This paper analyses innovation Microsoft implements in their management. You can find information on innovation approaches and activities, strategic decision centres, core competencies, and current issues. Discover Microsoft’s situation and solutions to the problems the paper discusses.
Microsoft Current Innovation Activities
For the last decade, product innovation at Microsoft appeared non-targeted, but the current strategy for the company has corrected that Microsoft has consolidated its innovative efforts to take advantage of a rich ecosystem that combines solutions for business partners, end-users and service providers within its business interests. The main innovation activity for Microsoft as an organization continues to be within the development of the Windows operating system. Currently, Microsoft is shipping Windows 10, which is an operating system that works on all devices targeted such as tablets, smartphones, and laptops or desktop computers and point of sale machines.
Microsoft has developed the Surface Book as a tablet-laptop device to enhance consumer productivity and choices. It has also started implementing its ‘focus on productivity’ strategy, which includes the removal of inter-product or service barriers and promotion of a unified Microsoft experience for its end users. It is developing flagship Lumia smartphones to run its Windows 10 operating system and serve as conduits for selling its numerous software and cloud computing services. It is setting up a platform to let Android and iOS developers to port applications to the Windows platform (Foley, 2015).
Microsoft Organizational Structure and Culture
Microsoft culture has been changing with successive chief executive officers (CEOs). Under the current leadership of Nadella, the company is shifting its cultural attributes from those that were dominated by Bill Gates and Steve Ballmer. Previously, the company focused on a warrior culture. It was emphasizing employee aggressiveness towards business opportunities so that the competition would not be able to access the personal computers (PC) market. The culture championed at Microsoft would be summarized as “each what you kill.” Many consumers eventually saw the company as unavoidable for their job, and the company effectively dominated the personal computer market with its operating system and computer software for office work. However, the culture has shifted to embrace more characteristics that are humane.
The new CEO for Microsoft is pushing for coordination and comprehensive outlooks rather than specific product performance. Satya Nadella has been in the office for a year and a half (Bort, 2015). In that time, he has made Microsoft a cooperative environment for innovation. Employees are becoming existed about the projects they are working on. The setting up of a common Windows 10 platform as the ultimate Microsoft project has also allowed many employees to refocus their innovation and research efforts with ease.
Also, the new Microsoft is now more tolerant of externally based innovations and solutions that can help advance its functionalities as an organization and as a business. For example, since Nadella took over, many new iterations of common Microsoft products have been released with inspiration from non-Microsoft products. Microsoft has also become more tolerant of new ideas. Consequently, there are many new products coming out of the company’s innovation labs such as translators and personal assistant software for mobile devices (Bort, 2015).
The organizational structure changed for Microsoft in 2015. With the change in business strategy, Microsoft opted to have a division for Windows and the devices headed by Terry Myerson. This department is in charge of pushing software and hardware. It currently manages Lumia phones, HoloLens, Surface Hub, Xbox and Surface line of laptops and tablets. Thus, hardware and software development programs in the company are under one department as part of a convergence strategy. The company also has a division for its cloud business headed by Scott Guthrie and this includes management of engineering assets that drive the company’s cloud business. There is also an education division for engineering assets headed by Qi Lu. Overall, the structure is streamlined to support faster collaboration between divisions (Wilhelm, 2015).
Microsoft Core Competencies
The success of Microsoft has mainly been doing to its aggressive nature of acquiring and developing core competencies. They include excellent leadership capabilities that are both visionary and transformative. Microsoft was able to dominate the Windows business by anticipating business and consumer needs then developing solutions to fill them. It also had successive leaders who have transformed its organizational culture to respond to the dynamic needs of its market. Leadership is an important attribute for innovation in any organization (Hill, Jones, & Schilling, 2014).
The company has also been dedicating a significant part of its revenues on research and development of existing products and services as well as new business divisions. So far, the company has had success in its gaming consoled business with its Xbox product. It is also eying success in the smartphone business with its Lumia line of phones. Meanwhile, the company recently launched the Surface Book, which is a mash-up of a laptop and a tablet as its flagship product for Windows 10 usage globally. There are examples that show the company’s research and development capabilities (Spence, 2015).
Development of Competencies
Acquisitions have played a major part in developing competencies for Microsoft. Rather than develop products from initial ideas, Microsoft has often used its large revenue base to acquire other companies and rapidly build its product portfolio or its organizational competencies. Acquisitions of other companies have also helped to bring talented staff and intangible resources like patents to the company. Besides acquisitions of other companies, Microsoft has also relied on its research and development efforts to develop its competencies. The company runs research programs throughout the world. It also runs a Microsoft Certified network for individuals and organizations around the world to standardized support for Microsoft products. As a result, it can collect a significant amount of end-user information about market intelligence (Sun, 2015).
For products and services that gain significant success in the market, Microsoft has been quick to use its other competencies to support these products. For example, in its Surface product, the company recognized market growth potential and, therefore, redistributed design and engineering efforts within the company to support its development. As a result, it has come up with a product that can effectively compete with other market leaders such as the MacBook Air from Apple (Spence, 2015). The company has not only been focusing on sales but also on building its reputation as a responsive and innovative company. Rather than focus on advertising its competencies, it has instead used the success of few products to push consumers into using more products within its ecosystem.
