Introduction
The management report of Samsung USA begins with a strategic analysis of the company with a detailed SWOT analysis of the organization based on its current position. It also identifies the specific strategic challenge that Samsung USA is facing and evaluates a number of potential alternative strategic options which the company possibly will consider addressing. This report also significantly discovers and critically evaluates a variety of key implementation alternatives and organizational changes which the company would be advised to take into account for further strategic development.
Short looks of Samsung USA
Samsung Electronics Inc., USA is a South Korea-based Multinational Corporation and the world’s second-largest cell phone manufacturing company. This paper would draw attention to analyze a number of aspects in the environment, resource capabilities, selection and implementation of strategies and their alternatives. Though the company has too many business wings, this paper would concentrate only on the mobile telecommunication sector. As a player in the telecommunication industry, it is crucial to have an obvious concept on this sector along with the global economic features, particularly in this company’s context.
The mobile phone market of the world had grown 22.2% in 2006 and is expected to be expanding by 125.50% within 2011 in relation to the growth rate of 2006 revolving it as one of the most competitive markets in the world while Samsung has detained the major market position of third with a total sale of 118 million mobile phones. In the third quarter of 2008, Samsung positioned second with a global market share of 15.20%
Environmental analysis
In order to analyze the environmental condition of Samsung mobile phones in the USA, it is necessary to consider PEST (Political, Economic, Socio-Cultural, and Technological) analysis which can be described as follows-
Political Factors
Samsung mobile phones are the most popular all over the world. As a result, it has been affected by the local rules and regulations when it imports its products. Kotler, P. (2006) mentioned that investment, investment policy, device supply, operation, and growth, as well as network development materials, could be an important topic of risk, over taxation, rate of exchange, savings of personal intelligence, recession, ups and downs of currencies and the other uncertainties. Global financial crisis creates some future uncertainty expenditure of the customer which may affect on discretionary of the customer for example now customers would like to purchase other essential products than a new model mobile phone.
Economic factors
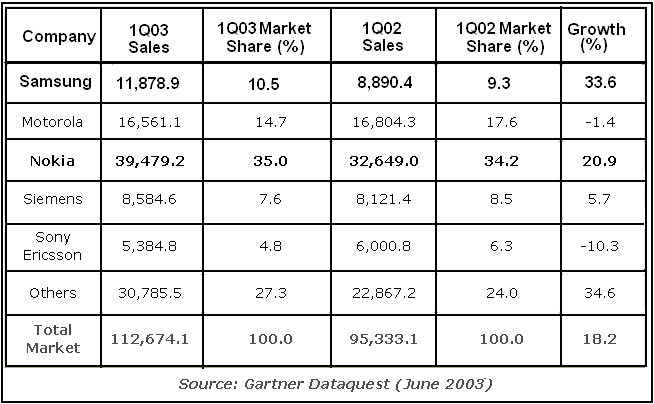
The sales of Samsung mobile phones are reducing than last year. As a result, it has a great impact on the net profit of this company. Therefore, it should be more careful with target customers. The recent global financial crisis may reduce its sales. The view of the economic condition of Samsung USA in comparing with global mobile phone manufacturing leaders can easily be seen through the following chart-
Table 1: Analysis and comparison of the economic condition of Samsung USA.
Socio-cultural factors
The commitment to corporate social responsibility (CSR) enables the company to provide social, economic, and environmental satisfaction to the public. Since 2005, Samsung Electronics is encouraging the Adopt-a-Village program contributing to the farming group of people in China. In 2006, over 4,650 staff of this company had volunteered for 150 different actions prearranged for these “adopted” communities. In Korea, more than 13,000 staffs are prepared to connect in a variety of programs, for example, support at social welfare foundations or helping children in require. It has 20% of total employees engaged in the R&D department, and it may increase up to 32%. Its culture influences quick decision formulation on a plain, formulated network though it is characterized by a huge bureaucracy.
