Introduction
McDonald’s is a multinational organization founded in 1940 by Richard and Maurice McDonald’s as a local restaurant in California, United States. The company’s growth strategy involves franchising and the establishment of corporate-owned stores in the global market. McDonald’s product position involves the focus on quality, efficiency, friendly environment, and safety. The company has enhanced the success of its business activities by adopting total quality management and six-sigma strategies in its operations.
These approaches facilitate customer satisfaction and commitment to environmental health through continuous improvement of processes and review of standard operating procedures. Additionally, McDonald’s maintains a lean production concept and chain of suppliers essential in the reduction of cost and promotion of profitability. However, the company faces a critical market challenge over rising concern of its contribution to health problems in the global society. Therefore, this research paper discusses the company’s environment, examines its supply chain, quality processes, and suggests a recommendation to facilitate future growth.
McDonald’s Overview
McDonald’s is a fast-food company with its headquarters in Illinois, United States. The company instituted its global growth strategy through an alliance with Ray Kroc, an executive who conceived the globalization of the fast-food concept to the organization’s business strategy. McDonald’s structures comprise institutional holdings that operate land ownership in all its facilities and franchisees with ownership totaling 80% of all organization’s restaurants in the global market (McDonald’s, 2018).
Cost leadership strategy alongside franchising has facilitated market entry in the global market. In its business framework, McDonald’s offers an almost uniform menu that comprises hamburgers, big Mac, Wraps, Filet-O-fish, desserts, cheeseburgers, shakes, chicken products, breakfast items, fresh fries, and soft drinks.
The key success factors significant in establishing strong market dominance include low-product pricing, commitment to quality, and fast food services in its branches. Companies must identify and communicate their performance dimensions in order to strengthen their market dominance (Nguyen, Nguyen & Bosch, 2017). McDonald’s adoption of regional food preferences positively influences consumer loyalty. Additionally, the company participates in sponsoring charity initiatives, youth sports in the United States, health lifestyle awareness and training, and accommodation support to the poor and refugees in its facilities. Some of the organization’s health promotion initiatives include training and monitoring of suppliers and employees to adhere to adequate safety and hygiene standards in the delivery of service.
Industry Overview
McDonald’s operates in the hospitality industry, which chiefly focuses on enhancing consumer experiences and satisfaction. According to Radojevic, Stanisic, and Stanic (2017), economic instabilities and social conflicts significantly affect consumer behaviors. Thus, environmental factors interfere with consumer-level of disposable income and leisure time, which negatively affect profitability and attractiveness industry. McDonald’s competitors include luxury brands such as Marriott Inc. and low-end global fast-food restaurants offering similar products such as Shake shack in America and Grill’d of Australia.
Industry Environment & McDonald’s Strategies
The intense rivalry in the hospitality industry has significantly contributed to fundamental changes in McDonald’s business strategies. One of the most significant changes involves the adoption of a new marketing outlook comprising redesigning of the company’s structural facilities to appeal to the millennial generation’s stylish demands. The structural changes involve the elimination of plastic chairs and shiny colors with the introduction of hanging lights and muted colors.
Disruptive Innovations
McDonald’s is consistent in modifying its services with the introduction of disruptive technology-based services. The company’s approval of a digital ordering system, which enables customers to use mobile apps and online services in placing and paying for their orders, has significantly facilitated the success of this customized product offering. The model allows customers to order and choose preferred ingredients on the menu, which enhances customer satisfaction and building loyalty.
Happy Meal Product
McDonald’s positioned happy meals as a product with capabilities to promote family relationships. The product is in the growth phase of its life cycle. After enduring a slowed introduction phase in the market due to brand market positioning, a happy meal is enjoying a significantly low level of competition from rival companies. Additionally, attempts by competitors such as KFC to venture into the happy meal market have not been successful with the introduction of burgers that act as its substitute. However, the global concern of improvement of population health has contributed to a decline in consumption of happy meal products. Conversely, McDonald’s counteracts these environmental challenges by re-inventing happy meals through a reduction in calorie content such as cheeseburgers.
