Introduction and Background
Background of the study
McCafe is one of the most popular coffee chains and one of the most recognized brands in the food and beverage industry owned by McDonald. The chain’s origins can be traced to 2003 as a franchise of MacDonald in Melbourne. In particular, these chain provides top quality coffee products in an intimate, engaging coffee-shop environment.
McCafe operates under the coffee industry which is global in magnitude. In fact, coffee beans, the essential raw material for coffee companies, is one of the most actively traded food commodities in the world scope. The coffee industry is significantly influenced by political, economic, and technological factors. For example, government policies affect the local and global importation and exportation of coffee products and influence coffee production processes. On the economic front, interest rates, foreign exchange rates, and supply and demand forces that influence prices also affect coffee production and consumption. Furthermore, technological trends come in the form of new machineries, equipment and devices that are constantly being developed to better grind, roast and brew coffee. The social factor pertains to income, lifestyle habits, and health issues, among others, that may influence coffee purchasing behaviour.
Research objectives
The prescribed objective of this report is served through evaluation of the identified target market and factors that could be identified as political, economical, social, technological, legal and environmental and having an impact on McCafe. All attempts are made to keep the research objective in line with the analysis of The McCafe and its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats to determine whether it is viable to change their business strategy.
Research Questions
The following research questions will guide the research to help find supporting evidence to present conclusions from the current research:
- Which factors does McCafe need to take into account when operating franchise?
- What are the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats that affects its decision to set up a franchises?
- What are the market conditions including consumers’ perception and competition existing in the market?
- What are the possibilities for success of McCafe operations?
Marketing Tools Used
The market research uses different market analysis tools for gathering useful information forming basis for the research. These include SWOT, Porter’s Five Forces Model, and PESTLE analysis that are already described in the Literature Review part of this report. Porter’s Five Forces Model and PESTLE analysis are used to draw important useful information regarding the business environment and factors that contribute to the development and sustainability of any business operating world market. While on the other hand, SWOT allows the company to assess its own capabilities and problems that could affect its business decision.
Theories and Framework
Research Methodology
The current research is aimed at exploring different elements of market research and evaluation for forming an opinion on performance of McCafe. The market research draws vital information from different sources regarding the company and its products; the world market and its beverage industry. The sources of information used in this include secondary sources that are described in detail in the following sections. The information retrieved for completion of different elements of the market research including HRM, operational and legal is drawn from various authentic secondary sources that are available to the researcher. These secondary sources include books, journals, reports, articles, websites, and any other relevant material that could assists in deriving most relevant information regarding the business opportunity in the industry (Cohen, Manion and Morrison, 2007).
Business environment
Smallman (1996) mentioned in his article about the recent times we live in being increasingly dynamic especially focusing on the social and business environments. These aspects of dynamic society brings along with it fear and uncertainty. For this reason businesses need to work on the major area known as risk management. He in his article defined a link between risk management strategy and organizational behaviour. From his perspective there are a number of factors that determines the performance of an organization as can be seen in figure 1.
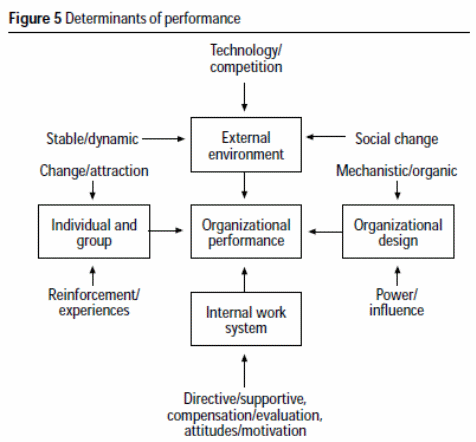
Robertson (1994) mentioned in his study that an understanding about how individuals working an organization get influenced by the different factors and organizational context is very important and plays a central role in the study of organizational behaviour. What can be done is to shape the behaviours in an organization emphasis is upon the managements of key characteristics present in the work environment and this has an important implication for the practitioners of the organization.
The goals of the work are found to be linked with the work setting behaviours and characteristics. The behaviours that are fond to be exhibited by the managers are found to be an important element that can influence the attitudes and behaviours of the employees. Job design is also another element that can influence the work behaviours of an employee that can lead to favourable outcomes in the work. The basic motivators in a job are mainly by autonomy, skill variety, task identity, individual identity, significance of the task and proper feedback.
Waldman and. Yammarino (1999) worked on a model where it they found that organizational culture and environment somehow affect the behaviours of a leader. They followed with the consideration proposing that a more flexible and adaptive culture will allows and create a leader with much of the charismatic qualities. And on the other side a very charismatic leader at the top of the organization can leave an impact on the culture of that organization. Their model also suggested that charisma is evident differently based on the followers as to whether they are close or distant followers. But in both the cases the leadership can lead to outcomes such as individual and group efforts, group cohesion and increasing the performance of both the group and organization.
An effective leader is a blessing in disguise. Frances (2005) mentioned the six main and essential leadership attributes a leader should have which are mostly developed over time and with highest level of commitment. These attributes are they set very high standards for both their own selves and for the ones who have to follow them; secondly they lead a life based on those standards and also provide help to the ones who are trying to follow them. Thirdly, they create and share a vision with their team and work force. Fourthly, they are decision makers and at times they make the necessary hard choices and decisions as well for the betterment of the organization. Fifth one is that they are visible and last but not the least they are the motivators as they provide hope to their follower.
