Introduction
In the e-commerce industry, Noon Company has become a significant online marketer of quality products. Noon is a privately held company specializing in warehousing, logistics, payments, shopping, fashion, retail, technology, and design. The company operates within the Middle East and has its headquarters in Burj Khalifa, Dubai. It was founded by Mohamed Alabbar in 2017, and has since developed to become an important online seller, accruing huge revenues (Vakhariya, 2020). The main objective of the company is to create first-class digital marketplaces for consumers and other businesses. The current study aims to analyze the strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities available to the company in the context of COVID-19 pandemic to develop strategies that will boost it towards achieving its set goals.
Brief History of Noon Company
Started in 2017 by the founder and director Mohamed Alabbar, Noon is one of the region’s leading online shopping platforms. A network of services should be developed to empower and inspire a generation of diverse digital consumers-oriented businesses (Alshaketheep et al., 2020, p. 832; Swapana, and Padmavathy, 2017; Ahmad, and Callow, 2018; Kusumawati, Kusumasari, and Lubis, 2019). The company has grown to entail a chain of several sub-departments, including the Noon.com, Noon Daily, Nownow, Noon pay, and Noon Food among others. It was initially formed to operate in Saudi Arabia but has since diversified to work in the entire Middle East, including the United Arab Emirates (U.A.E), and Egypt.
The company has actively employed a large number of personnel who draw a significant amount of revenue. On a daily basis, it serves thousands of potential customers and sells bundles of products and services. During the COVID-19 pandemic, many companies’ income has improved because of the increment in the number of people locally shopping online (He and Harris, 2020, p. 178). This situation has called for quick measures to be taken to account for inflation by making necessary business adjustments to accommodate the effect of the pandemic.
Situation Analysis (2017- 2019)
A SWOT analysis has been piloted to comprehend the internal and external factors touching on Noon’s productivity before the COVID-19 pandemic. The study was conducted and presented using Porter’s Five Forces Model, which aids in drafting strategies that can help Noon Company adjust to the new market condition. Besides, the COVID-19 presented emergency situations, which without an analysis; operations may fail to profit the company.
The Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces model is used to discuss five competitive forces that affect a company’s competitive environment. These factors influence Noon’s profitability, and they include such factors as competitive rivals (Amazon), new market entrants, suppliers, potential customers, and substitute products (Porter, 2008, p. 26). In the case of Noon Company, the Five Forces discussed below are derived from stiff rivalry from such competitors in the same platform as Amazon, bargaining power of suppliers and customers, negative feedback from customers, fluctuation in prices of commodities, and high taxation levels.
Stiff Competition from Rivals in the same Platform
Online marketing has recently gained popularity among entrepreneurs leading to an increase in companies participating in such businesses. The rise in the number of potential rivals has created a stiff competitive environment in the industry as they contend with sharing the limited customers. Such international online marketing companies as Amazon are considered to provide significant threats to Noon as they have a broader market base (Vakhariya, 2020). Buyers tend to prefer companies that have been in the market for a long time and have gained popularity, thus offering better quality goods. Rivalry from these major sellers limits Noon’s yields, therefore, affects its productivity.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers and Buyers
Noon does not manufacture its products because it depends on manufacturers to supply the goods it sells. Consequently, the suppliers may bargain for higher selling prices because they believe such companies as Noon make huge profits. The high cost of purchasing the goods affects the company’s revenue, hence reduced profit margins. However, buyers seem to be attracted to sellers who offer their goods at a relatively cheap price (Phadermrod, Crowder and Wills, 2019, p. 197). To obtain optimum customer satisfaction, the company is forced to make significant cutbacks in costs, thus suffering substantial losses. Therefore, by bargaining, suppliers and buyers fail to commit to set price tags, subsequently affecting the company’s sales procedure, hence losing yields.
Fluctuation in Prices of Commodities
Due to changes in the production cost, the prices of commodities in the market may rise or drop continuously. For instance, if a company bought a product at a given price and it follows that the cost of the same drops, then they will be forced to reduce their selling price. Such cutbacks might result in massive losses and a reduction in net profits (Palepu, Healy and Peek, 2019). A rise in prices of the goods and services may compel an enterprise to increase their selling cost resulting in a fall in demand for the commodities and thus, deprivations.
