Introduction
Modern business organizations are well defined with their structure and strategy to achieve their vision statement with skill of the management and workforce. Organizations are much more aware with their corporate social responsibility to as a part of their operation. Organizations are driving to the global operation after successful operation in local market. To analyses, a business organization this paper would go for Samsung Electronics. This paper would analyses the strategy of Samsung, its organizational structure, culture and environment. The paper also looks for the SWOT analysis of Samsung to draw the key Recommendations. Samsung Electronics was established seventy years back as a small Korean company dealing with agricultural commodities which is now a multinational company operating in more than 150 countries with fifty fields of operation including electronics, chemicals, and machinery.
Overview of Samsung USA
Samsung Electronics Inc is a South Korea based Multinational Corporation and the world’s second largest cell phone manufacturing company. Samsung has produced different types of products such as SGH-Z150, world’s slimmest 3G phone, The world’s fastest HSDPA phones, 512Mb GDDR4, the world’s fastest DRAM, CDs and DVDs, Bordeaux named “Super TV” in Europe and “Best TV” in US, video cameras, PC, digital still cameras, Mobile WiMAX, data recording system, fastest memory card, laser printer and so on. In 2007, its net sales was 174.2 billion dollars, total assets was 302.9 billion dollars, total liabilities was 192.7 billion dollars, total stockholder’s equity was 110.1 billion dollars, and net income was 13.9 billion dollars. Samsung’s revenue generated from the sales of Mobile phones 5.41 Trillion KRW1 in the 1st quarter of 2007, 6.62 Trillion KRW and 6.65 Trillion KRW in the first quarter of 2008. However, because of global financial crisis, Asian Stock market is seriously fall but Samsung is trying to recover its equity price by taking several initiatives. The figure- 1, 2 and 3 have shown the net sales, total assets and net income of Samsung from the year 2003 to 2007-
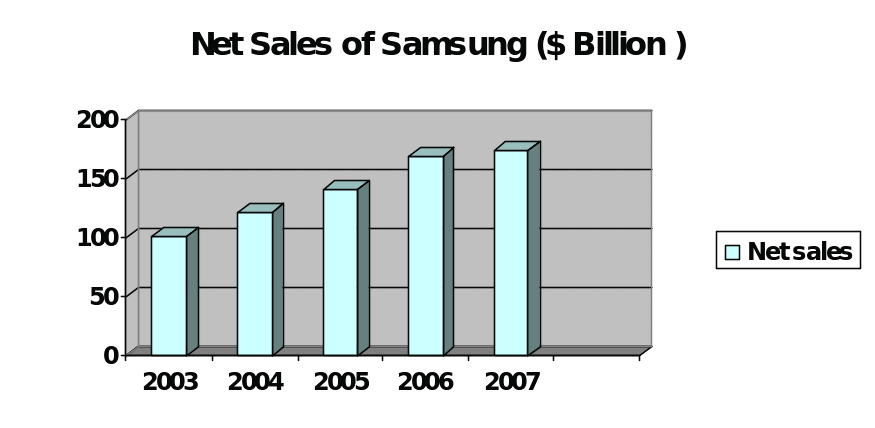
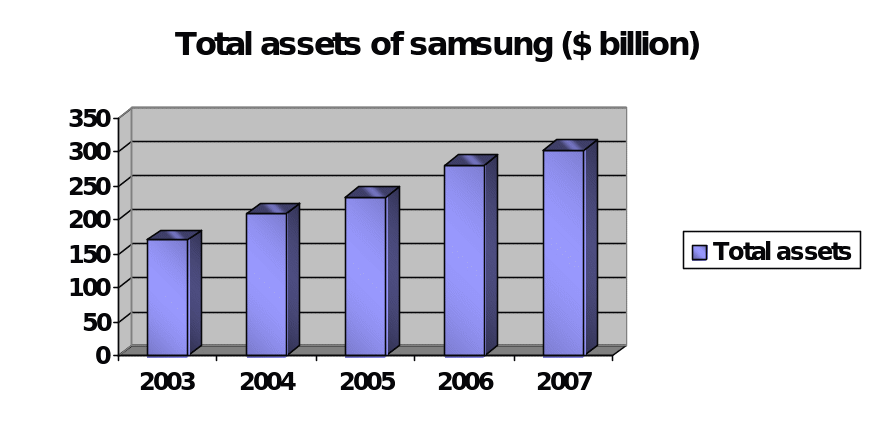
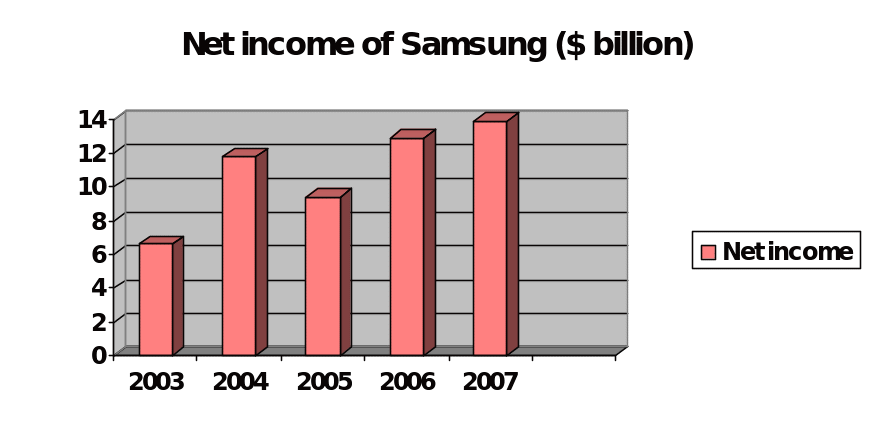
Environment in which the Samsung Operates
Customers: Samsung’s main target market for its electronic items are upscale and middle- earning households, teenagers with particular importance on female buyers. Customers are the main asset of Samsung, therefore it’s fix price and design product item considering consumers who think to get high quality at a reasonable price and customers who want luxurious sound system regardless the price.