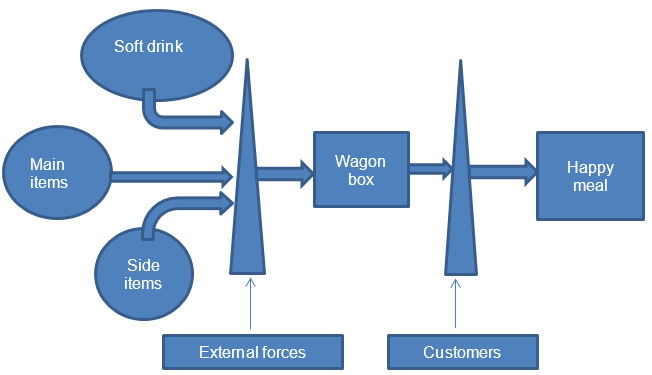
The productive process of a happy meal comprises a wagon box that contains the main item, drink, and a side item. The main items include a cheeseburger, hamburger, and chicken McNuggets, while side items include French fries, apple slices, and salad. Drinks are juice products, milk, and soft drinks. Uca, Altintas, Tuzunkan, and Toanoglou (2017) argue that product and channel-related factors significantly influence consumer choice and preference. McDonald’s product layout gives customers autonomy to select item combinations of their choice, branding McDonald’s like a family-friendly organization. The major output of this production process involves kids’ toys such as puzzle locks, spinning tops, wristbands, and stencils.
In the process map, the company designs the different items that are included in the happy meal menu, which involves a soft drink, main, and side items. However, environmental factors that include government regulations and lifestyle experts contribute to the process flow in controlling and transform public awareness on the consumption of healthy products. This move modifies consumers’ selections of the item resulting in a customized happy meal that enhances customer satisfaction. In line with this process mapping, McDonald’s follows a lead capacity strategy that enables the company to increase the production of the selected items in anticipation of an increase in consumer demand for the product.
McDonald’s Supply Chain Management
McDonald’s operates an extended chain of branches in the global market, making the company source its raw materials from different contracted suppliers to meet its diverse product requirements. For its beef products, McDonald’s receives its cow meat supply from different cattle farms in the diverse geographical regions of its markets. Proper management of supplies facilitates informed decision-making and quality enhancement in production (Russell, Lee, & Clift, 2018).
McDonald’s attaché identification tags on the animals, which traces the cows to the place of origin and processes. These tags facilitated the proper handling of the beef products in line with the established regulations. Major suppliers include Keystone Foods, Miratorg, Fresh Express, and Osi Food Solutions. These organizations have adopted strict animal welfare and quality requirements in the delivery of their products. McDonald’s has adopted an electronic supply system, the E-procurement, which allows qualified users to trade their goods.
The main customers include young children, parents with young children, and teenagers. One of the major marketing campaigns involves its marketing of happy meals to children and parents with young children. Additionally, the company has modified its infrastructural facilities to appeal to young adults through the provision of Wi-Fi services and coffee hotels.
The company has committed to outsourcing its information technology-based system to facilitate efficient service deliveries in its drive-through outlets. Varajão, Cruz-Cunha, and Fraga (2017) hold that outsourcing enables companies to reduce overhead costs while maintaining the delivery of high-quality services. The technology enables drive-through employees to process orders and accepts payment leading to increased customer satisfaction while improving the company’s competitive position since machines are faster and accurate in processing data.
Despite its global expansion, the company utilizes few supplier strategies with the aim to create market resilience. This business approach allows the company to form an efficient relationship with its suppliers that facilitate long-term planning and adaptation of a more sustainable supply chain. In addition to promoting sustainability, this supply strategy helps protect and support the economic viability of the collaborating firms leading to a win-win relationship for all.
McDonald’s Quality Management
McDonald’s approaches to quality involve the utilization of management teams in the inspection of food quality and control business operational criteria. The team performs proper checks of service through inspection of the facility, employees and assessment of feedback from the customers. Additionally, these management experts maintain a close relationship with the scientific community to guide the production of safe food for the people.
McDonald’s Total Quality Management
McDonald’s Total Quality Management focuses on employee participation, benchmarking, customers, and continuous product improvement. Since customers are the product end-users, the company utilizes customer satisfaction level as an element of evaluation in its total quality management. McDonald’s takes into account the nutritional content of its products, health concerns, and environmental responsibility. Topalović (2015) argues that quality implementation tools facilitate the improvement of key performance indicators within the production process. In enhancing product quality, the company observes regulatory policies such as the United States Department of Agriculture inspection policy.
