Introduction
The technology industry, similar to many other sectors, has expanded worldwide, resulting in developers, manufacturers, and resources often being located on various continents. The technology industry has established global supply chains to manage production flow. Large manufacturers import both minor and major components to electronic devices from various vendors, which are assembled into the final product that is shipped to the consumer (Barboza). This set up of the industry has allowed businesses to financially benefit from the rapidly growing sales of electronics and technology by delivering semiconductors and related components to other manufacturers, even if they are competitors (i.e. Samsung provides vital display components to virtually every smartphone maker in the world).
Tech Components International is a medium-sized business focused on filling gaps in the wider supply chain of the semiconductor industry and electronics components for major manufacturers of devices or network operators who outsource multiple aspects of production to smaller enterprises. Tech Components International company emphases the development and manufacturing of components such as semiconductors, processors and mobile network technology. As a medium-sized electronics component business, it is the strategic goal to increase sales through engagement with the established global supply chain through local channels in China and produce high-quality products that are recognized by major companies, allowing for growth and expansion of the business in the global marketplace.
Business Overview
History and Background
The business was founded in China by a U.S. technology venture who saw the potential of working directly in the region where the majority of electronics components are produced. The company was meant to establish stronger ties between Asian and American companies and integrate into the local supply chain in order to ensure there is a greater U.S. presence in the market for components that ensures a safe and reliable supply chain for producers. The local market is the key element to the company’s operation.
Despite, the supply chain stretching globally, the biggest concentration of the production supply chain remains in China and the nearby Indochina and Western Pacific regions. The region houses major electronics firms such as Samsung, Huawei, Lenovo, Sony, Samsung, Toshiba, and others that both develop and produce electronic devices, requiring a supply of components. This concentration occurs due to the region having the largest natural supply of rare metals required for electronics production, an abundance of cheap but skilled labor, and a business climate that promotes innovative strategic growth (Pham, 2017).
The competition consists of hundreds of supply chain vendors in the Asia-Pacific region on which global technology firms rely on. Each uses unique approaches to the business, and some offer new technologies and innovations in the manufacturing of these components that allow major producers to choose and place large contracts with these vendors as well implement significant supply chain integration (Sundram et al., 2016).
Competitive Advantage
Firms in the electronics industry are consistently in tough competition and implement innovative ideas and introduce the newest technology on the market. This creates significant pressure on development and engineering teams to consistently innovate. Companies that specialize in specific niches, such as Tech Components International, in components and semiconductor manufacturing have to maintain profitability (Shin et al., 2009).
Tech Components International maintains a competitive advantage in that it has been able to adapt its manufacturing technology and space to meet not only the demands of the semiconductor supply and electrical components segment but also towards networking and communication equipment. Both are rapidly growing sectors, but it is rare that a firm specializes in both. This creates competitive value for the company since it can work comprehensively with firms such as mobile device producers which require both electronic components and communication equipment. It opens up more opportunities and ensures better integration for the manufactured components within the specific order or device.
Market Analysis
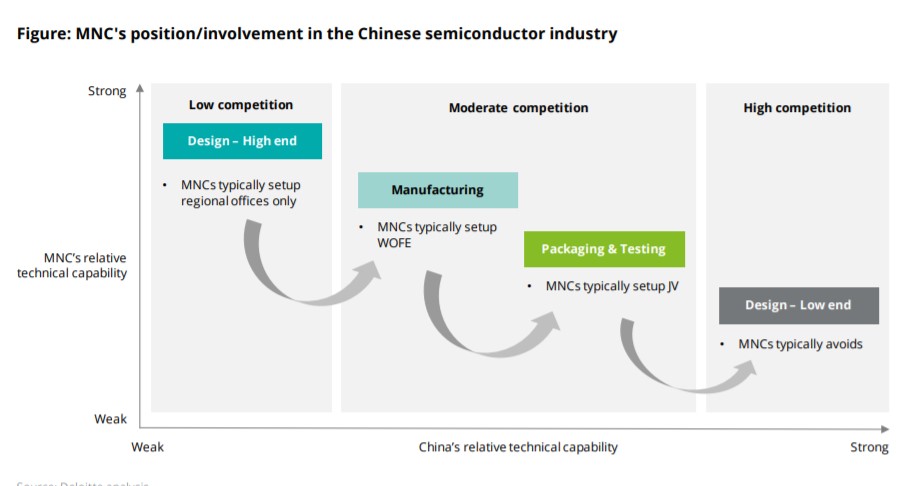
Component manufacturing firms such as Tech Components International, do not commonly engage in commercial sales but focus on attracting and fulfilling outsourcing orders from larger manufacturers, or potentially selling components directly to retailers. Although demand for consumer devices may flatten, semiconductors and related electronic components will be necessary for sectors such as the automotive industry or artificial intelligence. China is the largest semiconductor and electronics component market, accounting for 41% of the global total, assumed to grow to 57% of global consumption by 2024 (Deloitte, 2019).
