Apple is a leading firm in the global technology industry. It produces high quality computers, smartphones, software, and entertainment products. Apple is one of the most successful companies in the world in terms of innovation, profitability, market capitalization, and market share. The visionary CEOs who helped the company to achieve success include Steve Jobs and John Sculley. Currently, the company is facing intense competition, especially in the computer industry. Thus, the CEO must promote innovation to develop superior products that will improve the competitiveness of the company. This paper will analyze the performance and challenges that Apple faced from 1990 to 2014.
Apple’s History
Apple was founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak in the US. The two business partners focused on developing and selling computers, which were referred to as Apple I. Although the company was successful in 1980s and early 1990s, it was making huge losses in mid 1990s. It also lost a substantial market share to competitors such as IBM and HP. The main turning point came in 1997 when Steve Jobs rejoined the company as its CEO. Jobs introduced new innovative products that significantly increased the company’s profits and market share. The introduction of iPod, iMac, and iTunes in 1998 enabled the company to become the market leader. The greatest breakthrough came in 2007 and 2010 when Apple released iPhone and iPad respectively. iPhone made Apple the leading firm in the smartphone industry, whereas the iPad made it the leader in the tablet computer market.
The Personal Computer (PC) Industry
PCs are microcomputers that can accommodate one user at a time. Initially, PCs were designed as desktop machines that consisted of several components such as the display unit, CPU, and peripheral devices, which included keyboard, mouse, and modems. Currently, PCs exist in different forms, which include laptop computers, tablets, and notebooks. The brand name of Apple’s desktop PC is iMac. The PC uses operating system (OS) developed by Apple and components manufactured by suppliers such as Intel. Exhibit 1 shows the latest version of iMac.
The PC Market
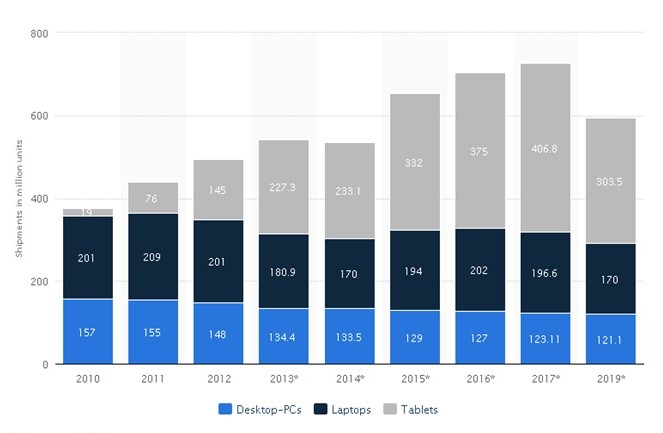
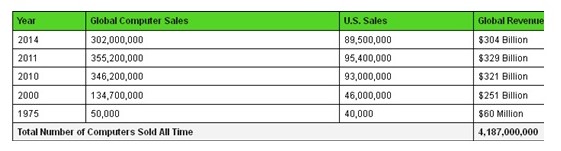
The PC market consists of four main segments namely, individuals, governments, enterprises, and educational institutions. The main benefits of PCs include lots of memory space and ability to access the internet. This allows users to access, store, and retrieve large volumes of information at a low cost. PCs also have fast processors that enable them to run several applications at the same time. This improves efficiency in businesses and learning institutions. PCs are also cheap and durable. In 2014, the global demand for PCs was approximately 536.6 million units as shown in exhibit 2. The exhibit shows that the demand for laptops and tablets is increasing steadily. However, the demand for desktop PCs is declining. North America, Europe, and Asia account for over 50% of PC sales. In 2015, the demand for desktop PCs is expected to decline by 3.37%. In 2014, total revenue in the industry was approximately USD 304 billion as shown in exhibit 3. North America accounted for nearly 38% of the sales.
Suppliers
The main supplies in the PC industry include hardware and software packages such as operating systems. The most important components (hardware) include processors, circuit boards, and peripheral devices such as keyboards. Contract manufacturing services are also important since they help vendors to reduce operating costs. The most important suppliers include Microsoft and Intel. Nearly 80% of computers use Microsoft’s OP and Intel’s processors. As a result, Microsoft and Intel have a high bargaining power.
