Introduction
Business organizations experience various challenges in the current market that thwart the operations and efforts to meet their objectives and goals. There is high level of competition in the markets owing to high number of players. Customers also exhibit changing patterns in their needs, with business organizations being forced to respond to these needs. The degree to which the companies can respond to the changing needs determine their survival in the competitive market environment.
In the contemporary business environment, marketing has a strategic role that “focuses on the business’s intentions in a market and the means and timing of realizing these intentions” (Jain & Haley, 2009, p.23). Therefore, a marketing plan should be developed in line with the goals and objectives of the business as stated in the business plan. A good marketing plan should indicate a thorough understanding of the vision, mission, and goals of the company and should be in support of the achievements of these goals, and accomplishments of the mission (Dolak, 2010). This paper provides a marketing plan for the next one-year and three years for GlaxoSmithKline Company.
It provides an analysis of the forces that prevail in the market for pharmaceutical products, and their effect on the operations of these companies. There is an assessment on how to counteract the opposing forces while capitalizing on the supportive forces like the strengths and opportunities of the company. The competitors in this market, their strengths and weakness, as well as the associated challenges are discussed.
Market Overview
Marketing mix and positioning
Companies in the pharmaceutical industry mainly deal with drugs and pharmaceuticals, as well as consumer health products. GlaxoSmithKline Plc. manufactures and sells products in three areas – prescription medicines, vaccines, and consumer health products (Consumer Watch, 2002). The company produces pharmaceutical products like Paxil/Seroxat (an antidepressant), Combivir (for the treatment of HIV/AIDS), Zofran (for the management of alcoholism), and Avendia (Consumer watch, 2002). The company also produces ‘dozens of well-known over-the-counter products- such as Aquafresh, Nicorette, and Tums’ (Beal & Strauss, 2008, p.276).
The company offer products with varied prices that are determined by the ability of the customers in the market. The organization has decided to attach its product prices to the per capita income in the different countries in which it operates and the result is that products of the same quality are being sold at different prices in different countries (Wachira, 2011). The management of the company has recently opted to reduce prices of its products in developing nations to increase market size in these regions. Most of these reductions in prices have benefited the African countries. Significant changes have been seen in the anti-biotic segment where products like Zinnat and Augmentin had their prices reduced by 30-40% in Kenya this year (Wachira, 2011).
GlaxoSmithKline plc operates in the global level. The organization has its operations in over 100 countries across the globe. The products of this company can be obtained from the several subsidiaries and branches established all over the world.
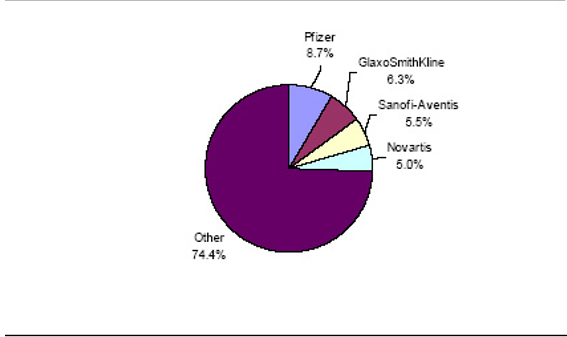
The merger of the two companies to form GlaxoSmithKline plc saw the organization climb the ladder in the global market. The company became the largest pharmaceutical company in the world in 2002 following the merger (Consumer Watch, 2002). The company has had a significant proportion of the market over long time. Before merging their operations, the two companies had 7% of the pharmaceutical market in the world (Consumer Watch, 2002). The companies also had 26% of the global vaccine sales in 2000 (Consumer Watch, 2002).
Market trends
The pharmaceuticals industry has expanded considerably in the recent past. The industry has witnessed mergers and acquisition of companies of the past years (Davidson and Greblov, 2005, p.4). The drug companies, like Glaxo Wellcome plc and SmithKline Beecham plc, were relatively small in the past but the recent mega-mergers of the companies in the industry have resulted into massive expansion of the industry. The industry has shown high rates of sales in the recent past owing to the advancements that have been recorded in the biotechnology industry (Management Center Europe, 2011, p.4; Davidson and Greblov, 2005, p.4).
