Introduction
The motto of this report is to discuss the impact of external and internal factors on Easyjet Plc. This report will concentrate on company background, SWOT analysis, PESTEL factors, competitive forces, primary internal influences, external influences, and the changing competitive environment.
Background of EasyJet
EasyJet is a British aviation company started its journey in 1995 by incorporating to pose as a low-cost air transportation services within home and abroad. At the very beginning, EasyJet operated inaugural flights from London to other UK cities like Edinburgh and Glasgow with only two rented aircraft and contracted staffs. Now, EasyJet carries highest number of passengers than all other UK based airline with its operation in the 500 domestic and global routes covering Europe, US and some Asian destination. The company also listed in the LSE (London Stock Exchange) with symbol EZJ and placed itself as one of the FTSE 250 Indexed Company (Easyjet, 2007). Beyond the global financial crisis of 2008, the company continues to keep its strong footprint in the aviation industry with its almost 7000 well defined human resource in UK and Europe.
SWOT analysis EasyJet
Strengths
- The brand name or reputation is one of the main strengths of Easyjet;
- It has advanced technological support as well as financial strength to increase its net profit margin in the recessionary economy.
- Easyjet is able to offset high fuel costs;
- The decision of acquisition with GB Airways enhanced its operation.
- It is present in the 37 of the top 50 European airports;
- It has presence on 422 routes with 45 of the top 100 European routes;
- Skilled, trained, motivated, and experienced staff are the key strength for the success of EasyJet;
- It has 672 cabin crew and 92 well-trained pilots;
- The strategy “Low fare, No frills” has reinforce its position.
- High quality customer services with provision of free flights and extra offers;
- By applying four major strategies, Easyjet increased its total revenue up to 12%;
- The websites of the company always provide latest information about its flights.
Weaknesses
- According to the annual report, EasyJet paid comparatively high remuneration to their employees and directors;
- Sometimes Easyjet has to face some unusual risks, for example, IT security and fraud risk, brand ownership, dependence on technology, Industrial action, Retention of key management, Financing and interest rate risk;
- In this recessionary period, many competitors of Easyjet, for example, Ryanair and Aer Lingus generated higher revenue then the company (Air Scoop, 2007).
Opportunities
- Easyjet has enough financial capabilities and experience to increase its operation in non EU zone;
- Most of the customers are loyal as Easyjet has maintained good relationship with its customer by providing exclusive service;
- It has huge opportunity to find out new routes to expand its business because it has all ingredients to serve quick customer service with high satisfaction (Easyjet, 2009).
Threats
- Competitors are the main threat for Easyjet as the profit margins of other low cost airways are increasing.
- Earning from tourism sector has decreased due to global financial crisis, for instance, the discretion of future expenditure of tourist has changed. As a result, the net profit of EasyJet Plc has adversely affected for economic downturn.
- The expansion rate in non EU zone of Easyjet is lower than its competitors;
- Some other external factors may become threat for the company like Swine Flu virus, volcano, threat of new entrants, and risk of terrorist attack.
The PESTEL framework of EasyJet
Political factors
Hitt, Ireland, & Hoskisson (2001) argued that political situation always changes the business environment. FDI policy of overseas government, hostile government attitude in non-EU countries, instable political environment in different region, various government incentives like tax exemption, tax policy, etc., are posing major influence on Toyota’s operation. However, Easyjet is committed to pursue the regulation of Emissions Trading Scheme. Moreover, Easyjet has to face the risk of changes of exchange rate, as UK joined in the single European currency.
Economic factors
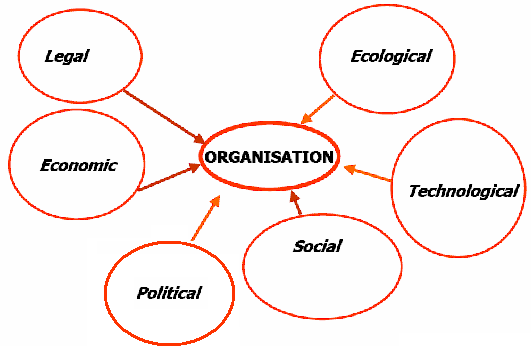
According to the annual report 2009 of Easyjet, it is in 37 number positions among the top fifty EU airlines. Increase rate of oil and gasoline price, fluctuated international demand for Airways services, rising competitive pressure and recessionary effects are notable economic factors in this case. Mintel (2009) pointed out that the price of its services is lower than rivals’ offered price, for example, Lufthansa, Air France, or British Airways asked high cost for similar services. However, this basic chart of EasyJet demonstrates that the share price of the company in LSE is in down turns for global financial crisis, for instance, the market share price was in highest position in 2007, but this share price is still less than 2007.
