Executive Summary
The intended business venture is a private limited company. The firm will deal in offering of travel services to the market. Its major operations will mainly focus on offering best tour and travel services to the ever expanding tour market. The decision to settle on tours and travel is due to the vast business opportunities in the tours and travel sector especially in the U.K (Diaz, 2001, p.5). The management’s initial location of operations will be in the U.K. With time it is projected that the firm will target international touring before embracing foreign direct investment. The company’s competitive advantage lies in enhanced customer service and better product development tailored to meet the ever evolving market demands. A comprehensive analysis with regard to the market will be conducted to determine the feasibility of the venture. The marketing plan that has been formulated will help in sustaining the firm’s positive growth. The company’s core business will be to plan, package and sell distinct and unique vacation products and services. Harrison, (2001, p.14) argues that there are vast opportunities in arranging, assembling and marketing of packaged tours both in the domestic and international markets. The main market segmentation will involve commissions and fees from sale of transport or accommodation and reselling tours acquired from other tour operators. From the market research it is evident that the market is not well exploited as there are many segments that have not been satisfied. The tour and travel industry is expanding its packages in order to incorporate other emerging markets and this is where the firm will majorly focus on (Caves, 1971, p.21). Due to the changing market trends in the tours and travel industry, the management has forecasted that there will be a steady increment in the level of profitability. To ensure the firms’ success, a competent management team will be included and put into consideration (Clarke, 1982, p.9).
Business plan
Business name – Smart travel tours limited.
Name of the proprietor –
Business form– Private Limited Company
Business activity
The firms’ core activities will include arranging, assembling and marketing packaged tours (both domestic and international). It will also incorporate Commissions and fees from sale of transport or accommodation and reselling tours acquired from other tour operators. Due to the divergent customer needs the firm will deal with tours within the U.K and in extension from international markets (Wood, 2009, p.58). The company will also offer more personalized services to guarantee their customers more satisfaction like wildlife and native cultural experiences.
Vision and Mission statement
The company’s mission is to provide integrated tour and travel services. The company plans to be reliable when it comes to discovering destinations and planning holidays to make their customers vacations truly memorable. The firm will be able to attain increased customer loyalty (International Journal of Management, 2008, p.1). Through this the firm will achieve greater customer satisfaction in the U.K and other markets with regard to better tour and travel products. The company plans to be a leader in the inbound tourism field and work closely with other related tour operator’s world wide. In the process it will specialize in special interest and incentive tours.
Management
Management styles vary from company to company and the right style has to be chosen so that it can contribute positively to the success of the company without any major hitches. Baumol(1997, p.18), suggests that the management style used will always define success and as such will be responsible to harness the professional ability that the company can utilize.The Company is a private limited company and therefore it’s wholly owned.
According to Goodall, (1988, p.11), the management will have to register with all the organizations that deal in international tour and travel business by conforming to international air travel rules and regulations. In addition to these the company will have to join the Federation of tour operators. The company will also have to sign contracts with other tour firms in order to incorporate Commissions and fees from sale of transport or accommodation and reselling tours acquired from other tour operators. The firms’ management will design a cash conversion cycle to determine whether it will need additional cash for operation. This will be done by determining the cash received and payable turnover. The management will run from:
Founder (Chief Executive Officer)
The founder will be involved with the overall running of the firm. He will be tasked with ensuring that all the departments of the firm function effectively. In the long run he will oversee the process of ensuring that the company offers the right products to the ever changing market of tour and travelling. This means that he will ensure that products offered meet the current needs of the consumers (Ghimire, 2001, p.25).
Vice president
The vice president will be involved in ensuring that there is a smooth flow of the administrative functions such as departmental relations. He will be needed to poses some expertise knowledge in the general tour and travel industry when it comes to marketing, management and public relations (Ghimire, 2001, p.25). These management roles will in co-operate others in the running of the firm. The management has a well crafted personnel management plan.The aim of the firm is to increase the level of compensation of its employees. Other senior staff will involve departmental managers who will oversee the smooth running of their specific sections.