Empowerment is also one of the most turbulent of all changes due to the changing nature of work environment. Hui, Au & Henry Fock (2004) worked upon empowerment and its affects on cross cultural variations. According to them Job satisfaction is in turn can be related to empowerment, power distance and customer orientation. It’s being considered that discretionary power will have a more defined effect on an individual’s job satisfaction especially for the service employees and these employees believe in power sharing and want to deliver superior customer value. This is an important aspect in case of a service industry where customer satisfaction plays a very vital role and the key is to make the customer happy. Empowering employees without proper focus and understanding of organizational culture and structure can lead to severe organizational behaviour issues. Proper lines of authorities are to be defined in this case so as to get the best out of the employees while keeping the motivation level high as well.
Klein (1989) proposed a model that was an integration of a number of motivational theories and also the control theory was presented. The main purpose was to come forward with a Meta theory which will be focused upon future theoretical and empirical efforts. This model is economical and mostly is place emphasis on self regulation and what are the cognitive level reasons behind the motivation.
Employees in an organization are known to be intrinsically as well as extrinsically motivated and the main task takes place when there is a need for tacit knowledge in and between the teams of an organization and this knowledge is to be transferred. Here as mentioned by Osterloh and Frey (2000), organizational forms play a fundamental role as they are a kind of enabler for different kinds of motivation and they also got the power to generate and transfer tacit knowledge. Tacit knowledge acts in the benefit of an organization as it’s a source of sustainable competitive advantage. The underlying reason behind this is that this knowledge is not easy to me imitated by the competitors and also this tacit knowledge of employees can lead to motivational outcomes.
Extrinsic motivation in employees mostly comes from their satisfaction based on monetary compensation and incentives that are linked to pay package. Intrinsic motivation on the other hand is basically self sustained and is one need it to have it for immediate need satisfaction. Although organizations are found not to be interested in working on intrinsic motivation of employees but intrinsic motivation can prove to be helpful in cases where the job demands creativity and also helps on performing multi task problems.
The need for the organizations is to make the best out of both and the firm managers can see and choose a best combination that will maximize the gains by taking motivation into account. Job satisfaction also is critical for the effective organizational behaviour. This satisfaction can be linked with the job demands, job requirements, and elements of extrinsic and intrinsic motivation, working conditions, supervisory control and many other organizational issues.
Hamermesh (2001) explained that the earnings inequality among the workers is one of the problems that are being faced by the many countries. According to his analysis a more satisfied worker is more likely not to leave his job voluntarily. Economic situation here can contribute towards this job satisfaction. It varies with the level of job satisfaction that a worker will work for an organization and invest more in firm’s human capital and in turn the result will be an increase in the level of commitment to his employers.
Janssen (2001) worked on the activation theory which focuses on the extent a manager can improve his/ her performance by regulating the fairness perception of the employees which caters to the gap between their efforts and the rewards they get. Catering well to the job demands while simultaneously appreciating the job performance implies factors of job investment which takes into account intelligence, experience, energy and the time they spent on work locations. If a proper balance is obtained and the manager’s job efforts are being rewarded well, the result will be good performance of the job demands.
But on the other hand if the efforts are not found to be equal to the rewards, there are chances that the employees will restrict their job investments. By restricting a job investment an overall change in the organization can take place if a large number of individuals are found to be restricting their selves on job investments. The organizational behaviours can and work environment both will get affected and the end results can be in terms of organizational performance taking a blow out.
BCG matrix
Managers using the BCG matrix plotted each of the company’s businesses according to market growth rate and relative competitive position. Market growth rate is the projected rate of sales growth for the market being served by a particular business. Usually measured as the percentage increase in a market’s sales or unit volume over the two most recent years, this rate serves as an indicator of the relative attractiveness of the markets served by each business in the firm’s portfolio of businesses.
Relative competitive position usually is expressed as the market share of a business divided by the market share of its largest competitor. Thus, relative competitive position provides a basis for comparing the relative strengths of the businesses in firm’s portfolio in terms of their positions in their respective markets.
The stars are businesses in rapidly growing markets with large market shares. These businesses represent the best long-run opportunities in the firm’s portfolio. They require substantial investment to maintain their dominant position in a growing market. This investment requirement is often in excess of the funds that they can generate internally. Therefore, these businesses are often short-term, priority consumers of corporate resources (Jones and Hill, 2009).
Cash cows are businesses with a high market share in low-growth markets or industries. Because of their strong positions and their minimal reinvestment requirements, these businesses often generate cash in excess of their needs. Therefore, they are selectively “milked” as a source of corporate resources for deployment elsewhere. Cash cows are yesterday’s stars and the current foundation of corporate portfolios. They are managed to maintain their strong market share while generating excess resources for corporate wide use.
Low market share and low market growth businesses are the dogs in the firm’s portfolio. Facing mature markets with intense competition and low profit margins, they are managed for short-term cash flow to supplement corporate-level resource needs. According to the original BCG prescription, they are divested or liquidated once this short-term harvesting has been maximized.
Question marks are businesses whose high growth rate gives then considerable appeal but whose low market share makes their profit potential uncertain. Question marks are cash guzzlers because their rapid growth results in high cash needs, while their small market share results in low cash generation. At the corporate level, the concern is to identify the question marks that would increase their market share and move into the star group if extra corporate resources were devoted to them. Where this long-run shift from question mark to star is unlikely, the BCG matrix suggests divesting the question mark and repositioning it resources more effectively in the reminder of the corporate portfolio.
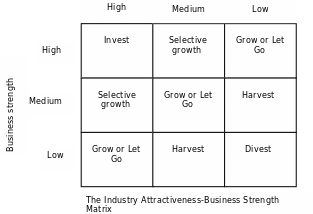
Corporate strategies found the growth-share matrix’s singular axes limiting in their ability to reflect the complexity of a business’s situation. Therefore, some companies adopted a matrix with a much broader focus.