For instance, sales at GSK have increased relatively steadily over the last four years. The sales were ₤22.7billion in 2007, ₤24.4 billion in 2008, ₤28.4 billion in 2009, and ₤28.4 billion in 2010 (GSK Annual Report, 2010, p.9). Some of the giant pharmaceutical organizations have company worth greater than the Gross National Product of some countries in the Sub-Saharan Africa (Corporate Watch, 2011).
Market growth and the size of the market
The pharmaceutical industry has expanded over the years, and is currently largest industry in the world. By 2004, it was estimated that the global pharmaceutical market was worth over ₤ 275 billion and it was projected that the sales would grow annually at a rate of 6% (Ivory Research Ltd, 2009). A substantial proportion of the sales in the industry were derived from the United States, the European Union, and Japan (Ivory Research Ltd, 2009).
The company has recorded significant expansion of its market over the last years. GSK has enjoyed the limitations imposed by patent laws and has been able to make certain acquisitions in the recent years. For instance, in 2009, the company acquired product portfolio of USB S.A worth ₤483 million in different countries in Africa, Asia, and America (GlaxoSmithKline, 2009). The country is also likely to expand its operations further since it has the capacity to determine the prices of the products. The companies also take the advantage that there is little price elasticity for the pharmaceutical products. It has also been observed that ‘the profit margins, not the global health needs, are what determine the next new drugs’ (Corporate Watch, 2002). The strict patent laws ensure that a company has the legal authority to manufacture a particular drug and the entry into the same businesses by other organizations is limited (Corporate Watch, 2011). It provides a barrier for new entrance into the business..
Company analysis
Financial summary
The company is one of the pharmaceutical companies with the highest revenue in the pharmaceutical segment. Information from Annual Reports of the Companies’ 04 on the global pharmaceuticals industry indicated that it had revenue of $31,434 (₤19,500) million being at a second place after Pfizer with $46,133 (₤28,600) (Mennen et al, 2010). The information on the revenue for these and the other top companies in the industry for that particular year is provided in the following table.
Table 2: Top ten companies with high revenue from pharmaceutical segment globally.
The company has been committed to accomplishing its objectives by focusing on the value of their products, extensive globalization of their operations and restructuring of their business models. The company has investment so much on research and development to develop products of high value to the clients. In 2010, the company spent ₤3.96 billion on promoting research and development with an aim of improving the returns on such an investment (GSK Annual Report 2010). This accounted for 14% of the total sales for that year.
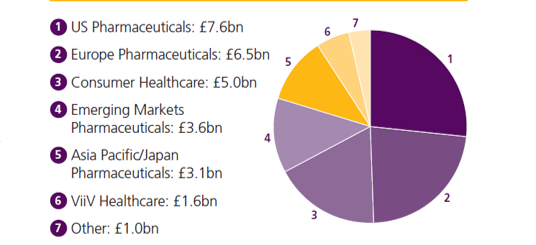
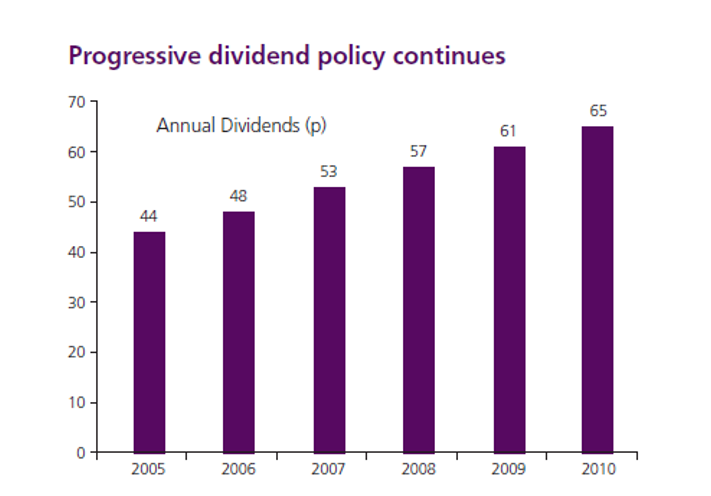
In the 2010 financial year, the company realized a turnover of ₤28.4 billion (GSK Annual Report 2010). Much of the company turnover was obtained from pharmaceuticals and healthcare products sold in the United States and the European Countries. The company recorded earnings of 32.1p per share and divided of 65p per share in that financial year (GSK Annual Report 2010). The report also showed that the emerging markets provided a substantial share of the total turnover. This information is provided in the following pie chart.
