Introduction
The Coca Cola Company is one of the most successful multinational corporations in the globe (Kontes, 2015). It manufactures and markets a wide range of non-alcoholic beverages in every corner of the globe. The company’s business model is characterized by many bottling partners across the globe. Such bottlers operate as franchises thus making the corporation successful. The firm embraces the most desirable business practices in order to achieve its potentials. This research paper examines the major business attributes that make Coca Cola a leading competitor in the global non-alcoholic beverage industry (Yoffie & Kim, 2011). The discussion also presents meaningful recommendations that can be used to improve Coca Cola’s business performance.
Coca Cola: Company Information
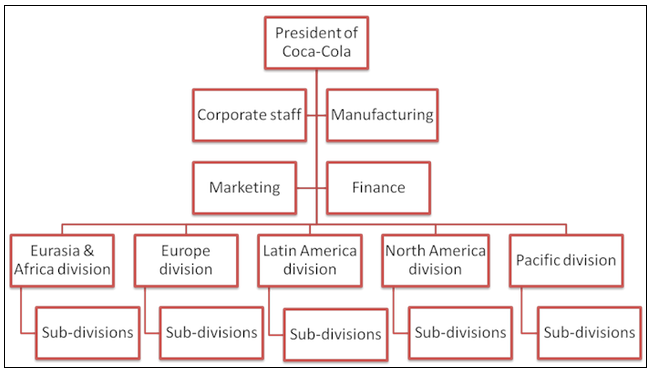
The legal name of this firm is “the Coca-Cola Company and has its headquarters in Atlanta, Georgia” (The Coca-Cola Company, 2016, para. 1). The organization has “a simple leadership chart characterized by a chief executive officer (CEO), regional vice presidents, and departmental managers” (Kontes, 2015, p. 31). The company’s website is www.scs.com (The Coca-Cola Company, 2016). The company has around 129,000 employees.
The firm’s current president is James Quincey. The CEO is called Muhtar Kent (The Coca-Cola Company, 2016). The CEO also serves as the company’s chairman. The company recorded revenues of around 44.3 billion US dollars in 2015. Coca Cola’s total equity is 25.5 billion dollars (The Coca-Cola Company, 2016). The company’s positive performance has led to increased profits. The company made a profit of $7.3 billion in 2015.
Mission, Vision, and Organizational Strategies
In order to remain profitable in the ever-changing global environment, Coca Cola’s business strategy is guided by a powerful mission. The mission focuses on three key objectives. These mission objectives include “refreshing the world, creating value and making a difference, and inspiring moments of happiness and optimism” (Humphrey, 2015, p. 39). This mission is used as a benchmark to dictate the firm’s business decisions and actions. The company’s vision is used to support the most desirable business model. The vision focuses on the needs of the people, the planet, and its stakeholders. The company works hard “to develop the best working environments, collaborate with sustainable partners, promote sustainability initiatives, and maximize shareholder value” (The Coca-Cola Company, 2016, para. 5).
The company’s organizational culture promotes the best behaviors and attitudes. For instance, the company encourages its workers to embrace “the power of integrity, accountability, leadership, collaboration, quality, diversity, and passion” (Kontes, 2015, p. 38). The firm also promotes the most desirable and sustainable practices that can result in accountability. These attributes have been critical towards making Coca Cola one of the strongest brands in the world.
Coca Cola uses powerful operational strategies in order to remain competitive in the industry. For instance, the company uses a powerful supply chain network. Bottlers are required to obtain concentrates from the parent company (The Coca-Cola Company, 2016). The concentrate is prepared using specified procedures in order to produce quality beverages. The beverages are then distributed using the most appropriate supply chain and logistical operations (Kontes, 2015). This approach has made the company successful and competitive in the industry.
