Abstract
The world market is increasingly becoming competitive due to globalization that has been enhanced by technology. It is coming out clearly that dynamism is very important for firms to survive market changes. Firms must be in a position to change with the changes taking place in the market and at a speed that will enable them to gain a competitive edge over their rivals. As such, scholars have widely published the importance of agility in firms. It is through agility that a firm can detect and respond to these changes with the desired speed. Four factors are widely believed to be creating dynamic organizations. The first is the human factor. Human resource plays a very important role in ensuring that a firm is flexible enough to respond to market forces. The second is leadership. With appropriate leadership, a firm can develop strategies that can enhance dynamism within an organization. The production makes the third factor, which creates a dynamic organization. A firm must develop production processes that are responsive to the changing environmental factor. Finally, technology has been identified to be another force, which creates a dynamic organization. Using emerging technologies can help a firm become innovative in its production. It is through innovative ideas that a firm can increase its productivity and profitability in the market.
Introduction
Background of the Study
The world is increasingly becoming competitive with advancing technology and increasing globalization. According to Daft (2009, p. 89), firms are forced to find ways in which they can manage this kind of competition to remain relevant in the market. Changes in the external environment are taking place at unprecedented rates, with various players coming up with new approaches to handling various activities in the market. This is in an attempt to gain a competitive advantage in this market. However, Hommel (2012, p. 79) says that in the current marketplace, a permanent competitive advantage no longer exists. What a firm may consider as a competitive advantage today may be a potential source of weakness in tomorrow’s market, depending on the nature of changes taking place in the market. This means that firms must constantly be ready to change with the changing environmental factors. This would include changing their strategies to gain new competitive advantages to suite the changing patterns in the market.
Dynamism in business has been experienced for a long time due to the constant evolution in technology and the way of life of humankind. Market factors have constantly been changing, especially since the 20th century, when technology started playing an important role in business operations. According to Kodama (2008, p. 67), there are different factors of dynamism that have a direct impact on the operations of a business unit. Technology is one of the leading factors of dynamism in business operations today. The emerging technologies have redefined the way business units operate in the market. Firms are forced to adopt these emerging technologies at a rate that is fast enough to gain some competitive advantage from them. Several firms, including Eastman Kodak, have lost their lead in the market due to their inability to use the emerging technologies to enhance their innovativeness. Another factor that has been very important in defining how successful a firm can be in the market is the management of employees within the firm. Employees are the most important asset within an organization. The success of a firm will always depend on how the employees perform duties assigned to them in the market. In the current world, the management needs to appreciate that employees are also changing with the emerging trends witnessed in the globalized society.
Agility is what many scholars have identified as the solution for firms in the current competitive market. According to Andrzej and Buchaman (2007, p. 69), agility is defined as “The ability of a [system] to rapidly respond to change by adapting its initial stable configuration.” Several other sources have defined agility is different ways. Still, one factor that comes out is that agility involves the ability of an individual or organization to respond to changes fast and in an efficient manner. The ability of an organization to change rapidly will demand that such an organization has a system through which it would detect these changes as soon as they occur. The system should also be able to determine the best approach to take in adapting to such change. This is because not all changes are relevant. There are other changes that are disruptive. For this reason, a firm needs to determine the best approach to take in adapting to these changes. This research focuses on examining the different factors creating dynamic organizations and their impact on productivity with the proper use of innovation.
Problem Statement
Recent reports have indicated that several large organizations may be faced out of the market because of their inability to manage change in the environment. Several other companies have fallen, some of which were considered too big to fall, such as the Lehman Brothers. Other large firms such as Eastman Kodak had to be rescued by financial institutions such as Citibank to remain operational in the market. Scholars have undertaken to discover some of the reasons why such firms once thought to be too big to be shaken by their competitors or other forces in the market have curved into dynamism in the market. Similarly, business start-ups around the world rarely celebrate their fifth anniversaries. In some cases, these business start-ups fail in their first year in operations.
Several scholars have stated that the main reason for this failure is organizational dynamics, which have a direct impact on the productivity of firms. These dynamics may harm the employees or the processes within the plant. For the employees, these dynamics may render their skills and experience needless within the organization. The dynamics may also disrupt the normal operations of firms in this market. For this reason, there is a need to find a way through which firms can manage these changes which take place in the market to be able to respond to them. When responding to these changes, speed is of value to the firm. Several scholars have indicated that agility may be the only solution through which firms can survive the environmental dynamism. It is through this that they can avert the possible failure and premature departure from the market.
Purpose of the Study
According to Daft (2009, p. 116), conducting research is a process that involves incurring costs. The researcher will need to spend time and material resources to complete the research process. For this reason, research should have a specific purpose that should be achieved upon its completion. This research has specific objectives that the researcher seeks to achieve upon completing this research. The following are the specific objectives for this research.
- To examine different factors that create dynamism in organizations and how they affect productivity within such organizations.
- To provide a new definition of an organization from the perspective of employees and how this may influence organizational productivity.
- To lay down a clear mechanism that an organization can use to manage the changing environmental factors, and how agility can be incorporated in organizational strategy.
The above are some of the specific aims of the researcher. The researcher hopes that this piece of research will help transform clumsy organizations in the market to firms that are able to respond to environmental changes with speed and accuracy. This way, Saudi Arabia will be able to have sustainable business units in the market. They will be able to sustain the pressure that has been emanating from multinational firms operating in this region. They will be able to view globalization as a tool for success and not a hindrance to their prosperity.
Significance of the Study
The government of Saudi Arabia has been concerned with the success of business units in this country. The case is not just isolated to Saudi Arabia but also other governments within this region that are determined to transform their business environment for the better in order to enable firms to operate in a sustainable manner. This study is significant in several ways. In the business world, the research focuses on how management can use agility in their business strategies as a way of ensuring that they manage the market changes. This research clearly gives the importance of having a business strategy that is flexible enough to respond to market changes as quickly as may be necessary. The research is focused on how management comes up with an appropriate method through which employees can be managed in a way that would make them able to respond to various environmental changes. As was stated above, the management must realize the importance of the employees and the fact that they hold the success of an organization in their hands.
As such, they should understand organizational dynamism and be able to respond to these changes in a flexible manner. It is this flexibility that can ensure that a firm remains profitable and sustainable in the market. Employee motivation would always lead to satisfaction among employees. As such, the management should find a way in which they can sustain employee satisfaction in the organization. This will help ensure that these employees are willing and ready to stretch their capacities to help in achieving the best of the results in the market. To the policymakers in the government, the study stipulates some of the factors they should consider in a firm before they can commit finance or other resources to it. To scholars, this study offers a rich resource through which they can advance their research in this field.
Research Question and Hypothesis
Conducting research requires a lot of focus on the side of the researcher to come up with findings that are valid enough to bring a positive impact in this field. According to Clement and Henry (2010, p. 112), research questions are always very important when conducting a piece of research. This is because it narrows down the focus of the researcher to the relevant topic under investigation. In most instances, researchers would always find themselves swayed from the main topic when collecting data. A researcher may be exposed to very interesting but irrelevant topics while collecting both primary and secondary data.
In such instances, the researcher may spend precious time gathering data that may not be of any use to the research. With research questions, a researcher will always be guided on what is to be done within the available timeframe. This way, the researcher will be able to discern relevant data from junk information that may not help in coming up with relevant answers to the research. In this research, the researcher developed several questions that would offer guidance when collecting both primary and secondary data for this research. The following are the research questions developed from the research.
What are the factors that create a dynamic organization, and how does the human factor influence this dynamism when applied well?
This research question was meant to help identify some of the factors that create dynamism within an organization. It also tries to bring to light how the human factor influences dynamism if applied appropriately within an organization.
What is the relationship between innovation and organization dynamic and its impact in terms of negative consequences if not managed well?
This question was based on the premise that innovation has a close relationship with organizational dynamics. It was developed with the knowledge that firms are currently struggling to be innovative to manage dynamism in the market. The researcher was also interested in finding the consequences of innovation to an organization that can manage it well. This would help give a true picture of what organizations can achieve if they manage their innovativeness well as a way of managing the dynamism in the market. The following are the research hypothesis for this research.
