Introduction
Creating a new venture has always been a very risky endeavor that entails multiple positive consequences for a business. Therefore, it is imperative to develop a coherent and competent approach toward human resource management (HRM) so that staff members could develop loyalty toward the company and engagement with its goals and projects. As a result, the extent of retention within the firm will increase, with the subsequent ride in performance rates as a result of improved work of motivated staff. By overcoming barriers to change and introducing the principles of incremental innovation into the company’s HRM framework, one will be able to encourage improvement in performance and a rise in motivation rates.
Strategic Perspective
Startup: Best Fit (Hard)
Using the line of the best fit, one will realize that, for a startup, it will be necessary to select the model that will allow propelling the company to the top of the market immediately. It is crucial to make a name for the organization shortly after launching it into the target economic setting. Boxall and Purcell (2016) argue that the model of the best fit suggests incorporating a “business savvy” approach toward HRM in the corporate environment, which also ties to the idea of coordinating the stages of the HRM process with the goals of the organization (p. 57). Moreover, the authors emphasize the challenge that underlies the specified task, namely, the multitude of ways in which the dilemma can be approached. By linking stakeholder interests to situational factors and long-term goals, a company leader will be able to exert enough influence to increase employee engagement, promote professional growth among staff members, and convince them to accept corporate values, simultaneously catering to their needs.
Matching Model: Devanna, et al. (1984)
Using Devanna’s model of HRM will allow locating balance between cultural, political, and economic forces. The framework suggests that the specified influences on the organizational structure, HRM, and the company’s mission and strategy need to be reconciled in the unique way that will meet the organization’s needs. In the context of the target setting, it will be necessary to focus on the use of the high-performance working (HPW) strategies. Combined with an approach base on diversity and talent management, the specified framework will encourage staff members to show initiative and better results.
Competitive Advantage Model
The introduction of the framework that will allow keeping the company ahead of its comeptitors is crucial for maintaining the quality of its performance and managing it accordingly. Therefore, the framework suggested by Schuler and Jackson (1987) will have to be utilized, including a strong HR strategy, development of the required skills and behaviors in staff members, provision of supportive HR practices, and the identification and control of outcomes (Devanna et al., 1984). The proposed approach will help to build premises for the introduction of the HPWS system, which will be rooted in the quality-oriented performance management based on the idea of effective talent management and the promotion of continuous improvement.
Cost reduction: Schuler and Jackson, (1987)
The framework for promoting connectivity between HRM and competitive advantage designed by Schuler and Jackson (1987) also outlines the importance of using a cost-efficient strategy. Therefore, while the company will need to reallocate its resources to sponsor the development of staff’s professional skills, it will also need to embrace the idea of cost-effective performance. For this purpose, the firm will have to deploy restructuring and downsizing in order to reallocate its financial resources (Khoo et al., 2017). However, since the specified approach has seen large criticism due to the threat of demotivating staff members, the organization will also have to introduce an additional frameset for cost management to encourage HRM development.
Michigan HR Life cycle
The significance of selecting an appropriate model for performance appraisal at the beginning of the company’s development is not to be underrated. According to the Michigan Model of Human Resource Cycle, the processes of selection and development are intrinsically connected with the appraisal of performance and the rewards provided to staff members (Farnham, 2017). As explained by Storey and Sisson (1993), the Michigan Model allows aligning the key HRM goals with those of an organization, which represents the essence of the best-fit approach.
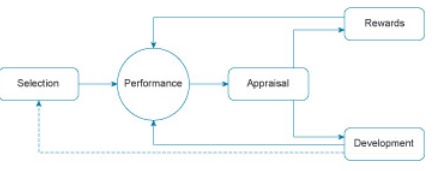
As the figure above exemplifies, the professional development of staff members is impossible without a comprehensive evaluation of their performance and the further guidance toward better management of their workplace responsibilities. In the context of the target organization, ineffective performance appraisal and the lack of coherent feedback has defined drop in the quality of work (Farnham, 2015). Therefore, the inclusion of a 360-degree appraisal tool is expected to improve the situation. Since the proposed tool will allow for greater objectivity and a more nuanced overview of staff’s work, it is expected to produce a positive effect.
