Introduction
Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories (Dr. Reddy’s) is a pharmaceutical company operating globally. It manufactures active pharmaceutical ingredients, intermediates, finished dosage forms, and biologics products (Datamonitor 2008). The company is headquartered in Hyderabad, India, and operates in India, the US, Europe, and Russia. The company employs 9,575 people.
The company has revenue earning of $12421 million in 2008, which decreased from its 2007 revenue by 23.2 percent. The company earned an operating profit of $83.4 million in 2008, a decline of 70.4 percent as compared to 2007 operating profit. The new profit posted in 2008 is $116.2 million, which is a decline from 2007 by 49.8 percent.
Background
The company was formed in 1984 by Dr. K. Anji Reddy. The company went public in 1985 and was listed on the Indian Stock Exchanges in 1986 and New York Stock Exchange in 2001. Then the company underwent a series of merger and acquisition adventures. In 1988, it acquired Benzex laboratories and expanded its bulk operations in business. In 2000, it merged with Cheminor Drugs and American Remedies. The first overseas acquisition of Dr. Reddy’s was in 2002 when the company acquired BMS Laboratories Ltd. and Meridian Healthcare in the UK. It went into agreement with PLIVA and Stumpp, Schuele & Somappa (SSS) for the development of marketing activities. In 2008, it acquired Dow Chemicals and BASF’s pharmaceutical contract manufacturing business. In 2008, the company also acquired Germany’s Betapharm (Wall 2008 ).
Its first international operations have begun in 1990 when Dr. Reddy’s started exporting Norfloxacin and Ciprofloxacin to Europe and the Far East. In 1991, they began their operations in Russia. In 2008 it went into a global distribution agreement with Albemarle Corporation, a US-based specialty Chemicals Company. The company ventured considerably in R&D and into an area like active ingredient AX200, a biological molecule in development by Sygnis for the treatment of stroke and other neurodegenerative disorders.
Problem
The vision of the company is to provide affordable medicine for all kinds of medicines. Thus to provide this vision life, the company is undergoing issues related to sustainability. The aggressive expansion plan that Dr. Reddy’s has shown in the there are sustainability issues that are arising. The primary reason is said to be:
- generic drugs gaining more acceptance in the market with the expiry of blockbuster drugs,
- increasing regulatory pressure has increased the need for extra spending on R&D which has started eroding the bottom line of big companies,
- business models fail to be sustainable (Wall 2008 ).
Given these problems, it is imperative for Dr. Reddy’s to look at their environment and the internal strengths that they have. This will help them to revamp their business model and strategy if required for sustainable growth in a highly competitive global industry.
Environmental Scanning
In order to understand the environment of the company in which it operates it is important to look at the political, economic, social, and technological aspects of the external environment. For this reason, we undertake a PEST analysis of the environment of Dr. Reddy’s. Dr. Reddy’s is a multinational company having its presence in many countries. It operates in Europe, North America, and India (Annual Report 2009). However, for the PEST analysis, we will consider India as it is headquartered in the country.
Political
India is the world’s largest democracy. It has a federal type of government. Congress emerged as India’s single largest Party in the 2009 Lok Sabha Elections. The present Prime Minister of the country is Manmohan Singh.
There have been repeated terrorist attacks in India. The states that have been soft targets of terrorism have been Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), Andhra Pradesh, and the North Eastern States. India’s relation with neighboring countries like Pakistan and China has been strained. India has though maintained positive bilateral relations with China; however, its relation with Pakistan has been full of political rhetoric.
Economic
India has been facing rapid modernization and the economy has been facing an average growth rate of 5.6 percent in 2009 (Narasimhan 2009). The real GDP growth rate of the country has been shown in figure 1.
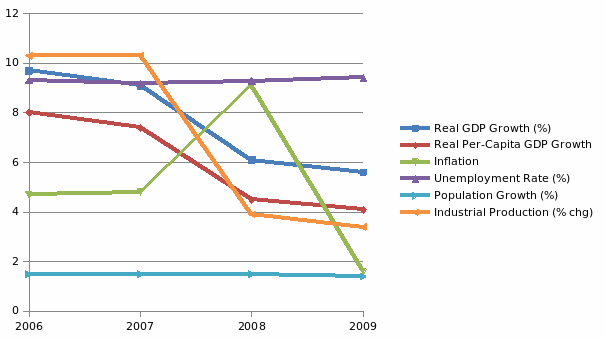
Inflation has been increasing from 2006 through 2008. However, it declined sharply in 2008-09. This indicates that the fundamentals of the Indian economy are strong. The growth rate of industrial production of the country has been declining due to the global recession.