The first research hypothesis was designed to determine the role of human resources in enhancing the dynamism of an organization. This hypothesis was developed out of the realization that a firm’s success in the market is always associated with the kind of workforce it has. It starts with the production process. It is the employees who are responsible for the direct production process at the plant. They are responsible for operating the machines, monitoring the production process, and ensuring that goods finally reach the market. It is the employees who are the ambassadors of an organization in the market. The way they relate with customers and other stakeholders in the external environment will determine the perception of the market, and the general public will have towards it. Given this importance of the human resource, the hypothesis was focused on determining how they influence organizational dynamics.
H1o. Human resource has no direct effect in determining how dynamic an organization can be in the market.
The above null hypothesis rejects the possibility of human resources affecting organizational dynamics in any other way. The researcher will test this hypothesis using the primary data, which will be analyzed using SPSS. The rejection of the above null hypothesis will mean that the alternate hypothesis will be accepted. This is stated below.
H1a. Human resource has a direct effect in determining how dynamic an organization can be in the market.
The second hypothesis focused on leadership and its possible effect on the creation of a dynamic organization. The researcher believed that leadership has a direct effect on the creation of a dynamic organization. This is because leaders will always dictate the policies used within the firm. These policies will always determine how dynamic an organization is in the market. When leaders create policies that are conscious of the changes that are taking place in the external environment, then chances are always high that the strategies would be dynamic enough to respond to the environmental changes. It is also in light of the knowledge that the actions of employees are always dependant on the leadership of that organization. It is the leadership that will determine whether or not employees will remain motivated in their respective tasks. For this reason, there are high chances that they are a factor that can help in creating a dynamic organization. The following null hypothesis was developed for the purpose of analysis using SPSS.
H2o. Leadership is not one of the main factors creating dynamic organizations in the current competitive market.
The researcher wishes to reject the above null hypothesis using primary data collected from the field. The rejection of this hypothesis will help validate the fact that leadership is a factor that can create dynamic organizations. Its rejection would mean that the following alternate hypothesis will be accepted.
H2oa. Leadership is one of the main factors creating dynamic organizations in the current competitive market.
The third hypothesis of this research focused on the production strategies applied by a firm. Researchers have had a consensus on the fact that production strategies always have an impact on the productivity of an organization. The emerging technologies have tried to ensure that the production process is made a lot more efficient. This is not only because of the need to produce standardized products but also because of the time factor. Time is one of the most important resources that an organization has. Any strategy that can help reduce the time taken to produce goods for the market is always welcome because it saves such a firm time. The emerging technologies have also tried to ensure that the products are of high quality. Given the great attention that these emerging technologies have given to the production process, it is evident that production is an important factor that may be creating a dynamic organization. The production strategies applied by a firm in its operations may determine the ability of an organization to be dynamic in the market. It was on this basis that the hypothesis below was developed.
H3o. The ability of an organization to be dynamic in the market successfully does not depend on successful production strategies applied by the firm in its operations.
The researcher intends to reject the null hypothesis above using the primary data collected from the field using SPSS. Its rejection would help validate the alternate hypothesis below. The alternate hypothesis below would validate the need to conduct further research to determine the specific ways in which production strategies may contribute to the creation of a dynamic organization.
H3a. The ability of an organization to be dynamic in the market success depends on successful production strategies applied by the firm in its operations.
The last hypothesis was developed to determine the role of technology in the creation of a dynamic organization. As was hinted in the sections above, the emerging technologies have had a massive impact on various processes within an organization. Organizations have come to embrace technology as a solution to some of the issues that are presented in a dynamic environment. As Coulter (2009, p. 91) observes, firms cannot afford to ignore technology is their production and marketing strategies. This is because technology always brings more efficient and cost-effective methods of handling various issues within an organization. This makes technology a force that determines the approach that a firm would take in the market. The researcher developed the alternate hypothesis below, which would be analyzed using the primary data collected from the field.
H4o. Technology has no direct impact on organizational dynamics.
The researcher wishes to reject the above null hypothesis. It is a fact that one may consider the above hypothesis as an obvious fact. However, Chaston (2009, p. 23) notes that not every technology can positively influence a firm. There are some technologies that are disruptive. Some of them may force a firm to spend a lot while the output that it shall deliver is not commensurate to the cost, which was incurred when integrating the new technology. It is, therefore, important to investigate from the employee and the management the role of technology in creating dynamic organizations. The researcher hopes to confirm the fact that technology plays a part in creating a dynamic organization. If the data confirms this, then the alternate hypothesis below will be accepted.
H4a. Technology has a direct impact on organizational dynamics.
The four hypotheses define some of the factors that have a direct impact on the creation of a dynamic organization. Indeed, they are not the only factors creating dynamic organizations. However, they are the major factors that may affect any firm irrespective of the size of the firm, the industry in which it operates, or the country in which it operates. The literature search in chapter two of this dissertation confirms the fact that other factors may contribute to the creation of a dynamic organization. As will be witnessed in the next chapter, these other factors are in one way or the other related to the above factors named in this chapter. This makes the hypothesis above the core of this research. Other factors find their relationship with these factors.
Scope of the Research
According to Wall (2010, p. 115), a piece of research is always important in developing a given field of study. This scholar says that several people rely on such pieces of research in several ways. Policymakers depend on researches to have a strong basis for making decisions when formulating policies. Researchers depend on other pieces of research to support their findings or as a basis upon which further research can be done. Learners depend on these researches to enhance their understanding of a particular field. This demonstrates how important a piece of research is to society. However, it is important to understand that not all pieces of research can be applied universally. The policymakers must know the limitations of particular research before committing the decisions made to it. For this reason, it is always important to specify the scope of research to clarify to the public the importance of the research, and the level to which its application can be relevant. This would also help in minimizing criticism of the research by other researchers who may base their research on a different context. The researcher, therefore, found it needful to define the scope and limitations of this research for the benefit of the users and critics.
This piece of research was conducted in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. All the primary data was collected from individuals working within this country. Any application of this report should, therefore, be limited to this country, or a country that has a similar socio-economic status to that of this country. Any application of this research outside this context should be made with reservations. The secondary sources of data were gathered from journals, books, and online sources relevant to this field. Although the researcher tried to use books that were based on this country, most of the books have global coverage, with some being inclined to the United States and European economies. This is why references have been made to global firms like Lehman Brothers and Eastman Kodak. This was a deliberate attempt by the researcher to put to focus on the economy of Saudi Arabia about that of other parts of the world. The researcher was also interested in giving this research paper a global image by incorporating various global organizations and world economies in the literature review. This would help in enhancing the understanding of how different factors of dynamic organizations impact on its productivity from a global perspective.
Definition of terms
A piece of research is always important not only to the policymakers who could have initiated and funded it but also to various other stakeholders such as learners. For this reason, it is always important to make a report understandable to everyone who intends to use it in one way or the other. The users of the report should not strain reading the report because this will make it be considered as a material that is difficult to use. This means that a researcher should use terms that are easy to understand. Complex words should be avoided as much as possible. However, every field has some specific terms that must be used to make sense, as would be expected. These terms may not be replaced by their equivalents for the sake of simplicity because this may compromise the quality of the report. This means that although not desirable, some terms will be jargon to some readers because they cannot be simplified. Some of the terms are always vernacular words that are used by the people where the research was conducted. For this reason, it is important to define some of the terms that may be strange to some users. The researcher identified some of the terms, and below is their definition.
- Dynamic: Characterized by continuous change, activity, or progress: a dynamic market (Evans 2012, p. 32).
- Agility: The ability of a [system] to rapidly respond to change by adapting its initial stable configuration (Ferrell 2011, p. 78).
- SPSS: statistical package for social sciences.
- Emerging technologies: the current technological changes which bring with them new approaches to handling various activities.
- Productivity: the rate at which factors of production can deliver products for a firm.
- Profitability: the level to which a firm can reap benefits out of its investment of the factors of production.
- Coevolutionary gaming: A planning strategy, which involves the creation of strategies and counter-strategies, always tested in the form of a game by the top management of a firm.
Literature Review
What is Organization Dynamics?
