Google Inc. is a successful internet technology company originally founded by Larry Page and Sergey Brin, who holds a computer science degree from Stanford University. Larry Page’s and Sergey Brin’s Back-Rub search engine was the starting point for developments that would make Google Inc. and the Google search engine what they are today. The creation of Back-Rub started back in 1996, with the efforts then focused on developing a search engine that would accurately determine the relevancy of a website using a portion of backlinks pointing to the website (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.2). On its release, Back-Rub became an instant success with a loyal following of internet users in Silicon Valley and particularly impressed with the search engine’s abilities was David Fillo, co-founder of Yahoo! (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.2).
In 1998, a meeting between David Fillo, Larry Page, and Sergey Brin ended with Page and Brin agreeing to move to Silicon Valley to start a huge Internet company. Subsequently, Back-Rub became Google and later Google Inc. was set up with $1 million in venture capital thanks to contributions from angel investors, friends, and the families of Page and Brin (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.2).
With the company’s “Google beta Version” in place, the company moved from handling 10000 search queries a day to 500000 queries a day. This success attracted two of Silicon Valley’s venture capital firms who gave the company $25 million to fund its growth and advance its search technology (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.2). Ever since the company has enjoyed a lot of success most notably was in 2009 when it became the worldwide leader in internet and mobile search advertising as well as registering growth and profits amid the economic recession in the US and developed countries (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.2).
Google’s search technology targeted market is made up mainly of people and/ or organizations interested in advertising their products over the internet. The company has strategically developed a range of features and products for internet and mobile phone users that have enabled it to become the advertiser of choice among its target market (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.2).
A list of these features and products as gotten from Gamble and Thompson include the capability to perform searches in different languages, the Chrome operating system, Google’s YouTube, wireless search technology and Google toolbar browser for internet users and the Android Operating System and short message service (SMS) feature for mobile phone users. Google Earth and Google Maps are two of Google’s products that were launched in 2005; they allow internet users to view satellite images of different places here on earth (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.6). The company, additionally, has an index of Web pages totaling over 8 billion and more than 150 country domains (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.3).
According to Gamble and Thompson, Google’s search technology for internet users is such that by inputting a search query at Google.com or entering it from a Google toolbar or Deskbar the search engine performs a multivariable and term computation that gives a list of results in a fraction of a second that best-match the query. The success in the technology is attributed to the text-matching techniques, PageRank technology, and the ability of the search engine to retrieve highly relevant results as pertains to a particular query. For mobile phone users typing your query and sending it in the form of a text message to Google will do (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.3). Google replies by sending the mobile phone using a text message that contains the results of the search.
According to Gamble and Thompson, Internet advertising in 2007 with revenues of $21 billion followed newspaper advertising at second place as the most popular form of advertising in the United States. It is projected to grow from this amount to $36.5 billion in the year 2011 whereas worldwide revenues from mobile search, another format of media advertising, are projected to increase by over $4 billion between 2007 and 2013. Internet advertising comprises of video and search-based advertisements both of which Google specializes in. Of these two forms of internet advertisement, search-based ads at $9 billion dollars generated the most revenue in 2007 in the United States (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.1). Video ads shown on Google’s YouTube and on other Internet Websites generated $505 million in revenues that same year with projections placing their revenues in 2013 at $5.8 billion in 2013. (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.1)
The internet according to the Macmillan English Dictionary (2002, p.752), is a worldwide system that allows people to exchange information by using computers. Today, the internet is more of a way of life if you consider E-banking, E-learning, and even E-safari services that are used on a daily basis. The use of the internet has grown astronomically from 1994 to 1.6 billion users in 2009 as Gamble and Thompson point out (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.1).
Statistics conducted in 2009 reveal that the United States has the highest Internet penetration rate in the world with about 220 million of its population having internet access (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.1). In the Asian continent only 17.4%, which is 657 million of its population, had internet access by 2009, this figure, however, makes it the largest and rapidly growing region for internet usage (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.1). Mobile phone usage has also increased dramatically, especially internet-enabled phones.
Google’s business model underwent a transformation that allowed the company to use other means of revenue generation (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.7). The business model at the time of the company’s inception allowed revenue generation through licensing fees to corporations wanting to use its search technology on company intranets and websites (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.7). In 2000, however, the business model evolved to include revenues generated from keyword-targeted advertising (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.7). This evolution of its business model paid off as the earnings from the company’s internet advertising platforms steered revenues from $220000 in 1999 to over $86 million in 2009.
As explained in the business model above, licensing its search technology to corporations requiring search capabilities is one way through which Google generates its income (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.11). This is made possible by the company’s Google Search Appliance for big corporations and Google’s Mini search Appliance for small corporations (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.11).
The companies that integrate either of these into their websites or intranets allow employers full access to company documents and authorized employees access to restricted documents (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.11). Internet advertising through the concept of AdWords is another way the company generates its income. Advertisers create AdWords that simply text adverts, which are to appear alongside other Google’s search results for a particular product or service (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.11).
Google provides internet advertisers with a way to determine the effectiveness of their marketing campaign with the company through performance reports it issues on the effectiveness of the advertiser’s AdWords (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.11). Google’s search-based advertising involves an auctioneering process in which advertisers bid for keywords that best describe their product. The bidding is done either on a cost-per-impression (CPI) basis or on a cost-per-click (CPC) basis (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.11).