Negative Feedback from Customers
Customers who are not satisfied with the services offered may culminate into posting negative comments on the company’s sales platform and other public domains. Such statements may waiver the trust of other clienteles who might have been interested in making purchases from a company’s website (Kannan, 2017, p. 23; Al-Weshah, 2020). Many customers believe that the goods and services with the most positive feedback are the best quality, and therefore they avoid the merchandise with negative feedback. Unwelcome input on the sales platform will ultimately lead to a reduction of trust and customers, resulting in a massive loss of profits.
High Taxation Levels
High taxation levels in the Middle East countries during this period greatly affected the online marketing industry. Commodities designated for importation or exportation underwent a series of taxations which affected their potential proceeds. As such, the company was forced to limit exports and imports, which resulted in the loss of potential customers and profit (Soundararajan, 2018, p. 98). The imposition of high tax levies by the concerned governments cost the company tremendous losses because of low productivity.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis was used to assess the strengths and weaknesses and identify the opportunities available for exploitation, including threats posed to the Noon businesses. The strengths and weaknesses are internal factors, while the opportunities and threats are the external factors.
Strengths
Noon is a major online marketing company with a good reputation. The fact that it operates internationally, Noon provides a large market for its commodities and provides an opportunity for expansion of trade boundaries, bringing in significant earnings from exportation (Al-Weshah, 2020; Triplett, 2020). In this case, most of its operating areas have good network coverage, allowing its customers to browse through its marketing sites freely and fast, thus improving purchase rates. Noon Company also receives large sums of money from the sales of petroleum products readily available at their disposal. These finances are used to expand the operation of the business leading to an increase in revenue.
Weaknesses
The company is highly dependent on other parties to supply them with trade commodities. The failure of these parties to commit to the supply schedule because of unforeseen circumstances such as COVID-19 could affect Noon’s production schedules and ultimately cost-effectiveness. Given that the business is internet dependent, any altercations in network connectivity delays transaction and reduces trading processes which eventually contribute to substantial losses (Kingsnorth, 2019). Since the company operates over a wide area, it is prone to delayed distribution and delivery of commodities. These delays discourage customers who are vulnerable to impatience, hence a reduction in purchase levels.
Opportunities
Noon Company operates in oil-producing countries of the Middle East. The oil products form a large portion of the trade commodities. In this regard, the company can expand the range of items they sell to their customers. The countries also have good infrastructure, including roads and airways, which act as ready transportation systems for the commodities (Bolos et al., 2016). Improvements in technology can lead to the growth of the market as advanced devices with better internet connectivity have been invented (Hudson, 2017). In this regard, Noon can take the opportunity of the availability of the already established infrastructure to increase its revenue.
Threats
There is stiff competition for the market with other companies within the online marketing industry who seek to expand their buyer capacity. These competitors introduce new trends, which are not ideal for the operation of the company. Noon Company is forced to adjust their operation protocols to outsmart their rivals, thus adversely affecting their sales procedures, leading to significant losses.
Assumptions and Missing Information
Noon Company only provides limited information about their operations, financial statistics, and background history; thus, most of the data is from secondary sources. The limit in records makes it hard to follow a company’s economic statistics on expenditure and transactions (Donthu and Gustafsson, 2020, p. 284). The data provided is obtained from the publication where there are continuous changes in time and thus, is subjected to constant alteration of the information supplied.
Problem Definition
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic led the world to make significant adjustments in their daily routines and operations. Countries have been forced to set up policies to counter the situation by putting up curfews and lockdowns due to COVID-19. Society has turned to online industries to offer such services and commodities at their homes’ comfort (Chaffey and Smith, 2017). Furthermore, there has been a large flux in online buyers creating a significant market than pre-pandemic period. Noon Company is, in return, forced to make significant adjustments in their operations to accommodate the rapidly rising buyer population.
COVID-19 has caused a rise in the number of online operations and users; people have migrated into online marketing, thus creating a competitive market. Many online marketing companies have been developed during the pandemic period, which creates stiff competition against Noon. The company reportedly has been forced to make many adjustments to accommodate the market’s fast-increasing competition (Bostanshirin, 2014, p. 9; De los Santos and Zanca, 2018, p. 70).
Despite having a ready market, the pandemic has developed significant shortcomings to the company causing it to make sudden and drastic changes which have affected its post-pandemic operation and strategies. Analysis of Noon Company’s situation in the post-pandemic era shows that measures have to be put in place to stabilize the company’s productivity. Below are the situation and SWOT analysis of the post-pandemic period until now.
