Introduction
Within the current fast-growing business environment, it is crucial to examine the fundamental role of the strategy that serves as the determining factor regarding the future of a particular organisation. A strategy defines the long-term direction of an organisation and encompasses the process of managing people, relationships, and potential resources, which is why it is referred to as strategic management. However, the core elements of strategic management differ according to the scope of the business, the target audience, location, strategy, financial budget, and human resources. As such, management strategies vary in small businesses, large multinational corporations, and non-profit organisations. Therefore, for the more comprehensive view on the strategic development and management of an organisation, the large international company, Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd, is chosen for the following in-depth strategic analysis.
When considering the strategy as a design approach, it is based upon two critical assumptions in terms of the manager’s work responsibilities. More specifically, managers should adhere to a rational decision-making strategy and focus on the optimization of the economic performance of their company. Furthermore, a strategy is also considered as the “deliberate intention of the leader” who is integral to the strategic vision of the organisation (Johnson, Whittington and Scholes, 2011, p. 398). Thus, a strategic leader takes a dominating position over the strategy development process. With that said, this strategic analysis provides a detailed study on Samsung Electronics, which is one of the leading multinational corporations in the economics sector. The main objective of this analysis implies a critical review of the external and market environments, evaluation of the company’s essential resources, and identification of the potential and future challenges of the company.
The Analysis of External and Internal Market Environments of the Company
Samsung Electronics is an international company and one of the global leaders in the technology sector, electronics and electrical equipment industry, and it ranks 15 in the Fortune Global 500 Companies. It is considered the second-largest technology enterprise that produces and provides electronic devices (Lee, Lee and Heo, 2015). The company is headed by a trio of CEOs, Ki Nam Kim, Hyun Suk Kim, and Dong Jin Koh, with the corporate administration office based in Suwon, South Korea. Samsung Electronics is a large multinational corporation operating on the global level through 169 subsidiaries.
Samsung is widely recognized on the international level for its transformative advancements in digital technologies. Starting as an analogue-driven product line, the company became a universal leader in technological innovation. As of today, Samsung Electronics positions itself as the world’s largest smartphone and mobile phone manufacturer. The company currently produces more than a hundred products of numerous varieties and models and involves operational branches in approximately 79 countries (Knöpfle, 2016.)
The company consists of three commercial divisions, including Consumer Electronics (CE), Information Technology & Mobile Communications (IM), and Device Solutions (DS) with the sub-division, such as Semiconductor (Semicon) and Display Panels (DP). In 2015, Samsung engaged “325, 677 employees in 80 countries, with 6 design, 34 R&D (research and development), 38 production, and 53 sales & distribution centres” with the key location across the world (Razdan, 2017). In 2018, the company withstood a challenging year when its industry-leading smartphone business encountered increased competition from Chinese manufacturers, including Huawei. Such smartphone competition lowered Samsung’s position in the market and made the company shut down one of its Chinese manufacturing plants. Despite the production outcomes, the South Korean technology leader managed to achieve the 4.5% rise in 2018 revenues compared to 2017 and increased its profits by 9.1%.
Analysis of the External Environment
Samsung Electronics provides the electronic devices and computing industry, which is marked by high growth rates and increased turbulence. According to Razdan (2017, p. 2), these factors are mainly determined by the “speed of technological obsolescence” and the prediction of Moore’s Law. This implies that companies in this sector have to put major investments into R&D and launch new products permanently. Despite the stabilized industry production growth, which demonstrates that it is on the point of reaching maturity, this sector still faces high turbulence because of technological advances, including OLED (Organic LED) display panels.
Samsung Electronics holds Eco-Council and working-level committees, whereby environmental experts and managers gather to share ideas about technological and regulatory trends for developing highly energy-efficient products. The company regularly monitors trends in domestic and international privacy and personal data protection and works on response plans to adjust to new or modified laws.
More specifically, this analysis reviews the external market within four significant sectors that define Samsung’s position in a global arena in the electronics business. The Korean conglomerate is the worldwide market leader in consumer electronics sectors, specifically in TVs with an international market share of 21.6% (Razdan, 2017). The industry encompasses other household equipment as well, such as refrigerators, washing machines, microwaves, and many others, which directly depends upon geographical scope. The market leader’s share in this sector comprises not more than 20%. Samsung Company is also a leader in the smartphones market, with a global market share of 21%. With the semiconductors, the company takes a leading position with a global market share of 45.3% in DRAM, considering that three companies govern 90% of the market (Razdan, 2017).