The business environment has been experiencing changes in various factors that constitute it. According to D’Aveni (1995, p. 78), the changing environmental factors are majorly attributed to the changes taking place in the field of technology. Technology is redefining various environmental factors. The world has been reduced into a small global village thanks to technology. It is through advancement in transport and communication technologies that the world has been reduced into a small village. Business units can operate thanks to the advancements in the two sectors globally. A logistics manager can trace the movement of products from their manufacturing plants in China through the United Arab Emirates into Saudi Arabia because of this technology. With advanced communication, an operational manager can manage various activities within the firm while miles away. These changes have a direct impact on the operations of business units. This is what scholars and social scientists have described as dynamism in the field of business.
Daft (2009, p. 82) describes organizational dynamics as the changes in the business environment of a firm that may have a direct impact on the normal operations of a firm. This scholar says that a firm should be able to deal with organizational dynamics in a manner that would help a firm avoid any negative impact that may result from these changes. Change is a factor that a business unit cannot avoid. It will always come in the normal running of a business unit. However, it is a fact that most organizations may find it very challenging to adapt to the changes in the environment. Some of the environmental changes may be very complex to implement, especially when it involves massive disruption of the normal operations of a firm. These dynamisms play an important role in the evolution of firms in the market. For a firm to be able to manage these dynamisms, it should try to embrace flexibility as part of its strategies of remaining competitive in the market.
Changes that take place in the business environment are always focused on making business units operate more efficiently, and therefore, become more competitive in the market. However, Doucet (2011, p. 79) says that not every change that came into the business environment is positive. Technology has helped firms operate in a more efficient manner, but the same technology can lead to a downfall of a firm. Given that market competition has gotten very high, competitors are always willing to apply any mechanism to bring down their competitors. Some of the strategies may be very unethical. The solution to such unethical practices has always been the same technology that has positively transformed the business world. Cobb (2011, p. 114) says that a competitor may come with a technological invention that is meant to convince its rivals to use for their own peril. They use such technologies as bait to trap their competitors. This has made the process of adopting the emerging trends in the market very complex for business units. It is complex because before a firm can embrace a given trend, a thorough analysis of the trend must be analyzed to determine whether it is viable or not.
According to Grantham (2007, p. 67), the only way through which a firm can manage dynamism within an organization is to develop a positive attitude towards it. Various players may not easily accept change because it always comes at a cost. However, it is a reality that a firm cannot run away from. Embracing dynamism is the best way through which a firm can succeed in the current competitive market. To achieve this, there should be systems within emerging trends can be detected, analyzed for their affectivity, and applied as soon as it is confirmed to be relevant. Agility is the way out in beating the market competition. The speed with which a firm is expected to monitor the changing environmental factors should be considerably high. Jeffs (2008, p. 93) says that it is only those firms that are competitive in the market, which can be able to benefit from emerging trends. The emerging trends are always meant to give firms a competitive advantage over their rivals in the market. However, it is only those firms that can apply these trends way ahead of its competitors that can be able to get a substantial benefit. This is because a competitive advantage can only exist when a firm uses a technological approach that is not used by its competitors. When a firm uses a strategy that is common in the market, then the strategy cannot give the firm a competitive advantage in the market.
Factors that Create a Dynamic Organization
According to Hitt (2011, p. 48), various factors can be attributed to the dynamic organization. This scholar says that most of these factors which create dynamic organization are in one way or the other attributed to the emerging technologies and the type of workforce within a firm. Firms are struggling to maintain agility in their operations. However, it is only a few firms that have been able to succeed in the market because of the constraints that various firms have not been able to overcome. It is important to understand some of the factors that are believed to be contributing to organizational dynamics. Daft (2009, p. 38) says that these factors can be categorized as human factors, leadership, production, and technology.
The human factor
For a long time, labor has not been given its rightful position in many organizations. Many of the management have not thought of viewing their employees as very important assets. However, the happenings of the recent past have proven that the labor force is one of the most important assets to any given organization. When the management lays down objectives to be achieved, it is always the employees who are expected to implement the policies that would bring the desired results. It is this workforce that would be expected to turn the policies from paper to reality. Therefore, the retention of employees is very important. Employees should be retained within the organization to ensure that the firm’s operations are consistent. The high turnover rate of employees is not healthy for the firm’s prosperity (Handlechner 2008, p. 118). This is because it does not only affect the smooth implementation of policies within the firm but also leads to the increased cost of training new employees. It is even worse than the employees would go away, having learned the strategies of the firm, making the firm vulnerable to its competitors.
The management should, therefore, device methods of hiring qualified employees and retaining them within the firm. One of the best ways to achieve this is through motivation. It is through motivation that employees will feel attached to the firm and therefore feel committed to the firm. According to McClelland’s three needs theory of motivation, irrespective of age, gender, or culture, there are three motivating drivers (Davada 2008, p. 71). These three motivating drivers include power, achievement, and affiliation. Depending on the culture and general life experience, one of the three motivating drivers will be dominant over others. People will always be motivated to work because they either need power; they want achievement from their work or because of affiliation.
Having categorically looked at the importance of motivating employees, it is prudent to determine ways through which a given firm can ensure that its grip on its employees is not shaken. However, some factors must be considered before determining how best a firm can motivate its employees. It is an accepted fact that for a firm to motivate employees, it must start by employing some of the best talents that would help it achieve its goals. As such, it is important to understand how best a firm can recruit new employees. After recruiting the best of the employees, as per the measures that have been put in place, it is also important to appreciate that not all of them would leave up to the expectations (Frynas & Mellahi 2011, p. 86).
As such, it would again be appropriate to determine who to retain because a firm can only retain the best of the workforce to be in a position to achieve the maximum. It is upon the determination of the best workforce to retain that a firm can now develop the best ways to motivate such employees. To ensure that there is a constantly motivated workforce, it would require the management to employ the right strategies that would ensure that it succeeds in this. It may appear as a simple task of making employees happy. However, it goes beyond this. To motivate employees within the firm, there are a series of strategies that a firm should employ to ensure that employees are constantly satisfied. The secret behind this retention lies in ensuring that the employee is satisfied and feels challenged by the present task. This will cause the drive in him to want to come tomorrow and beat the challenge.
Studies have shown that the ability of a firm to maintain agility depends on the type of employees it has and how these employees are managed within the organization. As Gerry and Scholes (2008, p. 38) states, employees form the most important part of an organization. They form a formidable asset through which an organization can achieve its objectives in the market. The market is increasingly becoming competitive for firms operating both in the local and global markets. To manage this competition, it is important to embrace agility in all the operations of a firm. Machines cannot achieve agility. As Cole (1997, p. 92) puts it, a machine cannot be agile. It is the people who are part of an organization that will determine the agility of a firm in the market. It is how flexible the workforce is to the changes that will dictate how fast such an organization will be able to adapt to the emerging trends in the market. This scholar emphasizes the fact that the carrot and stick theory that was popular in the past century cannot be relevant in the current century.
Thompson (2010, p. 27) says that employees can be the main source of success of a firm, just as they can be the source of failure. When top management formulates policies to be implemented in the organization, it is the employees who will determine how well such a policy can be to the firm. This is because they are the implementing unit within the firm. A good policy can yield disastrous results if it is implemented wrongly. On the other hand, when this workforce is positively charged in its duties, then a firm will be able to reap the best results in the market. According to Hommel (2012, p. 78), the human factor has a major role to play in organizational dynamics. The human resource will be responsible for undertaking various activities within an organization. They form that part of an organization responsible for actions that would determine how well a firm can meet challenges in the market.
Creativity and innovations are one of the main factors that Norton (2011, p. 115) says can help a firm manage the dynamism in the market. Coming up with creative ways of managing environmental changes will always determine how successful a firm is in the market. In most cases, this creativity does not always emanate from the management. Creativity is always attributed to human resources. As Witcher (2010, p. 38) observes, General Electric has remained a strong firm in the market, not just because of good management strategies and enough financial resources, but mainly because of the type of employees they have, and the freedom they are given in their operations. This scholar says that at General Electric, employees are always offered the opportunity to deliver something new to the firm at least once in a year. The employees of this firm have enabled it to maintain creativity in this industry, making it the global market leader. This is a clear demonstration that human resources form an important aspect of managing a dynamic organization. As Cole (1997, p. 86) simply puts it, employees from the most important factor in creating a dynamic organization. With the right workforce, a firm can easily turn into an urgent change in the market. This would ensure that such a firm constantly has a competitive advantage over other market competitors.