Competitors
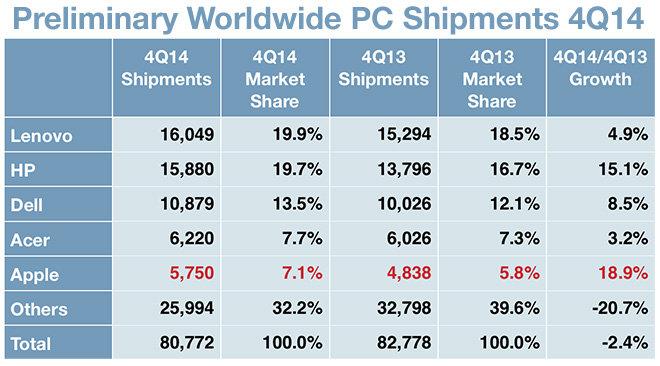
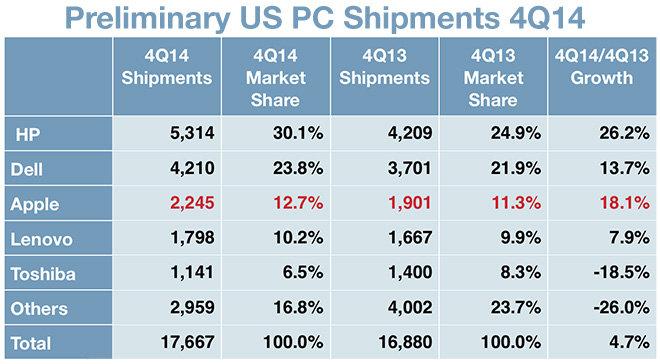
Currently, Apple is the fifth largest PC vendor in the world in terms of sales as shown in exhibit 4. However, it is the third largest vendor in the US as shown in exhibit 5. The main competitors of Apple are HP, Dell, and Lenovo.
HP
This company was founded in the US in 1939 by Bill Hewlett and Dave Packard. It has the largest market share of 24.9% in the US. HP’s market share of 16.4% is the second largest worldwide. The difference between HP and Apple is that the former produces a wide range of high quality products that it sales at a relatively low price. Exhibit 6 shows that HP experienced a steady decline in revenue and net income from 2010 to 2014.
Lenovo
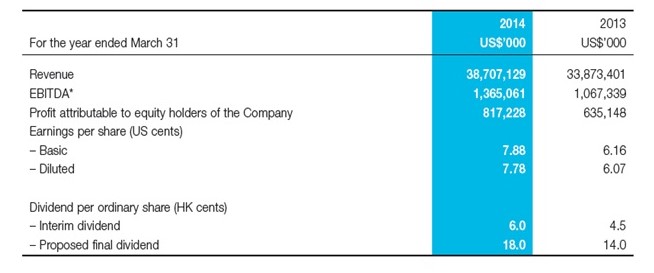
This company was established in China in 1984 by Liu Chuanzhi. Currently, it has the largest share of the global PC market (18.8%) and third largest (9.9%) share of the US market. Lenovo’s main strength is ability to sell its products at very low prices. This makes it different from Apple, which sells its products at a premium price. Exhibit 7 shows that Lenovo realized an increase in profits and revenue in 2013 and 2014.
Dell
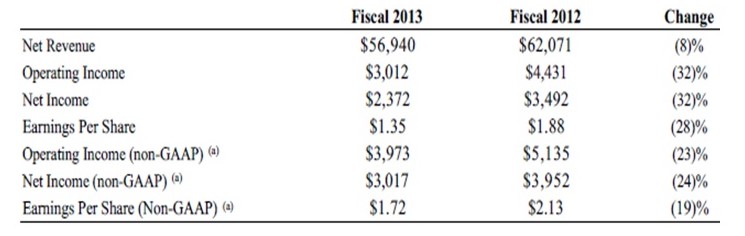
This firm was founded by Michael Dell in 1984 in the US. It controls nearly 23.8% and 12.7% of the US and global PC market respectively. The main strengths of Dell that make it different from Apple include expertise in product customization and a strong brand image in the PC market. Nonetheless, Dell’s profits and revenue have been declining since 2012 as shown in exhibit 8.