Samsung is the world market leader with 37.5% of the global share in NAND, where six companies control the total market (Omer, 2019). However, in the display panels sector, LG Electronics is leading the overall market. Samsung Company, in turn, is the market leader in the small display panel category with a 23% market share. Regarding the new technology OLED display panel area, the Korean company is once again leading the market with over 90% market share (Razdan, 2017). Nonetheless, Samsung is in a constant encounter with the international market competitors that also pursue a fast-growing development and focus on technological innovations, such as LG that launched a new OLED production facility. In addition, the analysis of the external environment includes a PESTEL analysis framework that is used to comprehend better the scope of external factors that, in some way, affect the competitive climate within the industry.
PESTEL Analysis.
Analysis of Internal Environment: SWOT Analysis.
A Critical Evaluation of the Company’s Key Resources
Samsung Electronics presents itself as a global player since its main ambition implies establishing a sustainable competitive position in the key markets across the globe. Therefore, as a global player, the leading Korean conglomerate is focused on building an integrated business system of designs that are distributed through the key markets. To reach such international recognition and become a leading multinational manufacturer, the company employs and enhances its key resources that help achieve successful strategic business outcomes. As described by Jung (2014), companies need to implement innovative strategies and open management approach, which eliminates all the restrictive and discriminatory institutions and practices to compete on a global scale. As such, the potential set of critical resources that the company obtains, including human resources, technology, marketing manufacturing, and design departments, dramatically increased their significance as competitive resources, more than ever before.
As reported by multiple researchers, Samsung Electronics is notable for using such essential resources very effectively. For this reason, several management scholars and practitioners used Samsung company as a successful exemplary case of the leading global company. When speaking of the company’s resources that define the potential and the future of the enterprise, it is also important to examine the concept of innovation momentum of the organisation. It is considered the impetus to autonomously increase energy and speed up the growth, which contributes to the reduction in using the resources and achieving high profit. Apart from transferring the company’s novelty techniques, supporting the access to the foreign market, and setting up IT infrastructure, Samsung Company also implemented suppliers’ innovative capability. This was accomplished through “financial support, plant advancement, technology development, and human resource development” (Lee, Lee and Heo, 2015, p. 5). With that said, Samsung Electronics’ innovation impulse reached a well-balanced arrangement of philosophy, conditions, and strategy for the past twenty years.
Key Company’s Resources
It is apparent that the main focus for Samsung, as one of the global market leaders, is to remain competitive in the international market instead of earning short-term instant results. Hence, Samsung Electronics employed and developed the business philosophy aimed at reinforcing the suppliers’ potential and taking a leading position as an internationally qualified organisation based on transparency and a trust-oriented culture. The Samsung Corporation reorganised its relationship with suppliers by transforming its management system. Lee, Lee and Heo (2015) analyse three main stages that led the multinational company to the successful supplier partnership strategy using the company’s potential resources. The first step implied framing support on the critical company’s resources, including finance, technology, and human resources. As the second step, Samsung Electronics developed an equitable trade system to carry out transparent management. This includes managing the company’s resources, such as a change in commodity prices and technology deposits. The third stage involves exerting efforts to form a confidential relationship for enhancing mutual partnership.
Human Resources
Human resource management encompasses the support activities section in terms of Porter’s well-known value chain model. Samsung Electronics adopts open management in the context of the personnel management system. According to Jung (2014), the key aspect of open human resource management implemented by Samsung is promoting equal opportunity, prioritizing skills, and recognizing human potential. Such an open approach to human resource management indicates respect to the autonomy and creativity of employees, as well as excluding any obstacles in systems and practices to improve the efficiency and competitiveness of the workforce. At the same time, this strategy implies facilitating transparent management to grow in compliance with their customers.
To be more specific, such a strategy regarding human resources entails that all the employees should be provided with equal opportunities available without any discrimination and restrictions. Therefore, compensation and promotion are openly distinguished according to the individual’s skills set. The payment is, thus, based on employee’s performance and performance-based promotion. One should note that human resource is of the utmost importance to Samsung’s strategic success. By establishing a new management system, Samsung moved ahead towards its primary objective of becoming a global first-class company based on its “People first” management philosophy (Fig.1). As a result, the improved HR promoted a new management system through capital accumulation in human resources, and it also changed the awareness and actions of employees.