Suppliers: In order to become a world-leading business organization, Samsung collaborating with suppliers and it always support suppliers to maintain market-leading competitiveness, therefore in 2004, it has announced a wide-ranging supplier support-plan worth KRW1 trillion over five years, moreover, in 2006, it has provided interest-free loans to small/mid-sized company to build new facilities and localize more of its product.
Competitors: Samsung’s major competitors in the electronics market are Sony Electronics, Aiwa, LG, Panasonic, Philips and Sonic. Each competitor has specific strategy, market segment and niche in the market. For instance, Sony Electronics generally offers four models offering the whole price range, sales primarily in department stores, and is heavy advertising spender. Aiwa plans to dominate the market through product proliferation and price discounting.
Regulatory group: Samsung Electronics is sets the corporate management policies, and incorporates appropriate laws and regulations, which has passed in the annual general meeting.
General Environmental analysis
In order to analyze general environmental condition of Samsung Electronics Inc, it is necessary to consider PEST2 analysis which can be describe as follows-
Political Factors: Samsung as a multicultural, it is operating in many countries in the world and the earning a significant amount of profits from them, it has been affected by the local rules and regulations, local stock exchange, taxation, rate of exchange, savings of personal intelligence, recession, up and downs of currencies. Recession creates some uncertainty future expenditure of the customer which may affects on discretionary of customer such as now clients would like to purchase other essential products than electronics.
Economic factors: Profits and sales of the products of Samsung Electronics are reducing than previous year as a result it has great impact on net profit of this company. From 2000 to 2007, its sales had increased gradually but from 2008, its sales decreased dramatically, for example in 2003, its net sales were $104.70 billion which $72.5 billion less then from 2007. It has to expense a huge amount of money for court proceedings, interest rates, and it has to calculate 6% of total earnings as damages. The following table has shown the financial condition of Samsung for the year 2007-
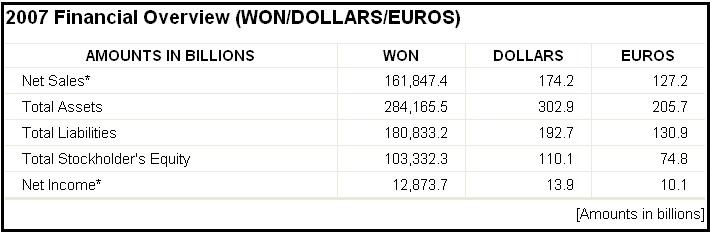
Socio-cultural factors: Its organizational culture encourages human resources to take on challenges bravely; therefore, the specialists at each location scrutinize local culture, lifestyles as well as business trends. In order to design the product according to choose of local customer, It has maintained separate Corporate Design Center, which has six supporting deign-center those engage with international research activities to find out people’s desires and demands. In 2006, over 4,650 staff of this company has volunteered for 150 different actions prearranged for these “adopted” communities and in Korea, about 14,500 staffs are support at social welfare foundations or helping children.