Socio-cultural factors
In 2009, EasyJet recruited about 6,666 people among them 4473 were British citizens. As a result, Easyjet has to spend more money for the salary purpose as more than 65% of total employees of this company are British citizen and rest 35% are come from European countries. This internal factor could adversely affect the company, as it would be difficult for Easyjet to bear the high payment of the employees in this recessionary period. In 2009 and 2008, Easyjet expended £33.8 million and £27.2 million respectively for Social security. However, this company always consider equal opportunities among employees in order to get better services from them.
Technological factor
The company is very much reliant on the application of technologies in the business; it uses its website for various purposes ensuring that the customers are receiving satisfactory services. The website deals with eRes, designed for seat purchases and reservations; RMS, intended to yield management; and AIMS, that handles operational information and team placements. Tim Newing, easyJet’s IT Director, has an extensive understanding in the technological field and he has fruitfully built up a sequence of programmes putting forward a foremost technical innovation, and improving order of architecture; he received the 2005 IT Director of the Year in the Jaeger LeCoultre Telegraph Business Awards.
Environmental factor
The company makes sure that its staffs are careful about reducing the ecological pollutions. Everybody involved in the company keeps the environmental concern in mind, starting from the cabin crew who gather waste materials for recycling, to the higher management who speaks with politicians on global warming issues and with suppliers for producing planes, which emits less CO2.
The business considers the fact that emanations from this industry must drop in recent years, but attaining this requires the effort of both the industry and the government by the introduction of innovative technologies, and by the enactment of strict legislations. EasyJet employs its staffs in airframe and engine productions as it has a vision by 2017 to produce the easyJet ecoJet that would emit 50 per cent less carbon dioxide and 75 per cent less NOx.
Legal Factors
Frequent change of aviation regulation due to protect the people from terrorist attack has both positive and negative influence on the operation of its business. For instance, BA had avoided to purchase new planes to support security issues in its destination after the 9/11 situation, which was another obstacle for growth of its business because it could not ignore the risk of terrorist attack. However, EasyJet followed the Companies Act 1985 though from last year, it considered Schedule 8 of the CA 2006 to operate consistent with the government policy.
Primary Internal Influences
- Corporate governance: EasyJet would like to manage the corporation by sustaining under strong corporate governance organism. The Board of directors, Leadership team, and Independent auditors are responsible to manage the company perfectly (EasyJet, 2009, p. 47). Combined Code 2008, Listing rules and several audit reports like Directors’ report, Audit, Nominations Committee, and Independent auditor’s report have huge internal affects on the company. According to the annual report 2009 of Easyjet, it sets the remuneration of the directors in accordance with the provision of CA 2006 and the report of the committee;
- Other important factors: High wages, the relationship among employees, effective communication, motivation, work ethic of workers, risk management system, internal control, and internal audit are the major internal issues for the development of the company.
Other External Influences
Costs: the total cost per seat is increasing each year and it has direct impact on the service price of the company.
- Low fare: The main competitive advantage of Easyjet is its low fare compared to other airlines that operates in Europe. It offers lowest fare for their travellers in various destinations in Europe and it makes the airline capable to generate more revenues for itself.
- Swine flu: This report has already mentioned that Easyjet had affected by financial crisis and this position has prolonged because of numerous external factors, for instance, swine flu virus reduced its number of passengers. Here it is important to mention that shares in Easyjet fell about 7.70 percent due to this virus (BBC News, 2009).