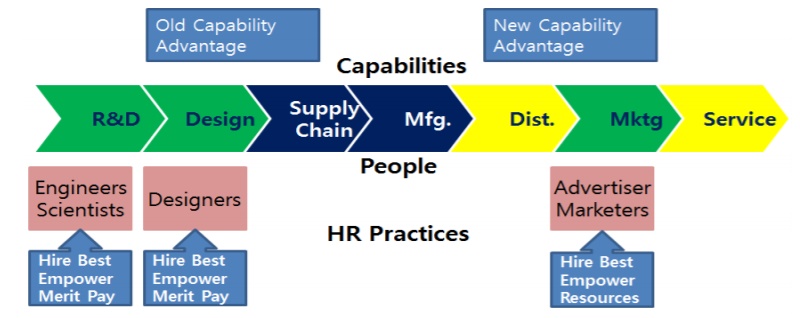
Supplier Partnership Strategy
Concerning the relationship-building process in HR, Samsung Electronics’ CEOs visit suppliers regularly to take into account their problems (Samsung Electronics sustainability report, 2019). In addition, the executive director incorporates open communication with the company’s suppliers through conferences and a cyber petition system. Samsung’s supplier partnership strategy helped the company to enhance its level of competitiveness in the manufacturing chain and obtain efficiency and flexibility by discovering and building new suppliers and integrating their ideas.
Samsung Electronics established its fundamental philosophical basis targeted at procurement improvement, fair management, and social trust management for developing a successful supplier partnership strategy and putting it into practice. Considering such a critical starting point for this strategy, the Korean multinational corporation effectively handled its management innovation process due to internal innovation and partnership with sub-contractors. Therefore, the successful strategic actions towards strengthening supplier partnership resulted in the incorporation of subparts group and process technology.
Financial and Technology Resources
Financial resources of the particular enterprise are engaged in the firm infrastructure’s operations in the face of financial assets that are responsible for the support activities in the value chain model designed by Porter. Financial support regarding the company’s strategic management consists precisely of “development fund, co-prosperity fund, and cash payment to ensure suppliers’ liquidity” (Lee et al., 2015, p. 5). Concerning the support of technology resources, it was conducted through customized support that Samsung Electronics allowed for assessing outstanding manufacturing sites and advised on advancing productivity and quality (Fig. 3). The company also supported the fresh patent technology transfer and environmental integrity. Moreover, Samsung Corporation aimed for achieving stability in managing its partners by organizing training and seminars for the personnel and future managers.