Mission statement
The mission of the organization can be traced from the initial move to merge the two initially competing organizations. The two companies merged their operations after studying the competitive market environment that prevailed at the time. The organization then had to state its mission that would distinguish it from the other companies. The mission statement of an organization explains why the organization has been established and how it is unique (Ogilvie, 2005, p.95). The mission statement provides the basis upon which the organizational plans are developed.
The company’s mission is “to improve the quality of human life by enabling people to do more, feel better, and live longer” (Ogilvie, 2005, p.95). The company is committed to improving the quality of human life. The mission statement is an appeal and reminder to all the stakeholders of the organization on why the organization was instituted. The mission is in line with the objectives and goals of the company of being the leader and pioneer in the pharmaceutical market. Innovation through extensive research and development is the main aim of the organization and this has been achieved through the effective organizational culture developed at GlaxoSmithKline plc (Ivory Research Ltd, 2009).
SWOT analysis and Competitor analysis
The merger of the two pharmaceutical companies to form GlaxoSmithKline plc had positive and negative impacts on the present and future operations of the company. The company has the following strengths and weaknesses as well as the opportunities and likely threats
Strengths
The company is one of the giants that dominate the market and as such, they can dictate the prices of their drugs. It has a large control in the anti-smoking drug market (Mennen et al, 2010, p.23). Besides, there are low manufacturing costs and yet the products in this industry have very little price elasticity (Corporate Watch, 2011). The merging of the two companies has led to a reduction in risk that can then be shared. The companies are able to combine their efforts in research and development leading to a reduction in the overall production cost. It has been observed that the pharmaceutical industry is a ‘knowledge driven industry and is heavily dependent on Research and Development for new products and growth’ (Saxena, n.d, p.2).
Weaknesses
The company also has some weaknesses. Firstly, it is likely that the organizations had different management policies before their merger. The different organizational philosophies may impede effective operations. Secondly, the operations of the organization require licensed agreements, involving other parties (Mennen et al, 2010, p.23). The organization has been unable to develop new quality product or services over the years.
Opportunities
The company has the opportunity to explore the emerging new markets. There is a promising market in the developing and underdeveloped countries. This provides the company an opportunity to expand its global operations and establish more of the manufacturing and research centers across the globe (Mennen et al, 2010, p.23). It should move its operational headquarters to these markets. The ability to determine their prices will enable the company to succeed in the foreign establishments.
Threats
As a player in the competitive pharmaceutical industry, GSK has certain threats. A common threat in the whole industry is reduced productivity (Mennen et al, 2010, p.23). The other dangerous trend that has been witnessed in the industry is acquisition of firms by other large investors. Serious acquisitions have been witnessed in the past like that of Pharmacia by Pfizer and the acquisition of Guidant by Johnson and Johnson (Davidson and Greblov, 2005, p.5). The company may also be acquired by other investors.
Competition with other pharmaceutical companies
The global pharmaceutical industry has several players. However, the industry has key giants that have much of the influence on the market. The giant pharmaceutical companies include “Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Bayer, Merck & Co, Pharmacia, Novartis, Johnson & Johnson, Abbott Laboratories, American Home Products, Eli Lilly, Schering-Plough, GlaxoSmithKline, and Allergan”(Corporate Watch, 2011). Thus, GlaxoSmithKline is among the global giants that dictate the market trends. The competition in the market is moderated by the patent laws that give companies the authorities to manufacture particular pharmaceutical products (Corporate Watch, 2011). This implies that a company cannot produce some product until it is licensed. There is a restriction in the entry to the different sectors of the industry.