- Decline in aircraft utilization: Due to unstable position in fuel price, the level of flying activity actively reduced. However, the following figure shows that Easyjet is in number one position in Short haul route in European market
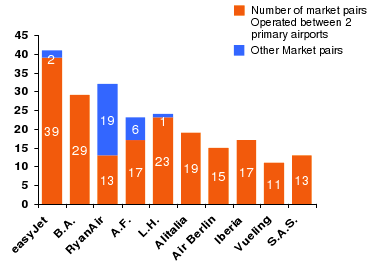
- According to the annual report fuel prices, hedging, US dollar, and euro exchange rates has significant influence on the company.
The changing competitive environment
Presently, the European aviation industry is facing intense antagonism between the low cost airlines like Ryanair, easyJet plc, Virgin Express, Aer Lingus and the flag carriers. The low cost/no-frills airlines are adapting with adverse environment rather proficiently comparing to the flag carriers; whilst the flag carriers are receding from several routes and cutting jobs, the budget sector is showing an increasing rate of success.
Because of the global financial crisis, many customers have shifted their choices to the low fare carriers like easyJet plc. Although the flag carriers still have a large number of loyal customers, many people now chooses the easyJet plc as it offers first rated customer service and is able to counteract elevated fuel prices by using new airbuses that consume lower amounts of fuel rather than raising the fares.
Conversely, flag carriers are unable to cope with the increasing fuel price by these methods and cover the additional cost by raising the fares; e.g. BA initiated until twenty-six % increase in fare to cope with high oil prices for its maximum paying travellers, as well as an augmentation for premium travellers (British Airways, 2009). However, BA will contract with some businesses for manufacturing fuel from waste materials in order to cope with oil price and to lower the emission of CO2 in the atmosphere. If this project brings success for BA, then it may be a threat for easyJet’s profitability.
Mergers between firms also accelerate the pace of rivalry, e.g. BA has tried to amalgamate with American Airlines although US authorities refused two of its earlier approaches; some also argues that BA is in negotiations with Bmi to purchase the British carrier. A successful merger between two organisations in the industry means that other businesses might face increased competition.
The EasyJet plc is leading on a number of intra European short haul routes, encouraging many others like Buzz, Bmibaby, Basiq Air, and Germania to join in. The penetration of new entrants in the market is also escalating the rate of competition.
Influences on polices and decision-making of easyJet
The strategies of easyJet plc to adapt adverse situations have been quite successful, which means that they are more likely to gain competitive advantage over others. To increase the profitability in this changing competitive environment, easyJet plc is making several decisions to acclimatize with external influences like mergers, oil price hikes, and recession.
Competition in the industry has forced easyJet plc to shift its strategy and focus on seeking partners; it has merged with GB Airways and easyTech to form a powerful company that can create trouble for many established airlines.
On the other hand, to cope with the increasing fuel price, the company is using the latest technology planes, because those are more fuel-efficient comparing to previous ones. This decision helps easyJet to gain competitive advantage as others are raising their fares to reduce the costs of fuel. This decision will also lessen the impacts on environment.
To compete effectively during the recessionary period, easyJet decided to stick to its low-cost and well-organized business model idea in order to ensure that the customers will use its services. The company decided to benefit from the recent financial crisis by pulling costs out of the business and cautiously focusing on increasing competence and on share growths in important markets throughout the continent.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis for Easyjet
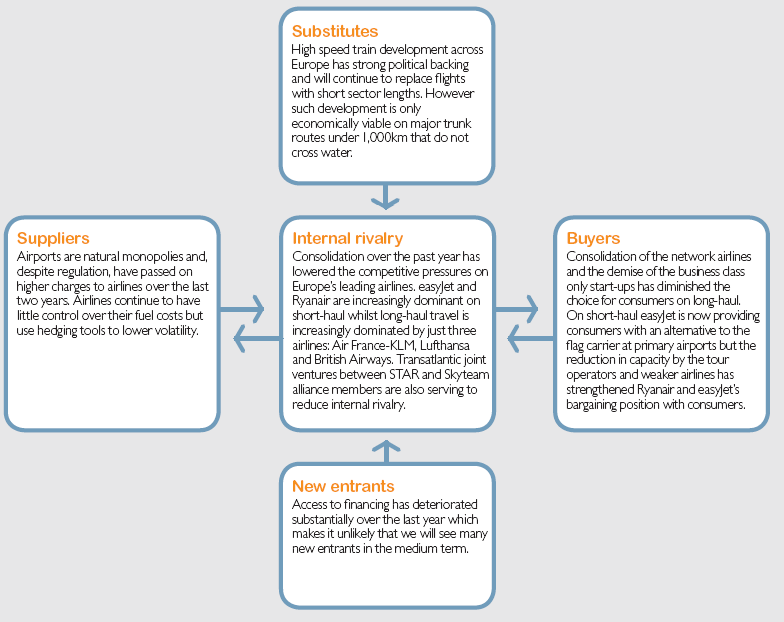
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
The chief providers of aircrafts in easyJet are Boeing and Airbus, and for supplying fuel its major suppliers are Shell, BP, Exxon and Q8; the switching costs of suppliers is great here, but the local airports have little bargaining power. Conversely, the major airports are innate monopolies and in spite of several rules, they have put on increased charges on the airline companies over a last couple of year.