Under cost-per-click, bidding is done on the number of times an ad is clicked whereas, in cost-per-impression, bidding is done on the number of times an ad is displayed by Google (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.11). Advertisers on their own can create Google AdWords or they can seek the help of specialists trained by Google for that purpose. Google’s YouTube is an internet site that a user can view various videos. YouTube is another avenue, which is exploited by advertisers who wish to advertise through video.
In 2004, Google did an initial public offering (IPO) that was intended to sell its 25.7 million shares and as a result raise a capital worth $3.6 billion (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.3). A second public offering was carried out in September 2005, 14,159,265 was the number of shares to be sold in this offering (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.11). The capital generated from the offerings funded the company’s research and development activities, which were aimed at strengthening its dominance in internet and mobile phone advertising (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.12).
Of interest to Google is “cloud computing” which is a computer technology aimed at enabling the concept of collaborative computing. Information technology expects to reach $ 95 million by 2013, which will project the market for the technology (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.13). This can be attributed to the fact that cloud computing has reduced software and computing support costs as well as provides easier remote collaboration among employees. Google has launched its Chrome operating system that supports cloud-computing applications to tap into the cloud computing market and has a competitive and offensive mechanism to Microsoft.
Google has a competitive edge among its internet rivals because it has continuously had a strong bond with internet users, advertisers, and websites (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.14). Below is a table that shows how internet searches were distributed between search entities in July 2006 and in June 2009.
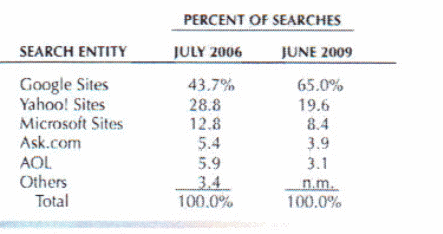
Google has identified Microsoft and Yahoo as its main competitors and rivals (Gamble & Thompson, 2010, p.14).
One recommendation to Google is to introduce the culture of knowledge integration into its research and development department (R&D). Knowledge integration enables the fitting together of different ideas into a single structure that is coherent (Clemens, 2004, p.4). By achieving knowledge, integration an individual or organization is able to, first, make use of available knowledge to formulate solutions to address various problems or challenges that they are facing during growth. (Clemens, 2004, p.3) Secondly, knowledge integration helps to expose underlying assumptions and inconsistencies through reconciling conflicting ideas (Clemens, 2004, p.5). Thirdly, knowledge integration helps an individual or organization to identify areas with incoherence, uncertainty and in disagreement; it does this through synthesizing different perspectives (Clemens, 2004, p.6).
Finally, by weaving different ideas together knowledge integration achieves a whole that is better than the total of its part (Clemens, 2004, p.7). Google is carrying out research and development in various areas to strengthen its dominance in the internet and mobile phone advertising market. Having in mind, not all of its acquisitions and innovations have been successful. Orkut its social net-working site, insight in knowledge integration would enable the company recycle such existing knowledge and formulate an approach or product that can be successful in the future.
Another recommendation would be for Google to maintain its critical thinking culture that they have displayed so far. This is evidenced by the strategic steps it has undertaken since the inception of the company, to become a world leader in internet and mobile phone advertising. So, what is critical thinking and critical thinking skills? Critical thinking skills are aimed at helping an individual or organization act purely objectively and rationally. According to Kurland (2000), the characteristics of critical thinking are rationality, self-awareness, honesty, open-mindedness, discipline and judgment. The ability to make right decisions is important in securing a better future for an organization such as Google. It is more of right decisions and less of bad ones that has seen it become a market leader in internet and mobile phone advertising. If they are to maintain this position then the decisions taken by its management will have to be vetted thoroughly through a critical thinking process. Because, it is the lack of critical thinking skills that is the starting point of the downfall of an organization.
As Gamble and Thompson pointed out, Google has had a competitive edge over its rivals because it has maintained a successful bond with its advertisers and users (Gamble & Thompson, 2009, p.14). Ethics are vital in making better relationships either among people or organizations or between people and organizations. Google having appreciated the importance of a good relationship with its environment, it will be recommendable that it sticks to ethics to maintain and improves it. Ethics, according to the Macmillan Education (2002), are the principles by which you decide what is right and wrong.Ethics form the basis on which a person or an organization determines which action is fit to take as a response to the various situations, which they encounter (Markkula Centre for Applied Ethics, 2010, p.2 ).
Ethics constitute the standards of behaviour that promote proper coexistence in a community or a society (Markkula Centre for Applied Ethics, 2010, p. 2). It is the case that a decision making process founded on ethics promises good decision making. It is therefore imperative for an ethical person or organization to match its standards with a proper ethical decision making model.
Another important recommendation in view of the fact that Google is a company that is continuously coming up with innovations is to pursue continuous quality improvement. This way they will develop applications that continue to amuse their users and as a result keep internet traffic coming their way.
References
Clemens, M. (2004). Knowledge Integration. Web.
Gamble J. E. & Thompson, A. A. (2009). Essentials of Strategic Management: The quest for competitive advantage (2nd ed.). Boston: McGraw Hill.
Kurland D. J. (2000). What is critical thinking?. Web.
Macmillan Education (2002). Macmillan English dictionary. Oxford: Macmillan Publishers.
Markkula Centre for Applied Ethics. (2010). A framework for thinking ethically. Web.