Although the strategic recommendations generated by the industry attractiveness-business strength matrix improves on the BCG matrix in three fundamental ways. First, the terminology associated with the Industry Attractiveness-Business Strength Matrix is preferable because it is less offensive and more understandable. Second, the multiple measures associated with each dimension of the business strength matrix tap many factors relevant to business strength and market attractiveness besides market share and market growth. And this, in turn, makes for broader assessment during the planning process, bringing to light considerations of importance in both strategy formulation and strategy implementation (Sadler and Craig, 2003).
One criticism of the first two portfolio methods was their static quality – their portrayal of businesses as they exist at one point in time, rather than as they evolve over time. A third portfolio approach was introduced that attempted to overcome these deficiencies and better identify “developing winners” or potential “losers”. This approach uses the multiple-factor approach to assess competitive strength as one dimension and stage of the market life cycle as the other dimension.
The life cycle dimension allows users to consider multiple strategic issues associated with each life cycle stage, thereby enriching the discussion of strategic options. It also gives a “moving indication” of both issues- those strategy needs to address currently and those that could arise next. It includes basic strategic investment parameters recommended for different positions in the matrix. While this approach seems valuable, its recommendations are virtually identical to the previous two portfolio matrices.
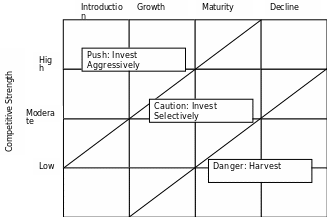
BCG’S Strategic Environments Matrix
BCG’s latest matrix offering took a different approach using the idea that it was the nature of competitive advantage in an industry that determined the strategies available to a company’s businesses, which in turn d determined the structured of the industry. Their idea was that such a framework could help ensure that individual business’ strategies were consistent with strategies appropriate to their strategic environment. Furthermore, for corporate managers in multiple business companies, this matrix offered one way to rationalize which business they are in business that share core competencies and associated competitive advantages because of similar strategic environment (Sekaran, 2006).
The matrix has two dimensions. The number of sources of competitive advantage could be many with complex products and services and few with commodities. Complex products offer multiple opportunities for differentiation as well as cost, while commodities must seek opportunities for cost advantages to survive.
The two dimensions then define four industry environments as follows:
Lean Manufacturing in Catering and Food Service Businesses
Lean Manufacturing is the process wherein an organization minimizes its time in processes. In order to have a positive and successful lean service, the organization should consider data, customer and quality. Data will give the catering or food service business a head start on what kind of people will be coming to the restaurant and how often, tag on customers will give the business house an idea of what a customer expects or requires and save time on services, and finally quality is a prerequisite. No customer will like the idea of waling into a food service business house and spend his/her hard-earned money on sub-standard products when there are many others who could do the same if not better. Thus, quality will have to be maintained at all times. A customer who frequents a restaurant does so because he is happy with the quality and service of that particular restaurant. Should one aspect of the service be compromised, the customer is not going to go back there again (Miles, 2003).
Earlier, business houses defined their products and sought strategies to attract customers for these products, but this has now changed. Today, business revolves around what values can be offered to customers to attract them and develop their business. Therefore business houses must address customer needs and demands rather than luring them with what they have. In order to develop a strong customer-vendor relationship, business houses like a restaurant for example, will have to build trust, provide value-added services and be highly reliable. Focusing on people, business processes, performance management systems and technologies are sure ways to satisfying customer needs. In order to do this, organizations use special software that improves customer service and relationships.
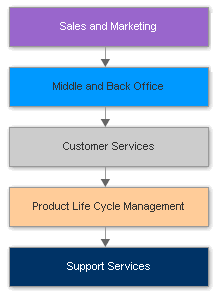
In order to develop a strong, positive and efficient customer-vendor relationship, an organization must involve all the departments shown on the left in a very coordinated and smooth manner. Once these departments work in a synchronized manner, the efficiency and value-added processes will begin to flow positively, leading to reduction in process time and wastage, and increase in profits and customer satisfaction.
In order to make this happen, it is imperative that the catering or food service business (in this case a restaurant), first of all, introduces a technology to support these initiatives and then, understand their customer’s eating behaviour, before it introduces a Customer Relationship Management plan. It not only enhances the quality of service, but also supports in the smooth flow of information required by the restaurant to decrease process time and cut waste. Be it the Front Office, Sales and Marketing, Stores and Inventory, Supplies or Maintenance, or Support Services, a Customer Relationship Management can improve the efficiency and reliability of processes within the restaurant.
Customer Relationship Management software will ask for certain details of a customer which is fed into the system and stored in memory for future reference. For a restaurant to become highly successful in the industry, it has to understand the needs of their customer (which would mean studying the eating habits of each customer who comes to the restaurant), what are his/her likes and dislikes, how they want their food to be served, how much time does he want for his food to be served, and what kind of food does he like.
Once the restaurant does this exercise with all his incoming clients, he will be able to cut time on preparing the food he/she likes, and serve it in the shortest possible time to make the customer happy. This again may not be easy. However, the best way to accumulate such information would be to place questionnaires before the customers who come in for the first or second time, and ask them to fill it so that in future they would not have to wait much long for someone to take their order, or wait for their food to be served (O’Brien, 2003).
Customer Relationship Management systems are “enterprise applications that support and integrate customer-oriented business processes such as marketing, sales, and customer services to manage business interactions with customers.” This is where strategy comes in. Strategic management is the organizing of products, services, processes and systems in a manner that not only meets customer needs but also reduces the entire process time. This is what lean is meant to do. By introducing the lean process, the restaurant would be able to understand the deficiency of existing practices and their customer’s behaviour (Zeithaml and Bitner, 2005).