Technological factors: Creative and innovative technologies are changing the lifestyle of people, therefore Samsung continue to advance its technology and its intention to protected technological leadership by being the first to expand core technologies. For all products, it used advance technology for example next-generation of Samsung mobile phone’s technology was applied to expand the world’s initial 1GB DRAM using 50-nanometer manufacture processes as well as 32 GB NAND flash memory through 40nm processing3. Technological factors are most important to increase net sales because only for technological development their sale raises 24% within last 11 years.
Samsung’s Mission/Vision and Goals
Vision of Samsung
From its beginning, it has been regulated by a particular vision and it was –to lead the digital-convergence movement. In order to develop the profit margin it has few long-term vision such as-
- By technology innovation, Samsung will determine the solutions which require to address the future challenges;
- Worldwide business expansion by tapping into the digital-economy and creates new opportunities;
- To improve modern technologies that form new-markets, and enrich individual’s lives.
Mission of Samsung
All activities of Samsung are directed by its mission and its mission is to be the best “digital-εCompany”, as a result, its stuffs are always provides new creative ideas to face new challenges and to advance its products and services, which lead in their markets as a profitable, responsible global corporation.
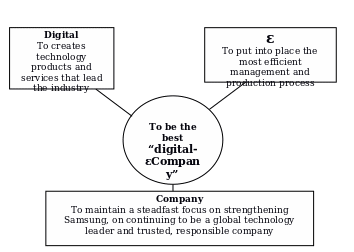
Samsung’s Strategy
To analyze the strategy of Samsung, it should require to considering the mission and vision of Samsung and the environment of this company. Samsung’s total current liability has increased 8,983,073 to 10,371,383 within one year and its sales have decreased for recession as a result it should require to consider its strategic analysis. So consistent with the strategic model, Samsung Electronics can create several strategic options through several systematic phases from business-level to international strategy.
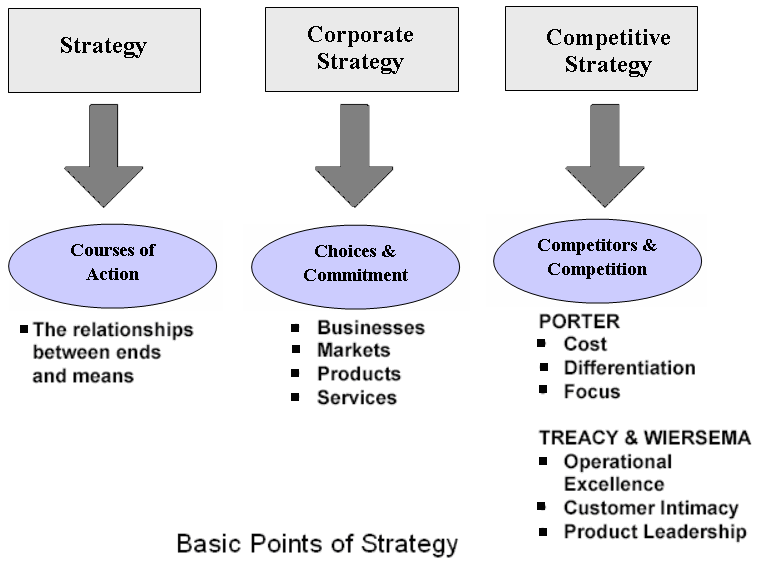
In 2007, its net sales was $174.2 billion, net income was $13.9 billion, which indicates Samsung’s industry position. Samsung can generate Porter’s five forces view as its business-oriented strategy for instance-
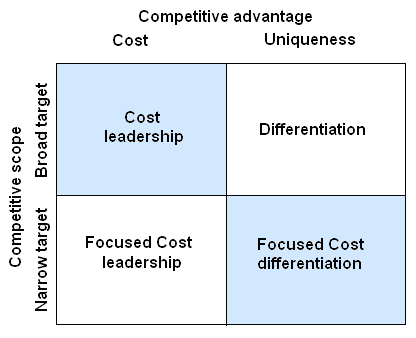
From the cost leadership strategy, Samsung can deliver the extremely sophisticated electronics home set and commercial cellular phones at lower costs relative to Nokia, Sony Ericsson, Motorola, Bird, Gionee and other major competitors.
- Competitive-level strategy
Under this level, Samsung Electronics can accomplish competitive dynamics by series of competitive actions and aggressive responding among the competitors of the industry by analyzing a number of factors such as market commonality, resource similarity, market dependency, own-size, innovation, and quality of the goods.
- Corporate- level strategy
Samsung Electronics can highlight on diversification from low to moderate to extremely high level whilst in moderate-level because it can earn less 50% of total profit from telecommunication. By a joint venture, Electronics can promote a new venture with other by combination of resources all over the world.