Growth: Universalist (Soft)
Harvard model: Beer et al. (1984)
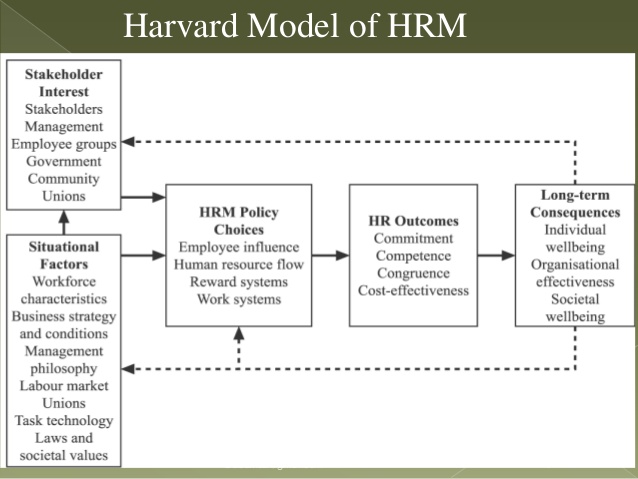
Another tool that can potentially improve the quality of staff’s performance and the overall competitiveness of the organization, the Harvard Model offers a more generalized and comprehensive approach. Specifically, the model links the process of corporate policymaking and the resulting behaviors and attitudes of staff members to the external, situational factors and the extent of stakeholder interest (Beer et al., 1984). In the context of the target firm, the framework for the corporate governance within the company will have to be revisited, with a detailed analysis of the role that shareholders play in its policymaking and decision-making.
Best Practice: Pfeffer (HPWS. HIWS, HCWS)
The introduction of high-performance work (HPW) practices is believed to be one of the best solutions to the problem of a drop in performance quality. Pfeffer insists that the following have to be considered as the essential components of HPW: “employment security, minimal status distinction, sharing financial and performance information, hiring selectively, self-managed teams/decentralization, relatively high rewards and extensive training” (Timiyo, 2014, p. 9). Currently, the HIWS model is preferable due to its focus on increased involvement.
In the context of the target company, the specified change will imply shifting toward the vertical and horizontal integration of SHRM, which, in turn, will have to be carried out with the help of the best fit practices outlined above. Leopold and Harris, (2008) explain that, by deploying a resource-based view and considering its employees as its main asset, an organization can multiply its sustained advantage. With the help of the suggested analysis tool, a company can access the issues that a usual analytical framework does not cover, namely, what Leopold and Harris, (2008) refer to as the “black box” (83). As a result, the inherent contradictions within the resource-based view will be addressed, whereas its advantages will allow a firm to focus on fostering talent management and allocating its resources in the way that allows for a cost-efficient approach.
Competitive Advantage Model
Increasing the competitive advantage of the target organization should be currently seen as the key priority, which is why it is essential to navigate wisely between the cost management strategy and the differentiation options (see Fig. 4)
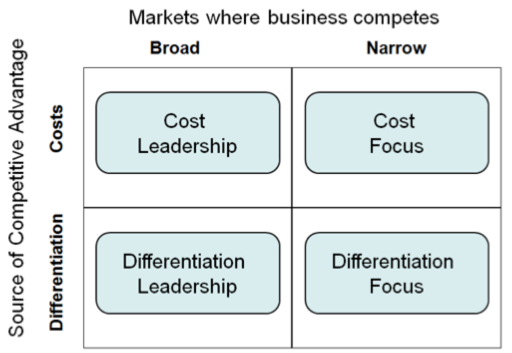
As seen in Figure above, in order to select the model that will reflect the company’s interests best, one will have to choose between differentiation and costs, as well as the broad and the narrow market. Since the target organization is striving to enter the global market, the broad framework will be needed. Given the need to reallocate the company’s resources for a more cost-efficient approach, the Cost Leadership framework will have to be chosen.