This is where technology is introduced. Manual practices will have to give way to automation. With the introduction of suitable Customer Relationship Management software, the restaurant can mitigate the risks involved in wastage of products, time, reduce over-production and inventory, and serve only value-added processes. This is where the introduction of a supply chain becomes important (Drummond, Ensor, and Ruth, 2007).
According to Daft (1998), “organizations usually like to have control of the direction in which they are developing and how. It is for this reason that they create a mission statement, a strategy, and goals.” The internet has many advantages and this is the reason why many companies opt for the internet.
Levels of strategy
Business strategy can be primarily classified into three levels based on their level of influence namely corporate unit level, business unit level and the operational level. While the strategy management inculcates all the aspects of the organization, it actually depends in the performance of all the functional units within that organization. The success of any organization depends on the maximized efficiency of each of its units (Coutler & Robbins, 2007).
Corporate level strategy of the organization is based on the mission and vision of the organization on the whole and is related to determining which business the company wants to be in and what it wants to do with it. It is also concerned with the development and enhancement of coordination of the portfolio of businesses. Any organization depends on creating value through all of its business practices and the strategies at corporate level inculcate the factors of managing the business units and seeing that they are profitable over a long time period (Coutler & Robbins, 2007).
In addition to that it also determines the developing factors of the business units along with ensuring that they remain compatible with other businesses in the portfolio. It is on the whole, also related to defining the responsibilities at corporate level, determining where the competition is to be localized, managing businesses interrelationships and managing their activities, and also determines how the business units are to be governed (Coutler & Robbins, 2007).
The business unit level strategy refers to the strategies implemented on the business unit level that are distinguishable from other business units. It includes developing a road map for gaining a competitive advantage and working on the development of goods and services. At this level the strategic development is basically focused on positioning of the business unit under consideration in relation to its rivals, adjusting the strategies as such that they integrate changes in the demand or technologies and influencing the nature of competitive advantage that the business unit is striving for (Aitken, Childerhouse and Towill, 2003).
On the third level comes the operational or functional level strategy that constitutes operating divisions and departments and is related to the value chain or other business processes. In addition to that it also includes development and coordination of resources to fit into the overall strategy. It relates to the overall hierarchy of levels of strategic management in terms of providing information on resources and capabilities on which the overall strategy of the organization is ultimately based (Coutler & Robbins, 2007).
Contemporary Strategic issues
Strategic management faces numerous issues at present owing to the changing organizational structure of the organizations being triggered by the factor of globalisation that is also influencing the factors shaping the organizational strategies along with the roles that the organization’s managers have to play. Such environmental changes have had a dramatic impact on the organizations working along with their priorities in the corporate sector (Johnson, Schools, and Whittington, 2008).
Traditionally the whole organization was being controlled and coordinated in accordance with a vertical hierarchal structure but with the advent of the awareness of the lower level employees as being an important entity in defining what the functions of the organization, as they are closer to the action and also constitute the touch points of customers, their involvement in the strategy building has become vital. This concept though being quite valid leads to quite a complication in terms of strategy management. Same goes for diversity that is a by product of globalisation. It also presents a multitude of issues as they may require a different approach to strategy for their accommodation (Hitt et al, 2009).
Technological advancement on the global level poses all the more challenges to the strategic management process as it requires the organization to keep its focus all around and not just the industry that it is currently working in. it may even pose a threat of existing business practices are products (Hitt et al, 2009).
Mintzberg’s schools of strategy and Whittington’s classification of strategic perspectives
Over the course of the development of the term strategic management, there have been various attempts at theorizing the min aspects of it and how it should be perceived. There have been numerous schools of thought in relation to strategic management which sometimes are quite differential in their perceptions. Strategy management is an aspect of management that is concerned with integrating all the functions of the organization in a systematic manner (Johnson, Scholes and Whittington, 2008).
Among these schools of thought, one of the most prominent one is the Whittington’s theory for the systematic classification of strategic management that categorizes the whole process of it into four categories which consist of the classical approach, the evolutionary approach, the procession approach and the systematic approach.
Now, among this classification, the first two of the approaches namely the classical and the evolutionary approach visualizes the maximization of profit at the core of the strategic management process. On the other hand the processual and systematic approaches envision more factors along with profit making in the management of strategies. All these classifications practice a different approach in providing a roadmap to the top management. The classical approach highlights a more systematic and sequential approach to the strategy process as is applied at the universal level. The evolutionary and processual approaches are a little different on that note as they are more sceptical of the strategists to direct strategy in such a systematic manner. On the other hand, the systematic approach is of the viewpoint that the ends and means of the strategy management process are primarily governed by the character of the social systems (Karami, 2007).
There are various issues with this approach as it restricts the strategic management process and by extension the duty of the managers to plan, organize, coordinate and control. Though these three aspects have dominated the field of strategic management since the time when they were first introduced by Henry Fayol in the year 1916, the management process cannot just be restricted to those three aspects as it is also concerned with productivity, in other words it can be said that it also inculcates the factors of efficiency and effectiveness which are not incorporated in Whittington’s theory of strategy (Karami, 2007).
In the following light the functions of the management strategy can be defined as the use of planning, organizing, leading and controlling tools with the purpose of attaining organizational goals in the most effective and efficient manner for the purpose of which the managers now have to attain a multitude of skills for such goals.
Another theorist that tried to summarize the definitions and understandings of strategic management is Mintzberg who defined ten specific schools of thought in the field of management. Each of these schools focuses on different processes of the development, evaluation and exploitation sections of strategy making based on a perspective and descriptive approach (Bilton & Cummings, 2010).