- International strategy
Samsung is operating and distributing its services all over world so this strategy is also applicable for this company. To be a successful performer in the international market it should consider the following issues-
- Features of production and distribution, and demand conditions,
- Supporting and related industries, and
- Finally, it requires to examining Samsung’s strategy, structure and competition.
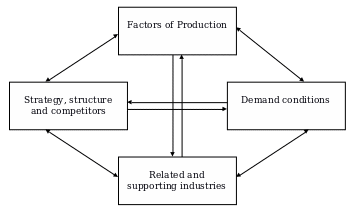
Organizational structure of Samsung
The organizational structure of Samsung consists of Financial, cost and pricing structure, R&D structure configuration, process, governance and control for implementing strategies as-
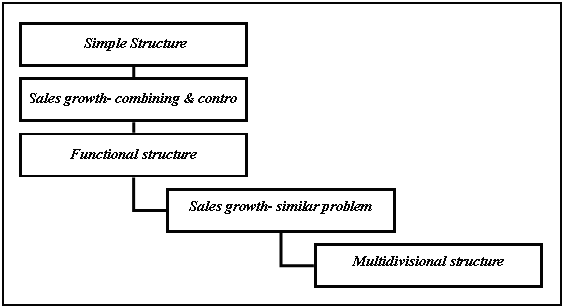
Since, Samsung is largely differentiation oriented, it should use the multi-divisional structure and the implementation of the multi- divisional structure has shown by the following diagram-
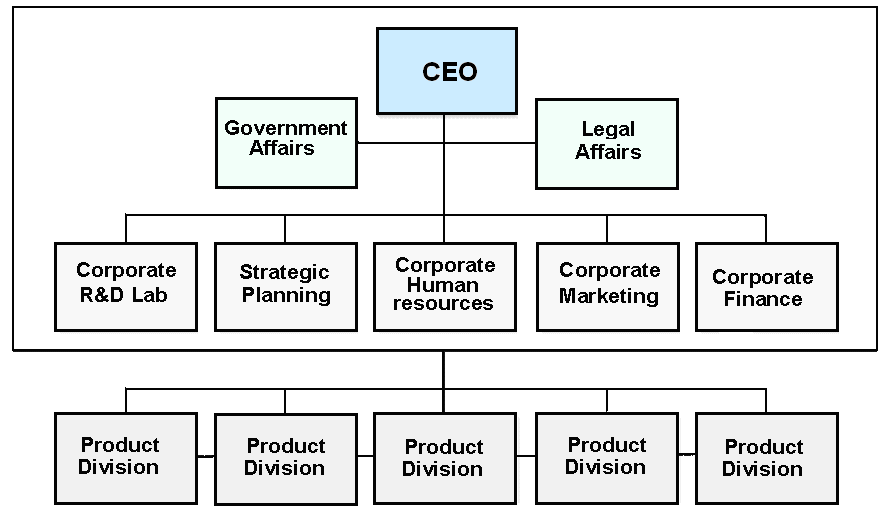
The Very High-Levels of Diversification: – In this level, most of the product of the Samsung Electronics is completely unrelated and less than 50% of the sales-revenue is generates from dominant-business and there will be no connection presents among businesses. Samsung implements multi-divisional structure because Production through different raw materials supplier of the world, technological platforms and outsider suppliers oriented R&D, and increase in structural finance in KRW 1,963,723millions is some key issues.
- Samsung’s organizational structure has five major departments such as corporate R & D Lab, strategic planning, corporate HR, Corporate marketing and Corporate- Finance, however, these are illustrated & controlled by CEO as well as both strategic controls & financial-controls are exercised in order to assess each department.
- The CEO is lie at the central power and control of the venture,
- It is an organizational structure where the horizontal integration is used so that resources as well as actions can be shared among product divisions.
- The product-divisions are processing information in relation to the resources & actions they intend to share, in addition to it decides how product-divisions intend to share them and production department will be responsible for controlling quality of the production.
Organizational Culture
Samsung’s culture influences on quick and relax decision formulation on a plain, formulated network though it is characterized by huge bureaucracy4.
Core values and beliefs: Its core values and beliefs pursue a straightforward business philosophy that is to devote its skills, intellect and technological invention to creating better products & services, which contribute to a better universal society. It believes that living by strong values is the main to good business; therefore, it has a set of code of conduct, which helps to take major decision.
Rules for behavior: products of Samsung Electronics are the most popular in all over the world. As a result, it has been affected by the local rules and regulations when it imports its products.
