Challenges Facing Managers Today
One of the challenges facing managers today includes the technological changes that differentiate today’s environment from that in the 1950s. Organizations today cannot operate effectively if the employees are not equipped with the latest technologies and techniques.
Today’s managers also face challenges with the rapid changes in the business world. For examples, there have been several changes in customer tastes and preferences. Managers also face challenges due to the changes that come about globalization. The changes in the techniques of production also pose a challenge to managers.
Functions of Management
The functions of management include planning, organising, staffing, directing and controlling. Planning involves the making of decisions prior to acting. It may involve determining objectives, formulating policies, programs and rules. Organizing involves dividing work into different functions.
It also involves specifying the roles and responsibilities of each employee. Delegation of duties is one of the processes during organizing. Staffing involves the assessment, appointment, evaluation and development of employees in an organization. The human resource department needs to find suitable individuals to fill positions in the organization. This should be done with the aim of achieving the organizational goals.
In order to ensure proper staffing, the characteristics of the job are determined then interviews are conducted in order to ensure that the best individuals are selected. Directing and controlling are closely linked. One element in directing includes supervision. Leadership, communication and motivation are also incorporated in this role. Controlling involves resource management and employee performance management.
Skills Required By Effective Manager
Effective managers need to be good in leading the organization. This involves managing change, solving problems, risk taking and setting of a vision. They should also be good in leading themselves and this may involve displaying purpose, demonstrating integrity and increasing capacity to learn. Another skill involves leading others. This involves enhancing communication, developing others and managing teams.
Despite the fact that all leadership skills are required across all management levels in the organization, some are labelled as key skills required in specific levels of management. These skills may be broadly categorised as interpersonal, business, strategic and cognitive skills.
Cognitive skills are applicable at all levels. This is mainly due to the fact that it helps in problem solving and learning new tricks. Individuals at higher levels of management need to be more competent in leading workers. Strategic and business skills are critical for individuals seeking to grow in the organization.
Scientific Management, Bureaucracy, Administrative Management and Human Relations Approaches to Management
The approach of scientific management is in use in most industrial business operations. It is useful in the various management practices. For example, it may be applicable during quality control, cost accounting, planning and process design. It involves the analysis and synthesis of workflows in order to improve economic efficiency.
Bureaucracy dictates that ideal organizations constitute individuals who are organized into a hierarchical structure. In such an organization, there is rigid division of labour and strict rules and regulations. This kind of governance is difficult to change once it is put in place.
Administrative management involves the creation of information systems that are used to pass information among the employees. This provides a platform where information can be stored and passed to other individuals within the organization in order to contribute to the success of the business.
The human relations approach to management involves the use of financial rewards and other social factors to ensure that employees are motivated to perform. For organizations using this form of management, leadership styles, relationships and attitudes are vital to the organization’s success.
Socio-technical Systems, Quantitative Management, Organizational Behaviour and Systems Theory Approaches to Management
The socio-technical systems approach argues that companies can succeed if the workers are equipped with the proper tools, knowledge and training. The quantitative management approach, on the other hand, suggests that management decisions should be made based on quantitative analyses.
These include the mathematical models and computer analyses. In order to ensure that the employees are effective, the organizational behaviour approach emphasizes on the need to understand the individual, group and organizational interactions. The systems theory approach argues that companies are dependent upon the contributions of the external environment.
Elements of an Organization’s Macroenvironment
There are generally five elements of an organization’s macroenvironment. The social-cultural factors, for example, constitute of these elements. They include factors such as values, lifestyles and customs of the population surrounding the organization. Technological variables are also considered while developing the organization’s strategic plans. This is mainly due to the fact that changes in technology influence the demand for products and the organization’s production capacity.
Political-legal variables also affect organizations. Politics greatly affect how business is practiced. The legal environment equally affects businesses since it may determine the type of organizations that can do business at a specific time. Economic variables also form part of the firm’s macroeconomic factors. These variables include state of the economic systems. The business cycle also affects businesses. International variables include practices of other states that may affect organizations.
Elements of an Organisation’s Competitive Environment
One of the elements of an organization’s competitive environment includes the consumer. Organizations survive solely due to the existence of the consumers. Therefore, the needs of the customer always come first. Another element is the organization. Every organization needs to do self-analysis in order to understand its own strengths and weaknesses. This would give it an understanding of where it stands in the competitive market. Another factor includes the market.
This is whereby the organizations come in contact with their consumers. Organizations strive to ensure success in the market growth rate, price sensitivity and technological structures in order to be competitive. The suppliers are also part of the competitive environment.
This is mainly due to the fact that they affect the working and cost structure of the industry. The competitive environment also includes the intermediaries. The agents help in increasing contact with the consumers. They greatly influence the business since they increase awareness of a product or service among the consumers.
Ethical Principles of Universalism, Utilitarianism and Egoism
Egoism mainly describes a situation whereby an individual pursues his own self-interests. This ethical principle asserts that leaders of organizations should only work towards finding ways of improving themselves or their organizations.
Individual egoism refers to the situation whereby a manager only works towards improving himself without considering the needs of the organization. Organizational egoism occurs when the management decides to delay the use of its resources to install environmental-friendly equipment in order to ensure maximum returns from its resources.
Utilitarianism mainly supports the decisions that produce the greatest good to many individuals. The consequences of each choice are assessed in order to understand the positive and negative impacts of adopting them. For example, if a business needs to make choices on how to benefit its shareholders, it would need to look at those factors that would serve the greatest number. Ethical principles of universalism propose that all individuals are governed by similar principles. They apply to individuals of any culture, sex, religion or sexual orientation.