Technological factors
For Samsung mobile phone, the technological factor is the most significant factor among other factors. Only for technological development, its sales rise 24% within the last ten years. In 1995, it sold only 41 million mobile phones all over the world. On the other hand, in 2006, it has sold worldwide 950 million phones. Samsung USA conducted research with NAVTEQ and CalTrans for further innovation. Sensor technologies offer huge consciousness about the environment. Samsung USA mobiles are able to contact and control household electronic instruments. Next-generation of Samsung mobile phone’s technology was applied to expand the world’s initial 1GB DRAM using 50-nanometer manufacture processes as well as 32 GB NAND flash memory through 40nm processing.
SWOT Analysis of Samsung Electronics Inc
Strengths
- Samsung hired and promoted superior R&D engineers to be equipped for the future.
- 26% of the whole workforce of Samsung has been occupied in research and development.
- In the US, Samsung has registered about 2,400 innovative patents in 2006 and scored second place.
- Samsung Electronics has coordinated world-class IT facilities with mobile communication in 2006.
- The next-generation wireless communication method Mobile WiMAX had been introduced by Samsung in 2006.
- IT sector integration with 1 GB DRAM, 50 nm (Nanometer) processing and 32 GB NAND, also a one step forward strength of Samsung.
- The unparallel design philosophy is a resourceful strength of Samsung Electronics that provides corporate competitiveness and draws customers’ attention.
- The skilled human resource, financial soundness, leadership in technologies, innovative products, secure creative markets, and momentum growth provide Samsung Electronics an aggregate strength.
- As a first-generation mover to China, Samsung takes pleasure in advantages over late-comers for labor costs and tax holidays.
Weaknesses
- Samsung would be obliged to continue its control all over costs to sustain success.
- The factory location in China has a status of the protected market.
- Japanese first comers in China enjoyed more advantages than Samsung.
- In the US market, companies such as Motorola had built strong sales and service networks that Samsung would have to achieve in that area.
- Samsung needed a more cost-effective solution for pricing and accessibility for all sorts of customers.
Opportunities
- The people working in team spirit at Samsung are dedicated to constructing the impossible into possible and rotate the calamity into an opportunity.
- The creative ideas of management Samsung and innovations would open a new dimension for further opportunities for the company.
- As an Asian-originated, Samsung has the wider opportunity to drive more seriously in the South Asian population density market like Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan than the other competitors.
- Samsung follows the Six Sigma methodology as well as cost-cutting practices.
- Samsung emphasizes training the top management of supplier companies.
- It also offers overseas training for its own staff to be experienced at the Toyota Production System.
- Samsung’s supplier chain support program drives to execute innovations at suppliers’ end.
Threats
- The most recent US economic recession is a burning threat for Samsung Electronics Inc.
- If the recession long lasts, then it will carry more market risk for Samsung in the USA.
- Samsung faces extreme competition in the global mobile phone market.
- The higher valued product possibly will not be sold in large volumes. Thus, pricing would also be a problem.
- Samsung lacks its traditional marketing strategy.
- Emphasis on Develop
- Declaim in profitability since related to over-employment among the majority services
- The decreasing per capita income in the developed markets like the US can affect Samsung’s sales of the product at every level.
- The increasing non-brand mobile phones are winning market share in less developed countries and raising a threat around the world.
Resources and Capabilities
Samsung wined and implemented the bid of Beijing Olympic 2008 to provide support for telecommunication and technical aspects of the event. As a sponsor and global coworker, Samsung spends $ 70 million, and it gained resulted in a big growth both in China and globally. Meanwhile, Samsung invested $ 21.7 million for its green strategy in 2008.