The tour and travel industry in the U.K.
The main goal of the firm will be to provide integrated tour and travel services more so when it comes to discovering destinations and planning holidays. All this will be aimed at making their customers vacations truly memorable. Holloway, (1998, p.16) argues that tourism seems to be the main market segment in the tour and travel industry. Most international tours are taking place within the developed world, hence the need to tap into these markets. In addition to these most international travels are taking place within regions which has made it easier to capture the target market. Briton, (1987, p.13) adds that U.Ks travel market has grown at a very high pace over the last few years.
Business strategy
Products
The company will offer unique products and services, distinct from the other competitors in the industry. These will include arranging and assembling of tours (both domestic and international). It will also offer transport and accommodation to those touring at a fee and commission. In addition to these the company will engage in reselling of tours from other tour companies. The main subject of contention is whether to use packaged tours or independent tours. The company will use packaged tours as these promises a large number of people and guaranteed returns According to Briton, (1982, p.25) the U.K market mostly likes sun and sea products, which has been growing consistently in recent years. The company will therefore target this niche market as it’s more appealing to the large market segment.
Trends in sun and beach tourism are moving towards growth in long-haul destinations. The company will put more emphasis on special market segments like boutique resorts, all-inclusive resorts, weddings and honeymoons. It will also target combination holidays, where the beach is one major component of tourism. There seems to be a link between accessibility (in terms of price, physical accessibility, distribution and marketing) and high tourist arrival numbers (Bull, 1995, p.17). A packaged holiday remains the most preferred travel arrangement for majority of UK residents. At the same time, evidence points to a growing preference for independent holidays.
The success of the firm will be built on competitive products that the firm will offer. Due to high competition there is need for innovative products and services (Briton, 1982, p.25). To ensure that the firm’s services are efficient it will focus on proper image creation and product differentiation. The services that the firm will offer will be offered in a unique way so that the customers can easily identify with them. All these will help in creating good customer loyalty that will guarantee business even in low periods
Holloway, (1998, p.16) adds that the current exorbitant prices being charged by tour operators have made customers to shy away from tour travelling. Smart tour and travels will engage in cost cutting measures that will allow it to charge low prices for its products and services. Another pricing strategy will be the use discounts to attract as many customers as possible. Since the firm will be aiming to get more revenue from reselling of tours, it will embrace mutual partnerships and relationships with the companies. This will help to ensure that they are more comfortable dealing with Smart travel tour limited.
Most services offered by other companies are not well appreciated by the customers and this can be exploited to work in its favor. To lock in its customers the firm will engage in more value addition of its services. This will reduce badmouthing that might affect the firms potential markets. Value addition helps in creating a good name that the company can later on use to expand to other frontiers and fight competition (Ghimire, 2001, p.25). Through this customers will end up getting real value for their money and appreciate what they have been offered.
According to Bull, (1995, p.17) time is very important as far as service provision in the tour and travel industry is concerned, so the company will pay more attention to time management. Customers need to reach their destinations on time. Through these the company can build a good image for its products and services by ensuring that everything is done within the stipulated time that had been agreed on with their the customers. The company will take advantage of this as there have been numerous complains about companies not being time conscious when taking there customers to their preferred destinations.
To increase its customer base the company will involve more creativity in their products and services especially in holiday destinations. All this will be aimed at ensuring that there is ultimate satisfaction as far as these trips are concerned. The company aims at achieving a high growth rate as far as holidaying and tour travelling is concerned. According to Forsyth, (1997, p.19) the UK market boasts of a high growth rate in tour and travel and the company will capitalize on these and benefit from this emerging market. Through diverse and distinct products the company will be able to achieve a better market position that will put it ahead of other competing firms.
Marketing Plan
Bruman (2001, p.12) argues that the tours and travel industry is expanding at a very high rate with very many new entrants joining the business. This has led to a high competition between new and existing players in the market. With all these manifestations the firm will have to come up with good marketing strategies that will enable it to operate effectively without being wiped out by competition.