Leadership
Witcher (2010, p. 67) defines leadership as an act of offering a sense of direction to followers not only by an authority one has over the followers but also by the ability of such a person to motivate the followers to act in a desired manner. Leadership is probably the most important part of a firm to human resources. Kodama (2008, p. 116) says that although management and leadership have a thin line separating them, leadership is a more elaborate way of managing followers. Leadership has attracted massive attention from various scholars around the world. According to Witcher (2010, p. 77), several theories of leadership have been put forth by various scholars. Leadership is one of the most important factors that always dictate the success or failure of an organization in the world today. Leadership has been in existence for as long as the history of humankind can be traced. As Hitt (2011, p. 50) put it, leadership goes beyond providing direction to followers. It entails going into details to discover the potential of the followers. It involves engaging the followers in a way that would make them discover themselves. It involves helping followers develop the urge to achieve. It is the art of making people realize that they have the potential to achieve beyond their current capacity. Leadership requires a leader to challenge the followers positively in a way that would make them feel that they need to rediscover themselves. Transformational leadership theory would, therefore, be important in achieving this.
According to D’Aveni (1995, p. 89), the current corporate world has become very challenging. New firms are coming into existence with new strategies that never existed before. Technology is changing the face of the earth. This poses a serious challenge to firms operating in the current market. Firms are currently facing challenges from various corners. The customer in the contemporary market has access to vast information, thanks to the advanced means of communication through mass and social media. These consumers know that they have an array of options to choose from when they want to make any purchase. They are, therefore, very demanding. They are willing to pay less for a product whose quality has been improved. Kodama (2008, p. 67) says that customers are currently asking for more, but are willing to pay less. This reduces the profitability of firms.
On the other hand, suppliers are now demanding more for the supplies they make to such an organization. Such suppliers cite increased standards of living, inflation, among other factors, as a reason for increasing the prices of their supplies. The cost of maintaining a business is very high. Various input factors have increased in price. The environmental conditions for conducting business have also been subjected to various other bottlenecks making the entire process very complicated. All these challenges are always presented to the leaders of various organizations to deal with.
A firm has to come up with means through which it can wade off these challenges and deliver quality products in the market in the best way possible (Witcher, 2010, p. 1980). This way, a firm would be able to come out as a successful business unit that can withstand market pressures. Firms share external environmental factors. Emerging technologies, good government policies, a promising market are factors that a firm cannot consider as a competitive advantage. They are factors that are shared by all the firms in that particular industry (Hitt 2011, p. 57). A firm must, therefore, develop the policies that will give it a competitive edge in the market. A firm should develop mechanisms through which it can challenge the existing market threats in the best way possible. It should be able to stand out among the rest as a firm that understands the market and can provide it with what it needs. A firm must appear positively special. All this depends on the leadership of the firm, and as Kodama (2008, p. 68) says, it is through leadership that a firm can appear unique in a market where the competitors share various factors.
This requires the proper management of the workforce. According to Hommel (2012, p. 117), this current delicate market conditions requires a strategy that will help it have the best workforce that can drive the changes required within the firm. This is what most firms have realized and are determined to achieve. They need to go beyond the simple management of the workforce. In management, there is a need for leaders (Hitt 2011, p. 75). This is because the current world has gotten increasingly democratic. Many organizations today have their employees being members of trade unions. They want to enjoy the maximum benefits that their employer can afford to give them, and hate restrictions. They resent strict rules and prefer working without strict supervision. This new crop of employees may not be able to be managed using conventional management approaches. They have to be managed from a different approach (Witcher, 2010, p. 87). They have to be managed in a way that would make them comfortable while at the workplace. This is what many firms are looking for in their management. This is what leadership offers to the management. There should be a leadership approach that allows employees to express their creative ideas in their areas of operations. When an employee proves to have a good idea that can be used to increase the productivity and efficiency of the firm, such an idea should be sponsored by the firm to help the firm manage market dynamism. As such, leadership has been considered as an important factor that creates a dynamic organization. The following three theories of leadership further emphasize the role of leadership in creating a dynamic organization.
Blake and Mouton’s Managerial Grid
Black and Mouton’s managerial grid is one of the most important leadership theories in the contemporary world. The grid is as shown below. As evidenced from the above grid, the theory emphasizes concern for people and concern for production. As a leader, there is always a concern to ensure that the organization functions effectively. This can be measured by the increased productivity of the firm. This theory says that productivity should not be overemphasized at the expense of employees.
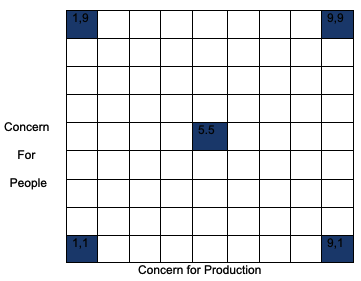
Employees are very valuable to any organization, and their interests should be taken care of. The need for productivity should be balanced with the need to protect the employees. At (1, 1) is impoverished management where employees’ concern is not taken care of, and production is poor. At (9, 1), the emphasis is laid on task while taking middle ground (5, 5) would help the firm achieve its objectives moderately with moderately satisfied employees. At (1, 9), the emphasis is given on concern for employees. The best grid is at (9, 9), always referred to as team management. Employees’ concern is emphasized while ensuring that production is put at maximum levels possible. Basing leadership upon this theory, a leader would need to realize that for there to be a change in the production. The change should start with the employees. The employees should feel that they are cared for by the management. When this is achieved, it is easier for the management to introduce change.
House’s Path-Goal Theory
According to McLaughlin and Aaker (2010, p. 115), “This theory has its basis on the premise that employees’ perception of expectancies between his effort and performance is heavily influenced by leader’s behavior.”
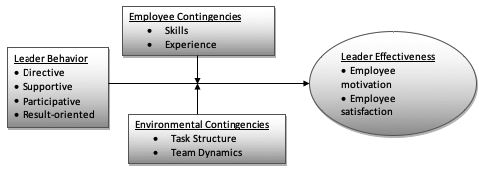
According to this theory, four leadership styles are important in ensuring success within an organization. The four include the directive nature of the leader, supportive leadership, participative leadership, and result-oriented leadership. These behavioral leadership characteristics will influence employee behavior and manage environmental factors to achieve leadership effectiveness. It is these characteristics that will make it easy or complex for a leader to initiate change within an organization when this is necessary.
Great Man Theory of Leadership
There has been an argument that some leaders are just born great. The great man theory of leadership holds that some people are born with leadership characteristics that are exhibited even before ascending to power. Porter (2007, p. 83) says that such individuals would have an aura of influence whenever they are. Such leaders would have the ability to influence people who are around them. Leaders such as Alexander the Great, Abraham Lincoln, Julius Caesar, and Queen Elizabeth I are some of the leaders who have been viewed to have exhibited natural leadership characteristics. In the contemporary world, leaders such as Barrack Obama and Bill Clinton have also been thought to have such leadership characteristics that make them be seen as people naturally born leaders. In the business world, leaders such as Richard Branson Steve Jobs also exhibited the same trait. This makes it very easy for them to influence change within their organization whenever it is necessary.
Production
According to Kodama (2008, p. 69), many people always view production from a narrowed scope of the creation of the products for sale. However, production, in this case, is taken from a broad perspective of analyzing all the operational activities that are undertaken by the firm to ensure that a product is delivered to the customer in good shape. This would involve all the activities taken from the time of acquiring the raw materials, the processing stage, and finally, the process of ensuring that the product reaches the customer. This is a very complex process that involves various departments within the firm. At this stage, firms are always obliged to employ value chain management in their attempt to ensure that products of high value finally reach the customer. Based on the changes taking place in the market, production strategy may be changed to ensure that such a firm delivers value to its customers.