The company provides a noble approach to gene patenting as a means of promoting research in the area of medicine (GlaxoSmithKline, 2007). The company respects and abides by the legal provisions on patenting as they apply in the global context. The companies in the industry have registered significant growth in their revenue in the past, most likely due to the protective laws. For instance, Sanofi-Aventis has recorded a revenue growth of 24.1% in the last five years, since 2006 (IMAP, 2011, p.11).The companies mainly concentrate on the production of pharmaceutical products.
An idea for a new product/service for the company
It has been stated that the merger has saw the company develop certain strengths and weaknesses. Similarly, there are opportunities that emerged as well as threats that could be exerted by the external forces. The company’s success requires an analysis of the strengths and weaknesses and the associated threats and opportunities. While capitalizing on the strengths and overcoming the weaknesses, the company is able to utilize the available opportunities to their advantage and beat the threats. A new idea can be developed upon such a basis that positions the company’s product above the other companies’ products in the market.
The pharmaceutical industry encompasses a wide range of products including pharmaceutical products, medical devices, consumer healthcare products, nutritional products, and animal health products (Davidson & Greblov, 2005, p.3). However, the major companies seem to be concentrated in the pharmaceutical products -and hence this field is saturated. GlaxoSmithKline plc has concentrated mainly in two segments- the pharmaceutical products and the consumer health products. Much of its investment has been in the pharmaceutical products. The GSK 2010 annual report indicated that the total revenue from the pharmaceuticals segment accounted for 84.22%. This suggests that much investment was put in this area.
In 2010, the direct project costs for pharmaceuticals were ₤1432 million, the research and development for pharmaceutical cost ₤2954 million, whereas consumer health care products cost ₤3806 million (GSK Annual Report, 2010, p.28).
The company should introduce a new segment of the animal health products in its operations coupled with the provision of veterinary services. The diversification initiative will enable the company to withstand the changing market. The company has to focus much of its research and development towards this new line of production for the next couple of years. Research and development provides a competitive advantage to the company (Ivory Research Ltd, 2009).
The initiative enables the organization to keep pace with the changing needs of the clients. It should allocate some amount to carry out market and marketing research for the intended product and associated service in the next financial year. The company should then allocate 25% of its total investment in this new segment. This will cater for the development of the new product and service as well as its advertisement to the potential consumers. The advertisement should be performed over the internet as it currently a good tool for communicating with individuals (Lerer, 2001, p.161). Investing in this area is likely to benefit the organization since most of the companies invest in the pharmaceutical products. In fact, companies like Eli Lilly and AstraZeneca have virtually invested in pharmaceutical segment (Davidson & Greblov, 2005, p.3).
It is likely that the company will receive little competition. The company will need to establish its operations mainly in the emerging markets that are promising. The performance of the new products can be monitored for the next financial years to check if the intended objectives are being achieved.
Market objectives and strategies
Market objectives of the company
Organizations merge their operations in order to gain competitive advantage over the others following the combined effort in research and innovations. The company’s main objective has been to be the pioneer in the pharmaceutical industry through innovations (Ivory Research, 2009). The achievement of such an objective has been possible through the merger that led to the current company. Before the merger, the two companies were major rivals in the market and thus the merger was aimed at eliminating the competition to provide a combined force on Research and Development. The motto of the merged company is to improve the quality of the life to human beings (Corporate Watch, 2002). This is achieved through carrying out extensive research and developing products that meet the needs of these clients.
Over the years, the company has shown focus towards the accomplishment of its mission. It has developed operational strategies aimed at increasing the growth of sales of the company and reducing the risks. The company aims at increasing its global operations by expanding its business to in the emerging markets and the underdeveloped markets. The change in its organization and the establishment of the research and development department has given the company a competitive advantage (Ivory Research Ltd, 2009). Developing a good model for its operations can be an effective method to achieve these objectives. Similarly, the organization is concerned with the improvement of its financial performance.
Market segmentation
Before an organization decides on what products or services to provide, it has to understand its competitive environment. The company then provides a range of products that meet the diverse consumer needs. Market segmentation is essential since customers are different (Greengrove, 2002, p.410). The market segmentation based on consumer needs is illustrated in the following chart.
