Background of the company
The largest automotive manufacturer Toyota Motor Corporation is a multinational entry occupying headquarters in Tokyo and Aichi of Japan formed in 1937, though it was just Toyota Industries from 1934 to 1936 and produced different types of engines and the 1st passenger vehicle- the Toyota AA. At present, the company has ownership of an assortment of worldwide renowned branded cars such as Lexus, Scion, Isuzu, Yamaha, and Mitsubishi and the company possesses almost 522 subsidiaries at home and abroad. Recently the company has enacted into a Formula 1 functionality group in the course of accruing Citroen and Peugeot, the French automobile company and started to manufacturing motor vehicles in France while the company has engaged 397.05 billion yen of capital including 320808 employees for its worldwide operation. Moreover, during the 1st quarter of 2008, it has achieved the great award of being 8th largest auto manufacturer in the world, while in 2007 the company introduced Tundra branded truck in Texas and Indiana and recognized as “Truck of the year” and Toyota branded Camry as “Car of the year” for the same year in US market. In 2008 due to global financial crisis, Toyota has experienced some uncertain events during its entire life journey and the company had to give up its continuous record of profits and accounted for its first serious loss within 70 years.
Recession Impact on Toyota
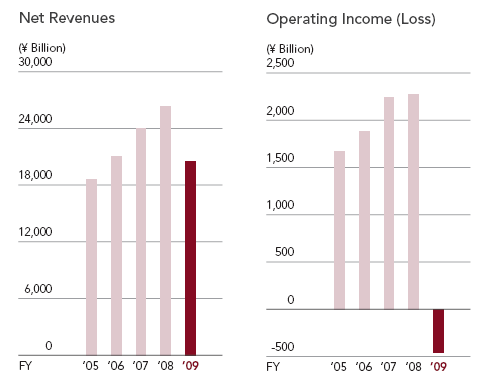
According to the annual financial report of Toyota 2009, the rapid deterioration of the world economy vehicles sales was down 1,346,000 units to 7,567,000 units, net revenues declined 21.9%, evidenced an operating loss of ¥461 bn, a net loss of ¥437 bn, operating loss of ¥850 bn, net loss of ¥550 bn, and increases operating costs of ¥491.30 bn.
Toyota Motor Co (2009) identified several reasons for this disaster situation, such as:
- Severely transforms the market demand including a marked shift toward small vehicles and low-priced vehicles, which is the major cause to reduce total sales;
- the fast appreciation of the Japanese yen against the US dollar as well as the euro decreased the profitability of exports;
- Increase operating costs due to unstable condition of foreign exchange rate
SWOT analysis of Toyota
The strength, weakness, opportunity, and threat of Toyota would consider to finding out its position in recession:
Strengths: Some stronger factors of Toyota are:
- Brand awareness is the main strength of Toyota to make positive image in customer’s minds;
- In 2005, large investment in US and China to offer the right mix of products showed increase of profit up to $11 billion;
- According to the annual report 2008, it is second largest car manufacturing company 6.78 million units in the world;
- TQM (2009) pointed out that evolvement of a variety of differentiated and present approaches excluding TQM involving JIT;
- Strong global supply chain management, and positioning strategy, for example, it has operated in 170 countries in the world.
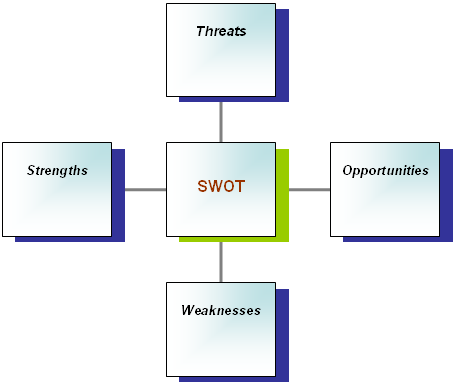
Weaknesses: There are some drawbacks, which need to change:
- Due to fluctuated economic and political situations in Japan and USA, Toyota has to change its selling vision towards rising automotive car market of China as these two countries are Toyota’s basic selling market;
- Lower profit margin, fluctuated market share and unstable position in new market;
Opportunities: Though it is in serious economic crisis, it has huge prospects:
- Surprisingly, Tata Nano is doing well in recessionary period due to its lowest price, so Toyota has the opportunity to earn huge profit by introducing similar products;
- It has already gained emotional support of the customer for the manufacture of environment-friendly cars known as Prius and new Aygo by targeting “urban youth”;
- It has innovative power to sustain in such changing environment.
