Executive Summary
Customer satisfaction results in customers’ loyalty, thus, the success of a business. Retailers should understand the needs of their customers and strive to satisfy them (Slack et al., 2020). Price is a significant factor that shoppers consider when in shopping centers. Some shoppers look for goods with a low price tag, while others believe that the higher the price, the better the commodity. This research paper aims at identifying the role prices have on the satisfaction of customers in shopping centers in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The researcher shall apply a qualitative method to collect the data. In addition, the information obtained shall be analyzed using the regression analysis method.
Introduction
Customers are the backbone of any business, and retail shopping centers are not an exception. For a business to maintain its customers, it is essential that the management understand their needs and strives to satisfy those (Slack et al., 2020). However, as new business models have emerged, there has been a significant change in what satisfies customers in retail shopping. In addition, pricing is a critical factor that affects a customer’s choice of the shopping center.
Price is a significant factor both in modern and traditional shopping centers. A huge percentage of customers aim to get a high value of goods at a low price. When doing their shopping activities, most customers check the price of a product as the first step in the buying decision process (Dai, 2018). Therefore, they visit other shopping centers comparing the prices of the product they intend to buy. When they come along a lower price than the initial one, they will most likely purchase. Ideally, customers aim at deriving a higher value or benefits as compared to the price offered.
Consequently, another group of customers believes that only goods with high prices offer high value or benefits (Dai, 2018). These customers look for products with a higher price tag as they perceive them to be of higher status or more valuable than low-priced products. Other customers are more interested in the brand of a product than the price. Therefore, shopping centers must develop their marketing niche and identify their potential customers before implementing a pricing strategy.
Expected Problems
The length of the study limits the researcher from carrying out a positivistic study through direct interviews on various shopping centers’ customers. Therefore, the geographic and time constraints faced during the research shall limit the researcher to use previous research works from other researchers in some sectors of the region. Another major limitation is the generalization of data for various customers, as only a small percentage shall participate in the study.
Purpose of Study
There is a direct link between customers’ satisfaction and their loyalty, as it is a significant factor in the success of any business. Anselmsson (2006) suggests factors that ensure customer satisfaction in retail shopping centers. Some of them include service, expectations, the value of products, and the availability of desired goods and services. Therefore, the mentioned above factors are crucial for customers during shopping in centers.
A shopping center can use a pricing strategy to attract and keep its customer base. Customers perceive pricing in two ways; the amount of money one is willing to pay for a product; the benefits derived from purchasing the product (Cao et al., 2013). For a retailer to achieve customer satisfaction, they must convince them that the amount paid for a product is equal to the benefits they obtain or exceed. The main purpose of this research paper is to identify how the pricing of products affects customer satisfaction in UAE shopping centers. Achieving customer satisfaction will ensure the success of a retail shopping center (Cao et al., 2013). The research shall help entrepreneurs understand the pricing strategies to apply to achieve customer satisfaction.
Literature Review
A shopping center, also referred to as a shopping mall, is a group of retailing businesses in one infrastructure that offer different services and goods. A shopping center is mostly located in a predetermined position in a large town or city (Khurana & Dwivedi). Recently, shopping centers have gained much popularity as customers prefer to shop in a one-stop-shop for most of their goods (Anselmsson, 2006). This trend leads to an increase in competitiveness between shopping centers as each one strives to satisfy their customers and increase sales. Marketplaces have adapted various strategies that enable them to gain a competitive advantage.
Abad et al. (2020) suggest that customers choose to shop in one shopping center over another due to ease of access, convenience in purchasing, design, and planning of the mall, recreation activities, utilitarian value, and pricing of products. Customers find it convenient to shop in a shopping center that is near their residential localities than travel long distances to shop (Kim et al., 2008). A shopping center that is located in big towns and cities has more customers and sales than those in rural areas (Maroco, 2013). In addition, a shopping center should simplify the method customers use to purchase products by allowing multiple methods of payment (Mohamad & Ramayah, 2010). Nowadays, most customers prefer to use electronic methods of payment than physical money (Abad et al., 2020). In addition, some customers have embraced the use of bitcoins as a form of money transfer, a technology that businesses should also adopt.
Recreation facilities in shopping malls are the most significant factor that influences customers’ choice of shopping centers currently (Abad et al., 2020). For most customers, shopping adds to their social life with family and friends (Lii, & Sy, 2009). Most shopping centers have embraced recreation activities such as sports, cinemas, and gaming (Abad et al., 2020). In addition, the design of the shopping center contributes to the ease of shopping and accessibility of most shops in the shopping center.