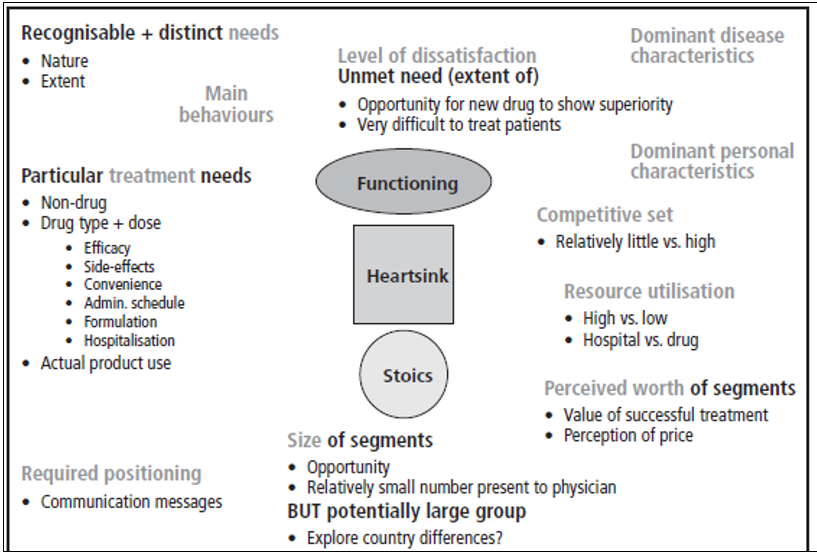
It has to be recalled that the success of an organization in the market depends on how the organization segments and targets its customers in the market. The organization will attract and retain customers if it provides unique products and services that are valued by the clients (Olgivie, 2005, p.95). GSK has targets a wide category of customers by investing on different products namely pharmaceutical products, consumer healthcare products, animal health products, nutritional health products, and medical devices. This distinguishes it from other companies that are mainly concentrated on the pharmaceutical products.
GlaxoSmithKline plc has concentrated in two main segments in the industry. The company engages in the ‘creation, discovery, development, manufacture, and marketing of pharmaceutical and consumer health-related products’ (Dividend.com, 2011).
The company’s market segmentation goes beyond the products for human consumption. Other than the consumer health and pharmaceutical products, the company has also focused on animal health product (Consumer Watch, 2002). The company also deals in a variety of pharmaceutical products like antidepressants and drugs for the treatment of HIV/AIDS.
Forecasts for the organization
The GSK annual report 2010 indicates that even though the company has its operations based in the UK, it received much of the revenue from the company’s outlets established in the other countries especially the United States. The emerging markets like India also accounted for a good fraction of the sales revenue. This suggests that the company should shift its headquarters to the regions with promising markets. As is indicated in Consolidated Income Statement in the 2010 report, there were some differences caused by the restructuring of the organization.
Table.6 Income Statement- 2010.
The sales of the organization have been increasingly steadily over the last couples of years. However, there have been different patterns in the turnover from different market segments (GSK-Annual Report, 2010) The US and Europe pharmaceuticals had significant reduction in turnover in 2010 from the 2009 figure. On the other hand, the emerging markets and the Asia Pacific/Japan pharmaceuticals had steady increase in turnover (GSK-Annual Report, 2010). Similar results were recovered for the consumer healthcare products.
GSK Turnover for the last 3 years.
In the beginning of 2010, the company settled on the expansion of its operation through a program that cost over ₤4.5 billion. It was expected that by 2012, the programme would yield pre-tax savings of approximately ₤2.2 billion (GSK-Annual Report, 2010, p.109).
The company has recently imitated the other players like AstraZeneca and Pfizer in reducing the budgets for research and developments. GlaxoSmithKline plc made such a decision following the increased sales that had been witnessed in the year (Wilkinson, 2010). The company has also reengineered its operational models whereby single plants could now serve large geographical areas. The initiative has enabled the organization to cut its cost of operations by over ₤300 million per year (Gelinas & Dull, 2007, p.540). At this rate, it is also projected that the company shall have saved ₤2.5 billion at the end of 2012 (Kollewe, 2011). The figure may rise well above ₤3 billion by the end of 2014 if the same pace is maintained.