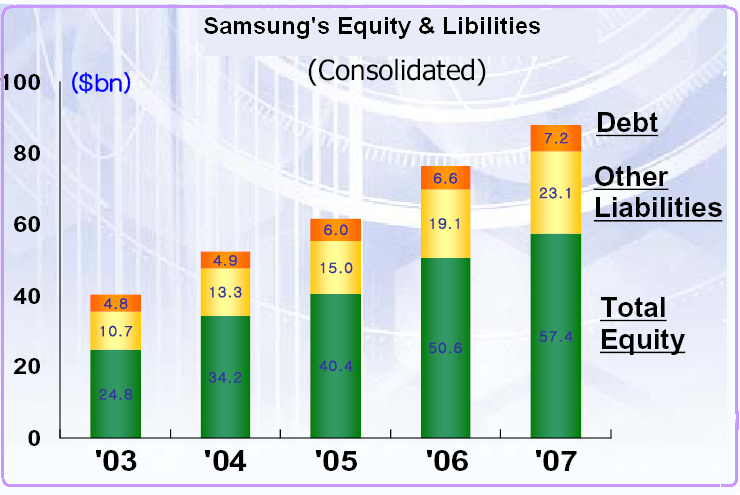
Samsung Electronics Inc generated total profit after tax in 2003 accounted US $ 7.7 billion, in 2004 US $ 9.1 billion, in 2005 US $ 9.0 billion, in 2006 US $ 10.0 billion, and in 2007 US $ 11.9 billion. As a result, the company’s ROE (Return on Investment) stands at 22%, 33%, 20%, 18%, and 15%.
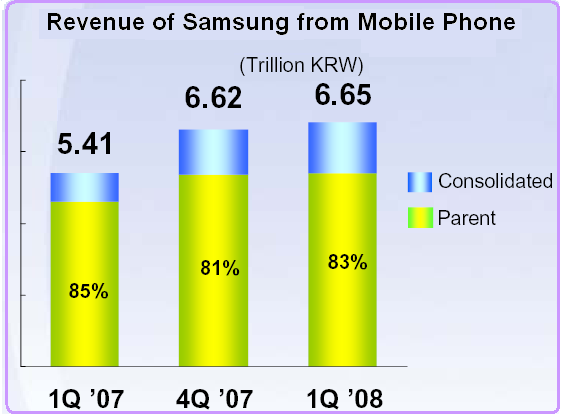
Samsung’s revenue generated from the sales of Mobile phones 5.41 Trillion KRW (South Korean Won) in the 1st quarter of 2007, 6.62 Trillion KRW and 6.65 Trillion KRW in the first quarter of 2008.
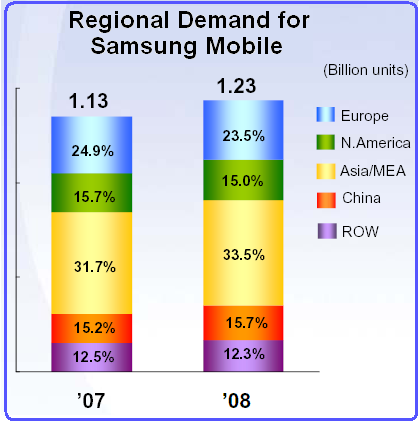
Samsung mobile phones had sold 1.13 billion units in the global market in 2007. In 2008, it accounted for 1.23 billion. Depending on the sales, the regional marker size has determined as 15.7% in the US market, 24.9% in Europe, and 31.7% in the Asian market in 2007. But in 2008, it stands 15.0% in the US market, 23.5% in Europe, and 33.5% in the Asian market. The significance is that the sales in US and European market declaimed in 2008 when. The Asian market is growing.
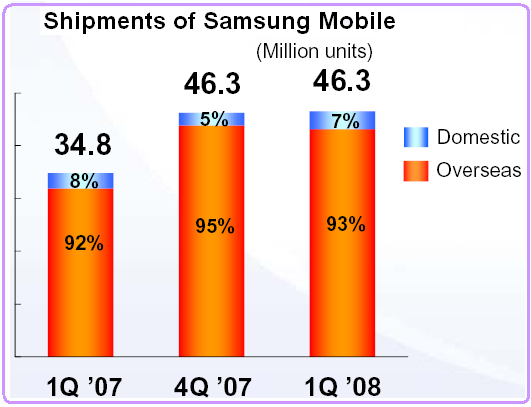
In the 1st quarter of 2007 Samsung Electronics accounted the sales of Mobile Handset were 34.4 million, in the 4th quarter of 2007 it was 46.3 million which remained same in the 1st quarter of 2008. Among them the domestic demand accounted in the 1st quarter of 2007 was 8%, 5% in the 4th quarter of 2007 and 7% in the 1st quarter of 2008.