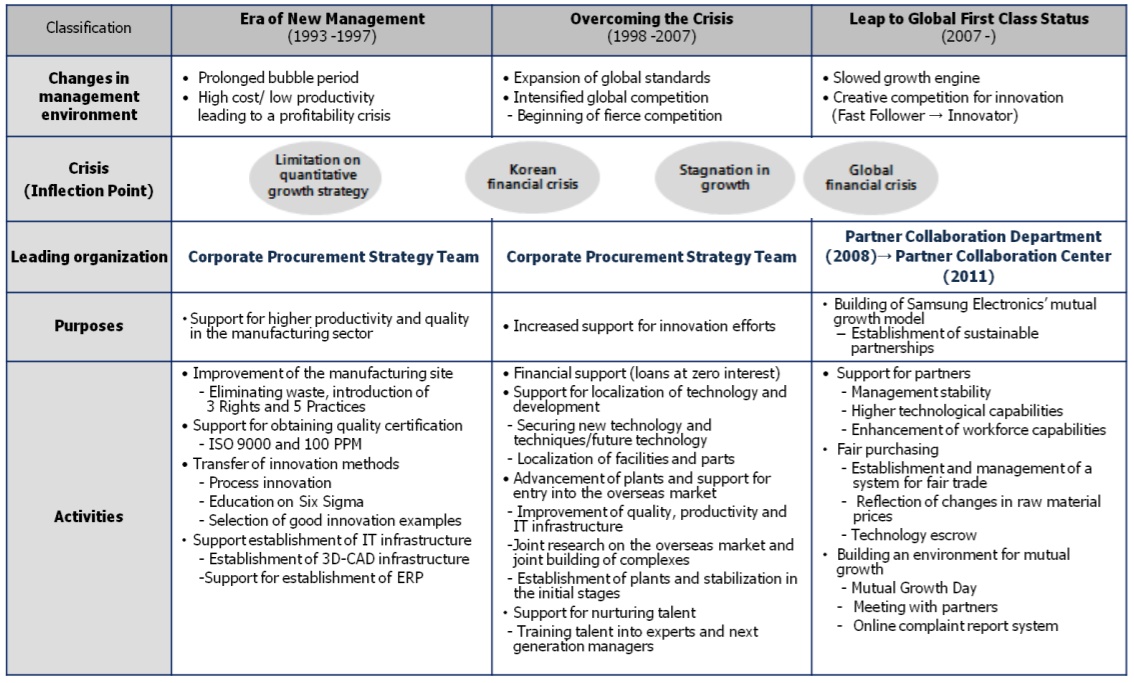
Company’s Core Competencies and Value Chain Analysis
Apart from the examined resources owned by the company, including talent and investments, there is another critical factor that defines a company’s success, such as the company’s core competencies. Any global organisation should possess vital competitive forces in both technology and process sectors to become leading in the marketplace. Within the electronics and computing industry, the companies aim for product affordability, its key features, and product quality.
Razdan (2017, p. 5) determines the critical success factors that facilitate these main requirements, including “low cost of production, investment in production facilities, high investment in R&D, and availability of talent.” The Samsung Company’s competitive advantages are based on RBV analysis conducted by Razdan (2017, Fig. 3). First, they include technology research and product development capability encompassing 34 research and design centres throughout the world. The company is also influential in its human resources talent, including “more than 50,000 research scientists, engineers and product designers,” which is 16% of the personnel (Razdan, 2017, p. 6). Furthermore, its key competence implies the brand value of Samsung as a superior company, with a valuation of US$ 51.81 million and 7th position at the world level in 2016.
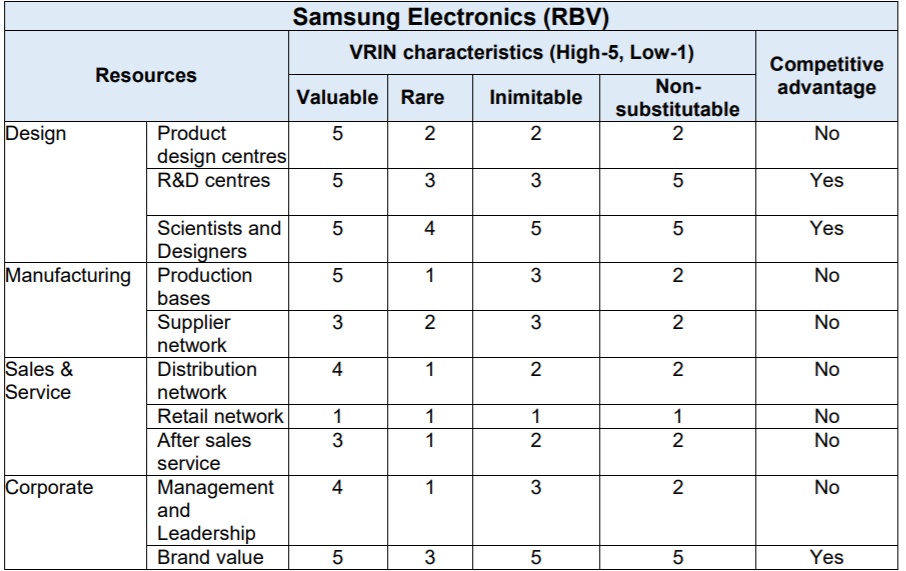
When Samsung was entering a global first-class status, the company expanded upon its management philosophy. This includes elaborating on advancement in procurement-related activities, equitable and social trust management to the increase in the international proficiency, transparent approach, and creating a trust-based corporate culture. Moreover, the validated supplier partnership strategy and its systematic practice helped the organisation achieve common growth in the global market with the corporate partners.