The company is offering a wide range of products and services. Among them, arranging and assembling of tours (both domestic and international). It will also offer transport and accommodation to those on tours at a fee and commission. In addition to these the company will engage in reselling of tours from other tour companies. Currently the industry is coming up with many innovative products that are well suited for the market (Forsyth, 1997, p.19). On the hand the services that are being offered are almost identical. The company will have to fight its market with other established players but to its advantage it will employ more creativity and innovation to its existing products and services.
This will help in product differentiation and make their products more unique. The company’s products have been tailored for the new emerging markets both domestically and internationally so as to be relevant to their needs. According to Marcussen, (1999, p.23) the UK market is ever expanding and as such it will need to be given a new taste of products and services. The market is characterized by a very small number of large tour operators and also on the contrary a large number of very small operators with specialized niche markets. Bruman , (2001, p.28) feels that the market is mostly controlled by four operators, that is, Thomson Holidays, Air tours, Thomas Cook and First Choice who account for 75% of the total market. In addition to these there are other 1500 niche operators in the market.
The nature of the products and services in these industry make it an obvious target for cooperate concentration (Cleverdon, 1979, p.16). The main trends that are being experienced in the industry are economies of scale and integration. Through these, tour operators can be able to achieve an enormous power to buy and have a considerable control in the supply of products and services. Competition has been increasing with a specific desire to capture specialized niche markets. Most of these companies have been competing through specialization. They are offering niche products and services to specific customer segments such as Cycling for Softies.
The tour and travel market seems to be more mature and it’s now demanding new experiences from the services that are being offered. This has later on come out to be a major competitive arena where companies have been fighting for more customers by giving them what they want. Competition has also intensified worldwide to get the customer’s time and money (Cleverdon, 1979, p.16). Smart travel tours limited will come up with strategies that it intends to use to capture the market.
Strategies to keep customers and reach more markets
Since the market is ever competitive the company will come up with measures to lock in customers. To market the company and increase more customers it will use Travel agents. They will help in giving a personal touch to the customers so that they feel appreciated by the company. Since these agents have a wide medium of coverage they will channel more customers towards their products and services (Cleverdon, 1979, p.16).
Bruman (2001, p.12) argues that online selling has come up as a very simple and easy way to reach as many customers as possible. The company will therefore use technology and capitalize on online sales so that it can reach a wider market than its competitors who have not embraced these great opportunity. More focus has been put on online sales because of a high internet penetration among UK consumers and the rapid development of low cost scheduled airlines that mostly focus on online booking.
Wap Mobile phone is another opportunity that the company will exploit to get more customers and reach new markets. This will create a more individual touch to the customers and leave them more satisfied and valued. Another opportunity that the firm will use is the presence of the Digital TV to reach a wide market base and in the process increase customers (Marcussen, 1999, p.23).
SWOT
Financial projections
Firms’ pro forma income statement
Pro- forma balance sheet analysis
Firms projected cash flow analysis
The firm has projected a positive cash flow in the effort of the firm to meet its milestones. In the initial phase the firm projects that there will be a fluctuation in profitability. These will results into negative cash flow within the first few months. The management intends to finance its first phase using a loan. It is assumed that the incorporation of selling using the e-commerce technology will enable the firm acquire more revenues in sales (Science, Engineering and Technology, n.d.)
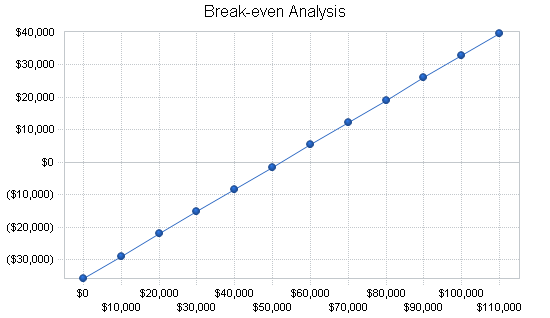
Break even chart
The following chart gives an illustration of the firms break even analysis basing on information in the financial plan.