In value chain management, the issue is always to create more value to the product at every stage; in the channels, it goes through before it reaches the customer. This process starts with the quality of raw materials, the processing strategy, transport system, package and storage, and the process of delivering this product to the customer in the market. With the changing environmental factors, a firm should always strive to achieve the best production strategies in the market. Maintaining dynamism in production will always help a firm deliver new innovative products in the market at desired intervals that would help the firm become competitive.
Technology
As mentioned in the discussion above, technology has contributed a lot to dynamism in the organization. For a long time, business units used traditional methods to enable a successful trading process. However, technology has been changing the approach consistently taken in the business. Technology has affected all the units of business. In the production department, technology has helped in coming up with various tools and machines of high capacity to support its operations. This has enabled firms to standardize their products in the market, besides the increased quality of products and the high speed at which these products are produced in the market. In the marketing department, there has been a massive change in which firms market their products in the market. After the Second World War, the production approach of marketing was used by various firms.
This is because there was a ready market for the industrial market in the global market. The market had to accept what was acceptable to them. However, this has changed massively with the changes brought about by technology. First, technology made it easier for various other firms to enter the market with products that are substitutes or competing for products to those that are already in the market. As such, stiff competition has emerged where only firms that understand market needs can survive the storm. For this reason, firms have used the same technology to develop social marketing as the best approach to meeting the market needs and delivering products of the highest value to the market. This is an outward approach where firms get to understand what the market needs, and make their productions based on their needs. Customers will, therefore, get products that meet their expectations.
The logistics department has also massively been influenced by technology. The world is now a global village due to the ease of transport that has been enhanced by technology. Technology has constantly been bringing new ways of transporting products, irrespective of their size, shape, or durability. It is now possible to transport flowers from South Asia in the evening, and the product is sold in the streets of New York the following day, thanks to air transport. Similarly, oil from Saudi Arabia can easily find its market in the markets of the United Kingdom because of the advanced sea transport. Technology has kept firms on toes in the market, always waiting for the next direction that it would dictate. Competitive firms in the market today are those that have been keen on embracing technology. As Kodama (2008, p. 19) puts it, technology is the source of dynamism in the current market. Any change that takes place in the market is associated with technology in one way or the other. These changes are either brought by changes in technology, or the change is intended to change a technological approach that is currently in use.
Scholars have advised firms to try to be early adopters of technology if they expect to benefit from a position revolution brought about by technology. Lagging in applying technology can be very destructive to a firm. This is because changing technological operations always comes at a cost. The cost should be recovered by increased productivity that would increase the profitability of the firm in the market. If a technological change is made when it is too late, such a firm may not gain any benefit from the change despite the cost involved in the change. As such, D’Aveni (1995, p. 89) says that firms should embrace technology and consider using it as a tool to gain a competitive edge over other competitors in the market.
The impact of the organizational dynamics on productivity and profitability
According to Hommel (2012, p. 81), firms always aim at increasing their productivity and profitability in the market as a sure way of ensuring that they remain sustainable in the market. Organizational dynamics have a direct impact on the productivity and profitability of an organization, according to this scholar. To understand the impact of organizational dynamics on the productivity of a firm, it is important to focus on individuals factors and determine how each of them impacts productivity and profitability in the market.
The human factor has a direct impact on the productivity and profitability of an organization. The type of employees that a firm has, and their ability to adapt to the changing environmental factors would always determine how productive a firm can be in the market. A group of motivated employees who are flexible to changes in the market can deliver a higher production for the firm. Such employees would be able to change their approach in the market, depending on what is expected of them. Such high productivity would easily translate to high profitability. The profitability will also be enhanced by the fact that the firm will be spending less on production, but reaping better results.
Leadership plays an important role in determining the productivity and profitability of a firm. For the employees to be productive, they need leadership that would ensure that they are constantly motivated. It is only the motivated employees that can deliver good results when assigned tasks. It is the responsibility of this leadership to ensure that the entire system in the firm is functioning optimally. This will involve formulating strategies that would ensure that every department is working as expected and that there are no overlaps that may result in cases where some duties are assigned to departments that should not be involved in them. Leadership also offers a direct link between the firm and external forces. It is through good leadership that a firm can get associated with other successful firms, or bring new ideas that can help transform the organization. With good leadership, there would be optimal operations within an organization, and this would increase productivity. Increased productivity would always enhance profitability. Good leadership will also help in the proper management of the resources of an organization, a fact that would enhance the profitability of a firm in the market. Production will also have a direct impact on the profitability and productivity of an organization. The cost of production has always been going up. For a firm to be able to be profitable, it must ensure that the costs of production are reduced to the minimal possible level. Reducing the cost of production will enable an organization to charge favorable prices in the market. This will increase their productivity.
Technology is a double-edged sword that can help a firm increase its productivity and profitability in the market if well managed, or enhance the reduction of the same if poorly handled (Hommel 2012, p. 79). These scholars say that poor application of technology or an attempt to ignore it can have a serious negative impact on the productivity of a firm. Eastman Kodak was almost thrown out of the market because it failed to embrace technology. It had to be rescued by Citibank to avoid being declared bankrupt. Other firms have also suffered due to their inability to use technology as a tool for gaining a competitive advantage in the market. However, when technology is applied appropriately, it would enhance the productivity and profitability of a firm. As D’Aveni (1995, p. 87) says, Fujifilm was able to emerge as the market leader in the film industry because of its agility towards technology. Google and Microsoft have also remained highly productive and profitable firms because their management has embraced technology in their operations.
Using Organizational Dynamics to Create Competitive Advantage
According to Porter, competitive advantage is the upshot of relevant competitive strategies (2007, p. 78). It was in 1980 that Porter coined the term as he was overwhelmed by the tremendous key players in an industry trying to initiate various strategies just to be able to make it on top of the vast red ocean of possibilities by providing value for their product or service offerings. The strategies are important because they would ensure the achievement of set goals or objectives. The achievement of these goals would lead to being able to ensure the provision of value for the customers and the creation of wealth. At the highest consideration, competitive advantage is another important construct in the area of strategy discipline (Kodama, 2008, p. 71). Competitive advantage is, therefore, a relevant element in the strategy discipline, as it could be an ultimate goal why a firm would employ competitive strategies in the first place.
It is important to note, however, that others are using the term competitive strategy differently from how Porter intends to use it in strategic thinking and innovation, and with “different meaning in different context” (Hommel 2012, p. 112). At this point, it is essential to define what competitive advantage is. Somewhere in the 1990s, the idea of competitive advantage exclusively existed as a way of creating economic value amid competing firms trying to do the same essential strategic actions. This is the relevant point of Barney in 1991, emphasizing further that competitive advantage will only have realization if a firm engages in value-creating strategies that its competitors do not employ (Kodama 2008, p. 58). However, Barney does not include the possibility of this idea whether competitive advantage may have to be eradicated by the innovation of rival firms resulting in some total changes in the market space. This is another significant highlight raised concerning the issue of competitive advantage somewhere in 2004 and 2005 as documented in the work of Tushman and O’Reilly, and Kim and Mauborgne, respectively (Witcher 2010, p. 80).
In contemporary society, the combined idea of the classical view and the issues explicated in the early 2000s concerning the competitive advantage surfaced. The works of Newbert, Powell, and ‘Shannassy highlighted this point, stating that competitive advantage is about pursuing a strategy that competing rivals cannot duplicate and should, therefore, leave no room for experiencing an erosion of innovative strategies over time (Hommel 2012, p. 89). For this reason, there are essential generic strategies that, according to Porter, will lead the firm to its competitive advantage.
Competitive advantage has been considered as a direct product of a dynamic organization. A firm that is dynamic to the forces in the external environment will always find it easy to adapt to the changes. Such a firm would easily understand forces in the external environment and adjust as fast as possible. This will make it have a competitive advantage over other firms. As has been stated in the above discussion, a firm can only develop a competitive advantage if other firms cannot imitate its production and marketing strategies. However, it is a fact that it may not take long for rival firms to understand strategies that are making a firm has a competitive edge over them. Once they get to know of such a strategy, the strategy ceases to offer a competitive advantage because it shall become a common practice in the market. As such, a firm can only maintain a competitive advantage if dynamic in the environment. It must find ways through which it can change its strategies whenever it feels that the competitors have learned their tricks. This would help it always remain a step ahead of the rival companies.