The pricing of products in shopping centers has led to the division of shopping centers into various classes (Bhattacharya and Friedman, 2017). The most common shopping center classes are the middle-income and the high-income earners’ classes (Nam et al., 2011). In the middle-income earners’ shopping malls, the prices of commodities are relatively average. To achieve customer satisfaction, these types of malls use a marketing strategy that convinces their customers that the goods and services offered are of a greater benefit than the monetary value exchanged (Markovic & Raspor, 2010).
Often, middle-income shoppers will visit various shops comparing the prices of commodities before settling on one that offers products at a slightly lower price (AbuKhalifeh & Som, 2012). Bhattacharya and Friedman (2017) believe that marketers should apply a marketing mix that convinces the customers that they stand out from the rest to achieve customer satisfaction. The customers perceive expensive products to be of high value than cheap products.
Conceptual Framework
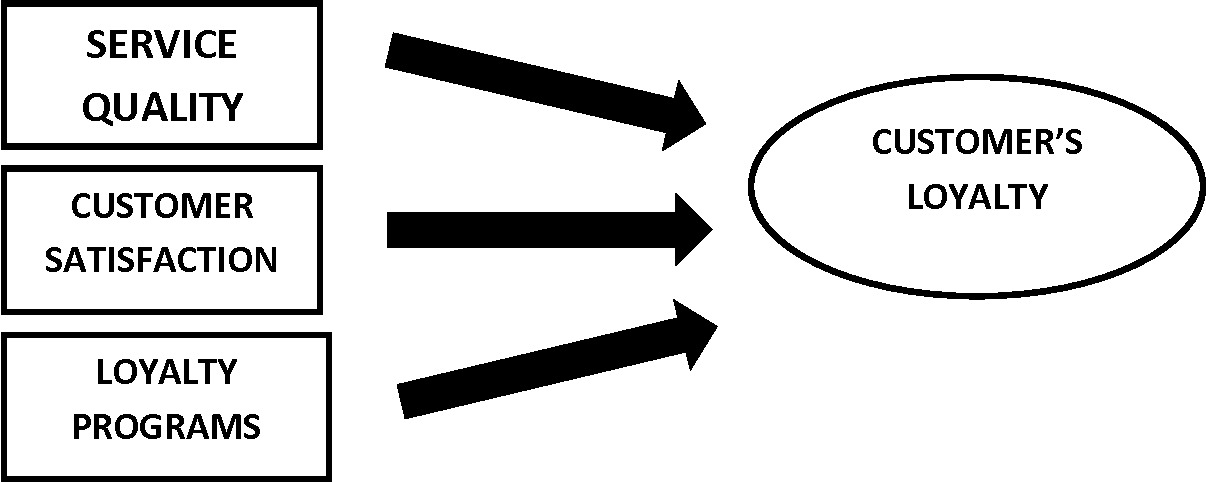
However, it is possible to notice the gap in the literature on how pricing influences visitors’ satisfaction in marketing centers. The researcher theorized a model to study the relationship between customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, and pricing in UAE shopping centers. In figure 1. Below, the researcher claims that good pricing strategies positively influence customer satisfaction and customer loyalty. The price mediates the perceived value of a product. The perceived product value is directly proportional to customer satisfaction and directly impacts customer loyalty, as shown in Figure 1.
Methodology
The researcher shall apply a mixed research method to collect primary data through surveys and interviews and use research from previous research. The researcher intends to sample shoppers from all age groups but subdivided them into three sections; 5-18, 18-40, 40, and above. The groupings shall help identify factors affecting the shopping centers for all age groups. In addition, the researcher shall conduct the study in two shopping malls of different classes, let say Center A and Center B, for middle income and high-income earners, respectively.
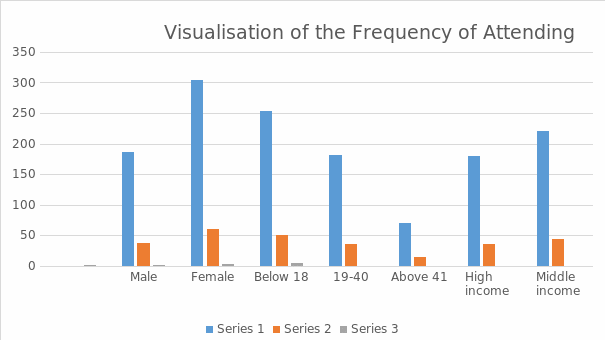
The researcher shall also collect data from the shopkeepers through surveys and interviews. The researcher shall provide 500 survey questionnaires to the shoppers in the two malls, 250 questionnaires in each mall. Moreover, he shall provide 50 questionnaires to different shopkeepers in each mall. Table 1 below shows the frequency of varying gender, age, and income groups’ attendance at marketplaces.