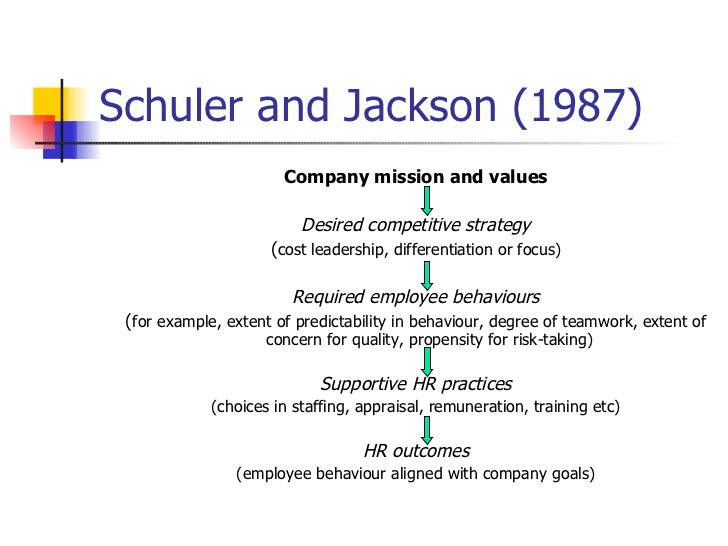
Quality Strategy: Schuler and Jackson (1987)
In an attempt to connect the approach toward HRM with the increase of the competitive advantage, one may also need to consider the issue of quality management. Schuler and Jackson (1987) offer a framework according to which quality control can be established in a company. Namely, the mission and values, which need to be geared toward innovation and communication in the target setting, will inform the competitive strategy. Specifically, the focus on innovation will allow the target company to improve the quality of its products. Simultaneously, employees’ behaviors will be shaped according to the said values, thus increasing the extent of their responsibility and effort. The supportive HR practices will determine the HR outcomes, specifically, an increase in engagement and performance quality, with fewer defects produced.
Michigan HR Life cycle (Fombrun)
Using Fombrun’s HR Life Cycle Model, one will be able to enhance performance by using an appropriate appraisal system and focusing on employee development. The specified process will launch the professional growth of staff members, introducing them to the opportunities of identifying and perfecting their talents. In this context, it is also important to recall the role that an appropriate performance management strategy plays in the corporate environment. According to Leopold and Harris (2005), applying performance management to the organizational setting allows reducing the tension between staff members and managers. Moreover, it can be seen as a device with a moderating effect on the anxieties that employees may have regarding the quality of their performance and their place in the organizational context: “Staff at all levels worry about whether they can prove to their bosses that they have met, or exceeded, the organisation’s expectations of them. Performance management is often the vehicle for quelling such anxieties and demands” (Leopold and Harris , 2005, p. 179).
Maturity: RBV: VRIO: Barney, (1991)
In order to examine the extent of the organization’s maturity, one will need to apply the resource-based view (RBV), specifically, the BRIO model. The proposed tool will help to evaluate the company’s competitiveness by assessing the characteristics of its product such as value, rarity, imitability, and organization (see Fig. 5)

As Figure 5 above exemplifies, the company’s current position is quite weak since it does not have the distinguishable characteristic that would make it prominent among others. Combined with comparatively low rarity of the product, the overall VRIO score of the firm is significantly low. Therefore, it will be reasonable to focus on improving the organization of the company and its functioning. Thus, one will be able to build a solid competitive advantage for the organization.
Competitive Advantage Model
Applying the framework developed by Porter to the case at hand, one will realize that the company’s current assets are mostly represented by its highly qualified staff and the innovation potential that the company holds. Therefore, the competitive advantage model, which implies using external and internal strengths to develop a cost advantage and a differentiation-based one, can be applied to the target setting. Namely, using Porter’s framework, the organization will have to build its differentiation advantage based on its ability to produce innovative solutions. In turn, the cost advantage will be created by the reallocation of the company’s finances and the development of a cost-efficient strategy.