Bargaining Power of Customers
The customers in this industry greatly responds to raising fares as their switching costs at other airlines like Ryanair are relatively cheap; most essentially, they possess a greater awareness on the charge of the services afforded, and loyalty is very little. However, acquisition of the network airlines has lowered down the option for customers on long haul; on short haul, easyJet serves the passengers with a substitute of British Airways, but the decrease in capability by the tour-operators and other frail companies reinforces its negotiation power with travellers.
New Entrants
The barriers to enter the market consist of vast amounts of capital investment and controlled slot accessibility making it more complex for the fresh participants to get suitable airports, besides, the recognized businesses participate instantaneously at price wars, creating tough situations for the beginners; Restricted Flight Authorisations constitutes further difficulties for them. Apart form these, the availability of financial support from banks and other financial institutes has weakened considerably from the previous year making it improbable that some new competitors may sustain in the market.
Threat of Substitutes
Deficiency of close customer relationship, inadequacy and of brand loyalties, and existence of abundant players like Virgin Express, Lufthansa, BA, Air France, and other forms of transportation lessens switching costs extensively. Super fast trains and improvement of railway system across the continent may lower down the switching costs; this sector possess good political support has the capacity to substitute air travel on short haul.
Competitive Rivalry
The European aviation industry includes flag carriers, independent airlines, and franchises of chief airlines. In the budget sector, the mainstream cost advantages could be copied instantly; yet, at this part, the rivalry is moderately less, as the two foremost low cost airlines have selected different routes for their travellers. However, when new companies come into this area, bigger strains fall on charges and subsequently on profit margins.
- In recent years, mergers has shortened the aggressive competitiveness on the continent’s principal airline businesses;
- EasyJet and Ryanair are mostly prevailing on short haul, whereas long haul tours are highly conquered by Air France, Lufthansa and British Airways;
- Joint ventures between STAR and Skyteam are also representing abridged rivalry in the industry.
Recommendation
- In order to reduce operating costs, Easyjet should recruit efficient employees from Asian countries;
- As the competition among airlines industry is too high, it should increase its operation in non EU routes to compete with similar airlines;
- It should more concentrate on environmental factors as it use low cost fuel;
- It should decrease the wage of directors and price of air ticket considering the oil price and global economic condition;
- It should strictly follow the listing rules for remuneration issue as lat year employee costs for easyJet were £342.9 million;
- It should spend more money for advertising, promotion, and R&D.
- It should follow brand extension strategies to diversify its product line and service range.
Reference List
- Air Scoop. (2007) SWOT analysis of Easyjet.
- BBC News. (2009) Swine Flu Fears Hit Travel Shares. Web.
- British Airways. (2009) British Airways Annual report 2009-2010. Web.
- Easyjet. (2007) Key Events in our History.
- Easyjet. (2009) Annual report 2009 of Easyjet.
- Easyjet. (2009) Financial report 2009 of Easyjet.
- Google finance. (2010) EasyJet plc (Public, LON:EZJ).
- Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2001) Strategic Management. 4th ed. South-Western Thomson Learning.
- Kentleton, R. (2009) Credit Suisse – June 2009. Web.
- Mintel. (2009) Short-haul Airlines – UK – July 2009: Market in Brief.
