Introduction
Volkswagen AG, popularly known as Volkswagen Group or just VW Group, is a German automotive manufacturer that has its headquarters in Wolfsburg. According to Gunnell (2017), Volkswagen is one of the largest automotive manufactures in the world, offering a wide range of cars to meet varying needs of international customers. Through mergers and acquisition, the company has been able to penetrate almost every segment of the car industry, from the high-end products to cars affordable to the middle class and low income earners. In order to protect some of the luxury brands that it had acquired such as the Bugatti and Lamborghini, the company decided to retain their brand name, identity, and mode of production to meet specific needs of its customers (Glen, 2017).
The strategy has helped the firm to retail a pool of loyal customer in an industry where competition remains very stiff. It has also maintained its Volkswagen brand for a wide range of its affordable cars. In this critical strategic analysis paper, the researcher will focus on evaluation of the flagship Volkswagen, one of the most successful brands under the Volkswagen Group to determine its current capabilities and the ability to achieve strategic growth in the global market
Brief Strategic Position of Volkswagen
The Volkswagen brand is one of the most popular car brands in the normal market that has achieved massive popularity among the middle class across the world. LeClair (2018) explains that the innovativeness of this company made it possible for it to develop a range of high performance cars known for their effectiveness in fuel consumption. The efficiency of these cars has made it very popular among its global consumers (Acker, 2017). The specific Volkswagen brand is positioned as a low-cost product that is affordable to the masses. This strategic positioning was embraced because the company also has a wide range of high-end products such as the Bugatti and the Lamborghini that target the very rich (Miller, 2019).
It also has other brands targeting the upper middle class. As such, the Volkswagen brand was specifically positioned for low to middle-income earners in need of a highly efficient car. The company has remained highly innovative in the market as it seeks to outperform its rivals within the same market segment. Figure 1 below shows one of the most recent models of Volkswagen cars.

Resources and Value Systems of Volkswagen
In the current competitive business environment, the ability of this company to achieve success in the market is defined by various factors, including resources and its value system. Understanding a firm’s core competencies and resources available to undertake specific strategic actions is critical in setting realistic goals (Bratton and Gold, 2017). It helps the management to understand what a firm can or cannot do as it seeks to expand its market share in the local, regional, and international markets. Dyer (2019) advises that when evaluating the resources, it is equally important to take into consideration the value system of the company. In this section of the paper, the researcher will evaluate these two issues critically.
Resource Audit
The concept of resource audit helps in analyzing a firm’s internal resources and competencies that can enable it to achieve its strategic goals. They include factors such as a firm’s financial capacity, technological systems needed to undertake various tasks, and the human resource responsible for undertaking these responsibilities. According to Miller (2019), Volkswagen has been ranked as the largest car manufacturer in terms of the value of sales from 2016 to 2019.
For the financial year ended in December 2019, the company recorded revenue of €252.632 billion and a net profit of €13.346 billion (Miller, 2019). These records show that the firm’s total assets were valued at €488.071 billion within that period. The strong financial capacity of this firm means that it has the capacity to support its research and developmental needs. It can also sustain its operations in case of a major economic meltdown in parts of its major markets.
In terms of technological systems used at the company, the firm has been keen on embracing emerging technologies to enable it gain competitive edge over its rivals in the market. LeClair (2018) explains that the company has been at the forefront in promoting virtual technologies in its operations. Most of the operational tasks at the plant are currently conducted using robots (Gunnell, 2017). This technological trend is meant to improve speed of production, improve quality, lower cost, and reduce occupational risks. They have enabled this company to increase its production output without compromising on quality or having to increase the number of its employees.
Human resource audit also helps in defining core competencies of a firm. According to the company’s reports, Volkswagen has over 304,170 salaried staff spread across the world (Miller, 2019). A significant number of these workers are involved in the actual production of the cars. Another significant population is in the sales and marketing unit and the logistics unit. The firm also has finance and accounting officers, risk management officers, public relations unit, and many other departments that keep it operational. It is necessary to ensure that these employees have the right skills and capabilities based on the needs of their departments.