Situation Analysis (2019- current)
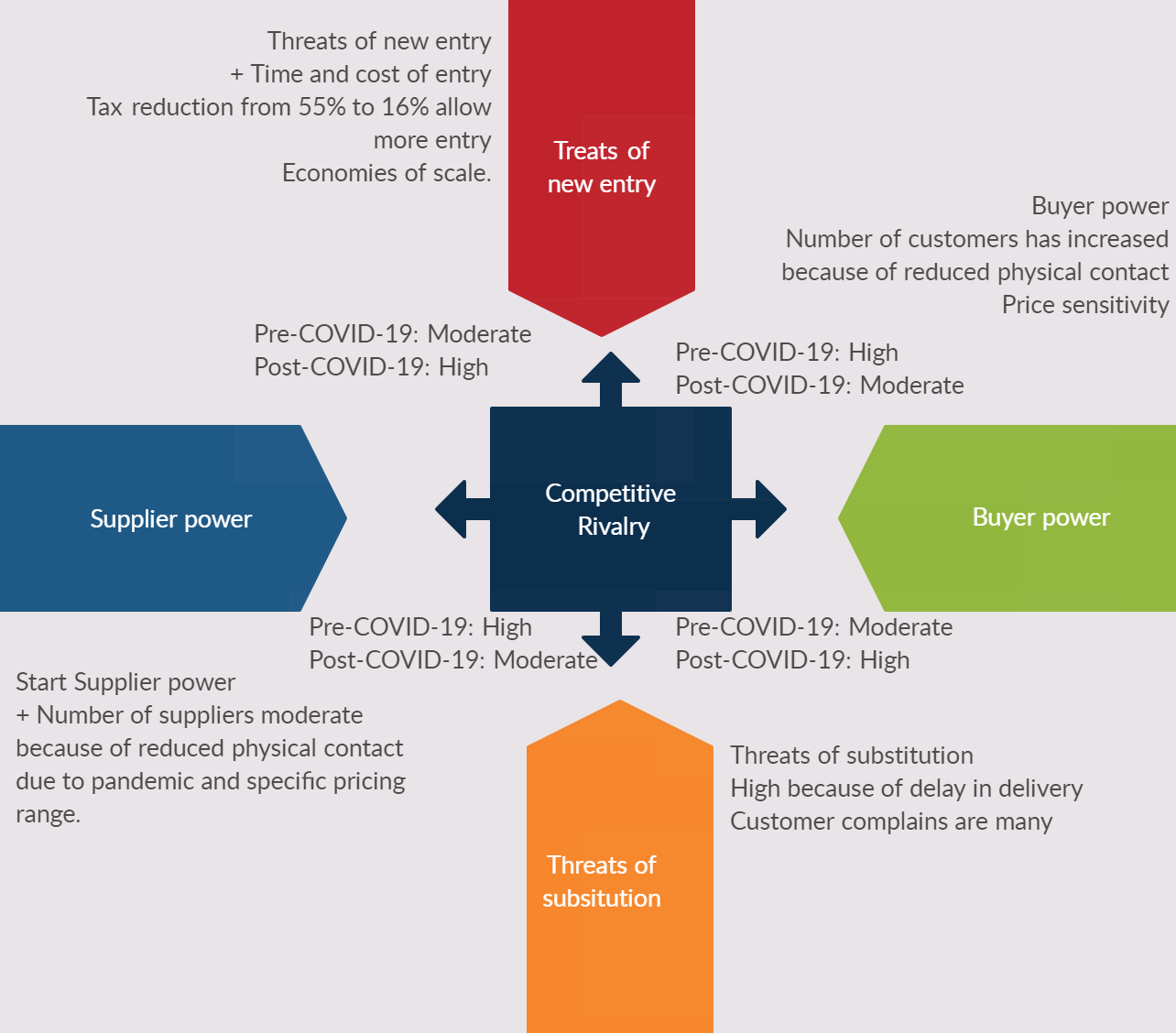
The Porter’s Five Forces
The analysis conducted after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic has shown that some adjustments have occurred to Porter’s five forces. The impact on the five forces influencing the firm’s competitiveness has either positively or negatively adjusted (Isabelle et al., 2020). In the case of Noon, the Porter’s Five Forces (see Figure 1), are as discussed below.