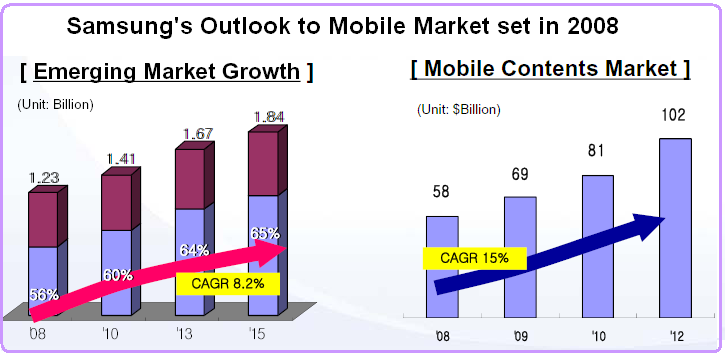
The forward-looking management of Samsung Electronics Inc has generated a steady growth for the last three decays, and the company has set up its future outlook to the mobile market with an emerging market portion in 2008, 56% → 15, 66%. The company’s net balance in 2003 accounted for the US $ 7.7 billion, in 2004 US $ 9.1 billion, in 2005 US $ 9.0 billion, in 2006 US $ 10.0 billion, and in 2007 US $ 11.9 billion. The management has fixed up its sales target of 1.41 billion units for 2010, 1.67 billion units for 2013, and 1.84 billion units for 2015.
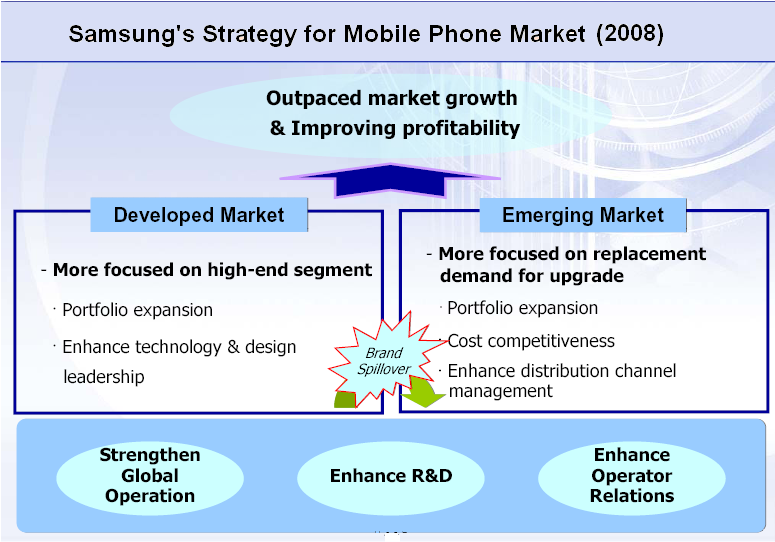
Existing Strategy of Samsung for Mobile Phone
Samsung Electronics published its Telecom strategy on September 3, 2008. Though the strategy has been designed with the concurrent momentum of the US recession. There is no significance or action plan on the recessionary economy of the US market. However, the present strategy emphasized on:
- To expand product assortment and carry on to outpace the market expansion.
- To increase product segments: Samsung emphasized style, connectivity, vital business, multimedia as well as infotainment integration.
- Smartphone: Samsung highlights on diversify effectual system and improve the user edge.
- To enhance product competitiveness, it emphasized content and mobile internet.
- by channel development and categorized products uninterrupted expansion in the rising market.