Table 1. Comparison of attendance frequency among different groups.
The visualization of frequency of shopping centers attending between different groups is shown on Figure 2 below.
Sample Questionnaire
It is possible to compose ten questions, which will significantly contribute to understanding the visitors’ experience through the feedback receiving.
- Which is your favorite shopping center?
- How frequently do you shop there?
- Why do you prefer the shopping center to others?
- What goods and services do you frequently purchase in the shopping center?
- How much time do you spend when shopping on average?
- Which is your preferred spot in the shopping center?
- Are you satisfied with the benefits you get for the value of money you give for the goods?
- Would you recommend a change in the pricing of the commodities?
- Is there any improvement you would recommend to the mall owners?
- Do you have any compliments for the retailers in the shopping center?
Data Analysis
The researcher analyzed the data from this study using the regression analysis method. This method uses all four factors; customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, pricing, and perceived value, as independent variables. The results of the analysis are shown in table 3 below.
Table 3. Results of the regression analysis.
The Table 4 shows percentages of answers. The researcher presented some of the answers to the questionnaires posed to the customer. However, not all questions could be analyzed on any statistical scale.
Table 4. Statistical proceeding of answers.
Conclusion
To conclude, marketers and retail shop owners should implement pricing strategies to satisfy the needs of various markets. The marketers should understand the shopping behavior and the needs of their customers and strive to fulfill them (Bhattacharya and Friedman, 2017). Some shoppers look for quality goods for a cheap amount of money, while others believe that the higher the product’s price, the higher the benefits and value. Customer satisfaction is proportional to their loyalty. Hence, achieving customer satisfaction is crucial to the growth of any business.
References
Abad, K. I. S., Mousavi, S. J., & Nasirzadeh, E. (2020). Analysis and classification of factors affecting customer satisfaction with shopping centers. Journal of Critical Reviews, 7(6), 966-973. Web.
AbuKhalifeh, A. N., & Som, A. P. M. (2012). Service Quality Management in Hotel Industry: A Conceptual Framework for Food and Beverage Department. International Journal of Business and Manegement, 7(14), 135-141.
Anselmsson, J. (2006). Sources of customer satisfaction with shopping malls: a comparative study of different customer segments. International Review of Retail, Distribution and Consumer Research, 16(1), 115-138. Web.
Bhattacharya, A. K., & Friedman, H. H. (2017). Using ‘smart pricing to increase profits and maximize customer satisfaction. National Public Accountant, 46(6), 34-38. Web.
Cao, Y., Gruca, T. S., & Klemz, B. R. (2013). Internet pricing, price satisfaction, and customer satisfaction. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 8(2), 31-50.
Dai, B. (2018). The impact of perceived price fairness of dynamic pricing on customer satisfaction and behavioral intentions: The moderating role of customer loyalty (Doctoral dissertation). Web.
Hafeez, S., & Muhammad, B. (2012). The Impact of Service Quality, Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Programs on Customer’s Loyalty: Evidence from Banking Sector of Pakistan. Web.
Khurana, T., & Dwivedi, S (2017). Customer satisfaction towards mall attributes in shopping malls of Udaipur. International Journal of Environment, Ecology, 7(2), 25-27. Web.
Kim, C. S., Zhang, W. H., Yang, K. H. (2008). An empirical study on the integrated framework of e-CRM in online shopping: Evaluating the relationships among perceived value, satisfaction, and trust based on customers’ perspectives. Journal of Electronic Commerce in Organizations, 6(3), 1-19.
Lii, Y. & Sy, E. (2009). Internet differential pricing: Effects on consumer price perception, emotions, and behavioral responses. Computers in Human Behavior, 25, 770-777.
Markovic, S., & Raspor, S. (2010). Measuring Perceived Service Quality Using SERVQUAL: A Case Study of the Croatian Hotel Industry. Management, 5(3), 195-209.
Maroco, J. (2013). Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty in 4- and 5-Star Hotels. European Journal of Tourism, Hospitality and Recreation, 4(3), 119-145. Web.
Mohamad, O. & Ramayah, T. (2010). Service quality, customer satisfaction and loyalty: A test of mediation. International Business Research, 3(4), 72-80. Web.
Nam, J., Ekinci, Y., & Whyatt, G. (2011). Brand equity, brand loyalty and consumer satisfaction”, Annals of Tourism Research. Annals of Tourism Research, 38(3), 1009-1030.
Slack, N., Singh, G., & Sharma, S. (2020). Impact of perceived value on the satisfaction of supermarket customers: developing country perspective. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management.