Stiff Competition from Rivals in the same Platform: High
Considering the rise in the number of online marketing firms, the competition has become much stiffer. The competing firms work tirelessly to establish their counterpart’s potential consumers by taking extreme measures which may be fatal to a particular firm (Jennifer, and Sofroniev, 2020; Pooranian, Conti, and Hadaddi, 2020). The firm is under high pressure to adjust its operating mechanisms to maintain its customers’ supply while attracting more (Bharadwaj et al., 2013, p. 480). This has enhanced competition as a factor into a significant threat to the company’s prospects.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers and Buyers: Moderate
The suppliers’ bargaining power has remained relatively constant since it is independent of the flux in market capacity. The suppliers tend to maintain a specific pricing range; hence Noon Company is not affected so adversely. On the other side, buyers have developed a strong tendency to bargain for lower prices while threatening to drop the company’s services (Aljuwaiber, 2020). However, because the company provides high quality online services, the buyer’s power has remained moderate. In as much, the company is compelled to create price cutbacks that have led to significant losses over the past short period.
Threat of Substitute Products: High
The prices of commodities have to a slight extent improved in their fluctuation tendency. The rise in prices of the goods and services may compel the company to increase their selling cost resulting in a fall in demand for the commodities and, thus, creating a gap which necessitates substitution. Furthermore, since the pandemic started, there has been delay in the delivery of online purchases because of lockdown and curfew related issues. This has resulted in buyers looking for alternative services that can be delivered on time, reducing customer complaints for non-delivery, hence, substitution.
Threat of New Entrants: High
Most Middle East countries have reduced taxation rates from about 55% to as low as 16% over the past few years due to the pandemic. Such decreases have reduced charges on the goods sold, leading to a reduction in the company’s net losses during the post-pandemic regime (Bruijl, 2018). Reductions in taxation have allowed the company to accumulate revenue that would have been used to cater for the former, thus maximizing profits. Noon Company has positively gained from the cutbacks made on the taxation rates.
However, in view of the low taxation, there is a threat of new entrants to utilize the opportunity availed by tax levies introduced by the government. Besides, more companies have gone online because of the reduction in physical contact imposed as a measure to curb the spread of the virus. Therefore, with more companies venturing online, there is a high threat of new entrants in the market.
SWOT Analysis
Some changes have occurred to the SWOT analysis as the company has gained some new strength to overcome weaknesses. Moreover, it has also developed some new opportunities and realized new threats as indicated in Figure 2 and discussed below:
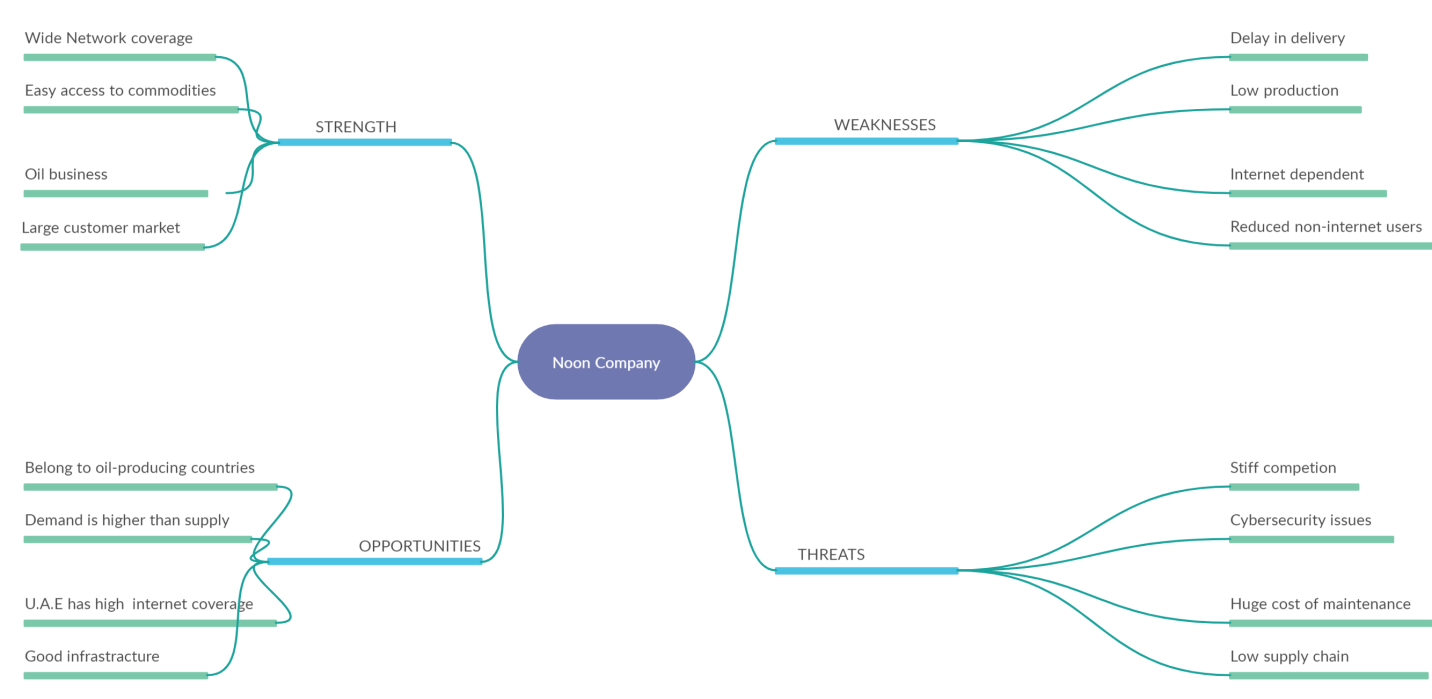
Strengths
In addition to the availability of capital, wide networking range, easy acquisition of commodities, and it being a leading company, Noon has added to its list of advantages the oil business. Its main shareholders are big dealers in the oil exporting industry hence they supply the capital for running the business (Aaker, 1984, p. 172). The firm has acquired a large customer market at its disposal, thus ready exit for its commodities. It has also enhanced such pre-existing strengths, thus improving productivity and subsequently maximizing profits.