Innovation Strategy: Schuler and Jackson, (1987)
To improve the organization’s competitiveness in the target economic setting, one will need to connect the selected HRM framework, specifically, the focus on talent management, with the promotion of innovation and learning. Following the account of Schuler and Jackson (1987), one will realize that the company requires the approach based on the concept of innovation. Specifically, the paper by Schuler and Jackson (1987) posits that the development of a competitive advantage implies addressing three key issues, namely, “innovation, quality enhancement, and cost reduction” (p. 208). Placing innovation at the forefront of organization management, one will recognize the need for the company to use innovativeness as the platform for introducing additional opportunities for staff members’ knowledge development, as well as the options for product and service diversification.
Employee Relations/EIP
Using the Employee Involvement and Participation (EIP) framework, one will recognize the necessity to create the environment for higher engagement among staff members. Presently, the company lacks the focus on meeting employee-specific needs, specifically, the need for higher participation in the company’s development. The described need aligns with the process of professional growth that staff members will have to undergo in order to deliver enhanced performance in the company.
Michigan HR Life cycle: Fombrun, Tichy, Devanna,(1984)
The Michigan HR Life Cycle Model suggests that the HR cycle should start with selection, continue by observing performance, conduct appraisal, and use rewards, as well as promote development, based on the outcomes of the assessment. In the context of employee relationships. The model in question can be used to increase the firm’s competitive advantage by creating a team of loyal experts. An appraisal performed to identify employees’ needs and create the strategies and rewards that will incentivize staff members to improve will contribute to building employees’ proficiency and loyalty. Thus, staff members will be eager to embrace the concept of self-improvement and lifelong learning, also staying loyal to the organization.
Strategic Perspective and the Company’s Life Cycle
In order to understand how the management of human resources can be aligned with organizational goals, one will need to dissect the core processes within it. For this reason, applying the Life cycle model by Purcell and Ahlstrand (2001) will be required. According to the authors, the management of organizational goals is typically galvanized by the need to multiply what they refer to as the human resource advantage (Purcell and Ahlstrand, 2001). Therefore, the key stages of the Life Cycle Model, which typically include the startup, growth, maturity, and decline, are inextricably connected to the process of managing the company’s HR assets.
To implement the necessary changes and improve the quality of performance management, a company will need to connect every aspect of its performance into a single structure with a unique hierarchy based on the life cycle outlined above. In the context of the target company, the specified change will imply shifting toward the vertical and horizontal integration of SHRM, which, in turn, will have to be carried o with the help of the best fit practices outlined above.
Performance Management within the Company
PM: Definition
Before proceeding with the development of an appropriate strategy, one will need to define the notion of performance management. Kulkarni (2017) defines PM as “an extension of business intelligence with the primary focus to manage corporate performance such as strategy formulation, budgeting and forecasting” (p. 75). Therefore, as a phenomenon, PM represents a complex notion that allows viewing a company as a diverse mechanism.
Managing Organisational Performance: A Strategic Approach
In order to address the issues at the target organization, one will have to consider reinforcing quality management in its setting. The specified change will allow building the foundation for the continuous improvement, which the company needs to develop a competitive advantage. In order to address the concern at hand, the firm will need a reconsideration of its HRM framework., Specifically, the vertical and horizontal integration of the principles of SHRM will be needed. Granted that the specified approach has several disadvantages, the key one being the
The Balanced Scorecard, Kaplan and Norton, (1992)
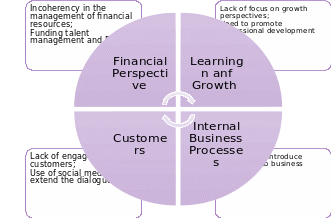
As the Balanced Scorecard analysis above indicates, the company will need to improve its strategic perspective in the way that will allow minimizing costs so that the newly acquired financial assets could be used to encourage talent management, improved communication, and enhancement of internal processes. Moreover, the current Balanced Scorecard of the company points to the inefficient communication strategy deployed in the organization. The firm will need the communication approach that will help to convey the company’s goals and philosophy, at the same time establishing a rapport with its employees. The latter, in turn, allows circling back to the need to encourage staff members to update their professional skills and focus on professional growth.