The introduction of the new product is not expected to alter the financial budget for the next year. With the continued reduction in operating costs, the operating costs for 2012 may be reduced to less than ₤5 billion. The intention of introducing the new business products is to increase the total turnover of the recent figure (₤28.3 billion) to over ₤30 billion in the next few years.
Conclusions
The current business environment is very competitive with different players and changing customer needs. A business organization that is to survive in the market should then be prompt in identifying the changing patterns in the needs of their clients and responding to these changes in good time. The organizations should develop a marketing strategy that is able to accommodate the dynamics in the market over a long period. Such competition is witnessed in the pharmaceutical industry. The industry has expanded considerably in the past due and remains the largest industry in the global market.
GlaxoSmithKline has competitors in the industry and yet it also ahs opportunities to expand its operations. The success of a business organization in the industry will be determined by its ability to study the market trends and adjust its operations according to the market demands. The initiative that is to be implemented by the organization is likely to provide a significant contribution to towards its financial performance. The company has to focus on product diversification and ensure that every attention is diverted to the introduced product. Much resource can be channeled to the new production line in the event that it proves to be profitable.
Reference List
Beal, A., & Strauss, J., 2008. Radically transparent: monitoring and managing reputations online. Indianapolis: John Wiley & Sons. Web.
Consumer Watch. 2002. GlaxoSmithKline plc: A Corporate Profile. Web.
Corporate Watch. 2011. Pharmaceutical Industry: Sector Overview. Web.
Davidson, L., & Greblov, G., 2005. The Pharmaceutical industry in the Global Economy. Indiana University Kelley School of Business. Web.
Dividend. 2011. GlaxoSmithKline PLC (GSK). Web.
Dolak, D. 2010. A Marketing Plan: Key Components and Plan Outline. Web.
Duke University 2011. The global pharmaceutical industry. Web.
Gelinas, U., & Dull, R., 2007. Accounting Information Systems. Seventh edition. South Western Thompson: Cengage Learning. Web.
GlaxoSmithKline. 2005. Policy Principles, Government Affairs Europe and Corporate. Web.
GlaxoSmithKline. 2010. Locations. Web.
GlaxoSmithKline plc. 2011. Consumer healthcare Products. Web.
Greengrove, K., 2002. Needs-based segmentation: principles and practice. International Journal of Market Research, 44(4); 405-421. Web.
GlaxoSmithKline. 2009. GSK to drive growth in emerging markets with acquisition of UCB products. Web.
GSK. 2010. Review. Web.
GSK-Annual Report. 2010. GSK-Annual Report. Web.
IMAP. 2011. Pharmaceuticals & Biotech Industry Global Report -2011. Web.
Ivory Research Ltd. 2009. Managing Change at GlaxoSmithKline. Web.
Jain, A., & Haley, P., 2009. Marketing Planning and Strategy. Sixth ed. South Western College: Thompson Learning. Web.
Kollewe, J., 2011. The Guardian. GSK gives UK economy boost with job and tax pledge. Web.
Lerer, L., 2001. Pharmaceutical marketing segmentation in the age of the Internet. International Journal of Medical Marketing, 2(2); 159-166. Web.
Management Center Europe. 2011. From Turmoil to Turnaround, Pharma Must Reinvent Itself. Web.
Mennen, A. et al. 2010. Mergers and Acquisitions in the Global Pharmaceutical Industry. Norderstedt: GRIN Verlag. Web.
Ogilvie, J., 2005. CLEP Principles of Management: The Best Test Preparation for the CLEP. New Jersey: Research & Education Association. Web.
Saxena, S., N.d. A Review of Marketing Strategies Work by Different Pharmaceutical companies. Web.
Wachira, P. 2011. PHARMACEUTICALS – GlaxoSmithKline Launches Ambitious Marketing Offensive. Web.
Wilkinson, M., 2010. More pharma R&D budget cuts. Web.