Threats: besides positive sites it has some challenges and these are:
- At this moment, global financial crisis is the main threat for Toyota because the buying power of customers is decreasing;
- Toyota has many national and international competitors, particularly in Eastern Europe and South Asia;
- Product recall is the major threat for the company;
- Instable condition of oil price, increase the rate of raw materials;
- The retailing policy of Japan & Australia is not favorable for the company;
Position of Toyota in BCG Matrix
The Boston Consulting Group approach is a portfolio planning process to assess Toyota’s market position in terms of relative market growth rate as well as relative market share:
- Star: before recession, Toyota occupies this segment due to high- growth, high-share business but it lost it position;
- Cash cow: It indicates the low growth with high- share business, which does not match with Toyota;
- Dog: It indicates low- growth with low- share business, which shows it needs huge investment to recover;
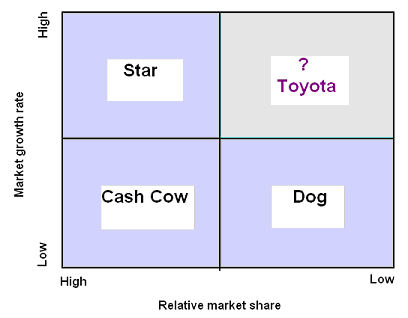
- Question mark: Toyota’s position in Question mark segment of the matrix due to global financial crisis, its recent fall of market share in Asian and European markets but with a favorable growth rate accompanied by growing buyer demand.
PEST analysis
It has featured for Political, Economic, Socio-cultural and Technological factors of the company (Hitt, Ireland, & Hoskisson, 2001), which are deliberated as follows:
- Political factors: The FDI policy of abroad regime especially China mainland, has twisted a major disclosure on Toyota’s Chinese operation as a joint venture imitative. At the same time, there are various governmental regulations and incentives; such as tax exemption, tax praise of automobile pool lanes due to plug-in crossbreeds proprietors. On the other hand antagonistic government mindset in Nigeria and socialist government in Venezuela, unrest environment in Middle East concerning Iraq war, Israel- Palestine conflicts for long run, and Iranian threats are posing major political influence on Toyota’s global operations.
- Economic factors: Recession directly affects the US and Japanese market of Toyota and the people of other regions choose cheapest products. In addition, escalating of oil and gasoline price, fluctuated worldwide demand for manufacturing cars, increasing pressure from new entrants and substitute products by domestic production intensity and purchasing power of buyers is the main reason to change the financial condition of Toyota
- Socio-cultural factors: Toyota is working to aware people in social interest issues, for example, corporate concern for natural environment, inconvenient trust of $42 million in box office in terms of huge celebrity endorsement for reducing greenhouse effect, which was also effective in creating positive image of hybrid vehicles (Toyota Industries, 2009).
- Technological environment: to keep competitive, it has introduced environmentally friendly technologies and it tries to strengthen technology to increase safety by considering customer’s demands, for example, decrease the weight of hybrid power train by 50% by decreasing cost of technology $2100, Intelligent Transport Systems, Anti- Lock Brake System e-TOYOTA, and Home Energy Management System etc.
Competitor analysis
This report will consider Porter’s five forces model of competition to evaluate the competitive environment of Toyota. These five forces are:
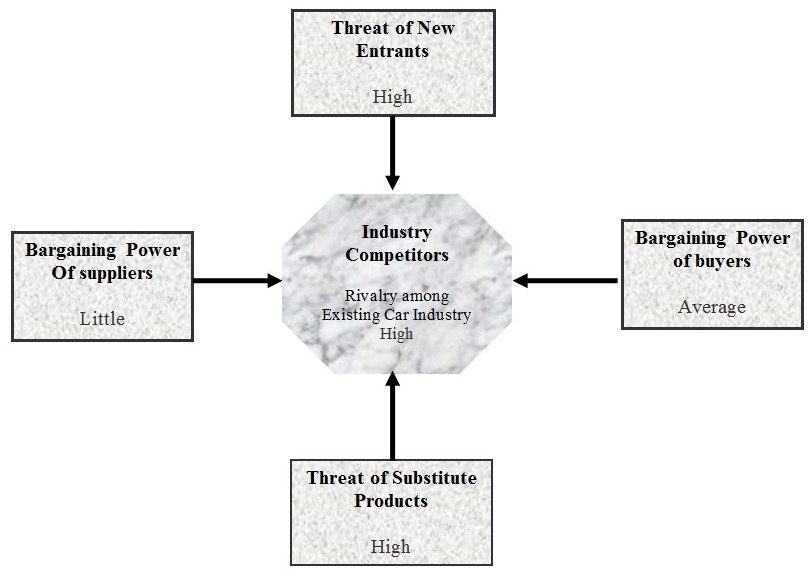
- Threats from new entrants: According to the annual report 2009 of Toyota, it is facing intense competition from automotive manufacturers in the global markets in which it operates because of a number of external factors (Toyota Industries, 2009). Such as, it has to suffer huge competitive stress from newer domestic carmakers of China and India due to parliamentary leverages and incentives concerning nationalism and these two countries are highly populated with low earner who intends to purchase the car of low price.
- Bargaining power of suppliers: for Toyota Corporation, the main suppliers are usually raw materials companies, which supply steel, aluminum, fuel, rubber, motor engine, and other body parts etc. The power of these suppliers varies considering area, such as, in China, bargaining power of domestic sellers varies concerning quality and price of the products. In addition, Lithium Lon Battery Manufacturers are the key suppliers’ group of Toyota for delivering technological components for manufacturing hybrid automobiles (Toyota Motor Co, 2009)
- Bargaining power of buyers: Before recession, buyers were comparatively less powerful in car industry because in most of the situations, they were mainly concentrating on quality and it differs from one marketplace to another. On the other hand, the current pressure for global financial crisis has altered this situation by escalating such power of customers.