In view of the changing world and the issues that are faced by the management today the organization should also inculcate the influence of lower level employees as well along with that of the top management. Also the management process should be aligned with the global vision. It has also become a necessity for the organizations to incorporate such a management approach that empowers the employees and their involvement for competition purposes. Along with that the management should also be framed as such that it incorporates the factor of diversity and increased technology involvement in the organizational sphere that has dominantly reshaped the whole structure of the organizations all over the world. All these of these factors highlights the fact of these theories of Mintzberg and Whittington as not being the only solutions on which the organizational structure can be based but the managers now have to rethink their approach to the same factors presented by them (Winterton, 1999).
Research: data/ information in terms of research
PESTLE
To evaluate the effect of the external conditions affecting the McCafe in the light of the above discussion a thorough analysis is conducted. The thorough analysis made would incorporate political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal parameters, which govern a company’s external environment. Herein, such an analysis is conducted over McCafe.
- Political Environment: – McCafe is found to be an active participant in the political environment of America. Moreover, the company also takes active participation in the political process of other American states wherein such political situations affects the business operation of the beverage firm. The active participation of McCafe in the political sphere reflects huge contributions made by the company in election periods for supporting candidates and institutions. The above activity pursued by the company helps it to generate a favorable political environment.
- Economic Environment: – In the economic front, it is observed that the demand for the products offered by McCafe is found to augment owing to competition. Moreover, it is also observed that the fall in the per-capita income level of the country’s population would lead to the reduction of quantity of demanded. However, the company is also found to have already generated significant reserves to counter the fall in the prescription volumes. The economic risk level is moderate. A major portion of the economy of Ireland is dependent upon foreign investment which indicates the existence of flexible policies. USA has a free economy, however, due to low freedom in monetary and financial terms and low government spending the ranking has declined from last year. Due to the global economic recession, the financial sector was affected. The government budget has become distorted as a consequence of increase in Ireland’s budget deficit. The economic freedom remains high regardless of the economic catastrophe. The stable government policies will help the country to recuperate its position.
- Social Environment: In regards to the social environment of McCafe, it is found that it focuses on the generation of huge employment opportunities. It is observed that McCafe, which belongs to the class of multinational. The company through a wide network of branches and employs many people. McCafe is found to pursue transparent employment opportunities, which aims to generate growth of individuals depending on their skills and competencies. Thus, the company is found to operate freely from any form of gender, class, race or color bias. The people of USA are diligent and honest. They are specially known for their friendly and fun-loving nature. Family structure is strong and due importance is given to all family members. The rural areas are traditional whilst urban areas are more modern; where people readily adapt to changes in the current era. The society, to some extent, is male dominant. The legal restrictions for gender and age discrimination are very few, and salaries for women are relatively low. A strong economic and social class system prevails in the country. Social class comprises of working class, middle class and gentry. Farmers are categorized in the social class depending upon their wealth and landholdings. People of high social class are widely noticed through their dressing, language, leisure activities, social networks and profession. The Americans are generally more polite and avoid conflict and focus more on good manners, therefore, communication should be warm. The meetings may be structured or unstructured depending upon the content or matter to be discussed. Long self-centred talks which include boasting about one-self are discouraged. While introducing oneself, professional designations should not be disclosed as it is considered arrogant. Generally, participative decision making is practiced
- Technological Environment: McCafe is found to implement active use of Internet technology to expand its nature of business operation. The company to expand its dealings with large number of outlets actively pursues the use of Internet technology. With Internet, the customers are regularly informed with changes made in the menu and products offered and other benefit services administered by the company. In USA, technology is developing at a fast rate. Owing to this fact, investors find it suitable to invest in the country. Internet is available in every house. This rapid growth of technology has affected businesses all over the world. Technology has helped improve communication not only within the organization but has improved inter-organizational communication as well. Customers can be easily accessed and their feedback can be generated in no time. Now business transactions are done without any hassle of travelling. With the evolution of Internet, services can be provided to customers throughout the world.
- Environmental Factors: – The Company in the light of taking care of the environmental factors is found to focus on the employment of energy saving technologies. McCafe in looking forward to pursue the activity regarding energy conservation throws light on innovating technological parameters to promote such. In fact, it is observed that the company looks forward to create energy savings through use of lights of low watts. The company is also found to focus on the reduction of emission patterns of commuting vehicles to promote a safer a greener environment. McCafe is also found to actively employ recyclable resource base for generating its production. Through such initiatives, the company is found to promote the idea of wastage reduction and other recyclable programs. An estimate revealed during the period of 2009 shows that the company through the recycling of around 4,300 tons of material reduced the rate of wastage in the country. Moreover, the company through the extensive use of bubble wrappers showed a positive direction to this end. The company also promotes the recycling of its technical equipments to promote a safer environment. Further, McCafe in regards to the environmental factors also looks forward to promoting a cleaner and safer work environment for its workers.
- Legal Factors: – The beverage company is observed to actively comply with existing legal statutes of the country pertaining to industrial activities. In promoting a safer environment for its workers, the company is found to comply with legislative measures supporting the protection of health and safer environments. Moreover, the company is also found to actively comply with legal statutes concerning employment activities. McCafe strictly follows the rules laid by the legal statutes, which governs the recruitment and retrenchment measures taken by the company. Further, the compensation schemes practiced by the company also comply with the legal regulations of the land in regards to employment generation.
The political environment of a country has a huge impact on the regulations of any business. In USA, the regulatory environment to carry out a business is fairly flexible. In order to establish a business, on average only 13 days are required as compared to an average of 35 days in rest of the world. Business license is given in a relatively short span. Moreover, the procedures for bankruptcy are clear-cut. The trade policies prevailing in the country are same as those in the rest of the countries.