Samsung Electronics also remodelled its procurement process team into a “partner collaboration department” that was expanded to a partner collaboration centre in 2011 (Lee, Lee and Heo, 2015, p. 6). The final stage of one of the Korean electronics leaders involved a well-designed and developed business philosophy. A new ideology aims at enhancing the suppliers’ capability and taking the role of a globally competent corporation led with transparency and trustworthy culture. To maintain the competence within the overseas market, Samsung increased support for supplier capacity to address the crisis that the company confronted. For this reason, it is essential to create a value chain that integrates core competencies of all areas regarding the particular organisation.
How the Company Adds Value
Based on the company’s robust competitive advantage, it is possible to say that Samsung Electronics creates more value than its rivals do. Nonetheless, the Korean conglomerate has a significant number of competitors in the global market, including Sony, Huawei, Xiaomi, Oppo; however, Apple is yet considered the biggest rival of the Samsung Company. Within international market research, Knöpfle (2016) defines the main reasons for how Samsung adds value to its marketing process. The first reason implies that the company makes considerable investments in research and development, which promotes the release of a new phone annually. Moreover, Samsung is proved faster in launching new technology products as compared to its main rival, Apple.
This is explained by the fact that one-fourth of the international workforce is employed in Samsung’s R&D department and the second position of the company in Fast Company’s “Most Innovative Companies 2015” (Knöpfle, 2016, p. 3). Another way for adding value and enhancing business outcomes is based on combining the strategy of Japanese and American approaches (Fig. 4).
To be more specific, the Japanese are known for introducing multiple products, while Americans are engaged in the selection and the emphasis on a small product range. By intertwining these two approaches, Samsung Electronics adopts horizontal diversification and vertical integration. Hence, the multinational brand is diverse with a broad range of products and is also specialized in manufacturing. One should also mention that the application of the Android operating system is considered both comparative advantage and disadvantage, which is the most popular customizable OS worldwide.
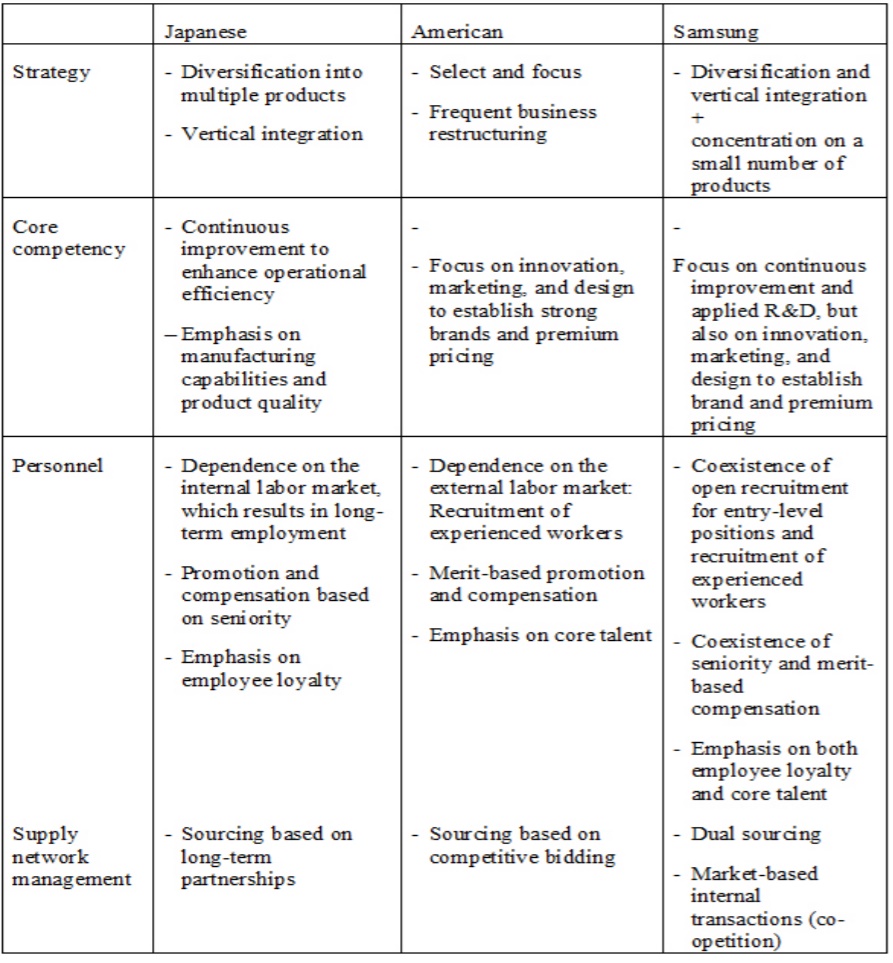
Future Challenges for the Company and Ways to Address Them
Despite the leading position of Samsung, the external business environment keeps posing new challenges due to its rapid growth and ongoing technological changes. The modern digital era is defined by the enhanced complexity and uncertainty regarding the corporate climate, specifically in the global arena. According to Jang et al. (2019, p. 12), such a business environment implies “increasing velocity of change,” which serves as a potential challenge for modern enterprises. As such, commercial companies must build capacities by innovation to respond to the change with promptness and resilience. It is important to understand that a good harvest is highly required for multiple nurturing steps, including effective planning, risking, and enterprise development.