In relation to revenue, the firms break even is estimated to be at $ 52,000.With time, it is expected that the business will grow and hence the break even will be updated accordingly
Critical risks, problems, and assumptions
The management assumes that there will be sufficient finances to ensure that the business idea is rolled out efficiently. The major competitors will not adjust their competitive strategies in a significant manner. This reduces the risk of the firm having difficulties in venturing into the tour and travel business. It is also assumed that there will be ease in being conquering emerging markets. This will ensure that the firm is able to conduct its market segmentation process effectively. The government will not make major changes with regard to legality and policies that have the possibility of affecting the tours and travel industry. This mainly is because the government is taking advanced steps in ensuring that tourism opportunities stay open and free for all businessmen who would want to venture this market (The National Trust, 2005, p.4).
Conclusion
The business is a noble idea that when actualized will be viable. The tour and travel industry is expanding very fast which presents a great business opportunity. Nevertheless, the idea will have to be well coordinated with the leadership strategy being top on this list. It has to find a way in which to attract more tourists in the most affordable rates possible. Smart Company’s marketing strategy has to overpower the rest of its competitors in terms of attracting more tourists to itself, while maintaining customer satisfaction to its best. It is also important that the company keep a check on itself. By constantly having a SWOT analysis, the company will adjust accordingly in order to maintain its high standards in the markets. In addition Smart Company will need to maintain growth in terms of monetary value as per the “break even graph” given above. This will be a mountain hill to climb fir the company, since the tourism industry has been a major economic earner in the country. Not only so but the industry has constantly registered growth over the years.
To do this, the management will put in place sound business strategies that will help the business to register positive growth. It is believed that the above table showing strategy will enable the company to advance from its current status to greater heights. All in all, it is intended that Smart Company will reach to its goals and attain the vision that it bears.
Reference List
- Baumol, W. J. (1977) Economic Theory and Operations Analysis, (4th edition). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Braman, S. (2001) Practical Strategies for Pro-Poor Tourism –Tropic Ecological Adventures, Ecuador. PPT Working Paper, N.6.
- Britton, S.G. (1982) The Political Economy of Tourism in the Third World. Annals of Tourism Research. Fiji: University of the South Pacific.
- Britton, S.G. (1987) Tourism in Pacific Island States: Constraints and Opportunities. Fiji: University of the South Pacific.
- Bull, A. (1995) The Economics of Travel and Tourism (2nd Edition). Harlow: Longman.
- Caves, R. E. (1971) International Corporations: The Industrial Economics of Foreign Investment.Economica, vol. 38, pp. 1-27.
- Clarke, W. C. (1982) Ambiguous Alternatives: Tourism in Small Developing Countries, Suva. Fiji: University of the South Pacific.
- Cleverdon, R. (1979) The Economic and Social Impact of International Tourism on Developing Countries, Special Report, No. 60. London: Economist Intelligence Unit.
- Diaz, B. D. (2001) The sustainability of international tourism in developing countries. WTO/UNCTAD Tourism in the Least Developed Countries. Madrid: WTO.
- Forsyth, R. (1997) Environmental Responsibility and Business Regulation: The case of sustainable tourism. London: Royal Geographic Society.
- Ghimire, K. (2001) The Native Tourist: Mass Tourism within Developing Countries. London: Earthscan Publications.
- Goodall, B. (1988) How tourists choose their holidays. Marketing in the Tourism Industry. London: Croom Helm.
- Harrison, D. (2001) Tourism and the Less Developed World: Issues and Case Studies. Wallingford: Cabi Publishing.
- Holloway, J.C. (1998) The Business of Tourism (5th edition). Harlow: Longman.
- Marcussen, C.H. (1999) Internet Distribution of European Travel and Tourism Services. Denmark: Research Centre of Bornholm.
- The National Trust. (2005). Policy from Practice. Tourism.
- Science, Engineering and Technology, (n.d.). E-commerce Technology for the Business of the Future.
- Wood, Brian. (2009). Building Maintenance.111 River Street Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons.