Similarly, the Balanced Scorecard results indicate that an improved communication framework will lead to much better customer engagement. Presently, the firm is facing stiff competition since other organizations have been deploying innovative solutions. In addition, the emergence of copycats has devalued the company’s products significantly. Thus, better rapport with customers would help the company to improve its business.
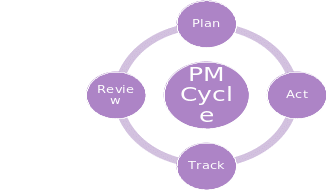
Purpose of Employee PM/PM Cycle/Stages of PM
Applying the four stages of the PM cycle, namely, reviewing, planning, acting, and tracking, one will learn that the company in question has been defaulting on the use of innovative, employee-oriented HRM techniques, as well as the inclusion of innovations into its performance, in general. The PM life cycle is a rather basic framework that implies controlling performance and promoting change so that it could continue evolving (Buckley et al., 2017). In the company in question, the employee MP cycle has been disrupted, with the lack of control and the absence of a clear innovation-driven strategy being evident (see Fig. 9)
Performance Appraisal
Definition of Performance Appraisal
To define the efficacy of performance, one needs to introduce an adequate and accurate assessment of performance delivered by the staff. For this purpose, performance appraisal is used. The current definition of the subject matter suggests that a performance appraisal is a “formal assessment and rating of individuals by their managers” and the “evaluation of an individual’s work performance in order to achieve at objective personnel decisions” (Islami, Mulolli, and Mustafa, 2018, p. 94). Therefore, a performance appraisal can be viewed as a tool for controlling the quality of service delivery and the prevention of possible quality issues.
Elements of the Appraisal Process
In the context of the target setting, the appraisal process has been taking place as a general performance assessment. However, the specified framework proven to fail at capturing the deficiencies in the organization’s performance. Therefore, a 360-degree feedback is recommended as a substitute for the current approach toward evaluating performance quality.
The Purpose and Benefits of Performance Appraisal
Performance appraisals are typically seen as the tools for keeping track of staff members’ progress and making sure that minor hindrances to their efficacy are removed promptly. Moreover, performance appraisals are traditionally believed to be the most common tools in managing performance. Leopold and Harris (2009) emphasize that leaders can use performance appraisals along with the reflections on their professional achievements when encouraging employees to excel in their performance (p. 180). Thus, the main purpose of a performance appraisal can be defined as that of controlling professional progress and quality management within a company, as well as receiving guidelines for further directions (Leopold and Harris, 2009). Moreover, the use of a performance appraisal allows aligning the analysis and management of staff’s performance with the principles of TQM (Soltani and Wilkinson, 2020). Thus, consistency in quality management can be achieved.
In turn, the key benefits of a performance appraisal include the opportunity to perform the assessment in accordance with the normal distribution framework, which allows delivering accurate results. Thus, the information concerning the progress that staff members have made, as well as the problems that require further improvements, will be delineated accurately. Another advantage of a performance appraisal that allows using it as a tool for providing an impetus for professional development.
However, performance appraisals as tools for assessing the quality of the staff’s work also have their problems. The extent of stress through which employees have to go in the process is typically regarded as one of the most glaring disadvantages (Wilton, 2019). As Harris (2005) noticed, performance appraisals may cause the following scenario: “Staff at all levels worry about whether they can prove to their bosses that they have met, or exceeded, the organisation’s expectations of them” (p. 179). The rise in anxiety in staff members may lead to underperformance caused by stress, which is an evidently negative outcome.