Relevant generic competitive strategies
The first generic competitive strategy is “overall cost leadership” (Porter 2007, p. 35). This one was quite popular in the 1970s because of the popularity of the curve concept. Porter emphasizes that cost control is an essential move of a firm to provide a defense for itself when buyers would have to employ their force to drive down prices. The second generic competitive strategy is “differentiation” (Kodama, 2008, p. 90). This highlights the ability of the firm to produce a unique product or service offerings under varying dimensions like design and brand image, technology, features, customer service, dealer, and others. According to Porter, differentiation is a viable tool to obtain above-average returns because it could lead a firm to achieve a defense position to cope with the five competitive forces. The third generic competitive strategy is “focus” (Porter, 2007, p. 38). This strategy emphasizes on segmentation, identification of product line, and definition of the geographic market that should be covered. While overall cost leadership strategy and differentiation are industry-wide, focus strategy is around serving a particular target in an excellent effort as possible. In any of the above approaches, Porter says that the guideline should be the ability to change swiftly whenever a firm feels that the strategy has ceased to offer a meaningful advantage. This dynamism will keep competitors guessing the next approach a firm will take to gain a competitive advantage.
Sustainable competitive advantage
Most firms in the current market are struggling to gain a competitive advantage that would give them an edge over their competitors. The various strategies in today’s setting, according to Oliver, would not last as a competitive edge due to the inability of most firms to embrace sustainable competitive advantage (2000, p. 67). The reason, according to him, is the fact that inevitable changes take place, and new market entrants are surging in number in an upward spiral leading to the conclusion among business analysts that there is no such thing as a sustainable competitive advantage today. This means that from time to time, firms would be able to formulate significant strategies just to be able to create a certain value that would allow them to take the lead in the competition and obtain their competitive advantage. For as long as new market entrants and rival firms continue to formulate something that would bring them a competitive advantage, a certain strategy that might have a potential edge in an industry may not remain as the ultimate best over time due to many firms that can formulate their best move forward from time to time. For Oliver, what seems to be a sustainable competitive advantage should relate with the ability of the firm to formulate strategic moves that are unique and hard to emulate or simply product and services that offer higher value in the marketplace and are difficult to imitate (Oliver 200, p. 173).
In essence, Oliver would want to explicate the idea that for a certain competitive advantage to be sustainable, firms should be able to produce competitive strategies that are hard to reproduce, making them unique in the marketplace that no other firms could eventually emulate them. For this reason, Oliver is trying to formulate a new idea concerning competitive advantage, and according to him, there could be no such thing as a sustainable competitive advantage because of the prevailing trending of discovering new essential ideas that would lead to the execution of new strategic moves across various industries or marketplaces. Concerning this point, Oliver tries to introduce the concept or idea linked up with temporary competitive advantage (2000, p. 174). In this regard, he says that the most prudent thing for a firm to do is to ensure that it is always dynamic to the environmental forces.
Temporary competitive advantage
Most firms always make it through in coming up with a temporary competitive advantage in the market. The only temporary competitive advantage that is sustainable is corporate learning (McDonald’s 2013, p. 1). This scholar believes that in reality, this could represent employees’ collective knowledge arranged in a way corporation designs, develops and delivers new ideas to the marketplace, may it be for new products, new segments of customers, and a new way of conducting business (Hommel 2012, p. 43). According to this scholar, the rapid change in information technologies, primarily in the 1980s, led to a shorter span of knowledge in electrical engineering. With this statement, Oliver is trying to imply that the rapid expansion of technologies in almost every area has also paved the way for the need to ensure learning at a higher level.
It is important to appreciate the importance of education as a fundamental source of learning because it has become a necessity in the age of rapidly changing technology and transforming competitive advantage. Oliver believes that success is prominent to those firms that can promote new learning and head on to new corporate initiatives (2000, p. 56). This means that he is trying to agree on the importance of innovation. Creating something new and executing a new initiative could have full realization through innovation. However, before the formulation of innovation, this scholar points out the idea that learning is necessary. It is the fundamental component of how the organization would be able to produce something new and sustain its competitive advantage. Corporate learning is, therefore, a fundamental component of the firm’s competitive advantage because it helps the firm to produce something new and execute the necessary changes that could be unique and would be able to produce a competitive advantage at some point.
At this point, it is clear that this scholar is trying to explain everything to us that a certain competitive advantage could be barely sustainable today. After all, corporate learning has become so pervasive that every firm has the potential to initiate or execute a highly competitive strategic output that would have to give them the chance of lifting them to competitive advantage. For this reason, for as long as a certain strategic move does not remain unique in the marketplace, a sustainable competitive advantage cannot be guaranteed to the full, according to Oliver (2000, p. 48). Corporate learning has increasingly become constant, and this is the reason why he would want to point out that new initiatives would surface from time to time in the marketplace, leaving the opportunity for every key player to hold a temporary competitive advantage. Temporary competitive advantage is, therefore, synonymous with corporate learning. Its significant existence based on the concept of this scholar has a clear association with how a certain firm can learn many things and something new from time to time. Without the ability to learn something new, indeed, firms may not be able to produce new ideas, concepts, and, eventually, a vital new execution of unique competitive strategies that would lead to competitive advantage.
Corporate learning is, therefore, a significant challenge for its competing firms within a marketplace because it serves as the ultimate force that would be able to help the other firm to achieve its competitive advantage. On the other point, this would also hinder the chance of a certain firm to continue to proliferate with its competitive advantage. Corporate learning is a remarkable capability of the firm, as one tries to include resources and capabilities just to be able to grab hold of competitive advantage.
Capability strength
The ability of a firm to develop a competitive advantage in a market depends on its capability strength. A certain idea arises concerning the prevailing academic background on how difficult it is to explain in detail how firms use resources and capabilities to create a competitive advantage (Hommel 2012, p. 53). However, these two scholars offer detailed information on how the capability lifecycle could explain the fundamental sources of the firm’s heterogeneity. These two scholars defined dynamic capabilities as “the firm’s ability to integrate, build, and reconfigure internal and external competences to address rapidly changing environment” (Chaston 2009, p. 28). This means that an organization must embrace dynamism in the market, and be able to formulate strategies through which it can change with the changing environmental factor. This also means that an organization must understand forces of change, and how each stage of change is important to the firm.
On the other hand, considering the point that capabilities follow a certain stage of development and maturity, it, therefore, provides us the idea that its measurement is possible. However, one could not measure dynamic capability somewhere in learning, change, and adaptation because none of these needs the intervention of capabilities as Witcher (2010, p. 118) would want to point out. As implied based on the above theoretical concepts, capability strength is an essential measure of the firm’s prevailing competitive advantage in its industry or marketplace. Therefore, it is crucial and necessary to understand more about this theoretical concept because this does not only allow us to explore a potential gap in the literature particularly on this matter, but it would also lead us to know the essential tool on how to measure the ultimate competitive advantage of a certain firm or organization. Montiel (2011, p. 98) says that Porter may not have sufficient empirical evidence to support their claim. Still, their discussion of the theoretical concept that would pave us the way for understanding capability strength provides a substantial start and even the essential idea on how to measure a firm’s competitive advantage (Coulter 2009, p. 76). With this, an empirical study may eventually surface that would either justify or debunk the primary theoretical concepts. For this reason, understanding capability strength would be a significant move that would fully contribute to further understanding the vast area of strategic entrepreneurship as this concept continues to be an integral part of understanding the firm’s competitive advantage (Chaston (2009, p. 56).
Capability weaknesses
Non-dynamic capabilities of the firm, according to Witcher (2010, p. 29), would change through the action of dynamic capabilities. This means that capability weaknesses would have to be recognized in the presence of dynamic strength. From the definition, as stated above, capability weakness has a strong link with an organization’s competitive disadvantage. The very justification of this claim lies at the point that the capability lifecycle deals with the firm’s capabilities and its ultimate evolution over time. Therefore, if the firm does not have substantial strength to mediate learning and potential change, competitive advantage may be remarkably a challenge to achieve, as, according to Oliver, corporate learning leads to the firm’s temporary competitive advantage. Turning capability weakness into a strength is, therefore, the most logical approach on how to help the firm obtain its competitive edge. Based on the above discourse so far, there is an implication that capability weakness would also stand as a potential measure of how far the firm has substantially reached its competitive advantage.