They must understand the value of teamwork even as they strive to achieve individual excellence (Dhir and Sushil, 2019). Figure 2 below shows a human resource model that Volkswagen can use to audit its human resource. The first stage emphasizes the need to maximize the performance of each employee. They should then be made to learn and appreciate the significance of collaboration and exploration. The management should also consider providing the entire team of workers with opportunities for them to develop their skills and overall competency (Dyer, 2019). Having regular on-job trainings or sponsoring them for further studies in local institutions of higher learning may be appropriate.
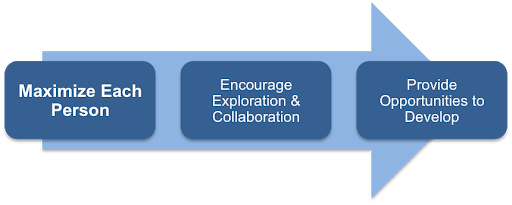
Value Systems
Value systems refer to ways in which activities within a firm may enable the value to be realized within a given industry. Volkswagen primary goal is to ensure that it delivers high quality cars to its customers at affordable price. Using the value chain model shown in figure 3 below, the management will understand a set of activities that the firm will need to undertake to deliver valuable products to its clients (Ansoff, 2019). The primary activities start with the inbound logistics where the firm will need to source for various materials needed for assembling its cars. It includes outsourcing some car parts such as batteries and tyres from some of the reputable manufacturers.
The next stage of operation involves assembling the cars at the plant. Once the cars are assembled, the logistics unit will need to find ways of ensuring that they reach the right dealers across the world. The marketing and sales unit will be responsible for promoting the brands and products of the firm, and ensuring that these products are sold to customers at the right time and at the right price. The final activity is offering relevant services that may be needed by the customers. In undertaking these activities, the management will need the support of the firm’s infrastructure, human resource, technology, and procurement to ensure that the desired success is achieved.
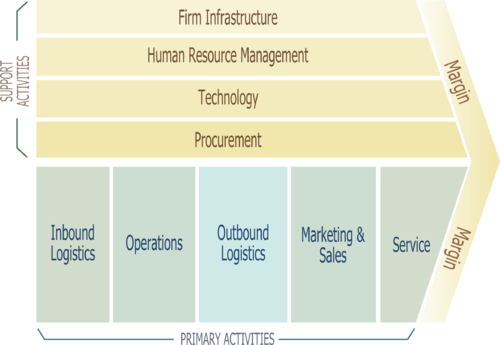
Evaluation Product/Portfolio Mix
Volkswagen has a large product portfolio to meet the wide range of needs of its customers. According to McPhee and Wheeler (2006), the primary reason why people purchase cars is to facilitate their movement from one place to another in a convenient and safe way. However, it is important to note that a car is one of the most important means of showing one’s class in the society. In its line of production, this company often seeks to capture various market segments with this brand of Volkswagen, especially from the middle upper class and below or reach people who are not interested in some of the fancy models.
Analyzing the product portfolio makes it easy to understand the revenue stream of the company. It is easy to understand products which are earning the firm attractive sales, those that have slowed in sales, and the ones that may need to be stopped from the line of operation because they have lost their appeal to customers. The Boston Consulting Group (BCG matrix can help in classifying various products that Volkswagen offers in the market.
Product/Service portfolio (BCG Matrix)
The BCG matrix classifies a firm’s product portfolio into four main classes. In the first quadrant are products classified as question marks. These are products with high growth rare but low market share. These products require significant investment, but their low market share means that the firm is getting relatively low profits. As Connor (2011) suggests, the management will need to increase the market share of these products so that they can become stars or cash cows. The Volkswagen Tiguan falls in this category. The second quadrant has stars. These are products with high market growth rate and high market share.