Indian pharmaceutical industry has been seen high rates of growth generating total revenue of $7.8 billion in 2007 (Datamonitor 2007). The industry had a compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.8 percent for a period of 2003-07.
Social
India has the second-largest population in the world. India has the youngest population in the world. It has a death rate of 8 per 1000 populations and a birth rate of 24 per 1000 population. The Indian median age is 25 years (U.S. Department of State 2009). The country’s religion, caste, and languages are numerous and varied. There are three main religions like Hindus, Muslims, and Christians with numerous other minority religions. India ranks high in power distance, long-term orientation, and masculinity and low in uncertainty avoidance as per Hofstede’s cultural dimensions (ITIM International 2009).
Technology
India has a record of accomplishment of developing cost-effective chemical synthesis for various drug molecules. India has given a boost in the production of generic drugs. Further domestic investment in the pharmaceutical sector has been $7.14 billion in 2008 (Government of India 2009). The Indian government has also provided a fiscal incentive to R&D to the sector. Steps are being taken to develop new drug molecules and for clinical research.
Internal Analysis
The internal analysis of Dr. Reddy’s will be divided into two parts. First will be an industry analysis, which will be done using the five forces model developed by Michael Porter. The second part will be an internal analysis of the company, which will be done through an analysis of the internal strengths and weaknesses of the company.
Five Forces Model
The model developed by Michael Porter has been used to describe the five forces of competition (Porter 1979) in the Pharmaceutical industry in India. The model demonstrates that the industry is highly competitive with low entry barriers and high growth prospects. This specifically makes it a coveted place for new entrants.
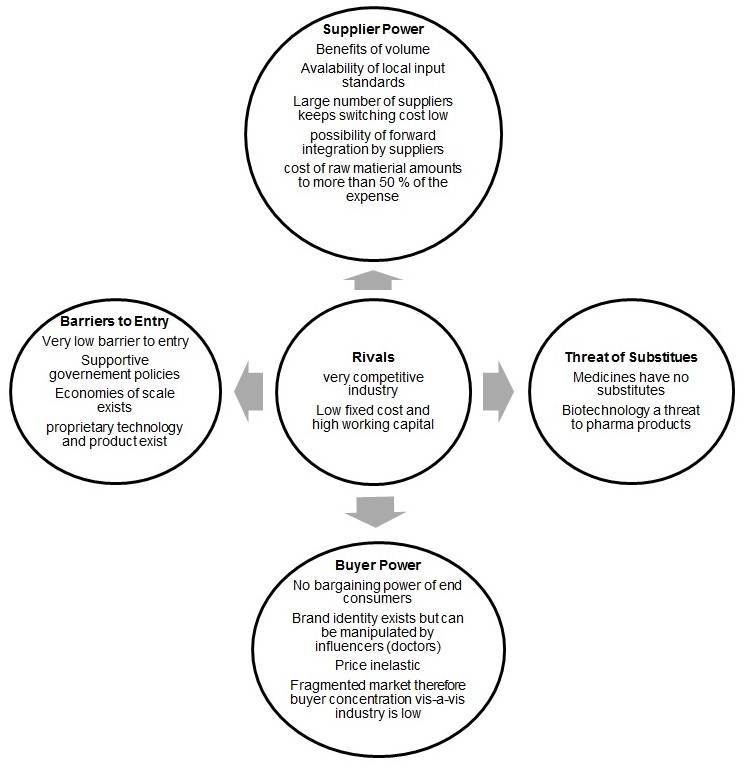
Product differentiation is not possible in the market due to the following of process patent India that has led to way for imitators. Therefore, cost competitiveness is the key to competitive advantage in the market.
One unique feature of the pharmaceutical market is that the buyers are distinct from influencers (doctors). Buyers have no influence over the product they choose to buy. Further, the buyers are large in number, therefore, yielding small bargaining power.
The suppliers of the pharma industry are chemical companies, which again is a fragmented industry. Buyers have very little power and therefore switching cost is low.