Employee strategies include training on proper food handling, use of gloves, teamwork, and adequate maintenance of hygiene. Employee training focuses on inculcating customer service skills through continuous training programs that teach efficiency and communicating multiple languages.
The company maintains its continuous product improvement through benchmarking performed both internally and externally to industry rivals. This process has significantly contributed to the company’s elimination of unhealthy food, which has facilitated is a competitive advantage in the industry. Due to this commitment to quality management, McDonald’s received ISO certification for environmental concern, maintained operation efficiency, and enhanced product quality.
Six-Sigma strategy
McDonald’s utilizes a six-sigma strategy in management, which focuses on key success factors that involve quality-oriented approaches, enhancing process capability, addressing product defects, and meeting customized tastes. The company design for the sigma model involves the development of a customer-centric business model allowing customers to make personal choices regarding product ingredients in order to customize individual taste preferences. Quality control strategy focuses on a food safety system that involves the establishment of good manufacturing practices and hygiene programs within the organization and its chain of suppliers.
In enhancing the capacity of its processes, McDonald’s has introduced a drive-through system allowing employees to deliver goods to customers inside their vehicles or to their homes. Additionally, the company has maintained its commitment to quality and customer satisfaction through appropriately addressing product complaints. McDonald’s resolve strategy involves reviewing customer complaints, processing a new product with the exact taste preferences, and delivering to their homes. Overall, the six-sigma model allows the company’s management to eliminate defects, identify needs, and address variability, which leads to a reduction of overhead cost and improved profitability.
McDonald’s maintains a lean focus on production. According to Shah, Naghi Ganji, and Coutroubis (2017), the maintenance of lean production processes eliminates wastes while meeting market demands. The company has adopted sophisticated technology and automation of processes through e-procurement that facilitates stock control, which significantly improves the sustainability of the business.
Recommendations
The company has received a lot of criticism on the health concern of its products. Therefore, McDonald’s needs to focus its research and development efforts on nutrition overhaul of the contents of these products. The company should prioritize developing high vitamin and mineral products from natural ingredients and maintain certification of health food standards. This strategic approach opens the unexploited opportunity to the organization that is in line with the global program for improvement of population health and acts as a marketing concept to the current health-sensitive consumers.
Conclusion
McDonald’s continues to lead as a fast-food company in the global market due to its competitive strategies that include a commitment to quality, cost leadership strategy, and maintenance of lean production process. One of the significant innovative strategies is the adoption of customized taste preferences that facilitates consumers’ choice of ingredients for their meals. This strategy positively enhanced its competitive position with the introduction of a happy meal product as a family-friendly product.
In order to maintain low overhead costs, the company manages a lean production concept through the building of a strong supplier relationship and a low level of inventory. Additionally, McDonald’s has adopted total quality management and six-sigma strategy in maintaining leadership in commitment to product quality and enhancing customer experience. However, due to health concerns over its products, the company must consider adopting high vitamin-rich products to remain competitive and maintain sustainable growth in the sensitive consumer market.
References
McDonald’s. (2018). Our history. Web.
Nguyen, T., Nguyen, N., & Bosch, O. (2017). Identifying key success factors in supply chain management for increasing the competitive advantages of Vietnamese coffee. Competitiveness Review, 27(5), 438-461. Web.
Radojevic, T., Stanisic, N., & Stanic, N. (2017). Inside the rating scores: A multilevel analysis of the factors influencing customer satisfaction in the hotel industry. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 58(2), 134-164. Web.
Russell, E., Lee, J., & Clift, R. (2018). Can the SDGs provide a basis for supply chain decisions in the construction sector? Sustainability, 10(3), 629-630. Web.
Shah, S., Naghi Ganji, E., & Coutroubis, A. (2017). Lean production practices to enhance organizational performance. MATEC Web of Conferences, 125(1), 1-7. Web.
Topalović, S. (2015). The implementation of total quality management in order to improve production performance and enhancing the level of customer satisfaction. Procedia Technology, 19(1), 1016-1022. Web.
Uca, S., Altintas, V., Tuzunkan, D., & Toanoglou, M. (2017). A study on the effects of demographic factors on hotel selection process. International Journal of Tourism Sciences, 17(4), 231-246. Web.
Varajão, J., Cruz-Cunha, M., & Fraga, M. (2017). IT/IS Outsourcing in large companies: Motivations and risks. Procedia Computer Science, 121(1), 1047-1061. Web.