Language: Though Samsung is a Korean company and it has employees from different culture, but officially, it uses English in speaking, documentation and the overall electronic communication. Moreover, all the website run in three separate languages such as English, Italian and Chinese and consolidated financial statements have been restructured and translated into English from other language.
Relationship with employees: It has about 450 executives and more than 198000 employees among them 52,000 employees are engaged in R&D departments, 13,000 employees are organized to engage in different programs for example assisting at social-welfare institutions or helping children in need. It has 20% of total employees are engaged in the R&D department and it may increase up to 32%. In 2009, many organizations have collapsed for not to maintain corporate social responsibility for example Samsung has cut 15,000 employee’s job for recession.
SWOT Analysis of Samsung Electronics Inc
Recommendation
To become more effective and successful organization, Samsung should concentrate on the following issues:
- For a real progression the Samsung mobile the company needs to re-design it’s strategy for US market and reduce its dependency of US market and at the same time it is urged to increase the market drive in the south Asian market specially in Bangladesh, India and Pakistan. However, Samsung in no. 1 position in US market in case of cell phone and television sales,
- Samsung needed to configure its products, services; solutions portfolio originated from competitive operations with an artistic image balanced design, as well as value recognition.
- Samsung should analyze the market opportunities,
- It should develop marketing strategies and Planning marketing programs to protect current recession because if the recession goes for long run, the situation of US market would turn in an unpredictable condition.
- In order to minimize the risk of US recessionary impact on US currency and probable inflation Samsung needed to invoice for its items in Euro or KRW other than US dollar.
- It should more careful for target customers because recent global financial crisis may reduce its sales,
- The market segment and market strategy is not strong to recover from recession, moreover, stock market fall in all over the world, so it should take decision after observing the competitors strategies,
- Samsungs wide expansion of suppliers, efficient and effective execution of logistics required to be more ensuring customer’s safety trust as well as values.
- Samsung has 52,000 employees in R&D department and it required to continuing its investment in the infrastructure of network equipment and R&D.
- It should not cut the job of employees to face recession rather it should cut unnecessary expenses and remuneration of executives,
Conclusion
This research paper has addressed the critical problems and drawn attention on the company’s recent position to the global market, its strengths and weaknesses major competitors, along with several opportunities and threats. This paper, presented feature of Samsung that produce multiple products, so it follows multi-product strategies. This paper would draws attention to analyze a number of aspects in environment, resource capabilities, organizational structures, recession, selection and implementation of strategies and recommendation.
Bibliography
- Chernev, A., 2007, Strategic Marketing Analysis, 2nd edition, Brightstar Media, ISBN: 978-0979003912
- David, F., 2008, Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases, 12th edition, Prentice Hall, ISBN: 978-0136015703
- Dibb, S. Simkin, L. Pride, W. M. & Ferrell, O.C. 2001, Marketing Concepts and Strategies, 4th ed., Boston, USA: Houghton Mifflin.
- Griffin, R. W. 2006, Management, 8th Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston New York, ISBN: 0-618-35459x
- Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Hoskisson, R. E., 2001, Strategic Management, 4th Edition, South- Western Thosmson Learning, Singapore
- Johnson, G. Seholes, K. & Whittington, R., 2006, Exporing Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases, 8th edition, London: FT Prentrice Hall.
- Kotler, P., Armstrong, G., 2006, Principles of Marketing, 11th Edition, Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited, New Delhi, ISBN: 81-203-2825-6
- Kotler, P., 2006, Marketing Management, 11th edition, Prentice Hall, NJ, ISBN: 0-13-0336297.
- Porter, M. E., 2004, Competitive Strategy, Export Edition, New York: The Free Press, ISBN-10: 0743260880
- Rudenko, Y. Nguyen, L. Kelly, J. Pirgiotis, M. Lee, J., 2008, Case # 2: Samsung, Working Paper: BUSA 499, Pacific Lutheran University, Tacoma, WA 98447
- Stoner, J. A. F., Freeman, R. E., Gilbert, D. R., 2006, Management, 6th Edition, Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited, ISBN: 81-203-0981-2
- Saloner, G., Shepard, A., and Podolny, J., 2001, Strategic Management, 2nd edition, John Wiley, ISBN: 9780471380719
- Samsung Electronics, 2008, Business Outlook, Telecom: SEC’s Strategy.
- Samsung Electronics (2008), Earnings Release Q3 2008.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., 2008, Financial Highlights – Performance.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. 2008, Financial Highlights – Performance.
- Samsung, 2009, Vision & mission.
- Samsung, 2009, Corporate Profile.
- Thompson, A. et al (2007), Strategic Management, 13th edition, Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company limited, New Delhi, India.