There are no legal entry barriers in the pharma industry. However, the key is to develop brand awareness and doctors’ network is key to long term survival.
There are no substitutes for medicines. They are not greatly affected by economic fluctuations and business cycle as demand for the products mostly remains same.
Financial Performance of Dr. Reddy’s
Dr. Reddy’s financial performance has been extremely good. Figure 3 shows the growth in revenue of the company since 2000. The company has undergone a continuous rise in revenue growth. The revenue growth fell in 2008 by 23.2 percent while it increased 32 percent in 2009. In 2009 international revenue increased by 46.6 percent. The company has diversified its geographical reach with international revenue consisting of 83.5 percent of total revenue. It has made advancements in generics drugs globally, which has increased its revenue considerably.
They are heavily inclined on research and development, which can be observed through their increased expenditure in R&D. they have growth through mergers and acquisitions. In 2008-09, they had three acquisitions: Dow Pharma’s Small Molecules facilities in the United Kingdom, BASF Corporation, USA; and Jet Generici SRL, Italy (Annual Report 2009).
SWOT Analysis
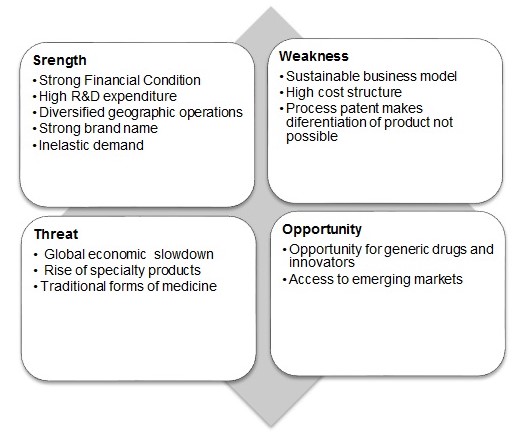
Figure 3 presents a SWOT (Piercy & Giles 1989) analysis of Dr. Reddy’s. The strengths and weaknesses are derived from the analysis of the internal analysis of the company while the opportunity and threats are derived from external analysis.
Strategies derived from SWOT
The main aim of any company is to derive strength from the given opportunities that a company has and to reduce its weaknesses and leverage opportunities. In case of Dr. Reddy’s, the main strategies would be to in case of strength-opportunity are to invest more in its R&D operations for developing more innovating and generic drugs as this is the market which is gaining more importance globally. Another strategy that the company must undertake is to expand its operations in emerging markets like Brazil, India, China, Korea, Mexico, Turkey and Russia as these markets will provide extensive growth opportunity. Therefore, the company must leverage its global presence to expand their operation in these markets.
Further product differentiation in pharmaceutical industry is not possible. However, if generic drugs become a specialty of Dr. Reddy’s they will be able to capture the new market opportunity of this new product and which pose a threat to traditional pharma product.
The strength-threat strategy is to use an underlying strength of the company to avoid a particular threat. Here Dr. Reddy’s should again utilize its specialty in innovating product and increased R&D expenditure to increase its dominance in specialty drugs as demand for these drugs are increasingly becoming high.
The company must be able to sustain its business model, as this will be key to keep its operations profitable in recessionary phase. Further, the company must thrive to keep its cost structure under control in order to keep its profits high.
