issue with Boeing 737-MAX, and the issues were likely exacerbated by COVID-19.
The company’s profitability and return on capital employed were reduced dramatically, and it spent much of its current cash. As such, recovering liquidity and improving the sales and profitability to an acceptable standard are prominent targets, for which multiple measures and initiatives were developed. Increasing the number of the company’s customers is a critical effort for this purpose, for which Boeing needs to secure their trust. To that end, it needs to continue delivering aircraft, return its 737-MAX planes to service (which it has not yet accomplished as of early 2021), and improving the environmental performance of their planes to comply with the demands placed upon airlines.
Innovation and Learning shows that Boeing has been steadily hiring over the recent years, including 2019. With that said, per Isidore (2020), the company has laid off at least 26,000 workers in 2020 and intends to continue doing so in 2021. With that said, it is essential for Boeing to retain its most skilled workers, which can be difficult as the average age of its employees is high and they are likely to consider retiring.
As such, hiring and training new workers are critical goals for Boeing to maintain its ability to operate competitively even as it lays off staff to manage losses. To succeed in doing so, the company needs to maintain a culture that encourages joining, improving the benefits that it provides. Lastly, in terms of internal business processes, Boeing needs to cut costs without compromising its quality. With that said, it has not been able to deliver as many aircraft as before due to lack of demand but kept producing them regardless, leading to an increase in inventory. Maintaining the unused fleet is costly but necessary because continued production can lead to innovation that saves costs and effort while improving the end product.
As such, Boeing should continue on its current trajectory while maintaining its research and development investment. Additional cost-cutting measures will need to be taken, as well, but most of them should emerge organically to minimize the adverse side effects.
BOEING Co. strategy map aligning Balanced Scorecard perspectives
The Balanced Scorecard
Financial Perspective
Boeing’s management planning strategies
Analysis of long-term objectives and strategy for Boeing Company
Boeing’s brand strategy should improve its image and increase awareness of its product’s efficiency, reliability, and sustainability due to the 737 Max single-aisle jet failure. On the other hand, although Boeing is known for its commercial aircraft production, the company is also very active in aerospace engineering and technologies, military aircraft, and defense systems (Brown, 2010). The most critical strategic alternative the company should pursue is the advancement of innovative research related to aircraft manufacturing and improving the quality drastically, reliability, and sustainability of its product.
As the Covid-19 situation is unstable and most airlines are not in operation, Boeing should take the opportunity to review its manufacturing strategy and the development of more energy-efficient aircraft is becoming more critical for Boeing in the long-run. The present state of the world’s technologies is much dependent on intensive research due to their intricate dynamics.
Boeing Company’s goals and their implementation.
Considering the current situation, Boeing will need to prepare for the future and anticipate the most critical issues it will face. In this case, one of the main crises Boeing Company might face is the reduction in production……
In light of the COVID19 crisis, Boeing should prepare for the crisis and prevent making things worse for itself.
Considering Boeing’s historic decline in aircrafts sales, the company has devised a strategic plan to build superior aircrafts capable of carrying more passengers for longer distances without immediate stops. The larger and less gas-hungry 787 is cost-effective because it can carry more passengers and travel longer distances without stops.
It has been an effective way to reduce the cost of gasoline by increasing fuel economy. One of Boeing’s primary strategies to survive in this economic crisis is extensive and intensive research on energy-efficient aircraft (Pearce & Robinson, 2010).
Conclusion
The future of the Boeing Company is contingent on their ability to respond to the global society’s needs. More so, the company should build larger aircraft to increase the cost benefit ratio between the various commercial airlines.
By investing in larger aircrafts which are able to transport more, the airline will have better relationships with the airline industry,………and taxes will not reduce its profits.
Boeing is a well-known company and currently struggling to maintain it’s status. Evaluating as to how much Boeing involves its employees in the decision making, it just seems like communication was amongst one of their main concerns.
Boeing recognized that it had to enforce discipline on its employees, and thus it circulated a direct telephone number to solve matters concerning the code of ethics.
Communication is crucial because it is normal for employees not to follow guidelines or breach the organization’s legal compliance set. This is often a regular occurrence in cases where there are stringent deadlines to be met. The leaders’ role in an organization is to have a clear vision of future requirements similar to Boeing Co.
References
Brown, J. (2010). Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology. International Journal, 72(5): 342-357.
Collopy, P. (2004). Military Technology Pull and the Structure of the Commercial Aircraft Industry. Journal Of Aircraft, Web.
Maierbrugger, A. (2011). Boeing expects robust growth in airline industry. Web.
Pearce, J. & Robinson, R. (2010). Strategic Management 12th Edition. New York: McGraw- Hill Publishers.
Vasigh, B., Fleming, K. & Tacker, T. (2009). Introduction to Air Transport Economics: Boeing Case. London: Ashgate Press.
Wilson, R. & Gilligan, C. (2005). Strategic Marketing Management Planning, Implementation and Control. (3rd Ed.). Burlington, MA: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Kimmel, P. D., Weygandt, J. J., & Kieso, D. E. (2018). Accounting: Tools for business decision making (7th ed.). Wiley.
Ganesh, K. Prakash. S. L., Begum, S., Mohapatra, S., & Rajendran, C. (2020). Total quality management in higher education: Study of engineering institutions. Taylor & Francis.
Boeing. (2020b). What we stand for: The Boeing Company 2019 annual report. Web.
Boeing. (2020a). Global environment report 2020. Web.
Isidor, C. (2020). Boeing will lay off another 7,000 workers as losses mount. CNN. Web.