Nevertheless, the specified tool can be considered a perfect device for managing the assessment of staff members’ performance and the evaluation of the quality of their work. The integration of the 360-degree performance appraisal is particularly useful in promoting an objective analysis of the changes that staff members have undergone and the quality of work that they deliver.
Forms of Performance Appraisal
Developing HPWS
For an HPWS to be deployed in the target organization, it will be necessary to focus on the incorporation of innovative technology into its setting and encourage staff members to engage in lifelong professional development. By deploying four foundational principles of HPWS, namely, connection between performance and reward, information sharing, knowledge development, and egalitarianism, one will be able to build the platform for motivating employees and keeping their engagement levels high (see Fig. 10).

Specifically, technology will be used to promote the participation of staff members in as many aspects of the company’s performance as possible. Staff members will be rewarded with incentives and offered an opportunity for training and development, which will spur their enthusiasm and loyalty to the organization (Thunnissen and Gallardo-Gallardo, 2017). The proposed HPWS-related principles will allow establishing an HPWS that will guide employees toward professional growth.
Conclusion
It is important to incorporate the principles of incremental change as a part of the firm’s HPWS approach and the framework for guiding the organization and its staff through the company’s lifecycle. The suggested solution will imply that the company will be able to integrate talent management strategies into its HRM framework organically and ultimately lead to constantly improving performance. In turn, with the focus on talent management and the promotion of incremental innovation in the corporate setting, the HR managers within the company will create an environment in which employee swill b inclined to accept the corporate values, namely, that one of innovation, and engage actively in the development of new skills and gaining new knowledge.
References
- Beer, M., Spector B., Lawrence, P.R., Mills, D.Q., & Walton, R.E. (1984). Managing Human Assets. New York: The Free Press.
- Boxall, P., and Purcell, J. (2016) ‘Strategic HRM and sustained competitive advantage.’ In: Strategy and human resource management. 4th edn. New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 82-103.
- Buckley, M. R., Wheeler, A. R and Halbesleben, J. R. B. (2017) Research in personnel and human resources management. New York, NY: Emerald Group Publishing.
- Devanna, M. A., Fombrun, C. J. and Tichy, N. M. (1984). Strategic human resource management. New York, NY: Wiley.
- Farnham, D. (2015) Human resource management in context. 3rd Edition, CIPD Publications.
- Farnham, D. (2017). The changing faces of employment relations: Global, comparative and theoretical perspectives. Palgrave, Macmillan Eduction.
- Islami, X., Mulolli, E. and Mustafa, N. (2018) ‘Using Management by Objectives as a performance appraisal tool for employee satisfaction’, Future Business Journal, 4(1), pp. 94-108.
- Kaplan, R. S., & Norton, D. P. (1992) ‘The balanced scorecard: measures that drive performance’, Harvard Business Review, 83(7), p. 172.
- Khoo, H. Y., Chan, S. L., Leong, C. F., Ng, K. M. and Siam, W. C. (2017) High performance work system (HPWS) and turnover intention in Malaysia retail industry. New York, NY: Routledge.
- Leopold, J., and Harris, L. (Eds.). (2009) The strategic managing of human resources. Pearson Education.
- Schuler, R. S., and Jackson, S. E. (1987) ‘Linking competitive strategies with human resource management practices’, Academy of Management Perspectives, 1(3), pp. 207-219.
- Soltani, E. and Wilkinson, A. (2020) ‘TQM and performance appraisal: complementary or incompatible?’, European Management Review, 17(1), pp. 57-82.
- Storey, S. and Sisson, K. (1993). Managing work and organisations. Buckingham: Open University Press.
- Thunnissen, M. and Gallardo-Gallardo, E. (2017) Talent management in practice: An integrated and dynamic approach. New York, NY: Emerald Group Publishing.
- Timiyo, A. J. (2014) ‘High Performance Work Practices: One best-way or no best-way’, IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 16(6), pp. 8-14.
- Wilton, N. (2016) An introduction to human resource management. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.