The Current and Future Challenges
The main challenges that Apple is facing include the following. First, the company has a very weak position in the PC market. In 1980s and early 1990s, Apple was the leader in the PC market. However, it has since lost its position to rivals such as HP and Lenovo. Therefore, how can Apple regain its position in the market? Second, Apple has failed to launch new innovative products after the death of Jobs in 2011. As a result, it has been overtaken by competitors such as Samsung, which are also able to provide high quality products. How can Apple introduce new exciting products to retain its customers? The managers in the company must answer this question to improve its competitiveness. Finally, Apple is facing difficulties in maintaining high product quality. For instance, its cloud computing services (iCloud), laptop computers, and social network products are relatively weaker than those of its competitors. Therefore, how can Apple improve its product quality?
Case Analysis
External Analysis
Trade liberalization is the main political factor that affects the PC market. Liberalization has led to increased supply of cheap computers from China and Japan, thereby reducing the market share of Apple in the US and the EU. Income per capita growth is the main economic factor that affects the market. Individuals and businesses tend to be price sensitive during economic downturn due to low income. As a result, PC vendors have to embark on cost cutting measures such as outsourcing production to maintain their competitiveness. Exchange rate fluctuation is also an important economic factor since it affects revenue from overseas markets.
Access to advanced hardware and software technology is an important determinant of competiveness in the industry. Only companies with superior technologies are able to produce high quality products that customers need. Social trends such as online shopping and learning, as well as, using computers for entertainment are increasing the demand for PCs.
At the industry level, the factors that influence competition include the high bargaining power of suppliers and buyers (users of PCs). The high bargaining power of suppliers limits PC vendors’ ability to negotiate for favorable prices for supplies. Buyers’ bargaining power limits the ability of vendors to increase profits by charging premium prices. Competitive rivalry is also high due to the large number of PC vendors. Apple failed to achieve success until Jobs returned because its CEOs could not identify and respond appropriately to the factors discussed in the foregoing paragraphs.
For instance, in 1995 Amelio failed to reposition Apple as a leading brand due to lack of appropriate technology. Jobs could have solved Apple’s problems by 1999 if he had a clear understanding of the external environment. For instance, the success of iMac could have been huge in 1999 if Jobs had realized that customers wanted PCs that could run third party applications. Moreover, he could have found it easy to attract the independent software developers who were needed to provide new applications to improve the quality of iMac.
Internal Analysis
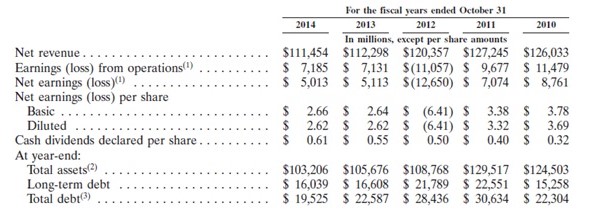
Apple’s strengths include the following. First, the company has a strong brand image. Its PCs are known for reliability and high quality. This enables the company to ensure customer loyalty. Second, Apple is capable of using disruptive innovation to improve its competitiveness. The company uses research and development to produce the best products. Finally, Apple has a strong financial position. In 2014, its net profit margin was 21.67% and return on equity was 33.61%. The debt-to-equity ratio was 31.64%. These statistics indicate that Apple is profitable and financially stable.
The main weakness of Apple is premium pricing. This weakness has allowed low cost vendors such as Lenovo to attract customers away from Apple. The company has also experienced technological problems. Customers have complained about dysfunctional features of key products such as iPhone and iPod.
Apple’s main source of competitive advantage is its product strategy. The company manufactures its own hardware and OS, thereby achieving a higher level of product differentiation than its competitors. The retail strategy of the company is also an important source of competitive advantage. The strategy also facilitates provision of high quality services through direct interaction with customers. Apple uses its own retail outlets, thereby enjoying high profit margins. Supply chain efficiency is also a source of competitive advantage because it enables Apple to reduce its operating costs.
Business Level Strategy
The business strategy that Apple is following is differentiation. This strategy involves producing products with superior attributes to satisfy specific market needs. In this respect, Apple positions itself as a vendor of high-end products that can be trusted by customers who are interested in the best PC experience. The functional level strategies that support differentiation include branding and manufacturing strategies. Apple achieves brand differentiation by conveying very simple marketing messages that customers can identify with and remember easily.