In order to achieve its goals and address the problem of competition, Coca Cola has been using desirable marketing strategies. It uses different promotional practices to sensitize more potential customers about its products. The informed customers support the company’s goals by consuming its products. Research and development (R&D) is another operational strategy aimed at producing superior products that can compete in the market (Yoffie & Kim, 2011).
The firm implements these strategies in a professional manner in order to achieve its corporate goals. Marketers, distributors, and researchers are empowered using the most appropriate resources. The company uses a wide range of promotional approaches to make the targeted strategies successful. As well, Coca Cola produces new products that have the potential to add value to the global consumer. The firm focuses on the global consumer in order to deal with the problem of competition. These strategic approaches have played a major role towards making Coca Cola one of the most successful and profitable companies in the non-alcoholic beverage industry (Yoffie & Kim, 2011).
Overall Supply Chain Mechanism
Coca Cola Company has a superior supply chain network characterized by different stakeholders. The supply chain network connects all stakeholders across the globe. This approach makes it easier for the company to support the needs of every global consumer. The company begins by producing different concentrates. Such concentrates are then shipped to different bottlers across the globe. The bottlers collaborate with outsources logistical companies in order to ensure every product is delivered to different suppliers and distributors in a timely manner. The supply chain network is customized depending on the needs of the consumers (Hasan, 2013). For example, the company can use distributors or consumer outlets such as shopping malls.
Each player in the supply chain process plays a positive role towards supporting the company’s business strategy. For instance, bottlers should acquire the concentrates using properly-guided procurements strategies. The final products should be transported to the distributors within the shortest time possible. Distributors and middlemen are required to undertake various advertising strategies in an attempt to attract more customers. The supply chain process is customized to address the varying needs of the final consumer. The use of modern technologies makes it easier for the company to track every product. Consumer needs and supply requirements are monitored using modern informatics (Hasan, 2013). The supply chain has become demand-driven thus reducing wastes (Hasan, 2013).
Work Processes that Create Value
Coca Cola’s success can be attributed to the organizational culture and work processes that are promoted by its leaders. Such work processes are undertaken to support various organizational strategies. The first operational work process is continuous innovation. This process is guided by different factors such as research and development (R&D), teamwork, and collaboration (Kontes, 2015). The company also encourages its workers to come up with the best ideas and innovations. The internal teams in the firm collaborate with different marketers in order to produce superior beverages that can address the emerging needs of more consumers.
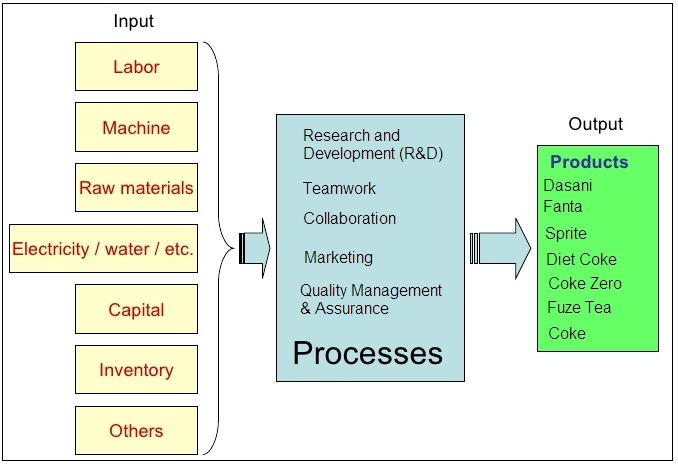
Marketing is another work process that has created value at Coca Cola. Marketers promote the best strategies that empower and address the needs of every global consumer. Managers and leaders present their inputs in order to ensure the marketers are aware of the company’s business objectives. Employees are encouraged to present new incentives that have the potential to support the company’s goals. Managerial practices are usually aimed at supporting more workers and stakeholders (Yoffie & Kim, 2011). The workers are guided to focus on the company’s mission and vision. Managers use their competencies to design proper models that can be followed by the employees.