However, there may be some entry barriers that include restriction or ban on imports of some goods and services, restriction on access to certain markets in some services’ segment, limiting standards and policies and incoherent customs management. Additionally, there are restraining procurement rules by the government. The income tax rate is high compared to the low corporate tax rate.
Foreign investment is encouraged in USA and equal treatment is given to foreign and local companies. No process of approval exists for the foreign investors. The regulatory administration is clear and well-organized. A disciplined and just legal system is present for foreign investors, facilitating them with acquisition and similar property rights. The legal framework of the country is highly efficient and comprehensive for the security of Intellectual Property Rights. Bribery is intolerable and prohibited for public employees. The regulations for labour and work hour restrictions are flexible (National Coffee Association of the United States, 2009).
Clearly, the economic factor remains the most significant variable that affects the long-term viability and sustainability of coffee chains. From an economic perspective, coffee drinking is vulnerable to economic downtrends which weaken demand, particularly for the special or gourmet coffee segment. Being a premium-priced product, specialty coffee is one of those discretionary expenditures, which consumers tend to cut back when the economy weakens. This was evident in the drop on the average per cup consumption of coffee drinkers aged 18 to 24 from 3.2 cups in 2008 to just 2.9 cups in 2009. Consequently, the economic recession, which has gripped the U.S. since 2008, has compelled many coffee drinkers to brew their own coffee at home. According to the NCAUSA, there was a five (5) percent increase in the number of consumers brewing their own coffee in 2009.
Consequently, it was already estimated that 80 percent of daily coffee drinkers brew their own coffee at home. From a cost-savings perspective, the practically of brewing coffee over buying over the counter has been clearly established. However, although customers in the coffee industry tend to be price-sensitive, a price reduction strategy is not the automatic option to pursue to maintain market share. According to an article made by Coffee Bean International, a specialty coffee company such as Peet’s has managed to remain immensely successful despite selling a higher priced coffee compared with McCafe (National Coffee Association of the United States, 2009).
Aside from the economic factor, industry competition is also a significant variable that affects coffee consumption. In the U.S., McCafe competes against a whole coffee retail brands that also provide quality coffee products, excellent customer service, and comfortable coffee shop atmosphere such as Caribou Coffee, Peet’s, Coffee Beanery, Starbucks, Tully’s, among others. Players in the U.S. coffee industry compete against one another in terms of product quality and diversity, price, and customer.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps in exploring the present activities of the organization- it is Strengths and Weakness- and then with the help of externally researched data supporting thing information, helps in setting out the various existing market Opportunities and Threats.
McCafe has vigour and taste beverage based in the US who are dedicated to development of this good brand. Apart from taste coffee, the brand has generated a strong finance base from the past sales which has necessitated the corporate to venture into various market niches.
Various opportunities exist for the brand and corporation as a whole. For example, the globalisation effect created by Internet has led to emergence of new market from various nations in the whole world. In addition, the current revolution of turning all societies to involve into social activities has created an opportunity for the corporation to expand its market share (Böhm, 2009).
On the other hand, the corporation and specifically the brand are facing various threats. Over the years, McCafe has become one of the biggest specialty coffee chains in the world. This success can be attributed to the company’s brand positioning strategy, which has been effectively implemented via sound marketing mix strategies. For example, McCafe has consistently marketed a broad range of the finest coffee beans, coffee-related food products and merchandize items possible. For its coffee shops, McCafe has greatly elevated the coffee dining experience to a higher level, one marked by excellent customer service, and innovation in terms of product offerings.
The combination of superior coffee products, excellent customer service, and aesthetically appealing coffee shops are the fundamental strengths of McCafe. The only palpable weakness of McCafe is rigidity. Indeed, the company’s main source of weakness is ironically, its size. McCafe has become a rigid giant that has lost its nimbleness and forward thinking capabilities. Evidently, complacency and lack of strategic focus hurt McCafe financially. Amidst an increasingly competitive coffee industry environment, McCafe needs to implement better strategies geared for the long term.
Porter’s 5 forces analysis
Further analysis of the operational activities of McCafe is conducted based on Porter’s Five Forces Model and Generic Strategies.
- Competitive Rivalry: – The McCafe is found to face competitive rivalry from various firms operating in the beverage. It is found that the company is venturing in the sector is strongly competed by firms such as Starbucks. All of these firms endeavor to reach a larger customer base through the extensive use of information technology like Internet and franchise.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers: The customers of the McCafe are found to possess larger bargaining power because of the existence of consumer courts. It is found that the customers vehemently oppose the wrong approaches taken by the company in addressing their needs. It is found that the company has to bear active bargaining power of its buying population. They have provided product differentiation in the market in order to increase the buying power among its competitors. The customer’s are price sensitive, so it is necessary to provide reasonable prices and diverse collection, which would help to attract more customers.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers: – In regards to the new practice of the beverage market, the bargaining power of suppliers is to be enhanced. It is observed that owing to the recent policies implemented in the market the distribution force is expected to gain further impetus in being able to sell larger volumes. The innovative practice in the beverage policies is expected to generate newer distribution models, which would help in generating wider coverage (Dacko, 2008). McCafe has established a reputation in the world. It is working with number suppliers who are trustworthy and reliable who are producing and supplying the products specifically coffee, and have fair trade business with them. Moreover, the key multinational suppliers of the industry are highly strong. They play a vital role in convincing the customers to switch from one brand to another. These suppliers have created brand awareness among the customers, and now most of coffee users prefer to use premium brand products. Majority of the local and international suppliers are targeting the customers Arabica coffee user.
- Barriers to Entry: – The significant barriers to entry in the market occupied McCafe constitute of need of technological expertise and access to wider markets. The wider market coverage is enabled through the involvement of McDonald and other franchising firms in this respect. Providing quality coffee at reduced and controlled rates is found to constitute a complex operation, which demanded considerable expertise in the field.