They earn the company a significant amount of money and they show signs of further growth (Hearn and Pace, 2006). The management will need to invest more on these products to ensure that they realize maximum growth in the market and become major products. Volkswagen Amarok and the newly released Volkswagen ID 4, which is an electric car, fall under this category. They have a bright future as there is a huge opportunity to grow. As fossil fuel becomes less desirable, such electric cars are likely to gain huge market share.
The third quadrant is the cash cows. These are products, which are no longer experiencing any market growth, but they already have a huge market share (Rose and Cray, 2013). They earn the company huge revenues because they are known and remain popular among customers. The company does not need to spend a lot of cash in promoting them because they have gained strong reputation. Volkswagen Passat and Volkswagen Golf are some of the main cash cows for the company.
The focus should be to prolong their desirability in the market. The last quadrant has products classified as dogs. They might have been stars or cash cows at one point in the company’s history, such as the Volkswagen Beetle or Volkswagen Touareg, but they have lost their appeal in the market. These products have already been pushed out of production.
Table 1: BCG Matrix.
Critical Analysis and Evaluation of Key Future Directions for Strategic Growth
The management of Volkswagen should ensure that its current lead in the market is maintained despite the stiff competition that it is facing from other dominant global manufacturers. It must have a clear strategy that defines its growth directions from where it is currently to what it seeks to achieve in future. As Bratton and Gold (2017) observe, change is a factor that a firm cannot ignore if it seeks to remain relevant in the market.
It must have the capacity to monitor emerging market trends and develop ways of responding to them effectively. Mittal and Jain (2012) believe that the ability of a firm to respond to the emerging market needs depends on its core competencies. It depends on the ability of its workforce to identify these forces of change in the market and respond to them adequately. It is evident that the automotive market is moving towards a greener future as environmental concerns continue to be a major concern. It is necessary to look at this firm’s potential future strategic growth based on the emerging trends in the market.
Potential Future Strategic Growth
Volkswagen has a huge potential for growth. As the size of the middle class continues to increase in the global community, the number of people who have the capacity to purchase cars for this company also continues to increase. However, Miller (2019) warns that for this company to take the advantage in the market, it should have a clear understanding of the trends in the market. It should understand changing tastes and preferences, evolving technologies, strategies that its rivals employ and government regulations that may redefine its operations. It should then develop an effective response mechanism.
Identification of Options
The management should start with the identification of strategic options that are available to it. It should understand the strategic direct that it needs to take to realize its long-term goals. These options are often based on the market forces. Figure 4 below identifies strategies that this firm can use to determine the possible options that it has in the market.
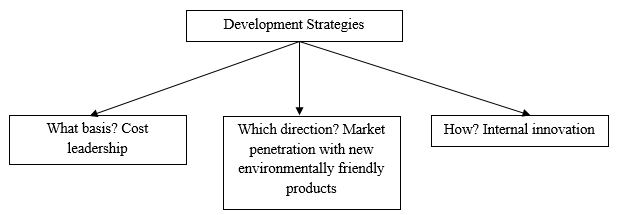
The figure above shows the options that this firm should embrace when defining its future in the market. In terms of the basis of embracing a specific option, the management should focus on embracing cost leadership approach. It should ensure that its costs of operation are maintained as low as possible to ensure that it can charge its products competitively in the market (Ansoff, 2019). In terms of the direction that the firm should take, it is advisable that the firm should focus on penetrating the global market with new environmentally friendly products. Volkswagen ID 4 is one of the promising products that this company is launching in the global market.
However, it is yet to make an emphatic entry into the market despite its environmentally-friendly nature. The management may need to invest in its promotion. In terms of answering how this company can achieve these goals, it is necessary to focus on internal innovation. It should use its highly skilled team of employees and improved operational systems to come up with new ways of operation and new products.
Evaluation of Options
When the management has selected an appropriate option that it seeks to pursue in its future development strategies, it is necessary to conduct an appropriate evaluation to determine if it will help it achieve its intended goals. As mentioned above, this firm should consider focusing on electric cars in its effort to achieve global growth. The problem is that this strategy may be a major threat to some of its currently successful products.