These input-process-output elements explain why Coca Cola is a profitable company. The workers at the company are usually empowered and mentored in an attempt to add value to the final consumer. Distributors and logistical managers present their inputs to ensure the needs of every consumer are met (Humphrey, 2015). However, some weaknesses such as inadequate use of input-process-output elements might affect the level of performance.
Coca Cola should consider new technologies and competitive advantages if it wants to overcome these weaknesses. A careful analysis of “the feedback and control system is something that has the potential to promote better practices at the company and eventually support the needs of more markets” (Humphrey, 2015, p. 47).
Product and Service Design
The most outstanding feature of Coca Cola is the strength of its brand. Kontes (2015) argues that “brand image is one of the valuable assets owned by business organizations” (p. 65). Coke is a strong brand revered by many people across the globe. The company’s products are believed to be tasty and revolutionary. The company undertakes numerous researches in order to come up with new products that can address the needs of different consumers. For instance, Coke has remained one of the most admired and consumed beverages in every corner of the globe (Kontes, 2015). The brand has resisted every form of competition from companies such as Pepsi.
The company came up with Diet Coke and Coke Zero in order to address the health concerns of different consumers (Yoffie & Kim, 2011). This fact shows that the firm focuses on the best product attributes that can add value to more potential buyers. The company came up with Dasani in order to deal with competition. The wide range of Coke brands explains how the firm supports the needs of more customers with diverse health needs.
On top of that, the marketing process delivers the best experience to the end user. The corporation’s marketing strategy delivers more products to different customers. Every person has access to the company’s wide range of offerings (Butler & Tischler, 2015). The supply chain networks and marketing strategies explain why more customers prefer Coca Cola’s products.
However, the company’s products still face numerous challenges because of various health concerns and the increasing level of competition. Indirect competitors such as Starbucks are marketing non-carbonated beverages to more customers (Butler & Tischler, 2015). Coke should therefore produce non-carbonated beverages that can address the problem of competition. The R&D department should also undertake more studies in order to come up with superior brands that can support the company’s goals.
The firm’s supply chain processes should also focus on every underserved region. As well, Coca Cola has been known to use an effective global supply chain strategy. However, the services associated with this global supply chain might not be appropriate for consumers in different regions (Butler & Tischler, 2015). The firm should therefore use suitable supply chain processes that are dictated by the needs of the consumers in the targeted regions.
Quality Management Issues
Quality management and assurance are critical processes in every business practice. Companies should embrace the best procedures in order to ensure every product or service is acceptable. Coca Cola uses strict procedures, principles, and policies in order to produce quality products. The company established a system known as the “Coca-Cola Operating Requirements (KORE) to replace the Coca-Cola Management System (TCCMS) in 2010” (Humphrey, 2015, p. 23).
KORE has been critical towards ensuring that every quality issue is taken seriously. Competent people are encouraged to “monitor products, ingredients, manufacturing processes, distribution networks, and bottling procedures” (Humphrey, 2015, p. 31). These strategies are undertaken in order “to ensure every product is in accordance with the company’s expectations and consumer needs” (Butler & Tischler, 2015, p. 49).
The quality management initiative is also taken further to different suppliers, bottlers, and outlet stores. These stakeholders are required to implement the most appropriate quality practices. As well, the company disperses quality assurance teams (QATs) to ensure every stakeholder acts ethically. The firm also promotes sustainable practices and initiatives in different parts of the globe. Working environments are also monitored in an attempt to improve occupation safety and support more workers. Basically, Coca Cola has been on the frontline to ensure every product delivered to the end-user is healthy (Humphrey, 2015).
In the recent past, Coca Cola has been accused of quality issues and business malpractices. For instance, the company was accused of discharging dirty waste water in India. This issue was publicized thus affecting the company’s image (Humphrey, 2015). As well, many customers believe that the company’s products are unhealthy. Such issues have forced the company to produce healthy products such as Diet Coke. If not addressed, such issues can affect the company’s performance and profitability.