Competitive Analysis
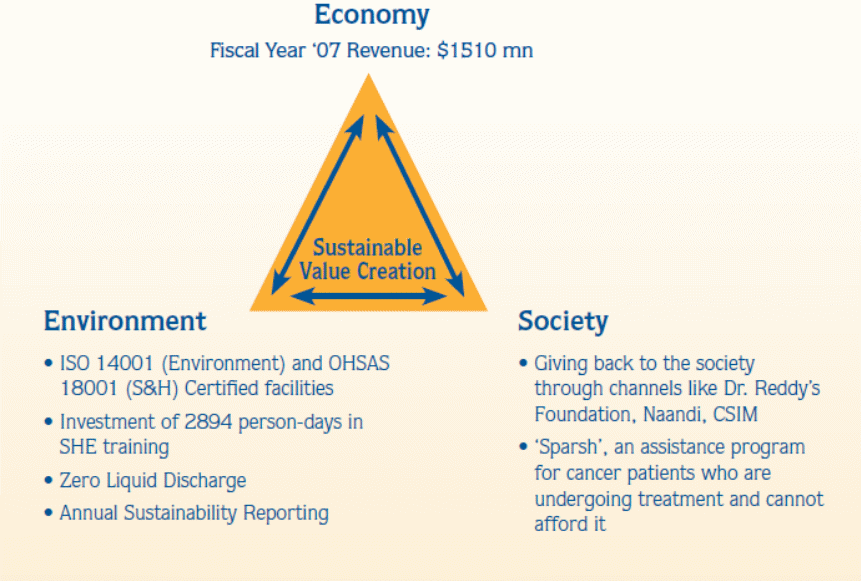
The main competitors of Dr. Reddy’s are Ranbaxy Laboratories, Cipla Ltd, and Lupin Limited. The pharmaceutical market is fragmented with top four companies having only 37 percent of the market share. The main offering of Dr. Reddy is generic drugs, which constitutes more than 50 percent of its revenue share. Dr. Reddy’s has aggressively expanded globally through innovation in its generic drugs (Somvanshi 2 May 2009). The value that they strive to provide to the market is “affordability” and “innovation” (Life Research Hope 2009). Their core business segments are Pharmaceutical Services and Active Ingredients, Global Generics, and Proprietary Products. Their stress of quality and supply chain management has made their operations effective (Drug Substance. Drug Product. 2009). They create value through coordination with environment, economy and society (see figure 4).
Generic Strategy
According to Porter (1996) that for a diversified company it is essential to have a competitive strategy, which he said to be differentiated into corporate and business unit strategy. As a company diversifies, its costs add up. Therefore, it is essential to remain competitive even when diversifying.
The concept of generic strategies, which allows companies to attain and maintain competitive strategy (Porter 1996). According to Porter, “companies can outperform rivals only if it can establish difference that it can preserve” (Porter 1996, p. 7). The pharmaceutical industry’s five forces analysis showed that pharma products could not be differentiated. This is especially not possible in India as the country follows process patent. Therefore, the only generic strategy that can be employed by the company in order to achieve a broad market is cost leadership. Therefore, Dr. Reddy’s must strive to attain cost leadership through increase R&D and innovation. Thus, the basis of sustaining this strategy will depend on the customer’s requirements. For instance, in case of developed countries, the main diseases that concern the masses are diabetes, obesity, heart diseases, etc. however, in less developed countries the there may be need for drugs to treat cancer. Therefore, the distribution and production must be based on this knowledge.
Further, the key functions of Dr. Reddy’s are R&D, manufacturing, and marketing. R&D is vital, as it is required to keep innovating in order to remain competitive. Manufacturing is important, as it has to drive down the cost of production, as this must be kept low in order to retain cost competitiveness.
Conclusion
The above analysis shows that the Dr. Reddy’s is a highly competitive company in an industry, which is growing. The company is moving towards the right direction with armed with a strategy to maintain cost leadership, which is demonstrated through the mission statement of the company.
Reference
Annual Report 2009, Web.
Datamonitor 2007, ‘Pharmaceuticals in India’, Industry Profile. Web.
Datamonitor 2008, ‘Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd’, Company Profile, Datamonitor, New York.
Drug Substance. Drug Product. 2009, Web.
Government of India 2009, DRUGS & PHARMACEUTICALS, Web.
ITIM International 2009, Geert Hofstede™ Cultural Dimensions, Web.
Life Research Hope 2009, Web.
Piercy, N & Giles, W 1989, ‘Making SWOT Analysis Work’, Marketing Intelligence & Planning, vol 7, no. 5/6, pp. 5-7.
Porter, ME 1979, ‘How competitive forces shape strategy’, in PJ Smit (ed.), Strategic Planning: Readings, 2006102117th edn, Juta and Company Limited, Cape Town.
Porter, ME 1996, ‘From Competitive Advantage to Corporate Strategy’, in M Goold, KS Luchs (eds.), Managing the multibusiness company: strategic issues for diversified groups, 285314th edn, Cengage Learning EMEA.
Porter, ME 1996, ‘What is Stratgy?’, Harvard Business Review, Web.
Somvanshi, KK. 2009, St gives thumbs down to cos with foreign ops , Web.
U.S. Department of State 2009, Bureau of South and Central Asian Affairs – Background Note: India. Web.
Wall, B 2008 , Health care faces new horizons, and new obstacles, Web.