- Threat of Substitutes: – The modern pharmaceutical industry is to be governed by the existence of three major substitutes. It is observed that the existence of a large number of alternative beverages, emergence of fast foods with soft drinks in the market and increased health consciousness of the American population constitute the substitutes for the industry.
Three Generic Strategies
- Cost Leadership Strategy: – The beverage company McCafe is found to have rightly implemented the cost leadership strategy in the context of the industry. It is found that the beverage industry was filled up by plans, which though of qualitative nature charged highly from the customers.
- Differentiation Strategy: – McCafe is also found to take resort to a differentiation strategy in rightly using the Internet technology to accumulate newer market base. It is found that with the use of Internet technology on a mass scale the company has helped the customers to gather needed information right at hand. Moreover, the customers can also make required queries through the Internet medium, which is addressed at a faster rate. This proves to be a differentiation strategy enabled by McCafe to cater to the changing market.
- Strategic Scope: – The strategic scope of the McCafe can be studied on two grounds. Firstly, with the opening up of the beverage market industry players are looking forward to it to gain advantage of higher margins. Secondly, the market is filled with coffee industry players of considerably higher costs.
Findings, Decisions and Presentations
McCafe Corporation is one of the world’s largest beverage chain and has not only created a brand image but it is making loyal customers all around the world because of its consistent quality and service providers. McCafe offers both counter service dealing and drive through, where customers are provided both indoor and outdoor seating arrangements.
Products Development
McCafe offer wide variety of product range for its customers, McCafe is an international brand and thus offers a regionalized version in its menu. McCafe operates in desserts and beverages. Its basic emphasis is on the coffee brands because high level of sales and due to this most of the promotion or brand extensions are made within this defined product line. Some of the beverages that McCafe is offering to its customers are soft drinks, both regular and diet, coffee; Iced Coffee, Espresso and Lattes, milks shakes, chocolate mint, IRN-BRU and others.
Type of Competition
McCafe is facing international competition as it is competing with lots of direct and indirect customers. Due to this it is facing tough competition from Starbucks and various other coffee shops. While on the other hand it is also facing competition from dine-in restaurants and cafe. These shops are offering beverages in their menu thus offering variety and differentiation to the customers. Further more it is also competing with local competitors in every country where they are serving similar products at cheaper price, thus creating intense competition.
Value Based Market Segmentation
Value based market segmentation involves a six step process and this process ensures that the right product should be sold to the right customer segment at the right price so that profits and growth can be maximized. Thus to satisfy the customers McCafe has to follow and adopt the Value based market segmentation in its pricing and operations process.
In the first step McCafe determines the basic segmentation criteria, i.e. dividing the market into subgroups in which each potential customer will have the same criteria that differentiate their buying behaviour. McCafe segments its market on the basis of geographic factors demographic factors and physiographic factors. McCafe focuses on both the male and female population, serves high income individuals, and those people who value style, quality and taste.
While determining the basic segmentation criteria, McCafe had to determine its expected customers buying pattern, define the customer’s description, define their current needs and make a list of al the unmet needs of the customers. In the second step, McCafe identifies its discriminating value drivers, i.e. those purchase motivators that yield highest results. So the age range of 16-40 years of individuals yields high profits for the company.
The third step is to determine the operational constraints and advantages. McCafe is a fast food chain and thus it enjoys its international brand identity, high quality food standard, good environment and consistent quality management in all the franchises all over the world. Further more when we look at its international operations, we can state that at some point McCafe faces issues as every country’s culture and values differ. Thus they have to carry out an extensive research before they start operating in one country. So to build a customer behaviour spectrum McCafe should map out its true costs for serving different types of customers.
This is followed by the forth step, i.e. creating primary and secondary segments. A primary segment consists of those customers that have the highest criteria, while the secondary segmentation refers to the next or second best criteria. Thus with in the demographic segmentation, McCafe chooses age range, the primary segmentation would consist of individuals of age range of 18-35, because they are not only willing to buy the McCafe products but they also have the ability to buy the product. While the secondary segmentation would be the children who are willing but they do not have the ability to pay.
In the fifth step McCafe Corporation would have to define and describe each segment in detail so that true analysis could be made and finally in the last step, McCafe should develop such segment metrics and fences that would provide customers with such guidelines that would qualify them for any kind of price discounts or rewards. As within different time periods, McCafe has provided its customers gifts on the purchase of certain products. Identifying the value-based segmentation, McCafe’s marketers could expand its profit margin by aligning its prices, service bundles and capacity could be utilized
Major Customer Profiles
There are two major market classifications or segments in the McCafe namely those that consume the “traditional” coffee products and the specialty category. The traditional coffee segment has long been associated with the packaged, pre-blended coffee brands such as Folger’s and Maxwell House (Mullins 2009). These coffee products are usually purchased on supermarkets and food stores and consumed at home or in the office. Meanwhile, the specialty category is associated with lifestyle-oriented retail coffee shops such as McCafe, Caribou Coffee, Peet’s, Coffee Beanery, and the like. Nevertheless, the growing popularity of premium, specialty coffee varieties have allowed these products to be distributed not just within specialty coffee shops, but also in supermarkets and groceries. In fact, specialty coffee has been increasing at a much faster rate than traditional coffee in recent years (Mullins 2009).