- Outlet optimization: It emphasizes the zone, regional, and national allocation as well as direct sales.
- Confined features: It highlighted long-time sequence, favored design, finest design, and color setting.
- It emphasized Segments integration of Multimedia, Business, Infotainment, Connected, and Basic Styles.
- It emphasized on Linux operating system in mobile.
- Samsung’s mobile strategy emphasized enhance cost competitiveness.
- Picked up R&D capability, distended overseas production, amplified consistency, and make the best use of operational efficiency.
Formulation of strategies
Samsung’s total current liability has increased 8,983,073 to 10,371,383 within one year. As a result, it should require to consider its strategic analysis. Chernev, A., (2007) explained that strategic options are a coordinated and interrelated set of actions, which has been designed for developing the core capacities as well as competencies for achieving competitive advantage. Therefore, consistent with the strategic model, Samsung USA can create several strategic options through several systematic phases from business-level to international strategy.
Business-level strategy
In 2006, its cost of sales was $63,479,833, and the net income was $8,531,848, which indicates Samsung USA’s industry position. Samsung can generate Porter’s five forces view as its business-oriented strategy. For example:
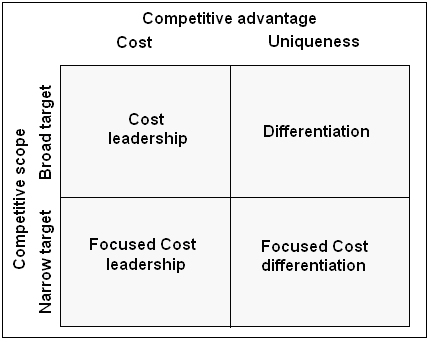
- From the cost leadership strategy, Samsung can deliver the extremely sophisticated electronics home set and commercial cellular phones at lower costs relative to Nokia, Sony Ericsson, Motorola, Bird, Gionee, and other major competitors.
- The separation strategy advocates the selling of non-standardization of mobile phones to go with the unique demand of consumers by adding Internet options, portable computers, TV, games, cameras, and other digital junctions with the Samsung mobile handsets. Consequently, further customer satisfaction along with connecting people would be possible to allege premium prices even though there are a variety of significant factors such as opposition with competitors, buyers, and suppliers’ bargaining influence, threats of new entries, and substitutes.
Competitive dynamics
In this stage, Samsung mobile can achieve competitive dynamics by series of competitive actions and aggressive responding among the competitors of the industry by analyzing a number of factors such as market commonality, resource similarity, market dependency, own size, innovation, and quality of the products.
Corporate-level strategy
Samsung USA can highlight diversification from low to moderate to an extremely high level whilst in low level it can earn 75% of total profit from telecommunication sector and 50% to 75% from the dominant business. By a joint venture, Samsung mobile can promote a new venture with others by the combination of resources.
Acquisition and restructuring strategies
By using the acquisition strategy, Samsung USA can purchase controlling or 100% interest in other businesses with the intention of utilizing an efficient core competency through converting that firm as its subsidiary. Each year it makes a huge profit from its subsidiary. It can apply such strategy to increase-
- Market influence.
- Effective service in consumer internet.
- Self-managed mobile organs.
- Formulation and share of photos, videos as well as customized media through the users’ mobiles and desktops.
- Enthusiast plan, execute, and optimize cell advertising campaigns.
In addition, by restructuring, Samsung USA will be capable of maintaining the fall in acquisition with others by altering the operating sets or financial structure. It can take numerous forms. For instance, downsizing will decrease the worldwide employees and existing units by or by not changing the company’s portfolio.
International strategy
Since Samsung is operating and distributing its services all over the world. In order to become a successful performer in the international market, it should consider the following aspects:
- Factors of production.
- Demand conditions.
- Related and supporting industries.
- Samsung’s strategy, structure, and competition.