Given the above reason, it is essential that when developing strategic policies, capability weakness would have a remarkable area of consideration for its further justification and even additional observation of its existence. Porter defines competitive advantage as a way of having a competitive position for a firm reaching the maximum benefit of its competitive strategies at some point (Daft 2009, p. 67). This eventually talks about the firm’s ultimate capability to achieve change and undergo the essential process of the positive transformation. However, it is clear that with capability weakness, a firm would not be able to achieve its competitive edge because what is necessary for a dynamically changing environment, according to Oliver, is an aggressive effort for substantial learning (2000, p. 78). Therefore, this scholar had an essential point when they said that dynamic capabilities do not necessarily have to mediate with learning and change. This, therefore, means that in the absence of dynamic capabilities, dynamic weakness is taking its place, leading the firm to get a remarkable hardship in obtaining its competitive advantage.
The relationship between innovation and organizational dynamic
According to Witcher (2010, p. 78), there is a close connection between innovation and organizational dynamics. Innovation and organizational dynamics can be analyzed from two fronts. In modern management science, innovation plays a vital role in an organization. The challenges that firms face in the market due to the emerging trends can only be solved through innovation. Coming up with innovative ideas can help a firm develop strategies that would enable it to increase its efficiency, hence reduce its operational costs in the market. Hommel (2012, p. 27) says that technological innovation is very important for any organization to survive in the current competitive market. This is because it offers a firm to act in a positively unique way that will enable a firm to have a competitive edge of its rivals.
Innovation and organizational dynamics are intertwined factors that contribute to the higher adaptability and productivity of a firm in the market. According to Kodama (2008, p. 89), it is through innovation that a firm can be dynamic. It is innovative firms that can be dynamic in their operations. Innovativeness encourages the constant development of new approaches to handling various activities in the market. Organizational dynamics and innovations are core in ensuring that a firm remains efficient in all its operational activities.
On the other hand, D’Aveni (1995, p. 117) says that organizational dynamics always encourages innovation within the firm. Firms that understand the importance of dynamism and its impact on the productivity of a firm will encourage employees to come up with innovative ways of carrying out various activities within the firm. This way, an organization would remain alert to changes in the market, always ready to counter challenges that may be brought by changes in the business environment.
According to Chaston (2009, p. 19), for a firm to be innovative, it should be able to have proper planning strategies that would allow it to develop strategies that can stand the test of time. There is a need to develop a plan that would enable it to create a strategy that the competitors cannot easily emulate. The strategy should be as dynamic as the external environmental forces. Scholars have always said that when developing an idea, it is important to take into consideration the fact that competitors might react. Their reaction would always be geared towards ensuring that they emerge better in the market. As such, the management should develop plans to counter such moves. There is a need to identify a planning method that would allow the firm to strive and defend itself at the same time. Witcher (2010, p. 39) describes a military planning approach where one strikes and defends self simultaneously. This is because the strategy of striking then defending one’s’ self has proven to be very dangerous in the current market. While striking, this scholar says that the competitor could also be in the process of striking. Both firms will be hit, and depending on the force each applied, one may be paralyzed in this process. This means that the firm can lose if the competitor struck with a greater force. There is also the possibility of the third party benefiting out of this rivalry without getting engaged directly. The only sure way of ensuring that this firm remains safe and prosperous would be to use the strike-as-you-protect strategy. This planning strategy is always referred to as coevolutionary gaming, as discussed in the section below.
Coevolutionary Gaming
Planning is a very important process in the current competitive business world. According to Daft (2009, p. 96), the market has become so competitive that firms are forced to come up with new approaches to managing their activities in a manner that their competitors cannot easily predict. Coevolutionary gaming has come at an appropriate time when firms are struggling to find the best approach through which they can manage their operations. This is because many firms have suffered serious losses in scenarios where they develop plans only to realize that their competitors can easily understand their strategy and counter it very easily. In such cases, a firm would be put in an awkward position trying to develop a different plan to counter that of its competitors who may seem superior in the market. According to Chaston (2009, p. 118), Coevolutionary gaming refers to a planning approach where top management creates two groups in which one group is responsible for developing new strategies, while the other group develops counteroffensive strategies. In this approach, the first group will be forced to develop new strategies every time the second group successfully counters every new strategy. This game may continue for some time until the units learn how to respond to the market competitors every time they master their strategies in the market. Hill and Jones (2010, p. 98) say that “Coevolutionary gaming mimics the dynamics fundamental to ecological competition to explore the effects of conflict and cooperation between teams.”
Coevolutionary gaming is fast gaining popularity in the current business environment. The process was first developed by the department of defense of the United States. When managing a small business unit, it is possible to collect data, obtain what the market needs, and develop strategies of providing this need to the market. However, military generals realized that when managing such large organizations as a military unit, such conventional strategies may not apply. This is because the same data that will be collected from the environment is the same data that is available to other competitors. This means that applying such strategies may not yield a competitive edge over other firms in the market. For this matter, it becomes necessary for the management to design approaches that are unique to other competitors. This is what large institutions have embraced in the market today. Daft (2009, p. 114) says that “Just as in real life –where strategic feedback occurs over long time horizons – staggering moves allows these bullwhip effects to fully develop and influence strategic plans.”
This means that management of these large firms must be conscious of the time they take to come up with appropriate strategies within a time limit that will give it a competitive advantage over other firms in the market. In Coevolutionary gaming, communication is a very important tool. When starting the game, it is important for the second group that will be developing strategies to counter the strategies developed by the first group to have a way of getting information about the strategies of the first group. This means that there should be a communication process that will enable this firm to obtain this information.
Hooley (2008, p. 56) says that in this strategy, each group should have a way of obtaining strategies from the other firm in time before the other group can gain a competitive edge. As such, time will be of main importance to both groups. The longer time an organization can take in concealing its strategies from the reach of the competing group, the better. This way, the management of the group, which can conceal information for a long time, will always be considered a victor. To emerge a victor, each group must devise a strategy where it can obtain information from the other firm within the shortest time possible, while still ensuring that its information is concealed away from the competitor. This is exactly what the firm will be expected to do when it goes to the market. In the market, the firm will have the two groups which will now work as a unit, but in their specialized roles. The first group shall have specialized in an offensive role in the market, having practiced it in the firm during the planning process. It will introduce its strategies to the market.
The second group shall have specialized in counteroffensive role. When in the market, it is expected that the competitor will respond to the strategies developed by this firm. Given the fact that the first group of management had specialized in responding to such intrusion, it shall devise a new approach to counter the response of the competitor. The second group of management, on the other hand, will be expected to make an intrusion into the strategies used by the competitors. The ultimate aim of this second group would be to eliminate any competitive advantage that this competitor may have due to its current strategies. Their role will also include diverting the attention of the competitors from digging into the strategies of this firm (developed by the first group of management) to finding ways through which they can conceal their strategies. In this manner, this firm would turn from being the aggressor to being the aggressor. This is the best way through which a firm can survive in the current market, a fact that has seen the strategy become very common among the firms in the United States. When a firm turns into an aggressor, its competitors may not have much time attacking it because this may divide their attention. These competitors will focus on how to protect themselves from this aggressor.
This way, the strategies developed by this firm may not easily be intruded upon by the competitors. As Viardot (2004, p. 85) says, Coevolutionary gaming will always have an impact on decision biases. Most of the biases in decision making are always as a result of a narrowed thinking. It is always caused by the belief that other firms are either inferior or superior to this firm based on several factors. However, while coevolutionary gaming appreciates the fact that there is a possibility of having firms that are superior, while others are inferior, it also appreciates that there are dangers of considering a firm as inferior or superior. When the management considers a firm as being superior, it may develop some unnecessary fear as it may feel inferior before that firm. This may easily make it fail to develop strategies to counter such firms because they are considered superior to be beaten in the market. This may not necessarily be true because beating a market leader may not be as difficult as others may think. On the other hand, underrating smaller firms can be very dangerous because such small firms can easily respond to market dynamics, giving them an edge over their competitors in the market.