Corporate Level Strategy
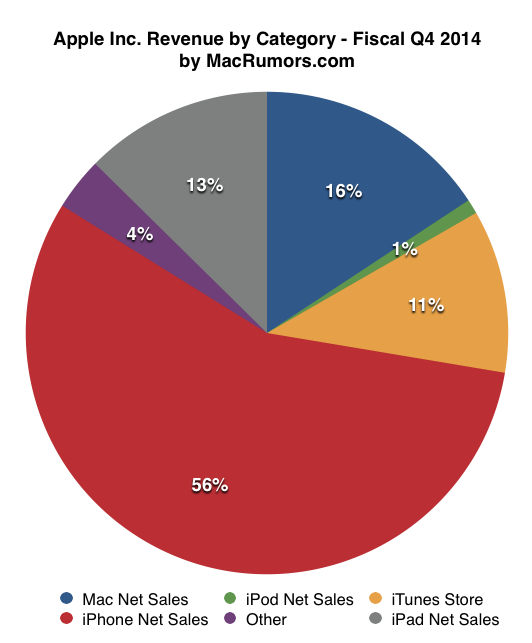
The corporate level strategy that Apple pursues is constrained diversification. In this strategy, a company “enters a new business only if it is based on its core resources or competencies”. Although Apple is inherently a PC firm, it has ventured into smartphone and entertainment businesses. This was a good choice since iPhone, iPod, and Apple TV are products that use the company’s core competency in manufacturing PCs. For instance, the aforementioned products use Apple’s OS. Moreover, the smartphone and entertainment business (iPod and iTunes) have greatly increased the profits and market share of the company. For instance, iPhones accounted for 56% of the company’s net sales in 2014 as shown in exhibit 9. Apple pursues diversification through internal development. It also uses acquisition to diversify its portfolio in the entertainment market.
Structure and Control
Apple uses a flat organizational structure, which has very few management levels. The rationale of using the structure is that it facilitates effective communication between the management and employees. This improves ideation and the process of making decisions, which in turn leads to innovation. Control is ensured in the company through clear rules and instructions that every employee is expected to follow.
International Expansion
Apple’s products are already being sold in nearly every country. The company entered foreign markets through licensing, exporting, and foreign direct investment (FDI). Apple has licensed third parties to produce and sell its products in countries such as China. It also exports its PCs to Africa, South America, and Europe. The company also establishes its own retail stores (FDI) in foreign markets to sell its products. International expansion has enabled the company to increase its profits and market share. Apple also focuses on new product development to improve its earnings. For instance, it is currently preparing to release iWatch to increase its revenue and counter competition from similar products such as Android Ware.
Recommendations
Apple should consider the following recommendations to overcome the challenges that it is facing. First, Apple can regain its market position by shifting its pricing strategy from premium to competition-based pricing. The rationale of this strategy is that the competitors of the company are able to provide high quality products at relatively low prices. For instance, the PCs produced by Dell and HP can match iMac in terms of quality. However, they are much cheaper than iMac. In the smartphone market, Samsung has been able to produce relatively cheap smartphones whose features are superior to those of iPhones. In this respect, Apple has to set prices that are comparable to those of its competitors to defend its market share.
Second, Apple should embark on research and development in order to introduce new products that will excite customers. Market research will enable the company to identify emerging needs that have not been satisfied. Technological research will lead to development of products that satisfy new needs. Consequently, the company will maintain high profitability and market share.
Third, Apple can improve product quality through talent acquisition. Apple is facing technological challenges because its engineers have been acquired by competitors such as Google and HP. Hiring talented employees will enable Apple to develop the technologies that it needs to improve its services. It can also access advanced technologies by acquiring startups.
Appendix

Works Cited
Apple. Apple Inc. Annual Reports 2014. Web.
Gartner. Worldwide PC Shipments in the Third Quarter of 2014 Declined, New York: Gartner, 2014. Print.
He, Ning. “How to Maintain Sustainable Competitive Advantages: Case Study on the Evolution of Organizational Strategic Management.” International Journal of Business Administration 3.5 (2013): 112-120. Print.
Kazmi, Sam. Marketing Management, London: Sage, 2007. Print.
McCray, Joan, John Gonzalez and James Darling. “Crisis Management in Smart Phones: The Case of Nokia vs. Apple.” European Business Review 23.3 (2011): 240-255. Print.
Pattie, Luke and Peter Rogers. Galaxy S5 Attracts some Apple Customers in Europe, but Sales Lag in Great Britain 2014. Web.
Peterson, Michael. “iPhone and Apps: The Brand Management and Marketing Aspects of Apple’s iPhone and Associated Applications Software.” Strategic Direction 27.3 (2012): 12-45. Print.