The analysis above indicated that VW Passat is one of the most successful products in this firm’s portfolio. However, it runs on petrol, which environmentalists have criticized for the increased carbon emissions (Dhir and Sushil, 2019). When promoting Volkswagen ID 4, this firm will have to emphasize on it being an emission free car. Such a promotional campaign will be a direct criticism against some of these current products. As such, there is the risk of cannibalism.
Addressing such a challenge may require unique marketing strategies. However, it should not be ignored. As Dyer (2019) observes, Eastman Kodak was the first company to come up with the concept of digital films at a time when it controlled over 80% of the global market share. However, it feared that this new product will cannibalize traditional film, which was the main product at that time. As such, it failed to introduce the new technology.
Its market rivals such as Fujifilm took that opportunity and introduced the new product. It did not take long for Fujifilm to become the dominant player in this industry (Bratton and Gold, 2017). Volkswagen should not risk following the same path as Eastman Kodak. As such, it should find unique marketing strategies that will enable it to promote ID 4 without compromising the sale of Passat, which is currently its cash cow.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Volkswagen is currently one of the dominant brands in the car manufacturing industry. However, the firm’s ability to retain its current market position or even achieve further growth depends on the strategies that it embraces. The analysis revealed that in this highly competitive business environment, it is necessary for the management to understand the emerging trends and respond effectively to external environmental forces. It should understand emerging needs based on technology changes and customers’ preferences. The following recommendations can help it achieve the desired growth:
- The marketing department of Volkswagen should embrace effective marketing strategies to market new electric car models without compromising the success of its current fossil fuel cars.
- The human resource department should consider hiring and retaining a team of highly skilled and talented employees. They should always be taken through regular training.
- The management should embrace innovation as the tool that will enable it to achieve competitive edge over its rivals in the market.
Reference List
Acker, A. (2017) Volkswagen in the Amazon: the tragedy of global development in modern Brazil. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Ansoff, H. (2019) Implanting strategic management. Cham: Palgrave Macmillan.
Bratton, J. and Gold, J. (2017) Human resource management: theory and practice. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Connor, T. (2011) ‘Internal resource audit for strategists: a proposal’, iBusiness, 3(1), 287-294.
Crain, D. and Stan, A. (2008) ‘Using value-chain analysis to discover customers’ strategic needs’, Strategy & Leadership, 36(4), pp. 29-39.
Dhir, S. and Sushil, A. (2019). Cases in strategic management: a flexibility perspective. Singapore: Springer.
Dyer, J. (2019) Strategic management: concepts and cases. Hoboken: Wiley.
Glen, S. (2017) Volkswagen type 3: concept, design, international production models & development. Dorset: Veloce Publishing.
Gunnell, J. (2017) The complete book of classic Volkswagens: Beetles, Microbuses, Things, Karmann Ghias, and more. Minneapolis, MN: USA Motorbooks.
Hearn, G. and Pace, C. (2006) ‘Value-creating ecologies: understanding next generation business systems’, Foresight, 8(1), pp. 55-65.
LeClair, E. (2018). How to restore your Volkswagen Beetle. Forest Lake, MN: CarTech Books.
McPhee, W. and Wheeler, D. (2006) ‘Making the case for the added-value chain’, Strategy & Leadership, 34(4), pp. 39-46.
Miller, G. (2019) The law of governance, risk management, and compliance. New York, NY: Wolters Kluwer.
Mittal, A. and Jain, P. (2012) ‘Mergers and acquisitions performance system: integrated framework for strategy formulation and execution using flexible strategy game-card’, Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 13(1), pp. 41-56.
Rose, W. and Cray, D. (2013) ‘The Role of context in the transformation of planned strategy into implemented strategy’, International Journal of Business Management and Economic Research, 4(3), pp. 721-737.