Multinational corporations (MNC’s) can enter and benefit from this market in China. This is evident especially when the firm has the upper hand in high-end technology design and manufacturing that are much weaker in the country unlike packaging, testing, and low-end design where China excels. The target market for the company is major electronic firms and manufacturers seeking to order components in bulk orders for their production. Tech Components International will utilize marketing that will focus on attracting major firms or governments needing electronic components, establishing quality and reliability, with the focus on establishing long-term contractual supply chains.
Strategic Planning
PESTLE Analysis
SMART Goals
SWOT Analysis
Operating Plan
Timeline
1st month – apply for appropriate licenses and establish the business, apply for financing if necessary, meet all regulatory requirements.
2nd month – establish physical facilities, begin hiring workers, install appropriate equipment. Begin engaging in negotiations or bids at this time. Begin talks on establishing supply chains for raw materials, finished products.
3rd month – Begin production on initial orders. Finish setting up the supply chain. Find appropriate storage space for components and finished products.
4-6th months – Finish delivery of initial orders. Simultaneously begin negotiations with larger firms for bulk orders. Expand production capabilities.
By the 12th month – accept and fulfill at least one major order. Begin plans for opening up a new manufacturing facility, expanding supply chain capabilities.
Use of Resources
The company will initially have 2 manufacturing facilities, both located in China. It will also have 2 warehouses in China, and 1 in the United States for optimal delivery of components to its consumers. It is necessary to establish a stable supply chain to receive the necessary raw materials for the production process as well as ensure that the company can safely deliver finished products in bulk that are fragile. The production process will be based on placed orders. When there are no orders, the facilities will continue to operate at a slower pace to produce fundamental electronic components that can be sold on the market and to retail.
Operational capacity can be potentially increased within the facility by adding work shifts and increasing efficiency and power output. The latest manufacturing equipment will be used for electronics and all processes will continue to be updated to upkeep with the industry. Management models will be utilized within the factories to improve efficiency output. In terms of human resources, the majority of work line staff will be hired in China. People will work in traditional 8-hour shifts in the facility. Appropriate conditions and salaries will be provided, abiding by local and international labor laws. High-end research and engineering talent may be hired locally and abroad to develop new processes for manufacturing and component improvement.
Conclusion
Tech Components International is a semiconductor and electronic components manufacturing business founded in China by a U.S. venture. Its purpose is to integrate into the global technology supply chain and provide a bridge between the local Chinese component market and major technology firms in the U.S. The company’s objective is to work with major technology firms locally that outsource manufacturing and gradually expand its production capabilities through large bulk orders.
As an American medium-sized business, the firm must navigate the complex socio-political and economic environment in China and strategically engage with established supply chains and competitors in order to develop capabilities and reputation that will allow it to expand to a level of recognition in the global component manufacturing and supply chain marketplace. Through taking advantage of the company’s strengths and opportunities, and having specific strategic goals, it is possible to achieve the objectives in the proposed time period.
References
- Barboza, D. (2016). An iPhone’s journey, from the factory floor to the retail store. The New York Times. Web.
- Cheng, E. (2019). China’s moves to boost foreign business also help Chinese companies. CNBC. Web.
- Deloitte. (2019). Semiconductors – the next wave. Web.
- Kaliani Sundram, V. P., Chandran, V., & Awais Bhatti, M. (2016). Supply chain practices and performance: the indirect effects of supply chain integration. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 23(6), 1445–1471. Web.
- Kolk, A. (2016). The social responsibility of international business: From ethics and the environment to CSR and sustainable development. Journal of World Business, 51(1), 23-34. Web.
- Lee, Y. N. (2019). The US and China are dragging currencies into their escalating fight. Here’s what you need to know. CNBC. Web.
- Pham, P. (2017). How Asia has become the world’s manufacturing hub. Forbes. Web.
- Shin, N., Kraemer, K. L., & Dedrick, J. (2009). R&D, Value chain location and firm performance in the global electronics industry. Industry & Innovation, 16(3), 315–330. Web.
- West, D.M., & Lansang, C. (2018). Global manufacturing scorecard: How the US compares to 18 other nations. Web.