Nevertheless, while coffee products in the traditional category are purchased by consumers simply on the basis of price and brand recall, the buying determinants in specialty category, particularly the gourmet coffee shops, is far more sophisticated and diverse. For McCafe, this experience defined by selling the finest coffee and related products and providing superior customer service in very clean, well maintained, and aesthetically appealing coffee shops. In terms of customer profile, McCafe customers are young adults coming from middle to upper income class segments. They tend to be highly educated individuals who lead active, social lifestyles and enjoy drinking coffee amongst friends and officemates.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Clearly, given the behaviour of the specialty coffee market and trends in the industry, McCafe needs to implement strategies that go beyond simple cost cutting measures. The strategies should focus more on reinvigorating which is the company’s key competitive positioning. This would entail motivating and inspiring personnel, developing organizational competencies, producing innovative better product and service development initiatives, and proper financial and market planning. The specific strategies and action plan McCafe can pursue are as follows:
- Provide more relevant and responsive training programs that focus on sustaining excellent customer service and strengthening professional competence;
- Further differentiate the company vis-à-vis competitors by offering innovative products and services;
- Conduct detailed store audit to determine long-term cost savings and productivity gains
McCafe has already developed a well-defined plan for corporate governance and hence managing its human resources. This is a major area, which it needs to improve especially in this kind of business sis its human resources or staff management. In this nature of business, it is important in general to maintain proper coordination and efficient information network, which will help the company to deal with any kind of situation. Overall, one may say that the company already has a lot to work with and despite it given its resources, it may sustain for long despite competition provided it keeps up religiously to the objectives of cost effective product management and innovation.
The four Ps of marketing might be applicable in case of the company – price, product, promotion, and place. Determination of the right price for the right product is the first step and then comes determining the appropriate product mix for the market. Promotion of the new product involves large scale marketing campaigns and advertising while deciding upon the proper markets or locations for distribution of the products should precede this. Amongst these 4ps of marketing, the company under discussion should maintain focus on the price strategy and he product mix given the nature of its industry (Weigl, 2008).
Reference List
Aitken, J., Childerhouse, P. & Towill, D. (2003). The impact of product life cycle on Supply chain strategy. Elsevier Science B.V, p.12-135.
Bilton, C., & Cummings, S. 2010. Creative strategy: reconnecting business and innovation. London: John Wiley & Sons.
Böhm, A. (2009). The SWOT Analysis. Norderstedt: GRIN Verlag Publishers.
Cohen, L., Manion, L., & Morrison, R. (2007). Research Methods in Education. New York: Routledge.
Coutler, M. & Robbins, S. (2007). Management. New Delhi: Pearson Education.
Dacko, S. (2008). The advanced dictionary of marketing: putting theory to use. Oxford: Oxford University Press Publishers.
Daft, R. (1998). Management: Academic Service. London: Thomson Press.
Drummond, G., Ensor, J., & Ruth, A. (2007). Strategic Marketing: Planning and Control. Burlington: Butterworth-Heinemann Publisher.
Frances, J. (2005). The Six Essential Leadership Attributes. Web.
Hamermesh, D. (2001). The Changing Distribution of Job Satisfaction. The Journal of Human Resources, Vol. 36, No. 1, pp. 1-30.
Hitt, M., Ireland, D. & Hoskisson, R. (2009). Strategic management: competitiveness and globalisation. Boston: Cengage Learning.
Hui, M., Au, K. & Fock, H.(2004). Empowerment Effects across Cultures. Journal of International Business Studies, Vol. 35, No. 1. pp. 46-60.
Janssen, O. (2001). Fairness Perceptions as a Moderator in the Curvilinear Relationships between Job Demands, and Job Performance and Job Satisfaction. The Academy of Management Journal, Vol. 44, No. 5, pp. 1039-1050.
Jones, G. & Hill, C. (2009). Strategic management theory: an integrated approach. New York: Cengage learning.
Johnson, G., Scholes, K. & Whittington, R. ( 2008). Exploring Corporate Strategy: Wimm-Bill-Dann: 15 years in business. 8th ed. London: FT/Prentice-Hall. pp. 773-778.
Karami, A. (2007). Strategy formation in entrepreneurial firms. London: Ashgate Publishing Ltd.
Klein, H. (1989). An Integrated Control Theory Model of Work Motivation. The Academy of Management Review, Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 150-172.
Miles, R. (2003). Organizational Strategy, Structure, and Process. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
Mullins, B. (2009). Coffee and the Recession: Few Four Buck lattes, but more Great Coffee. The Coffee Bean International Company.
National Coffee Association of the United States, Inc. (2009). National Coffee Drinking Trends. Web.
O’Brien, J. (2003). Management Information Systems. New Delhi: The McGraw-Hill Companies.
Osterloh, M. & Frey, B. (2000). Motivation, Knowledge Transfer, and Organizational Forms. Organization Science, Vol. 11, No. 5, pp. 538-550.
Robertson, P. (1994). The Relationship between Work Setting and Employee Behaviour- A Study of a Critical Linkage in the Organizational Change Process. Journal of Organizational Change Management, Vol. 7 No. 3, pp. 22-43.
Sadler, P. & Craig, J. (2003). Strategic Management. New York: Kogan Page Ltd.
Sekaran, U. (2006). Research Methods for Business: A Skill Building Approach. New Delhi: John Wileys & Sons.
Smallman, C. (1996). Risk and organizational behaviour: a research model. Disaster Prevention and Management Vol. 5, No. 2, pp. 12–26.
Waldman, D. & Yammarino, F. (1999). CEO Charismatic Leadership: Levels-of-Management and Levels-of-Analysis Effects. The Academy of Management Review, Vol. 24, No. 2 ,pp. 266-285.
Weigl, T. (2008). Strategy, structure and performance in a transition economy. Berlin: DUV.
Winterton, J. & Winterton, R. (1999). Developing managerial competence. London: Routledge.
Zeithaml, A. & Bitner, J. (2005). Services Marketing. New York: McGraw-Hill.