Capacity Planning
Several activities must be undertaken before the final product is marketed to the consumer. This issue explains why capacity planning is taken seriously by business organizations. At Coca Cola, a wide range of processes are undertaken in order to add value to the targeted consumer (The Coca-Cola Company, 2016). The company begins by identifying and hiring competent individuals who have the potential to support its business model. Raw materials are sourced from the right vendors. A powerful logistical process characterized by e-procurement is undertaken to ensure the right raw materials are acquired in a timely manner. The production processes are then coordinated in an effective manner (Humphrey, 2015). The quality assurance (QA) team also examines the effectiveness of every production process.
Monitoring systems are also undertaken to ensure every process is completed in a proper manner. The company has a response team that trouble-shoots systems and machines that fail. Marketing is also executed in accordance with the needs of the consumers. Inputs and opinions from different stakeholders are used to improve various processes. These aspects show clearly that Coca Cola has one of the most effective capacity planning strategies (The Coca-Cola Company, 2016). Continuous improvement (CI) is a powerful concept that is embraced at the company to promote better production processes and minimize wastes.
Forecasting Techniques
Every business process at Coca Cola is guided by evidence-based ideas. This fact explains why forecasting is done in order to address every emerging consumer need. The company has a powerful information and technology (I&T) system to improve every supply chain process (The Coca-Cola Company, 2016). The company embraces the power of e-procurement to improve the speed of product delivery. The R&D department uses powerful technologies to forecast the future needs of different consumers. As well, the managers identify emerging markets that can make Coca Cola successful.
The firm also considers emerging challenges that might affect its performance and profitability. For instance, insights from consumer behaviors and purchasing trends are use to forecast the major substitute products that might pose new challenges. This knowledge guides the firm “to identify new promotional practices and products that can level the playing ground” (Hasan, 2013, p. 45). These forecasting techniques will make it easier for the company to achieve its future business potentials.
Location, Layout, and Facilities Planning
Coca Cola locates its bottling plants in regions that have adequate clean water (Hasan, 2013). The company also selects regions that have proper transportation networks. Distributors are selected depending on the availability of potential customers. These decisions make it easier for the company to maximize its operational effectiveness. Every facility is planned in an effective manner in an attempt to improve logistical operations and reduce time wastage (The Coca-Cola Company, 2016).
The plan is designed in such a way that raw materials can be accessed without interfering with packaging and warehousing. As well, the issues of space and efficiency are taken seriously whenever designing different facilities. The important thing is to ensure various processes are completed efficiently while at the same time saving time and energy.
Recommendations and Conclusions
Coca Cola has succeeded because of its business models and strategies. The logistical processes undertaken by the company are exemplary. More customers across the globe consume Coke brands every single day. However, Coca Cola should acknowledge the presence of competition from companies such as Pepsi and Starbucks. A new business model focusing on the health needs of the global consumer and emerging competition will play a positive role towards making the firm more competitive (Butler & Tischler, 2015). Coca Cola should also be aware of the major issues affecting its sustainability image. The firm should therefore undertake the best practices in order to remain sustainable and profitable.
Reference List
Butler, D., & Tischler, L. (2015). Design to Grow: How Coca-Cola Learned to Combine Scale and Agility. New York, NY: Simon and Schuster.
Hasan, M. (2013). Sustainable Supply Chain Management Practices and Operational Performance. American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, 3(1), 42-48.
Humphrey, T. (2015). Supply Chain Maturity Assessment of Coca Cola Ghana Ltd. Haaga-Helia, 1(1), 1-72.
Kontes, P. (2015). The CEO, Strategy, and Shareholder Value: Making the Choices That Maximize Company Performance. New York, NY: Wiley.
The Coca-Cola Company. (2016). Web.
Yoffie, D., & Kim, R. (2011). Coca Wars Continue: Coke and Pepsi in 2010. Harvard Business School, 1(1), 1-23.