According to Witcher (2010, p. 78), “Often, teams discover fundamental strategies that will work in most of the likely trajectories – but usually not until the third or fourth set of moves. Knowing what they now know, they can write a more effective strategic plan, one that starts three or four steps ahead of the competition.” In what these scholars describe as taking the third step first, the strategy makes it difficult for competitors to have a mastery of what this firm may be planning in the market. Gerber (2008, p. 76) says that coevolutionary gaming might, at times, impede decision making within a firm. This is because it overemphasizes the possible counteroffensive strategies that may be applied by the competitors. This makes the firm take a lot of time thinking of the possible ways in which competitors will respond to the strategies of this firm, instead of focusing on the needs of the market.
Coevolutionary gaming has become very popular among business units in the current competitive market. This is because competition has become so stiff that competitors are forced to come up with ways in which their strategies can be unique. It is only through unique strategies that a firm can gain a competitive advantage in the market. This is what coevolutionary gaming offers to firms. Although some critics have faulted this approach as being oversensitive towards analyzing the response of the competitors, the strategy has been considered the most appropriate in managing market competition.
Summary
It is clear from the above discussion that there are a number of factors that create a dynamic organization. The current competitive market requires a firm, which is dynamic in order to deal with the changes which take place in the market. Firms have come to realize that agility is one of the best approaches in which they can sustain market competition. This is because of the speed with which some changes come into the market. It is only the firms that can respond with the speed that can be able to sustain market competition. Agility allows firms to make the best out of the emerging trends because it allows it to be among the first firms to benefit from it. As seen in the above discussion, four main factors have been confirmed to create dynamism in organizations.
The human factor plays an important role in creating dynamic organizations. Employees will always determine how a firm will respond to various forces in the market. Flexible employees will always make it possible for firms to manage the emerging trends with a lot of ease. They will be able to adapt to new strategies in their operations whenever there is a need for it. This will largely depend on their attitude towards the changes that such a firm may face. Leadership is closely related to human resources. The type of leadership will always determine the behavior of human resources that a firm has. Employees always need motivation. To have motivated employees, there is a need to have leadership that will foster this motivation. It is through leadership that a firm can have strategies that are conscious of the changes taking place in the market. Production is the third factor that creates a dynamic organization. When a firm can develop flexible production strategies that can easily be changed to reflect market demands, then such a firm will be considered efficient enough to manage the changes brought about by emerging market trends. The last factor is technology. Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing dynamic organization. It is through the emerging technologies that a firm can afford to manage the emerging market trends.
Dynamism always has a direct impact on the productivity and profitability of a firm because it is the basis upon which creativity is developed. A dynamic firm will always come up with innovative ideas for managing different forces in the market. It is through such innovative ideas that productivity can be enhanced. Time taken on various activities will be reduced, and the quality of the output will be high. This will have a direct positive impact on the profitability of the firm. With enhanced production strategies, it is clear that the costs of production will be lowered. This lower production cost will increase the profit margin of a firm. This will also make it possible for a firm to charge competitive prices in the market, making it easier for such a firm to increase its market share.
The literature review has been very elaborate and has responded to the research questions and research hypothesis, which were identified in chapter one of this dissertation. The literature search has confirmed that the four factors given in the research hypothesis have a direct influence on the creation of dynamic organizations. As seen in the literature search above, each of the four factors contributes to the creation of the dynamic organization in different ways. It, therefore, remains to be confirmed in chapter four whether this research approves this information. The researcher will analyze the primary data in chapter four upon completion of data collection to determine whether the views of the people interviewed is in line with what the report from other scholars is saying.
The review of the literature has also focused on the research questions that were stated in chapter one of this dissertation. The first question was as stated below.
What are the factors that create a dynamic organization, and how does the human factor influence this dynamism when applied well?
This question has fully been answered in the above literature search. The secondary sources of data have indicated some of the factors that create dynamic organizations. The four basic factors have been identified as the human factor, leadership, production, and technology. There are other factors that have also been identified to be working together with these four factors. The literature has also responded to the second part of this question by stating how the human factor has influenced this dynamism.
The review of the literature also responded to the second question of this research, as stated in chapter one of this research paper. Below is the second question.
What is the relationship between innovation and organization dynamic and its impact in terms of negative consequences if not managed well?
The research has talked intensively about the relationship between innovation and organizational dynamics. It is clear from the discussion that an organization that embraces dynamism will always be innovative. This innovation will further enhance dynamism within an organization. It is also clear from the review of the literature that not all technologies bring a positive impact on an organization. This means that if not well managed, innovation can result in serious negative consequences instead of the expected benefits. Some of the consequences may come in the form of reduced productivity and profitability of the firm in the market.
List of References
Andrzej, A & Buchaman, A 2007, Organizational Behavior, Prentice Hall, London.
Chaston, I 2009, New Marketing Strategies: Evolving Flexible Processes to Fit Market Circumstance, Sage Publications, London.
Clement, M & Henry, R 2010, Globalization and the Politics of Development in the Middle East, Cambridge University Press, New York.
Cobb, C 2011, Making Sense of Agile Project Management: Balancing Control and Agility, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken.
Cole, G 1997, Strategic management: Theory and practice, Thomson Learning, London.
Coulter, M 2009, Strategic Management in Action, Pearson Higher Education, New York.
Daft, R 2009, Organization Theory and Design, Cengage Learning, New York.
Daft, R 2009, Organization Theory and Design, Cengage Learning, New York.
Davada, F 2008, Strategic Management: Concepts, Pearson Higher Education, New York.
D’Aveni, R 1995, Hypercompetitive rivalries: Competing in highly dynamic environments, The Free Press, New York.
Doucet, G 2011, Coherency Management: Architecting the enterprise for alignment, agility and assurance, AuthorHouse, Bloomington.
Evans, D 2012, Social media marketing an hour a day, Wiley Indianapolis.
Ferrell, C 2011, Marketing Strategy, Cengage Learning, New York.
Frynas, J & Mellahi, K 2011, Global Strategic Management, University Press, Oxford.
Gerber, K 2008, Marketing communication, Pearson Education, Cape Town.
Gerry, J & Scholes, K 2008, Exploring Corporate Strategy, Pearson Education, Limited, New York.
Gountas, J & Mavudo, F 2008, Marketing Strategy: A Decision-Focused Approach, McGraw-Hill, North Ryde.
Grantham, C 2007, Corporate agility: A revolutionary new model for competing in a flat world, AMACOM-American Management Association, New York.
Handlechner, M 2008, Marketing Strategy, GRIN Verlag GmbH, München.
Hill, C & Jones, G 2010, Strategic management theory: an integrated approach, Houghton Mifflin, Boston, MA.
Hitt, M 2011, Strategic management: Competitiveness & globalization, South-Western Cengage Learning, Mason.
Hommel, U 2012, The strategic CFO: Creating value in a dynamic market environment, Springer, Berlin.
Hooley, G 2008, Marketing Strategy and Competitive Positioning, FT Prentice Hall, Harlow.
Jeffs, C 2008, Strategic management, SAGE, Los Angeles.
Kodama, M 2008, New knowledge creation through ICT dynamic capability creating knowledge communities using broadband, Information Age Publishers, Charlotte.
McLaughlin, D & Aaker, D 2010, Strategic market management: global perspective, Wiley, Chichester.
Montiel, P 2011, Macroeconomics in emerging markets, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Norton, M 2011, “Marketing Strategies”, Harvard Business School, vol. 1, no. 4, pp 11-91.
Oliver, U 2000, Total quality management: a practical approach, New Age International, London.
Porter, D 2007, Global Competitive Strategy, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Thompson, J 2010, Strategic management, Cengage Learning, Andover.
Viardot, E 2004, Successful Marketing Strategy for High-Tech Firms, Artech House, Boston.
Wall, S 2010, Strategic Reconfigurations: Building Dynamics Capabilities in Rapid Innovation-based Industries, Edward Elgar Publishers, Cheltenham.
Witcher, B 2010, Strategic management: Principles and practice, Cengage Learning, New York.