- Threats of substitute products: Toyota has to suffer hard competition from some other alternative transportation besides different motor vehicles from other direct competitors, for example, due to recession people would like to use public transports like buses, railways, and trams etc. Toyota Motor Co (2009) argued that People usually prefer these types of substitutes because of availability and cheapness as their buying power has reduced.
- Rivalry among existing firms: In addition, it has also to visage many minor and greater competitors at both domestic and international stages. Berthiaume, Joshi, Longdo & Seshadri (2007) mentioned that it has to face huge rivalry and the major competitors of the company are Honda, General Motors, Ford motors, Mitsubishi, Land Rover, BMW and so on. However the following figure shows the global market share of hybrid cars of Toyota compared with other market players:
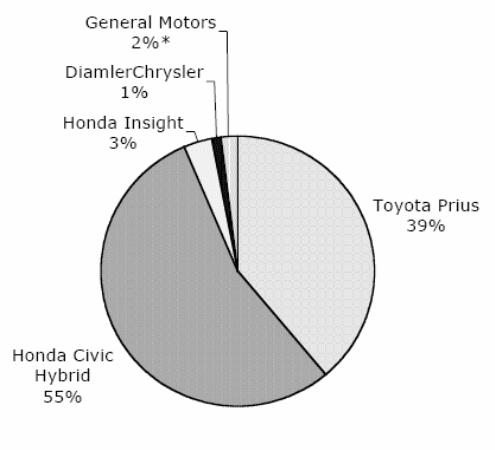
Though the competition is too high, all major companies have been adversely affected by the recession, for example, in 2009, GM’s sales had lowered by 30% than 2008 and cut a huge number of jobs with limited payments (GM Corporation, 2009).
Recommendations
The entire paper has considered the strategic issues, competitive advantages and some drawbacks of Toyota Company in present recessionary period. This paper would recommend few steps, which will help to recover from global financial crisis:
- Toyota has already recruited a management team to recover from recession and It should invest more for this team to research on the market and way out proper solution;
- It should maintain cost-effective strategy to sustain itself in global market;
- Toyota needs to be more responsive in meeting customer demand as the market is too competitive in terms of product, service, innovation, development cycle, loyalty, safety, price, fuel economy;
- The management should predict the market condition before lunch a new product because it would not be good decision to take high risk without considering purchasing power of buyer;
- It should introduce low-cost models like Tata Nano for both develop and developing countries;
- Toyota should keep more care on customers and should maintain good relationships with overseas suppliers, making a connection or mutual co-ordination with foreign policymakers by using latest technologies;
- As total sales are decreasing, it should increase the budget for marketing;
- It should use integrated marketing communication tools to aware customers about unsafe products;
- As e-commerce is becoming more powerful media for selling of various products, Toyota should develop B2B business;
- It should provide special offer for loyal customers;
- In addition, it should pay incentives, rewards and other facilities to formulate a better incentive plan
- Finally, it should control global distribution channel more carefully.
Conclusion
From the above discussion, it can be said that Toyota Motor Corporation is a giant auto manufacturer in the world but it would need a longer period to regain its glorious position in terms of more vehicle sales. However, this situation would not affect the firm for a longer period if would take some preventive measures to respond to that economic crisis and the recommendation of this report would help the company to recover from the recessionary impact.
Reference
Berthiaume, R. Joshi, B. Longdo, E. & Seshadri, V. (2007) Toyota Marketing Strategy for Plug-in Hybrids. Web.
GM Corporation. (2009) Form 10-K General Motors Corp – GM. Web.
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2001) Strategic Management. 4th ed. South-Western Thomson Learning.
IMI Research Department. (2009) The Automotive Retail Sector – Impact of the Recession. Web.
Mearns, E. (2010) UK new car sales and the recession. Web.
Pearce II, J.A. & Robinson, R.B. (2006) Strategic Management. 8th ed. London: McGraw-Hill.
Rodriguez, A. & Page. C. (2004) A Comparison of Toyota and Honda Hybrid Vehicle Marketing Strategies. Web.
Toyota Industries (2009) Corporate Philosophy: Basic Philosophy (Toyota Industries’ Corporate Philosophy). Web.
Toyota Motor Co. (2009) Annual Report 2009: The Right Way Forward. Web.
Toyota Motor Co. (2009) Company profile of Toyota. Web.
Toyota Motor Co. (2009) FY2009 Financial Results. Web.
Toyota Motor Co. Toyota in the World 2009. Web.
TQM (2009) Total Quality Management: 5S in Toyota Motor Corporation. Web.
UNCTAD. (2009) Assessing the impact of the current financial and economic crisis on global FDI flows. Web.
Wearden, G. (2010) SMMT says car industry faces bad year. Web.
Williams, B. (2010) Automobile Industry and the Recession. Web.