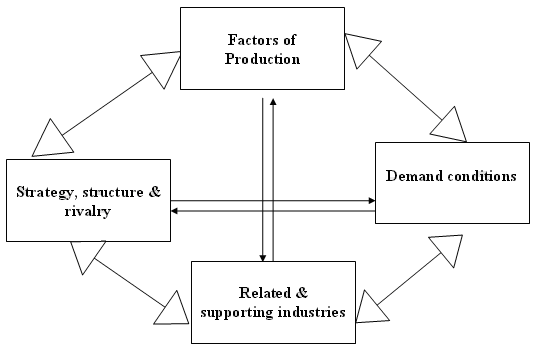
Thompson A. et al. (2007) stated that its global store base is growing vastly while the company is obtaining contribution of renowned global segments by the investment and the emerging that segment. Developing an international cost leadership strategy will enable Samsung to gain economies of scale with vast demand, like- third world countries. In 2006, Samsung sold about 118 million mobile phones and generated huge profit from its international market.
Strategic Challenges of Samsung Mobile
In this present digital era, as the world’s No-2 Mobile phone manufacturer, Samsung Electronics has to face the following strategic challenges:
The challenge of entry
The challenge of entry for Samsung Mobile depends on which digital features the company would like to integrate with its mobile handsets. At the same time, there are also challenges of entry with a new market drive. In this regard, Samsung would have a lower level challenge of entry from new companies. But from Big players like Nokia and Motorola, or LG, there are high-level challenges of entry. As Samsung already bid Motorola and gained the second position, Motorola would engage its effort. Moreover, Nokia would fight to keep its own position at the top when Samsung would like to achieve the first position.
The Challenge of Rivalry
The challenge of rivalry in the global mobile handset market is very high. When Samsung emphasizes its only competitive advantage of R&D, the company has to compete on the level of technology and price. The high strength and steady competition in the mobile handset market’s main competitors are concerned with new products variety.
The Challenge of Substitutes
Substitutes for the mobile handset rose with a company’s model by another model of a different company with more features with the suitable price level in order to compete and formulate profits. Moreover, Mobile phones are also substituted by LAN (Local Area Network) phones with Internet and email features. On the other hand, the I-phone of Apple is also a challenge for Samsung mobile, which could be a substitute for a mobile phone.
The Challenge of Suppliers
For Samsung, the challenge of suppliers would be high based on how many products the suppliers have differentiated. Developing the best supply chain management as well as long-term personal contact with suppliers is very significant for Samsung electronics to overcome the challenge of suppliers.
The challenge of Buyers
The challenge of buyers is huge for Samsung. Buyers are the essential factor in the retail process. In the consumer mobile phone industry, there are numerous products with diverse prices and unlike features. A buyer would decide where and how to buy. The buyer’s decision-making process is very complicated, which Samsung Electronics needs to take into account.
Appropriate selection of strategies
From the proposed strategies to choose the appropriate strategy, Samsung USA would consider the following:
- The first and principal strategy would be concerned to connect people worldwide in improved means.
- The differentiation strategy to lead growing and accelerating internet and business solutions for a mobility solution, connectivity, protection, service level, as well as marketing.
- It argued for balanced manufacturing capacities in the lower-wage zone like India and China.
- To strengthen consumers support and logistics on the basis of transformation of the infrastructural solution has been urged.
- The competitive dynamics and global strategy faced to the consumers, brand development, supply chain, and channels and technology.
- Outsourcing of assembling and mobile engine production amount encouraged.
- Preferences of multi-domestic strategy by worldwide supplier network developing.
- Collaborative strategy for research within the same industry.
Recommendation
The most recent political economy of the USA is very alarming. The recession has seriously affected consumption and customers’ purchase power. The Bailout Bill already failed to recover the market dynamics and prevent the current unpredictability of falling oil prices, account surplus, and overseas asset position. If the recession goes for the long run, the situation of the US market will turn into an unpredictable condition. For a real progression of the Samsung mobile, the company needs to re-design its strategy for the US market and reduce its dependency on the US market, and at the same time, it is urged to increase the market drivers in the south Asian market, especially in Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan. To continue implementing more effective strategy, Samsung USA recommended as:
- Samsung needed to configure its products, services, solutions portfolio originated from competitive operations with an artistic image balanced design, as well as value recognition.