Stakeholder and Shareholder Approaches to Corporate Social Responsibility
The shareholder approach to corporate social responsibility is the more commonly used approach in many businesses. In such businesses, the main purpose is to maximize the shareholder wealth. These businesses focus all their resources towards increasing their profits while engaging in open and free competition. Self-interest is the main human motivator. Environmental, social and human costs are usually reduced as much as possible.
However, the stakeholder approach suggests an alternative purpose of the business. It suggests that companies should not only focus on maximizing profits but also serve societal interests. Apart from serving the needs of the primary and secondary social stakeholders, these businesses also focus on serving the needs of the primary and secondary non-social stakeholders. Examples include serving environmental interest groups and animal welfare organizations.
Strategic Management Process
This process may be described in five stages. The first stage involves the setting of a goal. This is meant to show the direction that the organization wants to take. This may involve the definition of the short-term and long-term objectives and description of how the objectives would be achieved.
The second stage involves analysis. At this stage, relevant data is collected in order to understand the needs of the business. The third stage involves strategy formation. This is done after the analysis of the collected data. The available resources that may be useful should be determined. Other resources that are not available can be obtained externally. The fourth stage is strategy implementation.
This stage is most crucial to the organization. The employees’ roles and responsibilities should be clear and resources should be available. The last stage involves strategy monitoring. Performance management and reviews are done during this stage in order to determine the progress. The strategic management process may be summarised as shown below.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Group Decision-Making
One of the advantages of having group decision-making is the fact that there would be more information and knowledge provided due to the different specialties of the individuals. Implementation of the decisions would also be more effective because those involved in implementation are part of the group. Input from the different individuals also helps eliminate biases. Such groups also act as training grounds for subordinates who participate in the process.
One of the disadvantages is that the process is highly time consuming. The groups may also be inefficient due to the possibility of having interpersonal conflicts that arise as every individual tries to achieve self-centered interests. Some individuals may also agree with the ideas due to pressures to conform.
How Entrepreneurial Ventures Differ From Small Businesses
One of the differences between an entrepreneurial venture and a small business is the fact that a small business only deals with familiar goods and services. An entrepreneurial venture, on the other hand, mainly focuses on producing innovations. Another difference is the fact that small businesses aim at achieving limited growth and obtaining profits continuously.
Entrepreneurial ventures aim at achieving rapid growth and maximizing productivity. Unlike entrepreneurial ventures, a small business only deals with the common risks. An entrepreneurial venture would go headfirst and combat unknown risks. The effects of small businesses on the society are very limited. However, entrepreneurial ventures impact the society greatly.
How Franchises Differ From Other New Ventures
A franchise differs from any other new venture because it involves the leasing of another company’s brand for a limited period. New ventures develop their own brand and grow it from scratch. Therefore, a franchiser skips the part that requires building of chain stores and uses those already established by another company.
This way, the franchise is less risky than a new venture. However, a franchise would only be successful if the brand is already successful. A franchisor normally gives consent to the franchisee to use the franchisor’s trademark to supply the products. In this case, a franchisee pays some fee.
Side-Street or Corridor Effect of Entrepreneurship
This phenomenon describes how businesspersons develop multiple ventures and end up lengthening the lifetime of their entrepreneurial careers. This principle argues that starting a venture provides an entrepreneur with an opportunity to see the possibility of exploring other new ventures that were initially not anticipated. It opposes the linear single venture career model.
Advantages and Disadvantages of The Functional, Divisional and Matrix Forms of Organizational Structure
The functional form of organizational structure usually groups workers according to their specialization. For example, people may be grouped into finance, production, human resource and marketing teams. This structure is advantageous in that it fosters efficient communication, accountability and authority. Communication and coordination among employees within a department becomes easy. The disadvantage is that coordinating and communicating between departments may not be efficient.
The divisional structure segregates employees into groups that would focus on a particular area of the organization’s goods and services. The advantages include the fact that each product would be well marketed and the customer experience would be excellent. It is disadvantageous because there is duplication of roles that translates to less efficiency and greater costs.
The matrix structure is a combination of the two structures above. It is advantageous in that teams benefit from the expertise of each individual. However, the disadvantages include power struggles due to overlaps and issues of accountability.
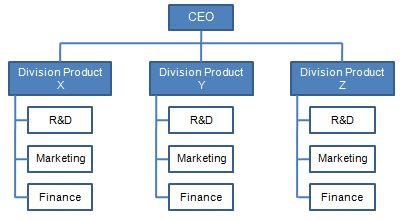
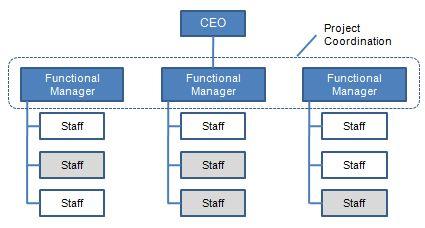

Difference between Business Strategy and Corporate Strategy
A business strategy and corporate strategy differ in the scope of the strategy. Corporate strategies mainly focus on activities that affect the organization as a whole. Business strategies, on the other hand, are narrowly focused. They only affect a specific business unit. These strategies are also focused on only handling tangible problems.
Corporate strategies are mainly formed at senior levels of management. However, an individual line manager may develop business strategies. Business strategies and corporate strategies are important for organizations but are not used simultaneously. Corporate strategies should be used while considering making major changes to the entire business.