The utilization of competencies also shows up in the way the company acquires new employees and leaders (Hitt, Ireland, & Hoskisson, 2009). Instead of following a traditional practice of filling employees into roles, Microsoft has in the past made changes to entire divisions just to change the working environments so that new employees and leaders find appropriate working support to deliver their best skills for the organization’s success (Wilhelm, 2015).
Microsoft Innovation Management Evaluation
Microsoft lagged behind the competition in harnessing its innovations. In the 2000s decade, it fell behind Apple, Google and Facebook. It managed to develop products such as Windows 8, Windows Phone7, and Xbox. It also acquired Skype and bought Nokia. These products would help the company become a dominant player in the technology industry as it was initial, however, poor strategic leadership cost the company the number one position. Its Bing search engine solution also fell behind after promising starts. Meanwhile, the MS Office product was very innovative and dominant throughout its introduction to its current iteration.
The successes of Microsoft Office also highlight the things that the company eventually did right to regain its innovative competencies. The office is very compatible with devices running Windows and Mac OS. It can also be ported to run on GNU/Linux systems. The suite has also been improved to include features such as MS Project and One Note that improve business and personal productivity. It also allows users to save and fetch documents from the cloud and use third-party enhancements. Part of Office has also been available to consumers free. Besides, there are different versions of Office functioning in a similar way without requiring users to relearn (Bradley, 2015).
For the rest of the organization, ensuring compatibility and supporting the widest number of devices has been a goal that influences innovation management. Microsoft has also sought ways to enhance already existing products by making acquisitions. For example, the buying of Nokia gave the company phone manufacturing competencies, which allow it to push for convergence of office and mobile computing solutions. As a result, Microsoft now sells its products as a complete package for productivity and entertainment. The company is in control of both hardware and software. The new strategy is a way that has allowed the company to move past its challenges of having many useful products with disjointed marketing and development efforts (Hitt, Ireland, & Hoskisson, 2009).
In the end, the effectiveness of innovation management by Microsoft has moved from mediocre to excellent through proper project management and convergence of development divisions. The hardware and software divisions are merged, and they are all developed to support the flagship Windows 10 service as applications, management services, and tools for use by business and retail customers.
Current innovation approaches of Microsoft
Microsoft is currently attempting to become a design leader in hardware and software. It has embraced functionality and aesthetics as core factors in its designs, after realizing that they place a central part in influencing consumer choices for its products. The company has produced a new operating system named Windows 10 that will be the last Windows version for the company. Henceforth, Microsoft is concentrating on fixing functionality and design issues within the operating system and enhancing its usage across different devices.
The company has also enhanced the surveillance of its ecosystem by including new ways to synchronize files, login, and connect with the shared systems. When consumers get a Microsoft product such as Xbox or a service like One Drive cloud storage, they become default users of Microsoft products and services under a similar identity. Thus, the company has introduced the easier transitioning of customers using different services. The company wants to focus more on continuity than on individual products for success. It wants to market its products as a complete solution by Microsoft, irrespective or personal or business needs. Microsoft is also making many of its software available for free. It is hooking users to its products free so that they can become dependent on its solutions and willing to pay for upgrades.
Today, a user can get office free online. He or she has free Skype, free Windows 10, free One Drive and Bing search services. As they get used to using the Microsoft portfolio, they allow the company to retain its dominance in the respective software and hardware categories. This is the new innovative strategy at Microsoft (Bort, 2015).
Brief Strategic Analysis of Microsoft
Microsoft is currently reforming its practices and establishing itself as a dominant integrated business and consumer technology solutions provider. It is shaping up to take on its business rivals with the two main ones being Apple and Google. In addition to copying their strategies, it has also come up with organizational changes and product changes to differentiate its offerings. It is no longer selling software and hardware as a distinct product. Instead, it is offering them a continuum of solutions for different life needs for personal, group and business needs.
A SWOT analysis of Microsoft is as follows. Its strengths are a competent leadership led to current CEO Satya Nadella and its free Windows 10 operating system. A refined engineering team now works in harmony with software development. As a result, the company is coming up with software and hardware solutions fast, and it can show great design and engineering prowess. Weaknesses for Microsoft include its excess exposure to the PC market while market trends show aggressive growth of the mobile computing market (Sun, 2015). However, Microsoft is quickly removing from this weakness with its Surface Book and universal Windows 10 strategy.
The reduced fragmentation of Microsoft products, services, and organizational structure is the company’s biggest opportunity for innovation and growth. Microsoft is no longer having periodic product upgrades, and its long-term strategy is already being implemented with Office 365, Dynamics CRM and Azure (Sun, 2015). The company is focusing more on rent-seeking strategies that have a very big potential for enhancing its revenues without limiting it to linear expansion or product development opportunities. Microsoft has also opened up to more acquisitions that enhance its product portfolio or competencies in software, hardware and cloud services.