- To minimize the risk of US recessionary impact on US currency and probable inflation Samsung needed to invoice for its items in Euro or KRW other than US dollar.
- It needed to take into account the US recession and its impact on the global market to consider adverse economic conditions for which the global effects may reduce.
- It is physically powerful and aware safeguarding of brand name to sustain and develop current market share and operation.
- Samsung would emphasize mass customization and co-branding with new companies.
- Due to the slow extension of global subscribers, substitute of sales of current devices by the demand precipitate services should be introduced.
- It needed to consider the changing dimension and characteristics of the global mobile market by sustaining quality, demand, and effort to guard the segment sales and profitability.
- Samsung is required to continuing its investment in the infrastructure of network equipment and R&D.
- Samsung’s cost management is mostly imperative to look after price erosion by analyzing the next generation pricing of the company through the introduction of cost-saving devices.
- Samsungs wide expansion of suppliers, efficient and effective execution of logistics required to be more ensuring customer’s safety, trust as well as values.
Conclusion
The present strategic analysis of Samsung mobile in the USA has addressed the critical problems and drawn attention to the company’s recent pose to the global market, its strengths, and weaknesses, major competitors, along with several opportunities and threats. It has been recognized that Samsung’s major goals and objectives have maximized profit by developing the advertisement, sales promotion, brand development using overall marketing mix components. The particular strategies that have been recommended would be functional to achieve the goals. This could be forecasted that Samsung would be ever triumphant with its strategic management in the long run for customer satisfaction by proper planning; implementation, and Samsung USA would be recognized as the enhanced adopter of strategic functions.
Bibliography
- Chernev, A., (2007), Strategic Marketing Analysis, 2nd edition, Brightstar Media. Web.
- David, F., (2008), Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases, 12th edition, Prentice Hall. Web.
- Dess, G., and Lumpkin, G.T. (2008), Strategic Management: Text and Cases, 4th edition, McGraw-Hill. Web.
- Doyle P. D, (2004), Adding value to marketing: the role of marketing in today’s profit-driven organization, 2nd edition, London: Kogan Page. Web.
- Dibb, S. Simkin, L. Pride, W. M. & Ferrell, O.C. (2001), Marketing Concepts and Strategies, 4th ed., Boston, USA: Houghton Mifflin.
- Griffin, R. W. (2006), Management, 8th Edition, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston New York. Web.
- Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Hoskisson, R. E. (2001), Strategic Management, 4th Edition, South- Western Thosmson Learning, Singapore.
- Hill, C., and Jones, G., (2007) Strategic Management: An Integrated Approach, 8th edition, South-Western College. Web.
- Johnson, G. Seholes, K. & Whittington, R. (2006), Exporing Corporate Strategy: Text & Cases, 8th edition, London: FT Prentrice Hall.
- Kotler, P., Armstrong, G. (2006), Principles of Marketing, 11th Edition, Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited, New Delhi. Web.
- Kotler, P. (2006), Marketing Management, 11th edition, Prentice Hall, NJ. Web.
- Porter, M. E. (2004), Competitive Strategy, Export Edition, New York: The Free Press. Web.
- Stoner, J. A. F., Freeman, R. E., Gilbert, D. R. (2006), Management, 6th Edition, Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited. Web.
- Saloner, G., Shepard, A., and Podolny, J., (2001), Strategic Management, 2nd edition, John Wiley. Web.
- Samsung Electronics (2008), Business Outlook, Telecom: SEC’s Strategy. Web.
- Samsung Electronics (2008), Earnings Release Q3. Web.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (2008), Busiiness Outlook.
- Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (2008), Financial Highlights – Performance. Web.
- Thompson, A. et al (2007), Strategic Management, 13th edition, Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company limited, New Delhi, India.