Weaknesses
Company has been able to operate within its weaknesses by strengthening and widening its distribution chain. They take large stocks from the suppliers and store them, thus nullifying any delays that may occur because a supplier has made some delay in delivering.
Opportunities
Middle East countries, where Noon as the Company is located, have good infrastructure, including roads and airways, which act as ready transportation systems for the commodities. Improvements in technology have led to the growth of the market as advanced devices with better Internet connectivity have been invented, leading to increased profits (Almoamen, 2021). Bulging of the market capacity has also resulted in creating an opportunity for expansion of the firm operations.
Threats
Large amounts of capital have been consumed in the firm’s adjustment to accommodate the increase in the number of potential buyers. Losses have also been incurred since the company has adjusted by reducing prices to attract more buyers.
Mitigation Strategy
To operate within the challenging effects brought about by the pandemic, Noon Company has opened a variety of departments within the business. These departments deal in different specific commodities and focus on serving a particular portion of the buyers only. This divide and conquer tactic has lowered lag in attending to customers, thus improving productivity. The company has also updated its sales website, making it possible for them to accommodate as many buyers as possible at the same time.
Gap Analysis and Recommendations
Despite making many adjustments to their schedule and operations, Noon Company has not eliminated their problems in attending to their customers’ numerous needs. To address these issues, the below policy options have been proposed, as they were assessed to be the most practical and useful and take into consideration any underlying risks for these recommendations (De, 2018, p. 74). These policies are aimed towards optimizing on creating better communication between the customers and the company.
Option 1: Expansion of the company’s operations into areas that have not yet been covered
- Phase I: Put up new stores where customers can pick up their commodities after ordering them online.
- Phase II: expanding their transportation network to reach customers in these uncovered areas.
- Phase III: employing more personnel to cater for the buyers in these locations:
- Type of intervention: Direct Intervention.
- Project Sponsor: The Noon Company.
- Legislative changes required: None.
- Timeline: half a year.
- Resources: Human resources, Consultancy, Funds, Feedback platforms.
Option II: creating online platforms to increase customer awareness
- Phase I: creating a better customer care service to attend to the buyers without putting them off.
- Phase II: venturing into newly created social media platforms such as Tiktok to create awareness of the services they offer
- Type of intervention: Direct Intervention.
- Project Sponsor: The Noon Company.
- Legislative changes required: None.
- Timeline: three months.
- Resources: Consultancy, Funds, Feedback platforms.
Conclusion
Noon Company is a leading online marketing firm within the Middle East. Thus, by analyzing its strengths and weaknesses, the company can adjust to serve its growing buyer population satisfactorily. This analysis outlined the changes in weaknesses, strengths, opportunities, and threats concerning the company and its relationship to the buyers. Policies, including the expansion of the company’s operations into areas that are not yet covered, have been proposed to help curb the shortcomings. Therefore, the company will have moved closer to achieving its mission of developing first-class digital marketplaces for consumers and businesses.
References
Ahmad, S. N., and Callow, M. (2018). ‘Free shipping” or “Dollar Off”? The moderating effects of list price and e-shopping experience on consumer preference for online discount’. International Journal of Electronic Commerce Studies, 9(1), 55-70. Web.