The company is facing a significant threat in the smartphone and PC market where Apple and Google are enhancing their innovativeness with new products and services. They are also finding innovative ways of locking in customers to their ecosystems such that switching costs to rivals like Microsoft will be difficult. Thus, Microsoft is facing the threat of increased difficulty in acquiring new users.
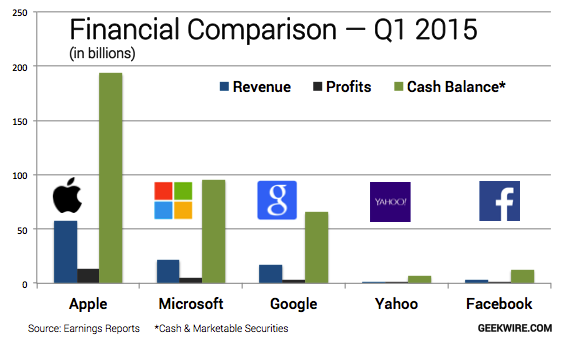
In innovation, Microsoft has become a leader again with its Surface Book. Its competitors, Google, and Microsoft are now copying it rather than leading innovatively. The iPad Pro from Apple is an adaptation of the Surface Pro from Microsoft that uses a stylus pen. Google also introduced the Pixel C to copy the flagship Microsoft product (Weinberger, 2015). Therefore, Microsoft is now a trendsetter for innovation. With its free software, Microsoft is facing a limited threat from the two rival companies, and it is likely to grow its market share. However, the company still lags behind in actual market share for device sales. The graph below shows that in quarter 1 of 2015, Microsoft was second after Apple in revenue, profits and cash balance.
Recommendations
Microsoft has decided to pare down its involvement in aggressive smartphone development. It recognizes that the phone business is not easy to penetrate given that the company is a late entrant. Nevertheless, here are recommendations that can help Microsoft gain sufficient profit margins from its implementation of smartphone technology. First, the company must continue highlighting its smartphones as a complement to its productivity services. People who want to enhance their productivity at work and elsewhere need awareness about the role that Microsoft smartphones play in delivering that solution. Therefore, the company should increase the marketing of its smartphone technologies in markets where the complimentary business is strong.
Secondly, Microsoft must refrain from trying to re-launch its smartphones as a separate business division. It might be tempting to do so and increase strategic focus for the technology. However, such a move will jeopardize the current strategy on universal productivity. Recently, the company started developing a platform within its Windows 10 OS that would allow easy porting of Android applications to the platform. This will enhance overall productivity, but it will also introduce new avenues for consumer frustration. The recommendation here is that Microsoft should maintain a quality assurance unit for testing Android and any other external system apps that are ported to its platforms and then maintain a curated list or a certification program to protect its consumer experience as part of its enhancements to the smartphone technology.
Addressing relevant issues/problems
Consumers are still affected by a high number of devices with similar functionalities. It is important to sustain the range of devices because of niche uses for each segment. The company has to consider overall usage and specific usage alike when promoting its continuum of products and services. It must also avoid too much convergence of its research and development divisions, which may lead to the development of similar products and services without realizing available opportunities for diversification.
Business diversification is an essential strategy for gaining new innovative and competitive competencies. Microsoft revenues are still a shadow of its largest competitor, and the company has plenty of room for growth. It must consider improving its sales processes and avenues for software services to limit purchase barriers for many consumers, especially in developing countries who may resort to only relying on freely available services instead of upgrading to become paying customers.
Another issue worth addressing is the emergence of competitors from different businesses. Microsoft has to remain wary of small competitors whose dominance in particular product niches can upset its universal productivity strategy. An example is Dropbox as a cloud service or Evernote as a productivity note-taking solution. Directly competing with the services is an option that the company is already pursuing. Besides, it must ensure that its hardware product supports the efficient use of these products so that the company maintains a positive reputation among customers, which will help build the overall Microsoft brand.
References
Bort, J. (2015). In just one year, Satya Nadella made Microsoft so much better. Business Insider. Web.
Bradley, T. (2015). Microsoft Office strategy takes the wind out of competitors’ sails. TechRepublic. Web.
Foley, M. J. (2015). Here’s how Microsoft hopes to get Android and iOS phone apps into its Windows 10 Store. ZDNet. Web.
Hill, C., Jones, G., & Schilling, M. (2014). Strategic management theory: An integrated approach (11th ed.). Stamford, CT: Cengage Learning.
Hitt, M., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. (2009). Strategic management: Competitiveness and globalization cases. Mason, OH: South-Western Cengage Learning.
Spence, E. (2015). Microsoft spinning the surface book story to fight Apple. Forbes. Web.
Sun, L. (2015). SWOT analysis of Microsoft Corporation. The Motley Fool. Web.
Weinberger, M. (2015). Everybody is suddenly copying Microsoft. Business Insider. Web.
Wilhelm, A. (2015). Microsoft shakes up its leadership and internal structure as its fiscal year comes to a close. TechCrunch. Web.