Furthermore, Samsung needs to follow the ongoing process of planting innovation by fresh thinking, creative ideas, scientific progress, and new technologies. Razdan (2017) suggests that Samsung Company should acquire a settled retail chain to get support in the market, thereby increasing its brand value to recover market participation. Such strategic options will help the multinational corporation achieve an increased engagement with a broad spectrum of customers. In addition, Samsung will be enabled to foresee future trends in the industry supported by a high level of confidence and will, therefore, develop innovative products and services according to these trends.
Regarding the smartphones space, the Korean company faced a critical problem when its revenue and operating profit from the mobile segment fell 7% quarter-over-quarter. The main challenges for the mobile business involved the strengthened Korean won that facilitated high prices of Samsung’s products. Also, the company addresses competition enhanced from Chinese handset makers that offer similar technology but at lower prices. Another crucial challenge was associated with particular products, Samsung’s high-end flagship product Galaxy S6, which failed to gain the sought revenue. This led the company to decrease the price of the device in only three months after its launch date, which, in turn, marked a slowdown in sales within the smartphones industry. Samsung’s key strategy to address such critical challenges is based on promoting revenue growth by implementing a double-digit margin in the mobile sector. This strategic action is achieved by rationalizing the smartphone product portfolio, capitalizing on smartphone demand, and enhancing competitive advantage through software, hardware, services, and wearable items along with the company’s smartphones.
Conclusion
By taking a leading position in the global market, Samsung proves its fundamental role and impact on the modern technology-oriented consumer. However, the company continually learns from its main competitors in the market. The superior corporations or the alternative cheaper technology companies pose a potential threat and, thus, encourage the Korean brand to maintain the ongoing development and focus on product innovations. A future consumer expects Samsung to create meaningful experiences and deliver the products that assist in the busy life. With the help of ambitious, focused, and long-term corporate initiatives, Samsung became the world leader in various technology segments. However, the increasing competitive factors require the corporation to focus on the development of new business strategies to maintain its dominant position.
Reference List
Johnson, G., Whittington, R. and Scholes, K. (2011) Exploring strategy: text & cases. 9th edn. Harlow: Prentice Hall.
Jang, S. H. et al. (2019) ‘Planting and harvesting innovation – an analysis of Samsung Electronics’, International Journal of Quality Innovation, 5(7), pp. 1-16. Web.
Jung, S. C. (2014) ‘The analysis of strategic management of Samsung Electronics Company through the generic value chain model’, International Journal of Software Engineering and Its Applications, 8(12), pp. 133-142. Web.
Knöpfle, G. (2016) Samsung Electronics and the global market. The history and the competitive advantage. Munich: GRIN Verlag.
Lee, J., Lee, K., and Heo, J. (2015) ‘Supplier partnership strategy and global competitiveness: a case of Samsung Electronics’, Eurasian Journal of Business and Management, 3(4), pp. 1-12. Web.
Omer, S. (2019) ‘SWOT analysis implementation’s significance on strategy planning: Samsung mobile company as an example’, Journal of Process Management. New Technologies, 7(1), pp. 56-63. Web.
Razdan, V. (2017) Analysis of Samsung Electronics’ strategy for the period 2014-2017, and development of strategic options for growth and sustainability. Web.
Samsung Electronics sustainability report: A fifty-year journey towards a sustainable future. (2019). Web.