Aljuwaiber, A. (2020) ‘Entrepreneurship research in the Middle East and North Africa: trends, challenges, and sustainability issues’, Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies. Web.
Almoamen, G.A. (2021) ‘How Saudi small business managers increase retail electronic commerce sales,’ Walden Dissertations and Doctoral Studies. 10020. Web.
Alshaketheep, K.M.K.I., Salah, A.A., Alomari, K.M., Khaled, A. and Jray, A.A.A. (2020). ‘Digital marketing during COVID 19: consumer’s perspective’. W.S.E.A.S. Transactions on Business and Economics, pp.831-841. Web.
Al-Weshah, G. (2020). ‘E-marketing practices from Jordanian tourism agencies perspectives: a qualitative evidence’, International Journal of Online Marketing (IJOM), 8(1), pp. 21-36. Web.
Bolos, C., Idemudia, E. C., Mai, P., Rasinghani, M., and Smith, S. (2016). ‘Conceptual models on the effectiveness of e-marketing strategies in engaging consumers’. Journal of International Technology and Information Management, 25(4), p. 3. Web.
Bruijl, G.H.T. (2018) ‘The relevance of Porter’s five forces in today’s innovative and changing business environment’, SSRN Electronic Journal. Web.
Chaffey, D. and Smith, P.R. (2017) Digital marketing excellence: planning, optimizing and integrating online marketing. Taylor & Francis. Web.
De los Santos, E. and Zanca, N.A. (2018) ‘Transitioning to online: a SWOT analysis by first time online business faculty’, e-Journal of Business Education and Scholarship of Teaching, 12(3), pp. 69-84. Web.
Donthu, N. and Gustafsson, A. (2020). ‘Effects of COVID-19 on business and research’. Journal of business research’, 117(1), pp. 284-294. Web.
He, H. and Harris, L. (2020) ‘The impact of Covid-19 pandemic on corporate social responsibility and marketing philosophy’, Journal of Business Research, 116(1), pp. 176-182. Web.
Hudson, D. (2017). ‘Value propositions for the internet of things: guidance for entrepreneurs selling to enterprises’. Technology Innovation Management Review, 7(11), pp. 5-11. Web.
Isabelle, D., Horak, K., McKinnon, S., and Palumbo, C. (2020). ‘Is Porter’s Five Forces framework still relevant? a study of the capital/labour intensity continuum via mining and IT industries’. Technology Innovation Management Review, 10(6). Web.
Jennifer, P., and Sofroniev, G. (2020). Exploring voice-controlled systems: services and consumer preferences towards future usage within the food industry. pp. 1-150. Web.
Kannan, P. K. (2017) ‘Digital marketing: a framework, review and research agenda’, International Journal of Research in Marketing, 34(1), pp. 22-45. Web.
Kingsnorth, S. (2019) Digital marketing strategy: an integrated approach to online marketing. Kogan Page Publishers.
Kusumawati, N. F., Kusumasari, T. F., and Lubis, M. (2019). The effectiveness of digital marketing for show up companies: issues and challenges. In 2019 3rd International Conference on Electrical, Telecommunication and Computer Engineering (ELTICOM), pp. 27-31. Web.
Palepu, K.G., Healy, P.M. and Peek, E. (2019) Business analysis and valuation. Cengage Learning EMEA.
Phadermrod, B., Crowder, R.M. and Wills, G.B. (2019) ‘Importance-performance analysis based SWOT analysis’, International Journal of Information Management, 44(1), pp. 194-203. Web.
Pooranian, Z., Conti, M., and Hadaddi, H. (2020). Online advertising security: issues, taxonomy, and future directions. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials. 20(20), pp. 1-25. Web.
Porter, M.E. (2008) ‘The five competitive forces that shape strategy’, Harvard Business Review, 86(1), pp. 25-40. Web.
Soundararajan, G. (2018) ‘Impact of e-commerce on global business environment: a conceptual study focus on the Middle East’, Eurasian Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 13(1), pp. 96-98. Web.
Swapana, M., and Padmavathy, C. (2017). ‘Factors influencing online shopping experience a conceptual model and implications’. Global Management Review, 11(1), 18-26. Web.
Triplett, V. M. (2020). An exploration of rural small business owners’ experience with internet marketing. Web.
Vakhariya, S. (2020) ‘A study of online shopping experience and swaying brand preference between Noon and Amazon in UAE’, South Asian Journal of Management, 27(2), pp. 84-112. Web.
